Abstract
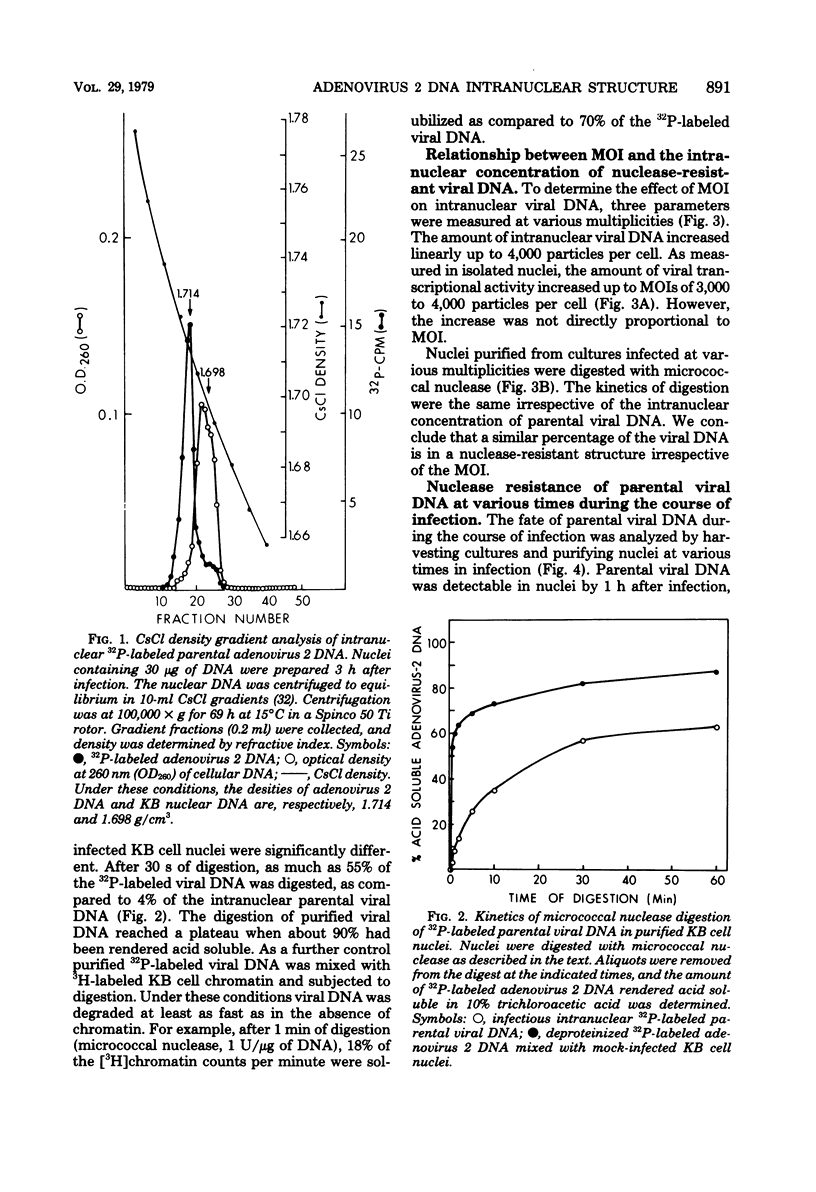
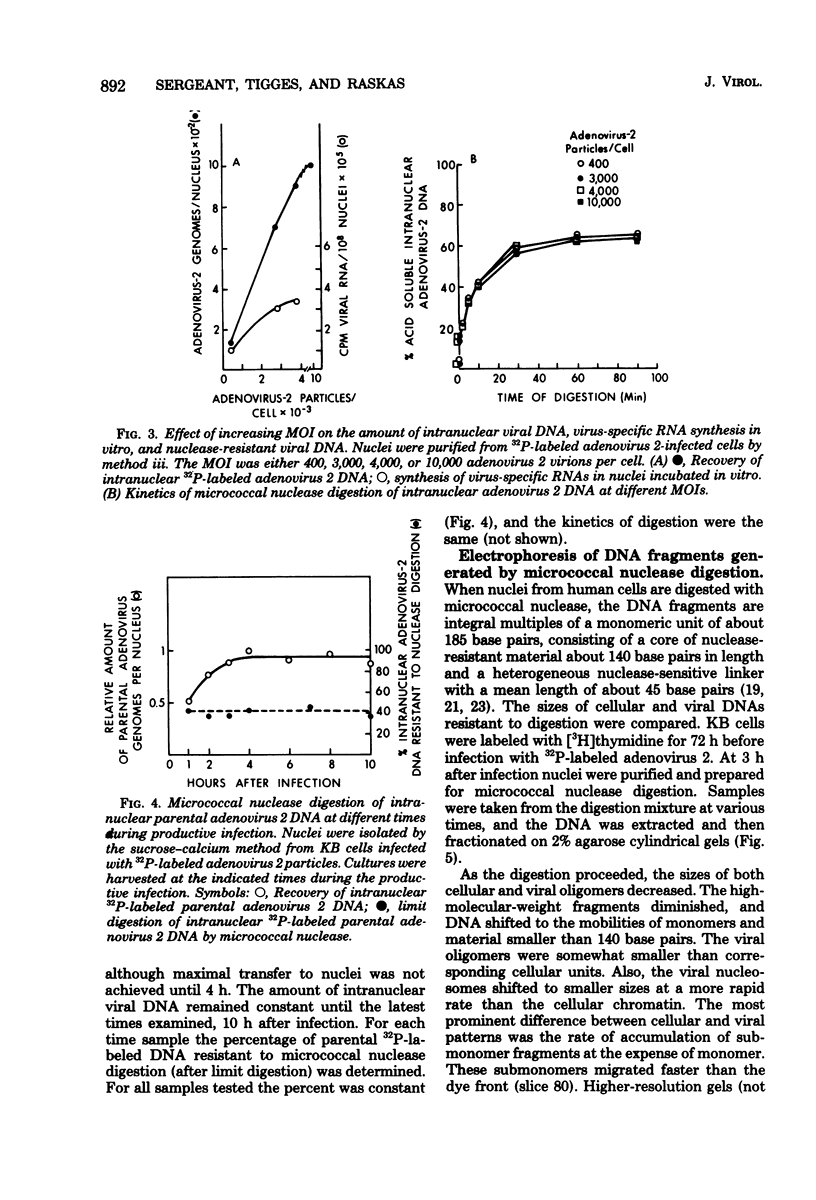
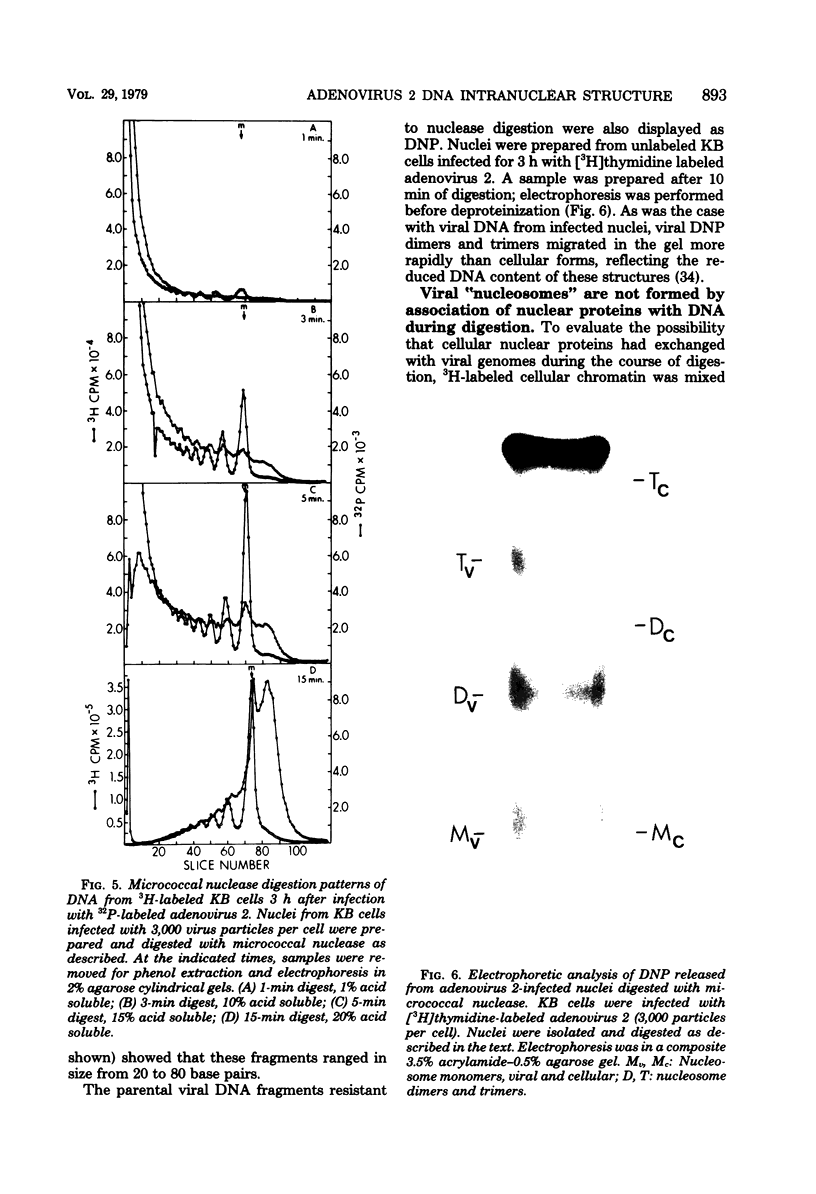
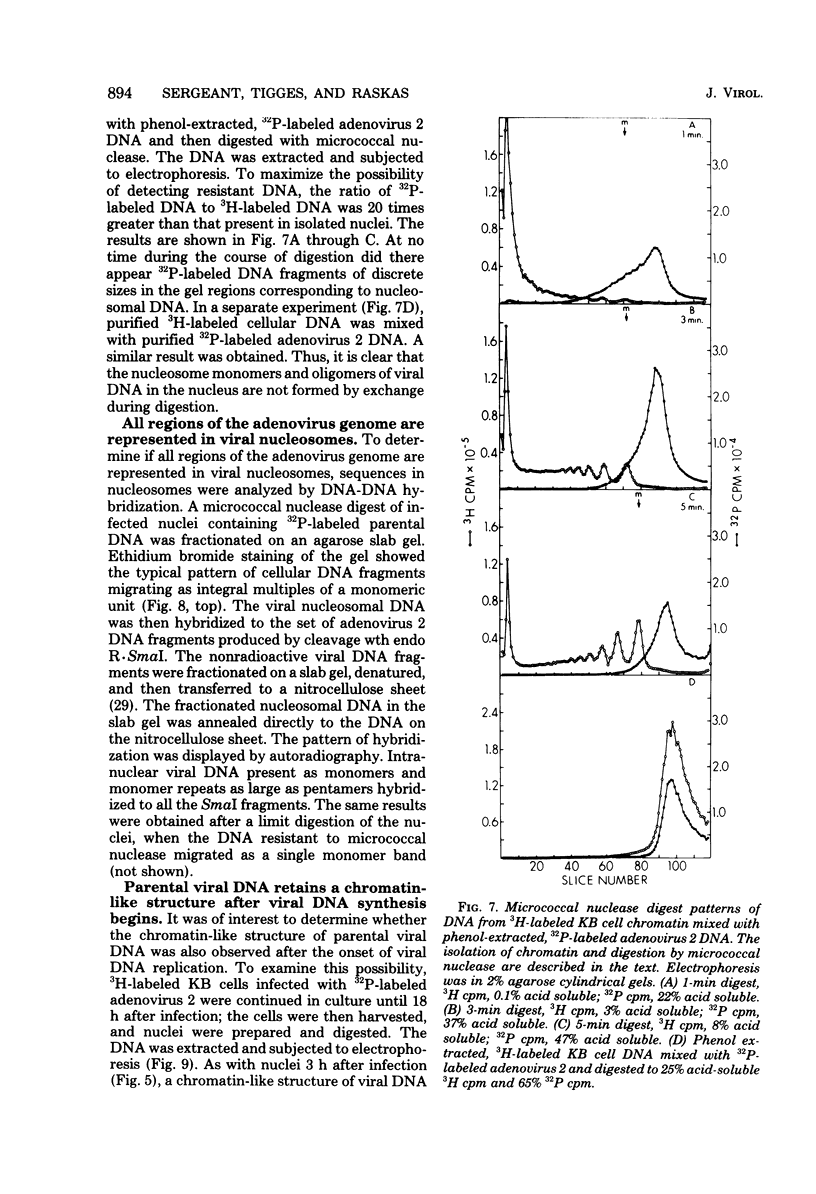
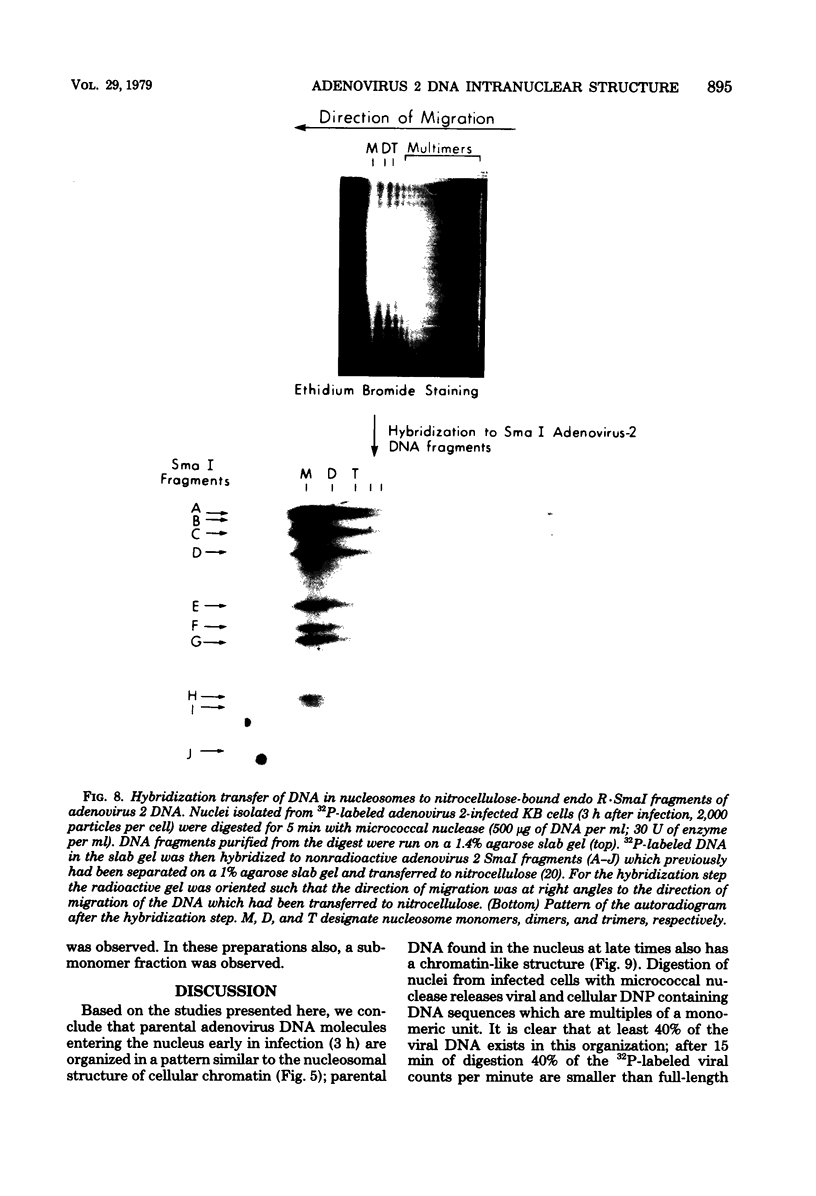
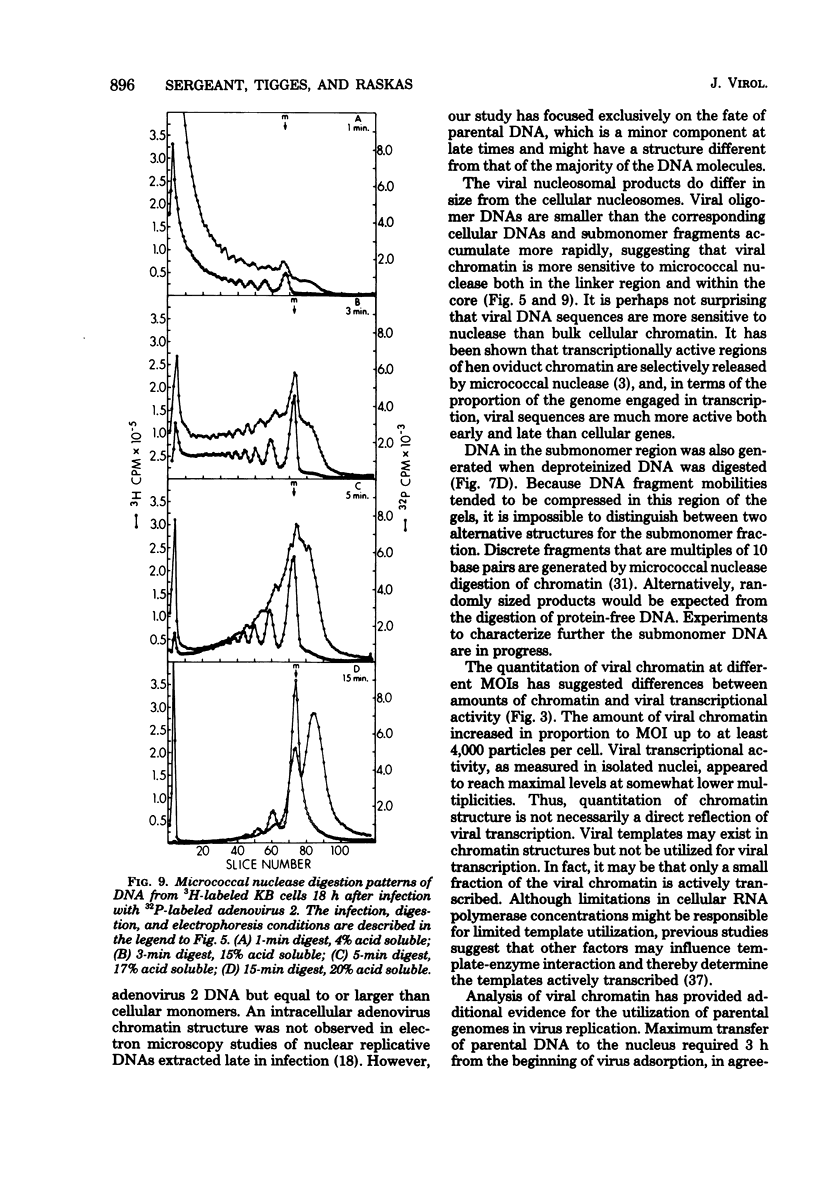
The intranuclear structure of parental adenovirus 2 DNA was studied using digestion with micrococcal nuclease as a probe. When cultures were infected with 32P-labeled virions, at a multiplicity of 3,000 particles per cell, 14 to 21% of parental DNA penetrated the cell and reached the nucleus. Of this parental DNA, 60% could be solubilized by extensive digestion with micrococcal nuclease. The nuclease-resistant fraction contained viral deoxyribonucleoprotein monomers and oligomers. These nucleosome-like structures contained DNA fragments which are integral multiples of a unit-length DNA of approximately 185 base pairs. The monomeric DNA is similar in length to the unit-length DNA contained in cellular nucleosomes. However, the viral oligomers are slightly smaller than their cellular counterparts. DNA-DNA hybridization demonstrated that all segments of the viral genome, including those expressed as mRNA only at late times, are represented in the nucleosomal viral DNA. The amount of early intranuclear viral chromatin was proportional to multiplicity of infection up to multiplicities of 4,000 particles per cell. However, viral transcriptional activity did not increase in direct proportion to the amount of viral chromatin. Maximum accumulation of intranuclear viral chromatin was achieved by 3 h after infection. The intranuclear parental viral chromatin remained resistant to nuclease digestion even at late times in infection, after viral DNA replication had begun.