Abstract
Objectives
There is a growing body of literature on malaria forecasting methods and the objective of our review is to identify and assess methods, including predictors, used to forecast malaria.
Design
Scoping review. Two independent reviewers searched information sources, assessed studies for inclusion and extracted data from each study.
Information sources
Search strategies were developed and the following databases were searched: CAB Abstracts, EMBASE, Global Health, MEDLINE, ProQuest Dissertations & Theses and Web of Science. Key journals and websites were also manually searched.
Eligibility criteria for included studies
We included studies that forecasted incidence, prevalence or epidemics of malaria over time. A description of the forecasting model and an assessment of the forecast accuracy of the model were requirements for inclusion. Studies were restricted to human populations and to autochthonous transmission settings.
Results
We identified 29 different studies that met our inclusion criteria for this review. The forecasting approaches included statistical modelling, mathematical modelling and machine learning methods. Climate-related predictors were used consistently in forecasting models, with the most common predictors being rainfall, relative humidity, temperature and the normalised difference vegetation index. Model evaluation was typically based on a reserved portion of data and accuracy was measured in a variety of ways including mean-squared error and correlation coefficients. We could not compare the forecast accuracy of models from the different studies as the evaluation measures differed across the studies.
Conclusions
Applying different forecasting methods to the same data, exploring the predictive ability of non-environmental variables, including transmission reducing interventions and using common forecast accuracy measures will allow malaria researchers to compare and improve models and methods, which should improve the quality of malaria forecasting.
Keywords: Infectious Diseases
Article summary.
Article focus
Accurate predictions of malaria can provide public health and clinical health services with the information needed to strategically implement prevention and control measures.
The diversity in forecasting accuracy measures and the use of scale-dependent measures limits the comparability of forecasting results, making it difficult to identify the optimal predictors and methods for malaria forecasting.
The objective was to identify and assess methods, including predictors, used to forecast malaria.
Key messages
When performing forecasting, it is important to understand the assumptions of each method as well as the associated advantages and disadvantages.
Common accuracy measures are essential as they will facilitate the comparison of findings between studies and methods.
Applying different forecasting methods to the same data and exploring the predictive ability of non-environmental variables, including transmission reducing interventions, are necessary next steps as they will help determine the optimal approach and predictors for malaria forecasting.
Strengths and limitations of this study
The strength of this review is that it is the first review to systematically assess malaria forecasting methods and predictors, and the recommendations in the review, if followed, should lead to improvement in the quality of malaria forecasting.
A limitation of a literature review is that unpublished methods, if any, are omitted from this review.
Introduction
In 1911, Christophers1 developed an early-warning system for malaria epidemics in Punjab based on rainfall, fever-related deaths and wheat prices. Since that initial system, researchers and practitioners have continued to search for determinants of spatial and temporal variability of malaria to improve systems for forecasting disease burden. Malaria forecasting is now conducted in many countries and typically uses data on environmental risk factors, such as climatic conditions, to forecast incidence for a specific geographic area over a certain period of time.
Malaria can be forecasted using an assortment of methods and significant malaria predictors have been identified in a variety of settings. Our objective was to identify and assess methods, including predictors, used to forecast malaria. This review is intended to serve as a resource for malaria researchers and practitioners to inform future forecasting studies.
Methods
We included in our scoping review studies that forecasted incidence, prevalence or epidemics of malaria over time. Whereas a systematic review is guided by a highly focused research question, a scoping review covers a subject area comprehensively by examining the extent, range and nature of research activity on a topic.2 The studies had to use models that included prior malaria incidence, prevalence or epidemics as a predictor. A description of the forecasting model and an assessment of the forecast accuracy were requirements for inclusion. Studies were restricted to human populations and to autochthonous transmission settings. We excluded studies that provided only spatial predictions, exploratory analysis (eg, assessing temporal correlations), mortality predictions and/or individual-level transmission modelling. Commentaries, descriptive reports or studies that did not include original research were also excluded. In addition, for studies that were related (eg, the same setting and the same methods with different time periods), the study with the most comprehensive data was included in the review.
A review protocol was developed and electronic search strategies were guided by a librarian experienced in systematic and scoping reviews. Papers were identified using medical subject headings and key word combinations and truncations: (‘forecast*’ or ‘predictive model*’ or ‘prediction model*’ or ‘time serie*’ or ‘time-serie*’; AND ‘malaria*’). The searches were not restricted by year or language although our searches were restricted by the historical time periods of the databases. The citation searches began on 18 April 2011 and the final citation search was conducted on 29 May 2012. We searched the following databases: CAB Abstracts (1910–2012 Week 20), EMBASE (1947–2012 28 May), Global Health (1910–April 2012), MEDLINE (1948−May Week 3 2012), ProQuest Dissertations & Theses (1861–29 May 2012) and Web of Science (1899–28 May 2012). We performed manual searches of the Malaria Journal (2000–29 May 2012) and the American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene (1921–May 2012). Grey literature was also searched using Google Scholar, based upon the same key words used to search the databases. In addition, the websites of the WHO and the US Agency for International Development were also examined for any relevant literature. To ensure that all appropriate references were identified, hand searching of reference lists of all included studies was conducted and any potentially relevant references were incorporated into the review process.
