Abstract
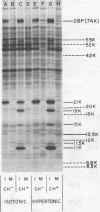
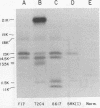
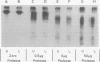
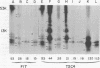
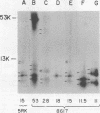
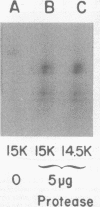
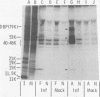
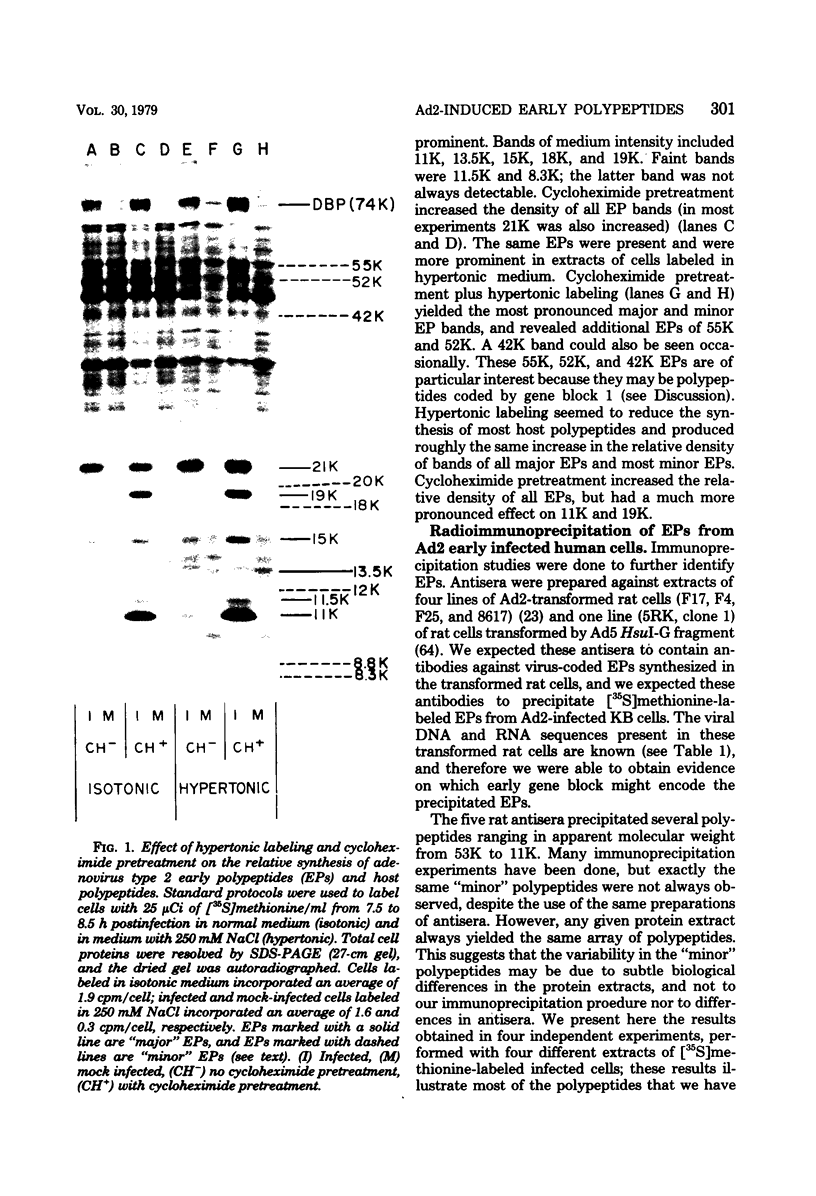
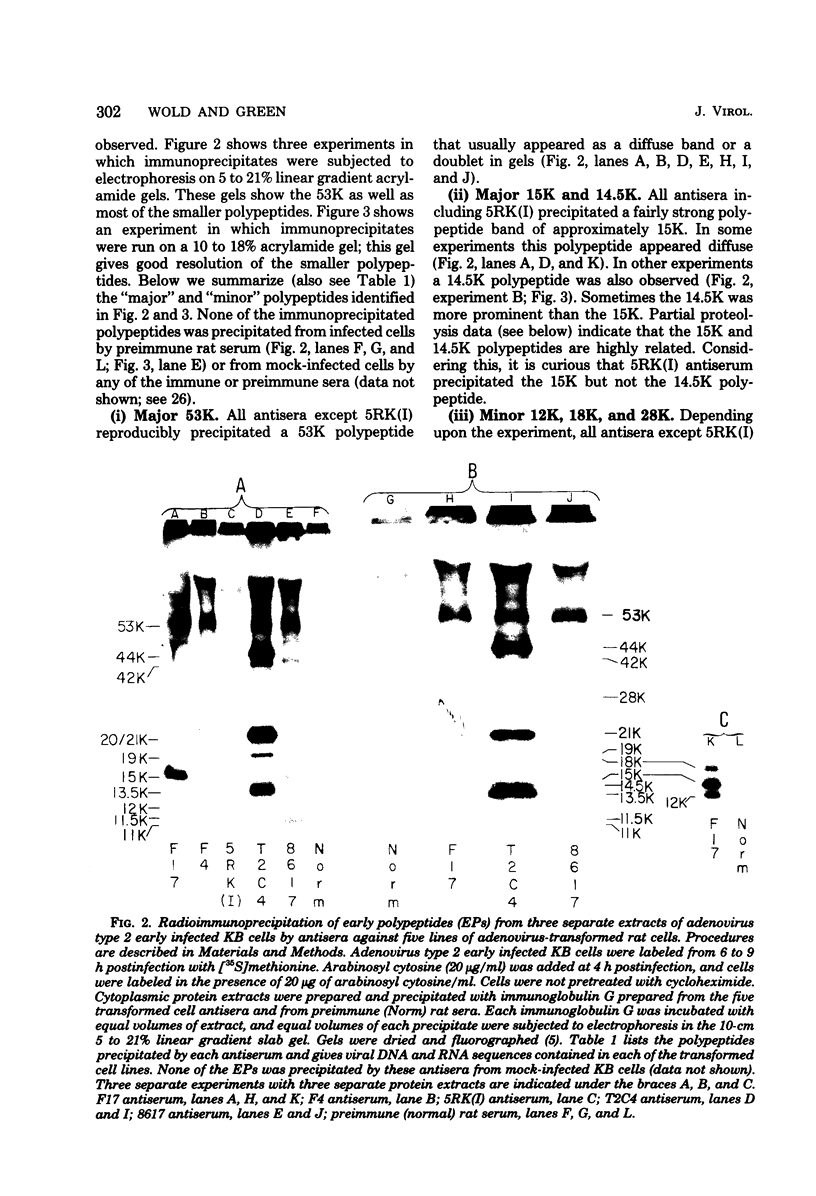
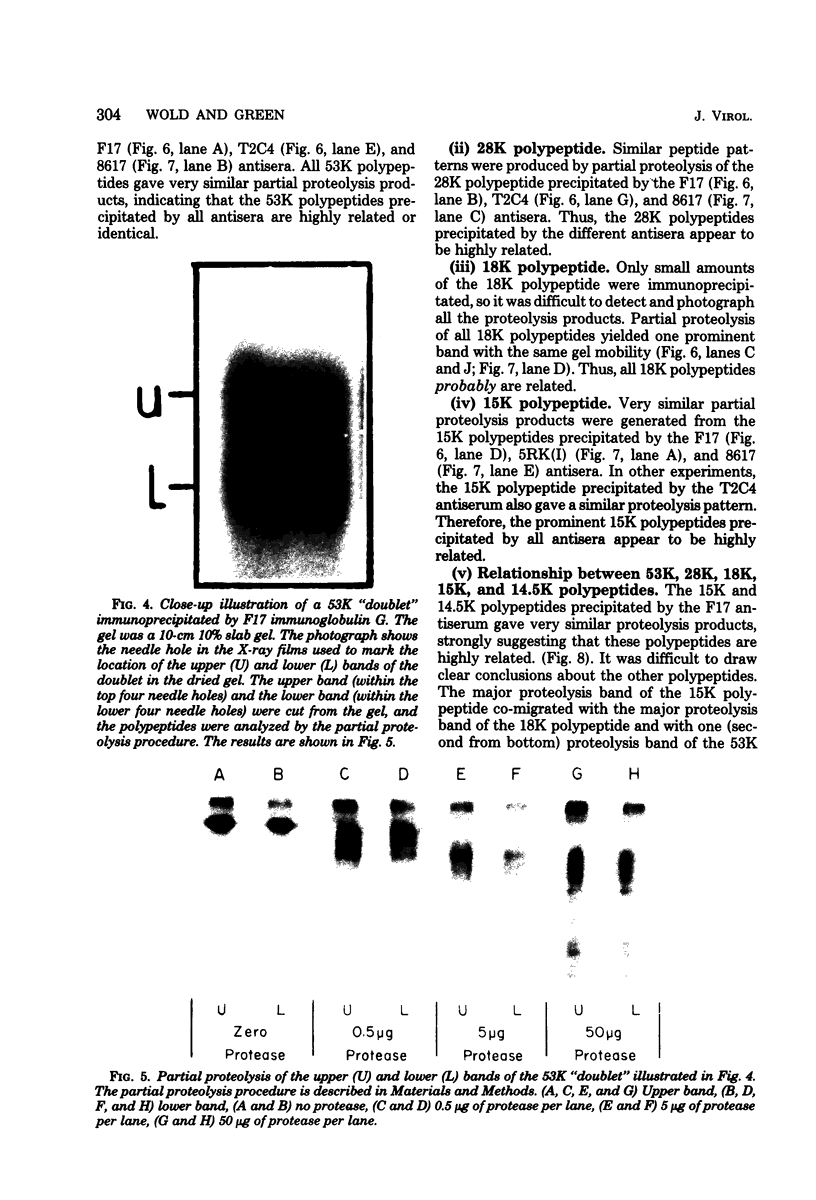
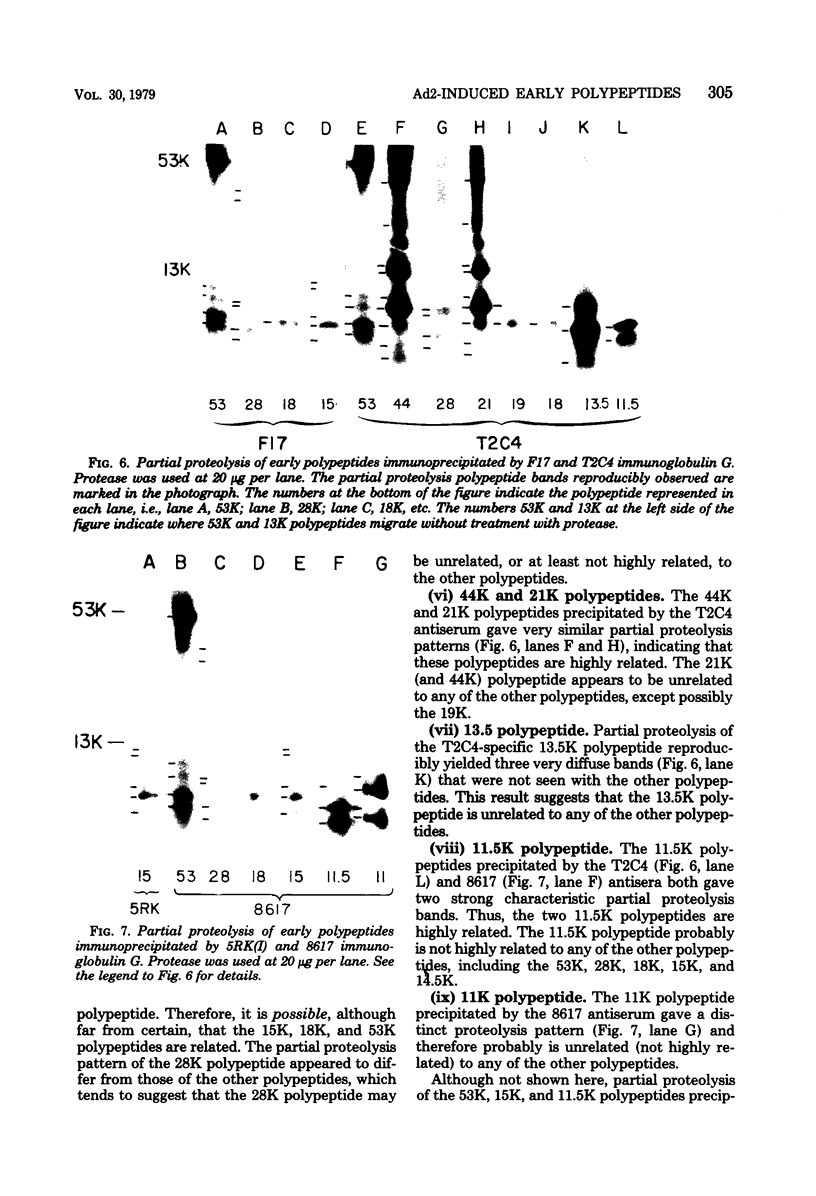
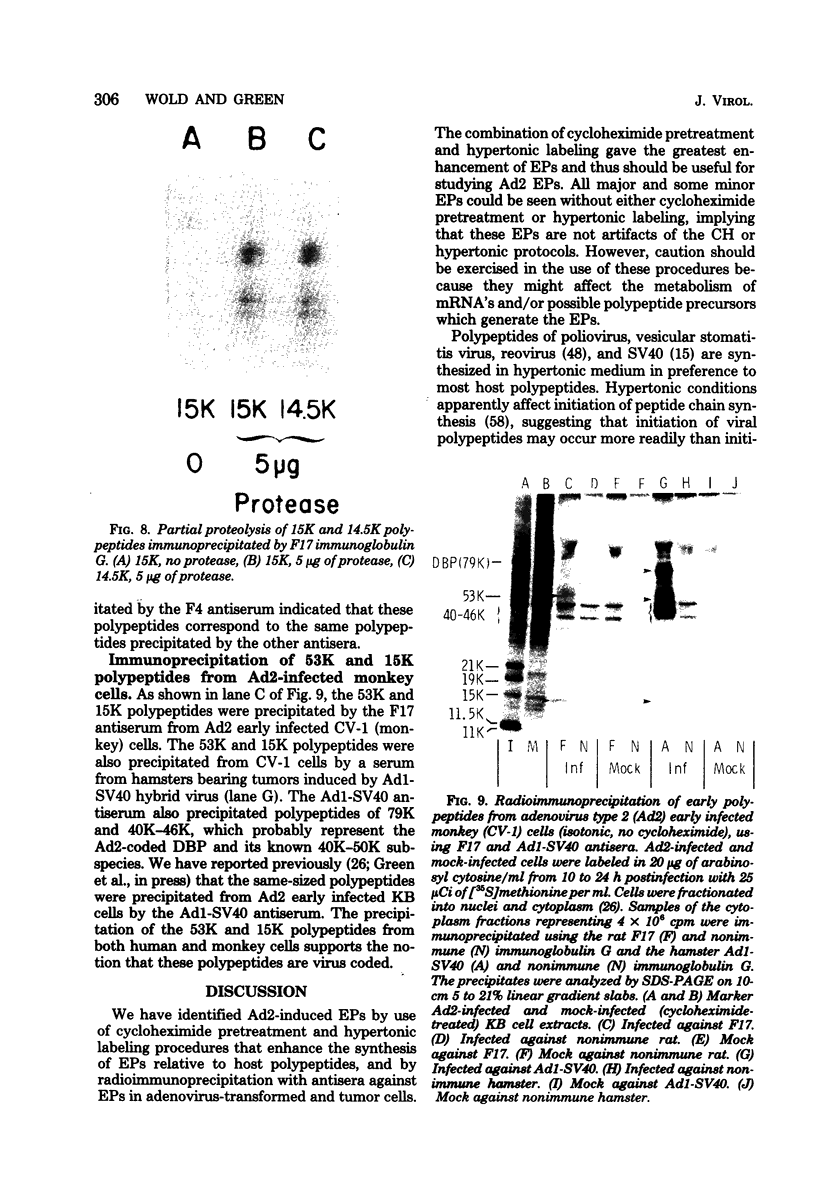
We have identified adenovirus type 2 (Ad2)-induced early polypeptides (EPs) and have attempted to determine which EPs are coded by each of the four early gene blocks. [35S]methionine-labeled EPs were resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Cycloheximide pretreatment followed by labeling in hypertonic medium (210 to 250 mM NaCl) facilitated the detection of EPs. Seven major (reproducible bands in autoradiograms) EPs were detected with molecular weights of 74,000 (74K), 21K, 19K, 15K, 13.5K, 11.5K, and 11K. Minor (weaker bands) EPs of 55K, 52K, 42K, 18K, 12K, 8.8K, and 8.3K were also often seen. To identify and map the genes for virus-coded EPs, we prepared antisera against five lines of adenovirus-transformed cells that retain different fractions of the viral genome. The lines were F17, 8617, F4, and T2C4 transformed by Ad2 virions and 5RK (clone I) transformed by transfection with the Ad5 HsuI-G fragment (map position 0 to 8). The early gene blocks retained and expressed (in part) as RNA in these cells were as follows: 5RK(I), block 1 (70% of left 8% of genome); F17, block 1; 8617, blocks 1 and 4; F4 blocks 1, 2, and 4; T2C4, blocks 1, 2, 3, and 4. The following major EPs were immunoprecipitated: 15K by all antisera; 53K and 14.5K by F17, T2C4, 8617, and F4 antisera; 11.5K by T2C4, 8617, and F4 antisera; 