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axel R. Cleavage of DNA in nuclei and chromatin with staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2921–2925. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axel R., Melchior W., Jr, Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. Specific sites of interaction between histones and DNA in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4101–4105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. S., Anderson J. N. Fractionation of hen oviduct chromatin into transcriptionally active and inactive regions after selective micrococcal nuclease digestion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Hancock R., Oudet P., Chambon P. Biochemical and electron-microscopic evidence that the subunit structure of Chinese-hamster-ovary interphase chromatin is conserved in mitotic chromosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 15;70(2):555–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Engelking H. M., Pearson G. D. Chromatin-like organization of the adenovirus chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):401–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. Analysis of early adenovirus 2 RNA using Eco R-R1 viral DNA fragments. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1202–1213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1202-1213.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Raskas H. J. Nuclear transcripts larger than the cytoplasmic mRNAs are specified by segments of the adenovirus genome coding for early functions. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Raskas H. J. Two classes of cytoplasmic viral RNA synthesized early in productive infection with adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):751–757. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.751-757.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Weintraub H. M. An altered subunit configuration associated with the actively transcribed DNA of integrated adenovirus genes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):783–794. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groneberg J., Brown D. T., Doerfler W. Uptake and fate of the DNA of adenovirus type 2 in KB cells. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):115–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. Interphase chromosomal deoxyribonucleoprotein isolated as a discrete structure from cultured cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 5;86(3):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Brison O., Perrin F., Wilhelm J. Structural analysis of viral replicative intermediates isolated from adenovirus type 2-infected HeLa cell nuclei. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):364–379. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.364-379.