The citations were imported into EndNote X5 (Thomas Reuters) for management. Two main reviewers (KZ and AV) examined all citations in the study selection process with the exception of articles in Chinese, which were reviewed by a third reviewer (ZS). The first stage of review involved each reviewer independently identifying potentially relevant studies based upon information provided in the title and abstract. If it was uncertain whether to include or exclude a study during the first stage of review, the citation was kept and included in the full article review.
The second stage of review involved each reviewer independently identifying potentially relevant studies based upon full article review; data abstraction occurred for those articles that met the inclusion criteria. From each study, we abstracted the following: setting, outcome, covariates, data source(s), time-frame of observed data, forecasting and model evaluation methodologies, final models and associated measures of prediction accuracy. Quality of the included studies was not assessed as the objective was to conduct a scoping review and not a systematic review. Any discordance among the reviewers regarding inclusion or exclusion of studies or with respect to the information abstracted from the included studies was resolved by consultation with another author (DB).
Results
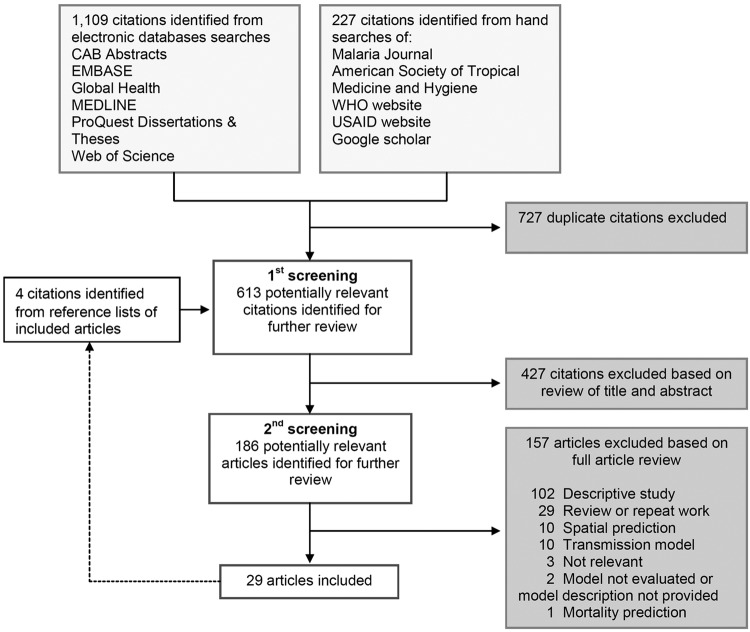
Our search identified 613 potentially relevant articles for the scoping review after duplicate citations were removed (figure 1). We identified 29 different studies that met our inclusion criteria for this review; they are described briefly in table 1. Malaria forecasting has been conducted in 13 different countries with China as the most frequent site of malaria forecasting. The size of the geographic region of study ranged from the municipal level to larger administrative divisions such as country and provinces or districts. Almost all of the studies (97%) used health clinic records of malaria infections from the general population as their data source for malaria infections, with one study using cohort data. Eleven (38%) of the 29 studies used laboratory confirmation of malaria cases (microscopy and/or rapid diagnostic tests), seven (24%) used clinical confirmation and two (7%) used a mixture of clinical and microscopic confirmation. Nine studies did not state whether they used clinical or microscopic confirmation of malaria.
Figure 1.
Flow of literature searches and screening process.
Table 1.
Characteristics of malaria forecasting studies included in review (n=29)
| Authors (reference) | Population and setting | Model specifics | Malaria outcome | Number of data points used for training/testing | Evaluation measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression forecasting studies | |||||
| Adimi et al3 | Community health post data from 2004 to 2007 for 23 provinces in Afghanistan; clinical confirmation | 23 linear regressions (1 for each province); included autoregressive, seasonal and trend parameters | Monthly cases | 31/6 (varied between provinces but last 6 months used only for testing) | Root mean squared error and absolute difference |
| Chatterjee and Sarkar4 | Municipal data for 2002–2005 for Chennai (city), India; microscopic confirmation | Logistic regression; polynominal and autoregressive parameters | Monthly slide positivity rate | 36/1 | 95% CI (for predicted value and compared to observed) |
| Gomez-Elipe et al5 | Health service data from 1997 to 2003 for Karuzi Province, Burundi; clinical confirmation | Linear regression; adjusted for population, lagged weather covariates, autoregressive and seasonal parameters | Monthly incidence | 60/24; 1 month ahead forecasts | 95% CI, correlation, p value trend line of difference (between predicted and observed) |
| Haghdoost et al6 | District health centre data from 1994 to 2001 for Kahnooj District, Iran; microscopic confirmation | Separate Poisson regressions for Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum; population offset, lagged weather covariates, seasonality and trend parameters | 10-day cases | 213/73 | Average percent error |
| Rahman et al7 | Hospital data from 1992 to 2001 for all divisions of Bangladesh; clinical confirmation | Four linear regressions (1 for each administrative division and one for all of Bangladesh); environmental covariate for weeks of highest correlation | Yearly cases | 10, 1 year was removed from series at a time | Root mean squared error and relative bias (observed-predicted) |
| Roy et al8 | Municipal data for Chennai (city) (2002–2004) and Mangalore (city) (2003–2007), India; microscopic confirmation | Two linear regressions (one for each city); adjusted for population, lagged weather covariates, autoregressive term, interaction terms, polynomial terms | Monthly SPR (Chennai), monthly cases (Mangalore) | 28/8 (Chennai), 48/12 (Mangalore); 1 month ahead | 95% CI |
| Teklehaimanot et al9 | Health facility data from 1990 to 2000 for all districts in Ethiopia; microscopic confirmation | 10 Poisson regressions (one for each district); lagged weather covariates, autoregressive term, time trend and indicator covariates for week of the year | Weekly cases | 572 (varied between districts, training and testing); 52 weeks (year) were removed from series at a time; 1–4 week ahead forecasts | Compared performance of alerts from predicted versus observed cases (using potentially prevented cases) |