44K, 42K, 19K, and 13.5K by T2C4 antisera; 11K by 8617 antisera. Minor EPs of 28K, 18K, and 12K were precipitated by all antisera except 5RK(I). The 53K and 15K EPs were precipitated also from Ad2 early infected monkey cells by the F17 antiserum and by sera from hamsters bearing tumors induced by Ad1-simian virus 40. The relationships between some of the immunoprecipitated EPs were investigated by the partial proteolysis procedure. All 53K EPs are the "same" (i.e., highly related), all 15K EPs are the "same," and all 11.5K EPs are the "same." The 15K EP is highly related to the 14.5 K EP. Although less certain, all 28K EPs appeared related, as did all 18K EPs. The T2C4-specific 44K EP is probably a dimer of the 21K glycopolypeptide. The T2C4-specific 13.5K EP and the 8617-specific 11K EP appear unrelated to any other polypeptides. These immunoprecipitation data provide evidence that early gene block I (map position 1 to 11) may encode major 53K, 15K, and 14.5K polypeptides, and minor 28K, 18K, and 12K polypeptides, and that all or some of the gene for 15K and 14.5K lies within map position 1 to 8. The surprisingly complex pattern of polypeptides coded by early gene block I raises the possibility that some polypeptides may be coded by overlapping "spliced" mRNA's. The possible block locations of the genes for the 21K, 13.5K, and 11.5K polypeptides are discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arens M., Yamashita T., Padmanabhan R., Tsuruo T., Green M. Adenovirus deoxyribonucleic acid replication. Characterization of the enzyme activities of a soluble replication system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):7947–7954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod N. Phosphoproteins of adenovirus 2. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):366–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90141-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bablanian R., Russell W. C. Adenovirus polypeptide synthesis in the presence of non-replicating poliovirus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Aug;24(2):261–279. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büttner W., Veres-Molnár Z., Green M. Preparative isolation and mapping of adenovirus 2 early messenger RNA species. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 25;107(2):93–114. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter T. H., Blanton R. A. Possible role of the 72,000 dalton DNA-binding protein in regulation of adenovirus type 5 early gene expression. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):664–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.664-674.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W. W., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. VII. Further studies of early polypeptides in vivo and localization of E2 and E2A to the cell plasma membrane. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):518–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W. W., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. VIII. The enrichment of E3 (11,000) in the nuclear matrix fraction. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90284-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G., Jeng Y. H., Gilead Z., Green M. Identification of early proteins induced by highly oncogenic human adenovirus 12 during lytic infection and in hamster tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 7;74(3):1199–1205. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91645-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadural G., Fujinaga K., Rho M. H., van der Eb A. J., Green M. Transcription of the transforming region of adenovirus type 5 in a rat cell line transformed by a small restriction fragment. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):1011–1014. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.1011-1014.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Roberts J. M., Lewis J. B., Broker T. R. A map of cytoplasmic RNA transcripts from lytic adenovirus type 2, determined by electron microscopy of RNA:DNA hybrids. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):819–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Raskas H. J. Nuclear transcripts larger than the cytoplasmic mRNAs are specified by segments of the adenovirus genome coding for early functions. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England J. M., Howett M. K., Tan K. B. Effect of hypertonic conditions on protein synthesis in cells productively infected with simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1101–1107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1101-1107.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fraser N., Ziff E., Weber J., Wilson M., Darnell J. E. The initiation sites for RNA transcription in Ad2 DNA. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J. The topography and transcription of the adenovirus genome. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Berget S. M., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. III. Mapping of viral RNA sequences in cells productively infected by adenovirus type 5. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):443–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Gallimore P. H., Sharp P. A. Comparison of viral RNA sequences in adenovirus 2-transformed and lytically infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):47–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Sambrook J., Williams J. F., Sharp P. A. Viral nucleic acid sequences in transformed cells. IV. