Abstract
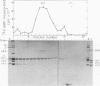
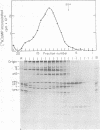
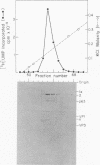
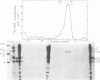
A poliovirus-specific polyuridylic acid [poly(U)] polymerase that copies a polyadenylic acid template complexed to an oligouridylic acid primer was isolated from the membrane fraction of infected HeLa cells and was found to sediment at 4 to 5S on a linear 5 to 20% glycerol gradient. When the poly(U) polymerase was isolated from cells labeled with [35S]methionine and was analyzed by glycerol gradient centrifugation and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the position of only one viral protein was found to correlate with the location of enzyme activity. This protein had an apparent molecular weight of 62,500 based on its electrophoretic mobility relative to that of several molecular weight standards and was designated p63. When the poly(U) polymerase was isolated from the soluble fraction of a cytoplasmic extract, the activity was found to sediment at about 7S. In this case, however, both p63 and NCVP2 (77,000-dalton precursor of p63) cosedimented with the 7S activity peak. When the 7S polymerase activity was purified by phosphocellulose chromatography, both p63 and NCVP2 were found to co-chromatograph with poly(U) polymerase activity. The poliovirus replicase complexed with its endogenous RNA template was isolated from infected cells labeled with [35S]methionine and was centrifuged through a linear 15 to 30% glycerol gradient. The major viral polypeptide component in a 26S peak of replicase activity was p63, but small amounts of other poliovirus proteins were also present. When the replicase-template complex was treated with RNase T1 before centrifugation, a single peak of activity was found that sedimented at 20S and contained only labeled p63. Thus, p63 was found to be the only viral polypeptide in the replicase bound to its endogenous RNA template, and appears to be active as a poly(U) polymerase either as a monomer protein or as a 7S complex.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Cooper P. D. Poliovirus polypeptides examined in more detail. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):199–213. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., EGGERS H. J., FRANKLIN R. M., TAMM I. Poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase and the effects of virus-specific inhibitors on its production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:843–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Purification and properties of poliovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):421–428. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E. A comparison of the virus-specific polypeptides of encephalomyocarditis virus, human rhinovirus-1A, and poliovirus. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):439–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Shimshick E. J., Yin F. H. Association of the polioviral RNA polymerase complex with phospholipid membranes. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.457-466.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. II. Nature of the defect. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):325–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Smoler D., Wimmer E., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. I. Isolation and physical properties. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):478–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.478-485.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Lund H. Untranslated vesicular stomatitis virus messenger RNA after poliovirus infection. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D., Rose J. K., Lodish H. F. Translation of individual species of vesicular stomatitis viral mRNA. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):1004–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.1004-1011.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz R., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in HeLa cells. 3. Inhibition during poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):661–668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.661-668.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Ehrenfeld E., Maizel J. V., Jr Isolation of a viral polypeptide associated with poliovirus RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4773–4777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub A., Duskin B., Rosenberg H., Kalmar E. Isolation and properties of the replicase of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):375–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.375-382.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Guttman N., Baltimore D., Lodishi H. F. Complete translation of poliovirus RNA in a eukaryotic cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4157–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., McDowell M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus mRNA, poliovirus RNA and bacteriophage Qbeta RNA in cell-free extracts of mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:709–723. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]