| Xiao et al10 | Medical and health unit data from 1995 to 2007 for Hainan Province, China; microscopic confirmation | Poisson regression; lagged weather covariates, autoregressive term | Monthly incidence | 144/12 | T-test (predictive value significantly different than actual) |
| Yacob and Swaroop11 | Medical data from 1944 to 1996 for all health districts in Punjab; clinical confirmation | 19 linear regressions (1 for each district); include coefficients of correlation between rainfall and epidemic figures from 1914 to 1943 | Seasonal epidemic figure* | Coefficient of correlation (between actual and predicted epidemic figure) | |
| Yan et al12 | Municipal data from 1951 to 2001 for Chongquin (city), China | Linear regression; logarithm curve | Yearly cases | 50/1 | Visual inspection of predicted within range of actual values |
| ARIMA forecasting studies | |||||
| Abeku et al13 | Health clinics data from 1986 to 1999 for 20 areas in Ethiopia; mixture of microscopic and clinical confirmed | 20 models (1 for each area) compared approaches: Overall average, seasonal average, seasonal adjustment, ARIMA | Monthly cases | 168/12 (varied between areas but last 12 months only used for testing); 1–12 month ahead forecasts | Average forecast error |
| Briët et al14 | Health facility data from 1972 to 2005 for all districts in Sri Lanka; microscopic confirmation | 25 models (1 for each district) compared approaches: Holt-Winters, ARIMA (seasonality assessed with fixed effects or harmonics) and SARIMA; lagged weather covariates | Monthly cases of malaria slide positives | 180/204 (varied between districts but approximately 50% of series reserved for testing); 1–4 month ahead forecasts | Mean absolute relative error |
| Liu et al15 | Data from 2004 to 2010 for China | SARIMA | Monthly incidence | 72/12 | Visual (plot of predicted vs observed) |
| Wangdi et al16 | Health centre data from 1994 to 2008 for seven districts in Bhutan; microscopic and antigen confirmation | Seven models (one for each district): SARIMA and ARIMAX; lagged weather covariates | Monthly cases | 144/24 | Mean average percent error |
| Wen et al17 | Data from 1991 to 2002 for Wanning County, China | SARIMA | Monthly incidence | 252/12 | 95% CI |
| Zhang et al18 | CDC data from 1959 to 1979 for Jinan (city) China; clinical confirmation | SARIMA; lagged weather covariates | Monthly cases | 84/120 (removed 1967 and 1968 from series) | Visual (plot of predicted vs observed) |
| Zhou et al19 | Data from 1996 to 2007 for Huaiyuan County, China; microscopic and clinical confirmation | SARIMA | Monthly incidence | 108/12 | Average error |
| Zhu et al20 | Data from 1998 to 2007 for Huaiyuan and Tongbai counties, China | SARIMA | Monthly incidence rates | 84/24; 1–12 month ahead forecasts | 95% CI and error |
| Mathematical forecasting studies | |||||
| Gaudart et al21 | Data from cohort of children from 1996 to 2000 in Bancoumana (municipality), Mali from 1996 to 2006; microscopic confirmation | VSEIRS model | Monthly incidence rate | 60 (training and testing); 15 day, 1 month, 2 month, seasonal forecasts | Mean absolute percentage error and root mean squared error |
| Laneri et al22 | Health centre data (passive and active surveillance) for Kutch (1987–2007) and Balmer (1985–2005) Districts, India; microscopic confirmation | 2 models (one for each district); compared two types of VSEIRS model to linear and negative binominal regressions | Monthly incidence for parameter estimation; seasonal totals (Sept−Dec) for epidemic forecasting | 240 (training and testing); 1 to 4 months ahead forecasts | Weighted mean square error and prediction likelihood |
| Neural network forecast studies | |||||
| Cunha et al23 | Ministry of Health data from 2003 to 2009 for Cornwall (City), Brazil; microscopic confirmation | Compared neural network to linear regression | Monthly cases | 72/12; 3, 6 and 12 months forecasts | Absolute error and mean square error |
| Gao et al24 | Data from 1994 to 1999 for Honghe State, China | Neural network | Monthly incidence | 48/12 | Percent error |
| Kiang et al25 | Hospital and clinic data from 1994 to 2001 for 19 provinces, Thailand; microscopic confirmation | 19 neural networks (1 for each province); various architectures used (varied by province) | Monthly incidence | 84/12 | Root mean square error |
| Other forecasting methods | |||||
| Fang et al26 | Data from 1956 to 1988 for Xuzhou (City), China | Grey and Grey Verhulst models (1,1) | Yearly incidence | 30/2 | Percent error |
| Gao et al27 | Data from 1998 to 2005 for Longgang District, China | Grey model (1,1) | Yearly incidence | 6/1 | Error and percent error |
| Guo et al28 | Data from 1988 to 2010 China | Grey model (1,1) | Yearly incidence | 21/2 | Visual (plot of predicted vs observed) |
| Gill29 | Medical data from 1925 to 1926 for health districts in Punjab; clinical confirmation | 29 forecasts consisting of visual inspection of rainfall, spleen rates and epidemic potential† | Seasonal epidemic (yes/no) | Qualitative comparison of prediction (presence of epidemic) to epidemic figure | |
| Medina et al30 | Community health centre data from 1996 to 2004 (14 centres) for Niono District, Mali; clinical confirmation | Multiplicative Holt-Winters model, age-specific rates (three age groups); compared to seasonal adjustment method | Monthly malaria consultation rates | 36/72; 2 and 3-month ahead forecasts; one step ahead forecasts | Mean absolute percentage error and 95% CI |
| Xu and Jin31 | Data from 2000 to 2005 for Jiangsu Province, China | Grey model | Yearly cases | 4/1 | Visual (plot of predicted vs observed number of cases) |
*Seasonal epidemic figure is the ratio of October incidence to mean spring incidence.