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Corden J., Tatchell K., Kovacic R. T., Van Holde K. E. Comparative subunit structure of HeLa, yeast, and chicken erythrocyte chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Kovacic R. T., Van Holde K. E. Quantitative analysis of the digestion of yeast chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):463–471. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E. On the occurrence of nucleosome phasing in chromatin. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90281-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Philipson L. Early events of virus-cell interaction in an adenovirus system. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):323–338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.323-338.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie A. J. The organization of proteins in polyoma and cellular chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):259–266. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Raskas H. J. Species identification and genome mapping of cytoplasmic adenovirus type 2 RNAs synthesized late in infection. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):240–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.240-249.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson M. O., McAllister R. M. Infectivity of human adenovirus-1 DNA. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):14–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Hutchinson C. A., 3rd, Harris J. I. A thermostable sequence-specific endonuclease from Thermus aquaticus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):542–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Felsenfeld G. A comparison of the digestion of nuclei and chromatin by staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2915–2920. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Melchior W., Jr, Felsenfeld G. DNAase I, DNAase II and staphylococcal nuclease cut at different, yet symmetrically located, sites in the nucleosome core. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):611–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90246-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts C., Johansson K., Philipson L. Hydroxyapatite chromatography and formamide denaturation of adenovirus DNA. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):218–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.218-225.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbetts C., Pettersson U., Johansson K., Philpson L. Relationship of mRNA from productively infected cells to the complementary strands of adenovirus type 2 DNA. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):370–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.370-377.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd R. D., Garrard W. T. Two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of polynucleosomes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4729–4738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Chumackov P. M., Georgiev G. P. Minichromosome of simian virus 40: presence of histone HI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):2101–2113. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlak J. M., Rozijn T. H., Spies F. Replication of adenovirus type 5 DNA in KB cells: localization and fate of parental DNA during replication. Virology. 1976 Jul 1;72(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Jaehning J. A., Raskas H. J., Roeder R. G. Viral RNA synthesis and levels of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases during replication of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.114-126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Raskas H. J., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases II and III in transcription of the adenovirus genome late in productive infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3426–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm J., Brison O., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Characterization of adenovirus type 2 transcriptional complexes isolated from infected HeLa cell nuclei. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):61–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.61-81.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer S. G., Goldenberg C. J., Carlson D. P., Craig E. A., Raskas H. J. Size distribution of polyadenylated adenovirus 2 RNA synthesized in isolated nuclei. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 3;17(20):4207–4213. doi: 10.1021/bi00613a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]