Abstract
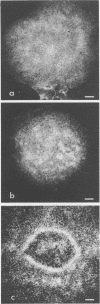
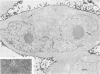
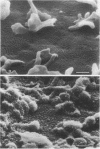
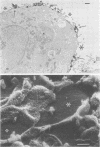
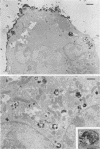
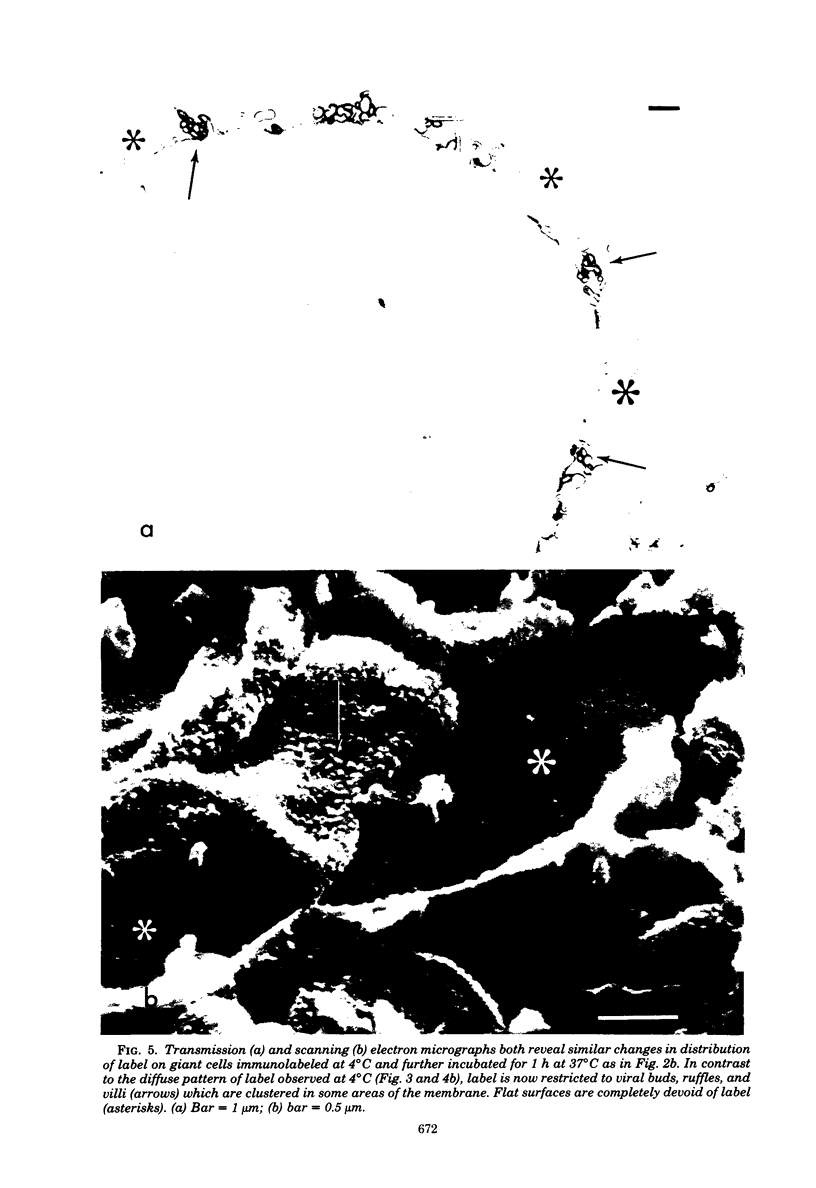
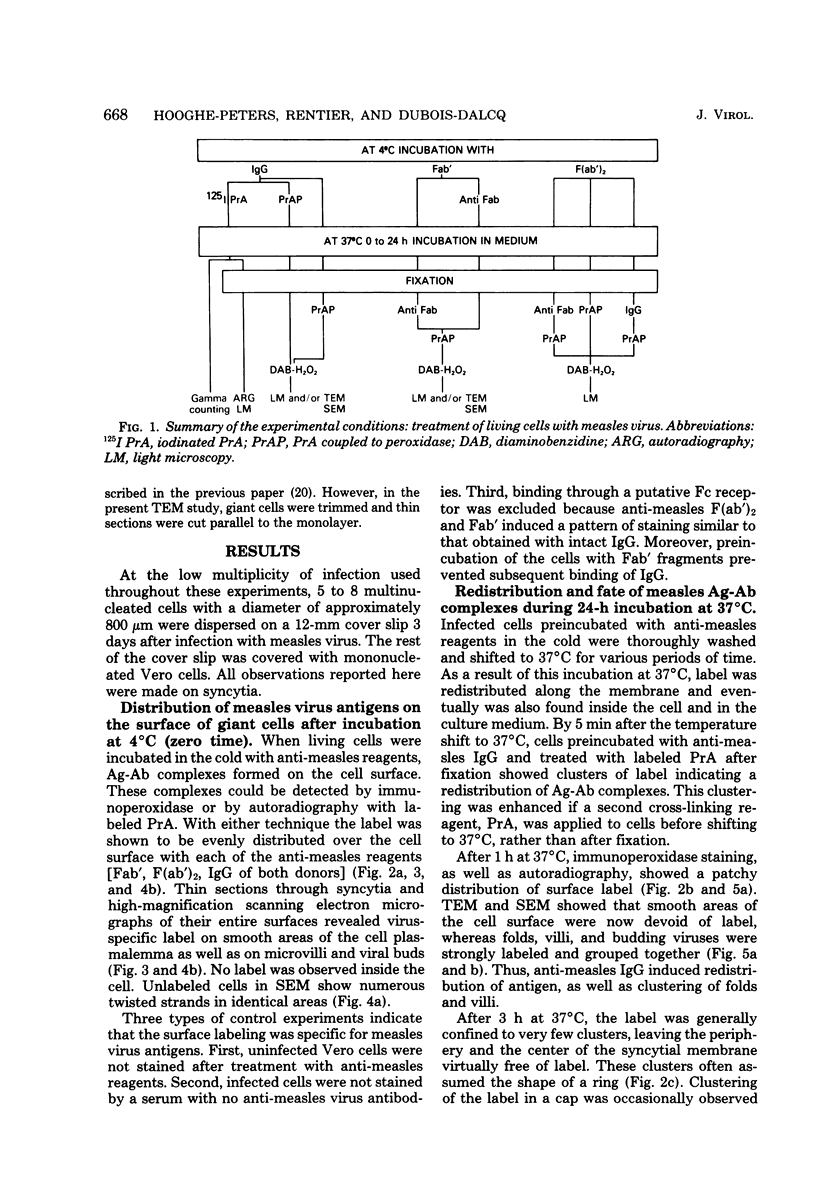
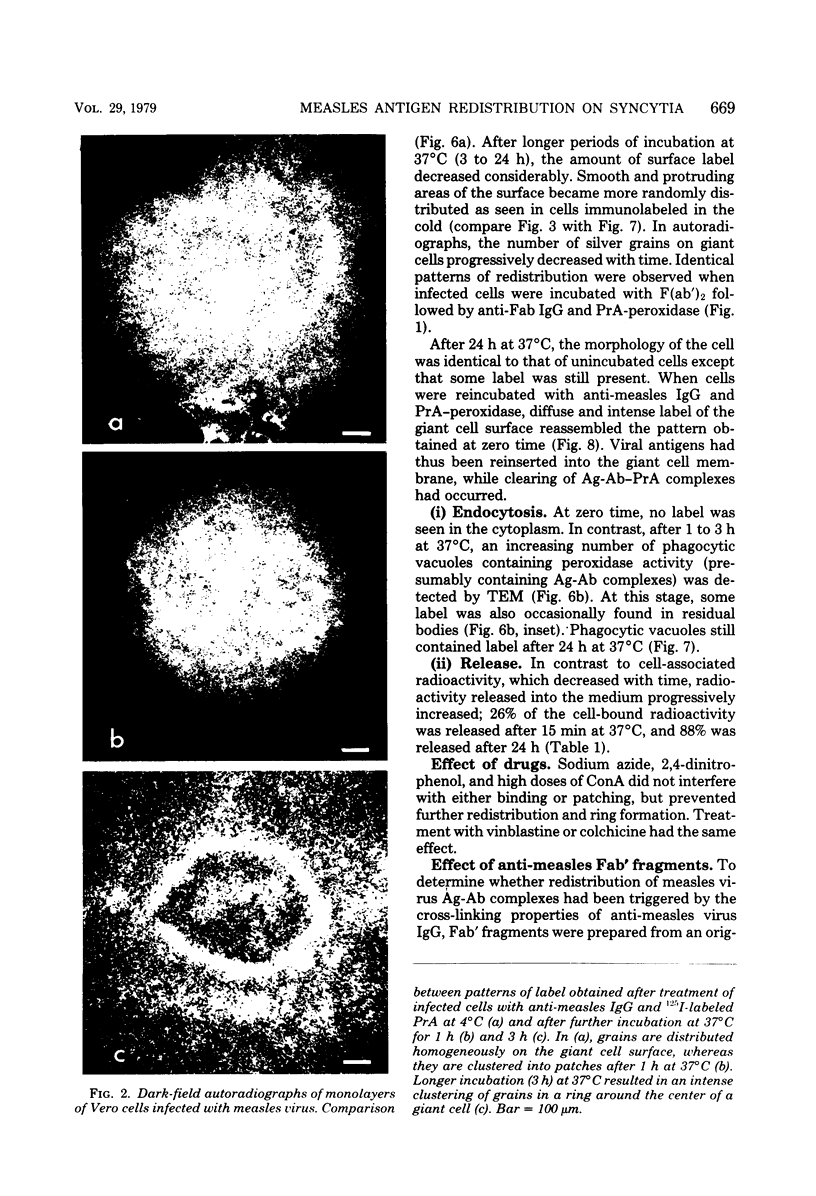
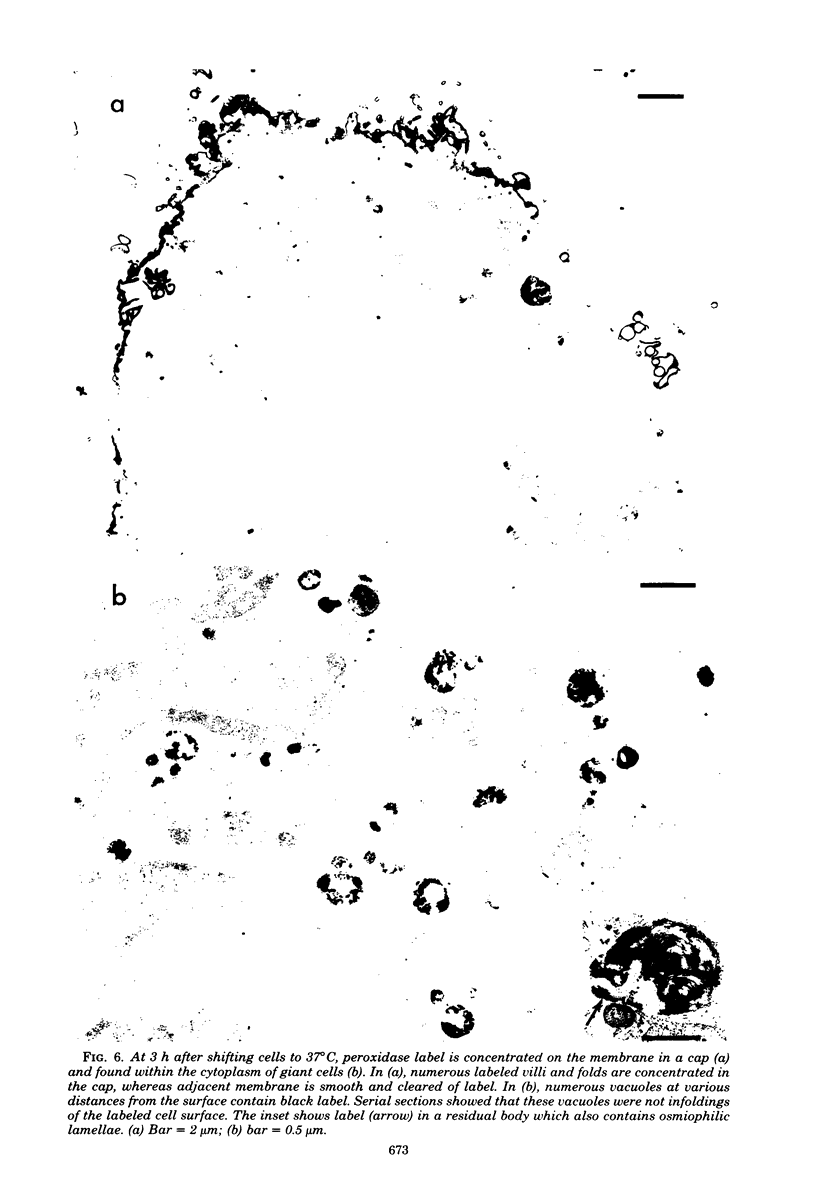
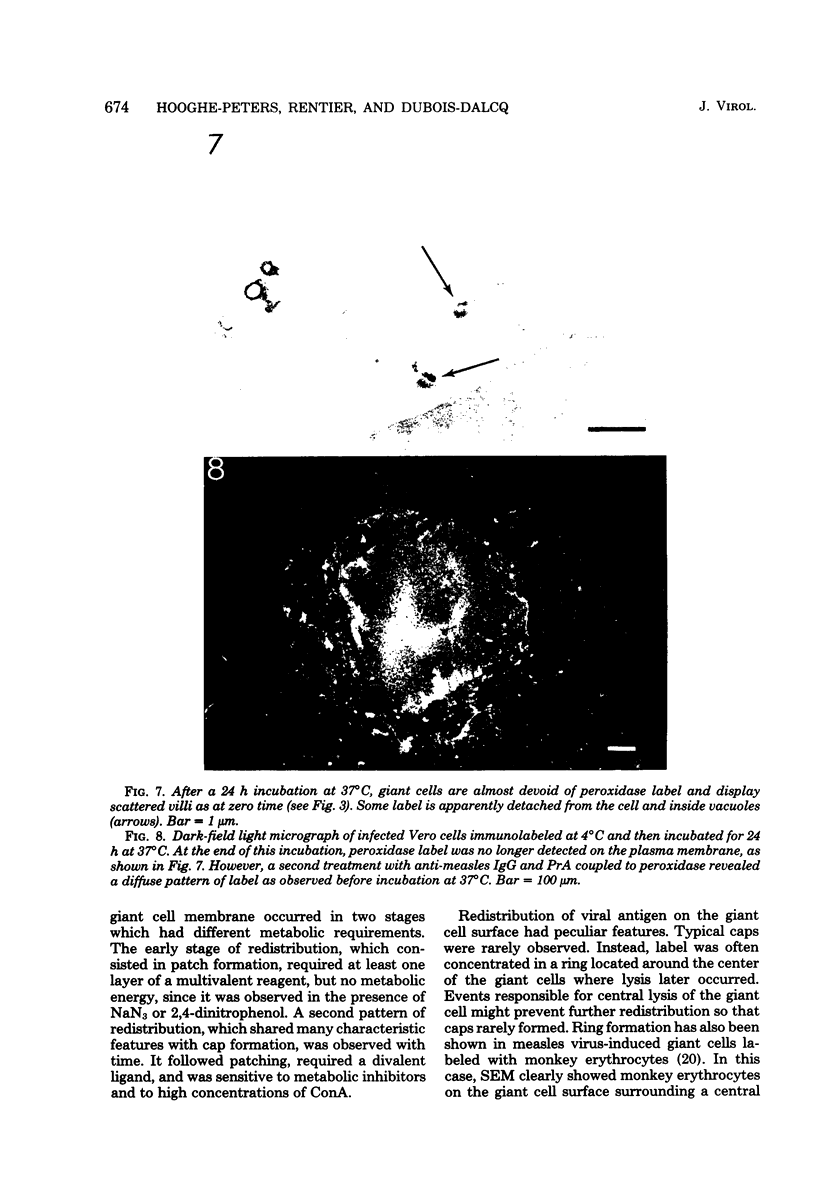
Vero cells infected with measles virus fuse to form multinucleated cells which incorporated virus-specific antigens in their membrane. The distribution of these antigens was analyzed after a brief treatment with human anti-measles immunoglobulin G, using autoradiography and immunoperoxidase labeling combined with transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Virs-specific antigens were distributed over the entire surface of giant cells treated at 4 degrees C with human anti-measles immunoglobulin G and labeled Protein A. When cells were shifted to 37 degrees C, labeled antigen-antibody complexes were redistributed in two stages. Patch formation occurred in 5 to 15 min. Later, antigen-antibody complexes became concentrated in a paracentral "ring" rather than typical caps. Patch formation occurred in the presence of metabolic inhibitors, whereas ring formation was inhibited by metabolic inhibitors. These rings contained membrane folds, villi, and viral buds, whereas the rest of the membrane was smooth. In