†Epidemic potential is the coefficient of variability of fevers during the month of October for the periods of 1868–1921.
ARIMA, auto-regressive integrated moving average; ARIMAX, auto-regressive integrated moving average with exogenous input; SARIMA, seasonal auto-regressive integrated moving average; SPR, slide positivity rate; VSEIRS, vector-susceptible-exposed-infected-recovered-susceptible model.
Forecasting studies
The forecasting approaches included statistical modelling, mathematical modelling and machine-learning methods (table 2). The statistical methods included generalised linear models, Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models32 and Holt-Winters models.33 The mathematical models were based upon extensions of the Ross-MacDonald susceptible-infected-recovered (SIR) malaria transmission model.34 Other authors predicted malaria incidence using neural networks, a machine-learning technique.35
Table 2.
Summary of malaria forecasting methods (n=29)
| Forecasting method | Number of studies (reference) |
|---|---|
| GLM | 123–12 22 23 |
| ARIMA | 713, 14 15–20 |
| Grey methods | 426–28 31 |
| Smoothing methods* | 313 14 30 |
| Neural networks | 323, 24, 25 |
| Mathematical models | 221 22 |
| Visual | 129 |
References in bold indicate multiple comparisons. ARIMA, auto-regressive integrated moving average; GLM, generalised linear model.
*Includes Holt - (Holt-Winters) Winters, seasonal average, seasonally adjusted average and simple average.
Twelve studies (41%) included in the review used generalised linear models to forecast malaria counts, rates or proportions through linear, Poisson or logistic regression. All but one of the regression models included climate-related covariates such as rainfall, temperature, vegetation and/or relative humidity.12 Typically, the weather covariates were lagged, to account for the delayed effects of weather on malaria infections. Two studies4 8 explored the effects of including covariates as higher-order polynomials. Several of the studies used a generalised linear model approach to time series analysis by including previous (lagged) malaria incidence as an autoregressive covariate in the model. Some models included terms for season or year to account for seasonal and annual variations.
Seven studies (24%) used forecasting approaches based on ARIMA modelling with some including a seasonal component (SARIMA). While not explicitly stated, many studies used a transfer function model, also known as ARIMAX. Typically, these ARIMA-based models incorporated various meteorological series as covariates although one study also included data on the malaria burden in neighbouring districts.14
Four studies (14%) from China used the Grey method for malaria forecasting, none of which incorporated predictors other than malaria incidence.26–28 31 There were two studies (7%) that used mathematical models.21 22 Gaudart et al21 included a vector component in a SIR-type model and used data from a cohort of children, remote sensing data, literature and expert opinions of entomologists and parasitologists. The study by Laneri et al22 used a vector-susceptible-exposed-infected-recovered-susceptible (VSEIRS) model although they incorporated two different pathways from recovery to susceptibility that were based upon different timescales (seasonal and interannual), mimicking different transmission intensities. They found that rainfall had a significant effect on the interannual variability of epidemic malaria and including rainfall as a predictor improved forecast accuracy. The parameters in their models were based on literature as well as laboratory findings.
We identified three studies (10%) that used neural networks in their analyses, and each study used different input data and a unique network structure.23–25 Two of the studies used weather variables to predict malaria incidence.24 25 Gao et al24 also included evaporation and sunshine hours to predict malaria incidence; two variables that were not included in any other study.
As shown in table 3, climate-related predictors were used consistently in forecasting models, with the most common predictors being rainfall, relative humidity, temperature and normalised difference vegetation index. One study accounted for the effect of malaria incidence in neighbouring districts, but it was not a significant predictor and was excluded from the final model.14 The mathematical models included non-time varying parameters such as the reporting fraction of cases (proportion of malaria cases in a population that is reported to public health), average life expectancy and several vector characteristics, which are listed in table 4.
Table 3.
