Abstract
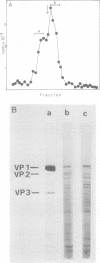
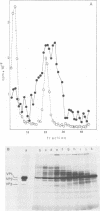
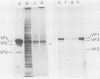
Simian virus 40 capsid proteins VP-1, VP-2, and VP-3 have been synthesized in wheat germ and reticulocyte cell-free systems in response to either poly(A)-containing mRNA from the cytoplasm of infected cells or viral RNA purified by hybridization to simian virus 40 DNA linked to Sepharose. All three viral polypeptides synthesized in vitro are specifically immunoprecipitated with anti-simian virus 40 capsid serum. VP-2 and VP-3 are related by tryptic peptide mapping to each other but not to VP-1. The most abundant class of L-strand-specific viral mRNA, the 16S species, codes for the major capsid protein. The relatively minor 19S class directs the cell-free synthesis of VP-1, VP-2, and VP-3. Whether the 19S RNA represents more than one distinct species of mRNA is not yet clear. VP-1 mRNA can be isolated from the cytoplasm, detergent-washed nuclei, and the nuclear wash fraction. The mRNA from the nuclear wash fraction is enriched for VP-2 mRNA when compared to other viral or cellular polypeptides.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Shani M., Reuveni Y. RNAs of simian virus 40 in productively infected monkey cells: kinetics of formation and decay in enucleate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2587–2591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratosin S., Horowitz M., Laub O., Aloni Y. Electron microscopic evidence for splicing of SV40 late mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Overlapping of the VP2-VP3 gene and the VP1 gene in the SV40 genome. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):529–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. A peptide comparison of proteins in the simian virus 40 virion. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):539–543. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Prives C. L., Aviv H. Purification of SV-40 messenger RNA by hybridization to SV-40 DNA covalently bound to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4215–4220. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E., Smith I., Penman S. Electron microscopic studies of detergent-treated HeLa cell nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):131–135. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Gibson W. Characterization of the mRNA's for the polyoma virus capsid proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):240–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.240-253.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Winocour E. Acquisition of sequences homologous to host deoxyribonucleic acid by closed circular simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):309–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.309-316.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Weinberg R., Ozer H. L. Translation of mRNA from simian virus 40-infected cells into simian virus 40 capsid protein by cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):590–595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.590-595.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Dulbecco R. Induction of cellular mRNA synthesis in BSC-1 cells infected by SV40. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Koch G. Individual translational efficiencies of SV40 and cellular mRNAs. Arch Virol. 1976;52(1-2):123–134. doi: 10.1007/BF01317871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. L., Aviv H., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. The cell-free translation of SV40 messenger RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):309–316. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. L., Aviv H., Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Rozenblatt S., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA of simian virus 40: synthesis of the major capsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Mulligan R. C., Gorecki M., Roberts B. E., Rich A. Direct biochemical mapping of eukaryotic viral DNA by means of a linked transcription-translation cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2747–2751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus has three late mRNA's: one for each virion protein. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):427–431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.427-431.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Kamen R., Mangel W. F., Shure H., Wheeler T. Location of the sequences coding for capsid proteins VP1 and VP2 on polyoma virus DNA. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Roblin R., Dulbecco R. Protein synthesis in Simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):921–924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Warnaar S. O., Winocour E. Isolation and characterization of simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.193-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T., Bayley S. T., Harvey R., Crawford L. V., Smith A. E. Cell-free synthesis of polyoma virus capsid proteins VP1 and VP2. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):215–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.215-224.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ysebaert M., van Heuverswyn H., van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of part of the simian virus 40 Hind-D restriction fragment. The presumed initiation region of the VP2 gene. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):195–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]