addition, shedding, endocytosis of antigen-antibody complexes, and reexpression of antigens were observed. Antibodies to nonviral membrane antigens induced the same pattern of redistribution. Infected cells treated with anti-measles Fab' fragments maintained a homogenous distribution of label throughout the experiments. In conclusion, intact immunoglobulins, but not Fab' fragments, were able to induce a dramatic redistribution of viral antigen on the membrane of giant cells infected with measles virus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini D. F., Anderson E. Microtubule and microfilament rearrangements during capping of concanavalin A receptors on cultured ovarian granulosa cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):111–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois-Dalcq M., McFarland H., McFarlin D. Protein A-peroxidase: a valluable tool for the localization of antigens. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Nov;25(11):1201–1206. doi: 10.1177/25.11.199666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois-Dalcq M., Reese T. S. Structural changes in the membrane of vero cells infected with a paramyxovirus. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):551–565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnst A., Sundqvist K. G. Polar appearance and nonligand induced spreading of measles virus hemagglutinin at the surface of chronically infected cells. Cell. 1975 Aug;5(4):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould J. J., Almeida J. D. Antibody-modification of measles "in vitro" infection. J Med Virol. 1977;1(2):111–117. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890010204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-induced redistribution of measles virus antigens on the cell surface. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1205–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Immunologic injury in measles virus infection. II. Suppression of immune injury through antigenic modulation. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):864–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-induced capping of measles virus antigens on plasma membrane studied by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1248–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1248-1255.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor F. Structure and dynamics of the lymphocyte surface, in relation to differentiation, recognition and activation. Prog Allergy. 1977;23:1–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa T. Studies on the persistent infection with measles virus in HeLa cells. I. Clonal analysis of cells of carrier cultures. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971 Jul;15(4):325–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1971.tb00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Turner M. W. Localization of Gm markers to different molecular regions of the Fc fragment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 May;8(5):685–700. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E. A carrier cell line of measles virus in Lu 106 cells. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(2):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01241275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Tishon A. Immunologic injury in measles virus infection. IV. Antigens modulation and abrogation oflymphocyte lysis of virus-infected cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jan;9(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin L. H., Oldstone M. B. The formation and fate of virus antigen-antibody complexes. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):316–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips E. R., Perdue J. F. The dynamics of antibody-induced redistribution of viral envelope antigens in the plasma membranes of avian tumour virus-infected chick embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1976 May;20(3):459–477. doi: 10.1242/jcs.20.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives J., Shinitzky M. Increased membrane fluidity precedes fusion of muscle cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):761–763. doi: 10.1038/268761a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentier B., Hooghe-Peters E. L., Dubois-Dalcq M. Electron microscopic study of measles virus infection: cell fusion and hemadsorption. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):567–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.567-577.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff S., Potter M., Segal D. M., Padlan E. A., Davies D. R. Crystals of phosphorylcholine-binding Fab-fragments from mouse myeloma proteins: preparation and x-ray analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3689–3692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustigian R. Persistent infection of cells in culture by measles virus. II. Effect of measles antibody on persistently infected HeLa sublines and recovery of a HeLa clonal line persistently infected with incomplete virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1805–1811. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1805-1811.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter G., Mannweiler K. Antibody-induced redistribution of virus antigens on the surface of influenza virus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):321–332. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., LEY A. C., WOLMAN F., CAPLAN B. M., CROCKETT P. W., TURNER H. C. UTILIZATION OF DISPOSABLE PLASTIC PLATES, WITH A SEROLOGIC MICROTECHNIC. Am J Clin Pathol. 1964 Feb;41:167–170. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/41.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]