Time varying predictors considered in malaria forecasting models
| Predictor | Number of studies (reference) |
|---|---|
| Rainfall | |
| Total rainfall | 113–6 9 10 14 16 18 22 25 |
| Average rainfall | 28 24 |
| Rainy day index* | 114 |
| Number of rainy days/month | 124 |
| Humidity | |
| Average relative humidity | 76 8 10 16 18 24 25 |
| Minimum humidity | 14 |
| Maximum humidity | 14 |
| Temperature | |
| Maximum air temperature | 84–6 9 10 16 18 24 |
| Minimum air temperature | 74 5 9 10 16 18 24 |
| Average air temperature | 48 10 24 25 |
| Average LST | 23 25 |
| Temperature condition index | 17 |
| Vegetation | |
| Average NDVI | 23 5 |
| Maximum NDVI | 221 25 |
| Vegetation condition index | 17 |
| Other environmental predictors | |
| Average air pressure | 218 24 |
| Average air evaporation | 124 |
| Sunshine hours | 124 |
| Other | |
| Malaria in neighbouring districts | 114 |
| Population | 14 |
*Rainy day index: the number of days per month when rainfall was larger than zero divided by the number of days that a reading for rainfall was available.
LST, land surface temperature; NDVI, normalised difference vegetation index.
Table 4.
Parameters included in the mathematical forecasting models
| Predictor | References |
|---|---|
| Vector | |
| Mean developmental delay | 22 |
| Number of bites per night | 21 |
| Probability of a susceptible becoming infected after one single bite from a contagious human | 21 |
| Mortality per day | 21 |
| Density | 21 |
| Length of gonotrophic cycle | 21 |
| Time lag of NDVI influence | 21 |
| Lowest NDVI value to influence behaviour | |
| Humans | |
| Probability of a susceptible human becoming infected after one single infected bite | 21 |
| Probability of becoming susceptible after being resistant | 21, 22 |
| Probability of acquiring contagiousness | 21, 22 |
| Probability of losing contagiousness | 21, 22 |
| Average human life expectancy | 22 |
| Infectivity of quiescent cases relative to full-blown infections | 22 |
| Other | |
| Reporting fraction* | 22 |
*Reporting fraction is the fraction of malaria cases in the population that are reported to public health.
NDVI, normalised difference vegetation index.
Evaluation methods
Authors used different approaches to evaluate the accuracy of forecasting models. A typical approach was to segment the data into a model building or training portion with the other portion (the ‘holdout’ sample) used for model validation or assessing forecast accuracy. The cross-validation approach used by Rahman et al7 and Teklehaimanot et al9 excluded 1 year of data at a time, the model was fit to the remaining data, forecast errors (prediction residuals) were computed using data from the missing year and then this process was repeated for subsequent years. The accuracy of the predictions was then estimated from the prediction residuals. Some of the studies used all the available data to fit a model and did not reserve data for assessing forecast accuracy.21 22
Studies compared the forecasts to observed values using various measures: mean-squared error, mean relative error, mean percentage error, correlation coefficients, paired t tests (between predicted and observed values), 95% CI (of predicted values and determined if observed values fell within the interval) and visualisations (eg graphical representations of observed and predicted values).
Comparison of forecasting methods
We could not compare the forecast accuracy of models from different studies due to the lack of common measures and the lack of scale-independent measures. However, we briefly discuss the findings from studies that compared different methods within a single study.
Abeku et al13 found that their ARIMA models provided the least accurate forecasts when compared with variations of seasonal averages, and the most accurate forecasts were produced by the seasonal average that incorporated deviations from the last three observations (SA3). In contrast, Briet et al14 found that the most accurate model varied by district and forecasting horizon, but the SARIMA approach tended to provide the most accurate forecasts, followed by an ARIMA model with seasonality modelled using a sine term, then Holt-Winters, with the SA3 providing the least accurate forecasts. They also considered independent time series, such as rainfall and malaria cases in neighbouring districts, in the models. Medina et al30 determined that their Holt-Winters method provided more accurate forecasts and the accuracy did not deteriorate as rapidly as with the SA3 method. Cunha et al23 found that their neural network provided more accurate predictions across all three forecast horizons (3, 6 and 12 months) when compared with a logistic regression model.
Discussion
Malaria forecasting can be an invaluable tool for malaria control and elimination efforts. A public health practitioner developed a simple forecasting method, which led to the first early-warning system of malaria.1 Forecasting methods for malaria have advanced since that early work, but the utility of more sophisticated models for clinical and public health decision making is not always evident. The accuracy of forecasts is a critical factor in determining the practical value of a forecasting system. The variability in methods is the strength of malaria forecasting, as it allows for tailored approaches to specific settings and contexts. There should also be continued effort to develop new methods although common forecasting accuracy measures are essential as they will help determine the optimal approach with existing and future methods.
When performing forecasting, it is important to understand the assumptions of forecast models and to understand the advantages and disadvantages of each. Forecast accuracy should always be measured on reserved data and common forecasting measures should be used to facilitate comparison between studies. One should explore non-climate predictors, including transmission reducing interventions, as well as different forecasting approaches based upon the same data.
