Abstract
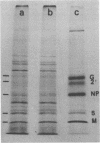
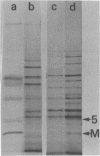
Hamster embryo fibroblasts persistently infected with a derivative of the Schwarz vaccine strain of measles virus spontaneously released virus particles with an average buoyant density considerably lower than that of the parental virus. The released virus contained all of the measles virus structural proteins and interfered with replication of standard virus. All of the virus structural proteins were associated with a membrane-free cytoplasmic extract from the persistently infected cells. Membrane-free cytoplasmic extracts prepared from Vero cells lytically infected with Schwarz strain measles contained little or no virus envelope structural protein. Maintenance of persistent infection may involve both the presence of virus variants and a defect in the ability of the infected cell to replicate the virus efficiently.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gould E. A., Linton P. E. The production of a temperature-sensitive persistent measles virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jul;28(1):21–28. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Martin S. J., Gould E. Defective interfering particles produced during the replication of measles virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1974;160(2-3):155–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02121722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Bussell R. H. Glycoproteins of measles virus under reducing and nonreducing conditions. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):687–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.687-692.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Knight P. R., Duff R. G., Rapp F. Activation of a latent measles virus infection in hamster cells. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):690–695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.690-695.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight P., Duff R., Rapp F. Latency of human measles virus in hamster cells. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):995–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.995-1001.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Separate pathways of maturation of the major structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1128–1139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1128-1139.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle W. E., Choppin P. W. A comparison of the polypeptides of four measles virus strains. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Youngner J. S. Temperature-sensitive viruses and the etiology of chronic and inapparent infections. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):467–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F. PLAQUE DIFFERENTIATION AND REPLICATION OF VIRULENT AND ATTENUATED STRAINS OF MEASLES VIRUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1448–1458. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1448-1458.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rima B. K., Davidson W. B., Martin S. J. The role of defective interfering particles in persistent infection of Vero cells by measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Apr;35(1):89–97. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Fields B. N. Intracellular synthesis of measles virus-specified polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):285–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.285-297.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild T. F., Dugre R. Establishment and characterization of a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (measles) virus persistent infection in BGM cells. J Gen Virol. 1978 Apr;39(1):113–124. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]