Differences between forecasting methods
The regression approach to time series prediction attempts to model the serial autocorrelation in the data through the inclusion of autoregressive terms and/or sine and cosine functions for seasonality. Generalised linear regression models are used commonly and their main advantages are their flexibility and the intuitive nature of this approach for many people relative to ARIMA models. For example, the temporal dynamics observed in time series plots can be feasibly managed in generalised linear models by including several cyclic factors, interaction terms and numerous predictors.36 The main disadvantages are that generalised linear models do not naturally account for correlation in the errors37 and the models may need to be complex to capture all the dynamics of the relationship within a series and between two or more series.38 Failure to accurately model serial autocorrelation may bias the estimation of the effect of predictors as well as underestimate the standard errors. Crucially, regression model residuals must be examined for autocorrelation and it was not always evident that this occurred in the studies we identified using this method. In addition, it was not apparent if any remedial measures were used to account for the effect of autocorrelation on estimates of variance, for example, re-estimating standard errors using heteroskedasticity and autocorrelation consistent (HAC) estimators.39
ARIMA models are designed to account for serial autocorrelation in time series; current values of a series can be explained as a function of past values and past shocks.38 With ARIMA models, once the series have been detrended through differencing, any remaining seasonality can be modelled as part of additional autoregressive or moving average parameters of a SARIMA model. A rule of thumb is that 50 observations are a minimal requirement for ARIMA models,37 whereas SARIMA models require longer time series. The transfer function model, ARIMAX, extends ARIMA by also including as predictors current and/or past values of an independent variable. An advantage of ARIMA models versus GLMs is that ARIMA models naturally represent features of temporal patterns, such as seasonality and autocorrelation. As with generalised linear regression models, the residuals of ARIMA models need to be examined for residual correlation. Also, when incorporating an input series into the model, prewhitening should occur prior to the cross-correlation assessment for the transfer function models. Prewhitening is when the residuals from an ARIMA model for the input series are reduced to ‘white noise’ and the same ARIMA model is applied to the output series.37 The authors did not always report that they prewhitened the series prior to assessing cross-correlations. The relationship between the two resulting residual series is then estimated by the cross-correlation function. Without prewhitening, the estimated cross-correlation function may be distorted and misleading.
Four studies from China used the Grey method for malaria forecasting.26–28 31 This forecasting method is essentially a curve-fitting technique based on a smoothed version of the observed data.40 41 The Grey model appears most useful in predicting malaria when using a very short time series and when there is a strong linear trend in the data. This is due to the nature of the GM(1,1) model which will always generate either exponentially increasing or decreasing series.42 Its value in malaria prediction beyond that of the simpler statistical modelling approaches is yet to be determined.
The approach to prediction differs between mathematical models and other approaches such as generalised linear models, ARIMA and Grey models. The Ross-Macdonald mathematical model divides the population under study into different compartments such as SIR, and uses differential equations to model the transition over time of individuals from one group to another. By using differential equations, these models can represent explicitly the dynamics of malaria infection, mosquito populations and human susceptibility. The disadvantages of mathematical models include the difficulty in finding appropriate, setting-specific data for the parameters. Also, the computational complexity of these models increases with the number of parameters, resulting in the omission of relevant features of malaria dynamics for the model to be manageable.43
A neural network is a machine-learning method that connects a set of inputs (eg, weather covariates) to outputs (eg, malaria counts).44 The connection between inputs and outputs are made via ‘neurons’ and the number of links and corresponding weights are chosen to give the best possible fit to the training data. Neural networks have been proven to be useful in their capacity to handle non-linear relationships as well as a large number of parameters, and also their ability to detect all possible interactions between predictor variables.45 Mathematical models and neural networks are able to capture thresholds or limits on malaria transmission, which cannot be readily captured by statistical approaches. For example, in generalised linear models, a small decrease in the temperature leads to a small decrease in malaria incidence. Neural networks and mathematical models can express explicitly that there will be no malaria transmission below a certain temperature. The disadvantages of neural networks include difficulties in determining how the network is making its decision and its greater computational burden,46 both of which depend upon the number of input parameters included in the model. In addition, neural networks have a greater susceptibility to overfitting45 and several thousand observations are typically required to fit a neural network with confidence.46 Malaria time series are unlikely to contain several thousands of observations, perhaps unless the observations are aggregated over time (eg, monthly) and location (eg, national level).
Researchers have examined many forecasting methods, but published articles tend to describe the application of a single method to a unique dataset. Direct comparison of methods would be easier if multiple malaria forecasting methods were applied to the same data. This approach would allow the identification of methods that provide the most accurate short-term, intermediate-term and long-term forecasts, for a given setting and a set of predictors. It would also allow the exploration of gains in forecast accuracy by using a weighted combination of forecasts from several models and/or methods.47
Malaria predictors
It has been suggested that climate and meteorological predictors have greater predictive power when modelling malaria incidence in areas with unstable transmission compared to areas with stable endemicity.48 It is interesting to note that nearly all of the models focused narrowly on a small number of environmental predictors despite the importance of other predictors of malaria incidence, such as land use, bednets, indoor residual spraying and antimalarial resistance. Forecast accuracy may be weakened if transmission-reducing interventions are not considered in the models.
Forecast evaluation
Model selection based upon model-fitting criteria, such as Akaike's information criterion, Bayesian information criterion or the coefficient of determination, are standard measures considered when choosing a regression model. Using such measures to guide forecast model selection may result in selecting models with a greater number of parameters and ‘over-fitting’, which tends to result in inaccurate forecasts.49 For the purposes of forecasting, visualisations of forecasts compared to observations and forecast accuracy measures, such as the mean absolute forecast error, provide more direct and intuitive model selection criteria.
When choosing how much of the series to reserve for testing the model, it is recommended to reserve at least as much as the maximum forecast horizon.50 Cross-validation is a more efficient use of data than partitioning a data set into train and test segment, although it is more computational intensive. It is recommended in cross-validation that only prior observations be used for testing a future value.50
Various direct measures were used to estimate forecasting error. Absolute measures, such as the mean absolute error (MAE), are relevant for measuring accuracy within a particular series but not across series because the magnitude of the MAE depends on the scale of the data.51 percent errors, such as mean absolute percent error (MAPE), are scale-independent but are not recommended when the data involve 0 counts as MAPE cannot be calculated with 0 values. Also, the MAPE places a heavier penalty on forecasts that exceed the observed compared to those that are less than the observed.52 In economics, a measure called mean absolute scaled error (MASE) has been recommended as an accuracy measure for forecasting.51 We recommend incorporating MASE into malaria forecast evaluation as this evaluation measure will facilitate comparison between studies. We also recommend reporting MAE as it allows an intuitive interpretation of the errors. In addition, MAPE should be reported and a constant such as 1 could replace the 0 values in the series, allowing the calculation of MAPE. An advantage of MAPE as that it considers scale variance. For example, if we observed 70 counts of malaria but predicted 60, MAPE would be 14.3, MAE 10 and MASE 0.7. If we observed 15 counts of malaria but predicted 5, MAPE would be 66.7, MAE 10 and MASE 0.7. MAPE and MASE could be used to compare findings across series and studies, and also compared to one another to understand if and how they differ in their ranking of forecast accuracy. The MAE, MAPE and MASE should be provided as site-specific measures for each forecasting horizon, as summary measures for each site, and finally as summary measures for each forecasting horizon across all sites (within a study).
Conclusion
Accurate disease predictions and early-warning signals of increased disease burden can provide public health and clinical health services with the information needed to strategically implement prevention and control measures. Potential barriers to their usefulness in public health settings include the spatial and temporal resolution of models and accuracy of prediction. Models that produce coarse forecasts may not provide the precision necessary to guide targeted intervention efforts. Additionally, technical skill and lack of readily available data may reduce the feasibility of model utility in practise, which should be considered in developing malaria forecasting models if the intent is to use these models in clinical or public health settings. Applying different forecasting methods to the same data, exploring the predictive ability of non-environmental variables, including transmission-reducing interventions, and using common forecast accuracy measures will allow malaria researchers to compare and improve models and methods, and lead to the improvement in the quality of malaria forecasting.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank various authors for responding to our questions and also to gratefully acknowledge LK for her assistance in our literature search strategies. We would especially like to thank the reviewers for critically reading the manuscript and providing insightful suggestions.
Footnotes
Contributors: KZ, AV, KC, TB and DB contributed to the study concept and design. KZ, AV and ZS contributed to the article review and data abstraction. KZ, AV, KC, TB, JB and DB contributed to the interpretation of the data, and draughted the manuscript. All authors critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved final version submitted for publication.
Funding: This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Interdisciplinary Capacity Enhanced Team grant no HOA-80072.
Competing interests: None.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: There are no additional data.
References
- 1.Christophers SR. Epidemic malaria of the Punjab: with a note of a method of predicting epidemic years. Trans Committee Stud Malaria India 1911;2:17–26 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Levac D, Colquhoun H, O'Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci 2010;5:69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Adimi F, Soebiyanto RP, Safi N, et al. Towards malaria risk prediction in Afghanistan using remote sensing. Malar J 2010;9:125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chatterjee C, Sarkar RR. Multi-step polynomial regression method to model and forecast malaria incidence. PLoS ONE 2009;4:e4726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gomez-Elipe A, Otero A, van Herp M, et al. Forecasting malaria incidence based on monthly case reports and environmental factors in Karuzi, Burundi, 1997–2003. Malar J 2007;6:129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Haghdoost AA, Alexander N, Cox J. Modelling of malaria temporal variations in Iran. Trop Med Int Health 2008;13:1501–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rahman A, Kogan F, Roytman L, et al. Modelling and prediction of malaria vector distribution in Bangladesh from remote-sensing data. Int J Remote Sens 2011;32:1233–51 [Google Scholar]
- 8.Roy SB, Sarkar RR, Somdatta S. Theoretical investigation of malaria prevalence in two Indian cities using the response surface method. Malar J 2011;10:301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Teklehaimanot HD, Schwartz J, Teklehaimanot A, et al. Weather-based prediction of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in epidemic-prone regions of Ethiopia II. Malar J 2004;3:44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xiao D, Long Y, Wang S, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of malaria and the association between its epidemic and climate factors in Hainan, China. Malar J 2010;9:185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yacob M, Swaroop S. Preliminary forecasts of the incidence of malaria in the Punjab. Ind J Malariol 1947;1:491–501 [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yan W, Jiang S, Li J, et al. Establishment of a dynamic model of malaria outbreak in Chongqing municipality. J Trop Med (Guangzhou) 2007;7:801–3 [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abeku TA, De Vlas SJ, Borsboom G, et al. Forecasting malaria incidence from historical morbidity patterns in epidemic-prone areas of Ethiopia: a simple seasonal adjustment method performs best. Trop Med Int Health 2002;7:851–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Briët OJ, Vounatsou P, Gunawardena DM, et al. Models for short term malaria prediction in Sri Lanka. Malar J 2008;7:76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu J, Qu B, He Q. Epidemiological analysis on malaria incidence in China from 2004 to 2009 by time series model. Chin J Vector Biol Control 2011;22:134–6 [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wangdi K, Singhasivanon P, Silawan T, et al. Development of temporal modelling for forecasting and prediction of malaria infections using time-series and ARIMAX analyses: a case study in endemic districts of Bhutan. Malar J 2010;9:251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wen L, Xu D, Lin M, et al. Prediction of malaria incidence in malaria epidemic area with time series model. J Fourth Military Med Univ 2004;25:507–10 [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhang Y, Bi P, Hiller JE. Meteorological variables and malaria in a Chinese temperate city: a twenty-year time-series data analysis. Environ Int 2010;36:439–45 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhou S, Huang F, Shen Y. Application of ARIMA model on prediction of malaria incidence. J Pathogen Biol 2007;2:284–6 [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhu JM, Tang LH, Zhou SS, et al. Study on the feasibility for ARIMA model application to predict malaria incidence in an unstable malaria area. Chin J Parasitol Parasitic Dis 2007;25:232–6 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gaudart J, Toure O, Dessay N, et al. Modelling malaria incidence with environmental dependency in a locality of Sudanese savannah area, Mali. Malar J 2009;8:61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Laneri K, Bhadra A, Ionides EL, et al. Forcing versus feedback: epidemic malaria and monsoon rains in northwest India. PLoS Comput Biol 2010;6 doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000898 1–13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cunha GB, Luitgards-Moura JF, Naves ELM, et al. Use of an artificial neural network to predict the incidence of malaria in the city of Canta, state of Roraima. Rev Soc Brasil Med Trop 2010;43:567–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gao CY, Xiong HY, Yi D, et al. Study on meteorological factors-based neural network model of malaria. Chin J Epidemiol 2003;24:831–4 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kiang R, Adimi F, Soika V, et al. Meteorological, environmental remote sensing and neural network analysis of the epidemiology of malaria transmission in Thailand. Geospat Health 2006;1:71–84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fang Y, Deng D, Gu ZC, et al. Interval division, forecasting and decline tendency estimation model of malaria incidence in Xuzhou City. Chin J Parasitol Parasitic Dis 1991;9:284–6 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gao S, Liu J, Zhang R, et al. Establishment and estimation of a GM (1,1) grey model for forecasting of malaria epidemic situation in Shenzhen Longgang areas. J Pathogen Biol 2007;2:357–9 [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guo H, Ding H, Qu B, et al. A study on the trend of malaria incidence in China in the recent 20 years with GM (1,1). J Trop Med (Guangzhou) 2011;11:639–40 [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gill CA. The forecasting of malaria epidemics with special reference to the malaria forecast for the year 1926. Ind J Med Res 1927;15:265–76 [Google Scholar]
- 30.Medina DC, Findley SE, Guindo B, et al. Forecasting non-stationary diarrhea, acute respiratory infection, and malaria time-series in Niono, Mali. PLoS One 2007;2 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.00011811–13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xu X, Jin X. The application of GM (1,1) grey model in the forecasting of malaria epidemic situation. Chin J Parasitic Dis Control 2005;18:178–9 [Google Scholar]
- 32.Box GEP, Jenkins GM, Reinsel GC. Time series analysis: forecasting and control. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2008 [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chatfield C. The Holt-Winters forecasting procedure. J Roy Statist Soc 1978;27:264–79 [Google Scholar]
- 34.MacDonald G. The epidemiology and control of malaria. London: Oxford University Press, 1957 [Google Scholar]
- 35.Anderson JA. An introduction to neural networks. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, 1995 [Google Scholar]
- 36.Darlington RB. A comparison to ARIMA. http://www.psych.cornell.edu/darlington/series/series2.htm (accessed 30 May 2012)
- 37.Chatfield C. The analysis of time series: an introduction. London: Chapman & Hall, 2004 [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shumway RH, Stoffer DS. Time series analysis and its applications: with R examples. New York: Springer, 2006 [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zeileis A. Econometric computing with HC and HAC covariance matrix estimators. J Statist Software 2004;11:1–17 [Google Scholar]
- 40.Deng JL. Introduction to Grey system theory. J Grey System 1989;1:1–24 [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lin KH, Liu BD. A gray system modelling approach to the prediction of calibration intervals. IEEE Trans Instr Measure 2005;54:297–305 [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tseng FM, Yu HC, Tzeng GH. Applied hybrid grey model to forecast seasonal time series. Technol Forecasting Soc Change 2001;67:291–302 [Google Scholar]
- 43.Koella JC. On the use of mathematical models of malaria transmission. Acta Trop 1991;49:1–25 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chatfield C. Neural networks: forecasting breakthrough or passing fad? Int J Forecasting 1993;9:1–3 [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tu JV. Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol 1996;49:1225–31 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chatfield C. Forecasting in the 1990s. J Roy Statist Soc 1997;46:461–73 [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jose VRR, Winkler RL. Simple robust averages of forecasts: Some empirical results. Int J Forecasting 2008;24:163–9 [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hay SI, Rogers DJ, Shanks GD, et al. Malaria early warning in Kenya. Trends Parasitol 2001;17:95–9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Shmueli G. To explain or to predict? Statist Sci 2010;25:289–310 [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hyndman RJ, Athanasopoulos G. Forecasting: principles and practice. 2012. http://otexts.com/fpp/ (accessed 3 May 2012)
- 51.Hyndman RJ, Koehler AB. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int J Forecasting 2006;22:679–88 [Google Scholar]
- 52.Armstrong JS, Collopy F. Error measures for generalizing about forecasting methods—empirical comparisons. Int J Forecasting 1992;8:69–80 [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.