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 5 DNA and RNA in four lines of adenovirus 5-transformed rodent cells using specific fragments of the viral genome. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):456–470. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. V. Quantitation of viral RNA sequences in adenovirus 2-infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):749–774. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J. Two "early" mRNA species in adenovirus type 2-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):44–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.44-52.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Interactions of adenovirus type 2 with rat embryo cells. Permissiveness, transformation and in vitro characteristics of adenovirus transformed rat embryo cells. J Gen Virol. 1974 Nov;25(2):263–273. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden R. V., Kern J., Freeman A. E., Martin C. E., McAllister R. C., Turner H. C., Huebner R. J. T and tumour antigens of adenovirus group C-infected and transformed cells. Nature. 1968 Aug 3;219(5153):517–518. doi: 10.1038/219517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilead Z., Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Sugawara K., Rho H. M., Harter M. L., Green M. Immunological identification of two adenovirus 2-induced early proteins possibly involved in cell transformation. Nature. 1976 Nov 18;264(5583):263–266. doi: 10.1038/264263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilead Z., Sugawara K., Shanmugam G., Green M. Synthesis of the adenovirus-coded DNA binding protein in infected cells. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):454–460. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.454-460.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg H. S., Ensinger M. J., Kauffman R. S., Mayer A. J., Lundholm U. Cell transformation: a study of regulation with types 5 and 12 adenovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):419–426. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Anderson C., Sambrook J., Mathews M. B. The physical locations of structural genes in adenovirus DNA. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T., Graham F., Williams J. Host-range mutants of adenovirus type 5 defective for growth in HeLa cells. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Lewis J. B. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins synthesized in vitro and in vivo: identification in infected cells of the 38,000- to 50,000- molecular-weight protein encoded by the left end of the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):736–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.736-749.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Shanmugam G., Wold W. S., Green M. Detection of adenovirus type 2-induced early polypeptides using cycloheximide pretreatment to enhance viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):232–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.232-242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi M., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. VI. Early and late glycopolypeptides. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):345–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Green M. Evidence for an adenovirus type 2-coded early glycoprotein. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):314–323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.314-323.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Sugawara K., Gilead Z., Green M. Adenovirus type 2 coded single-stranded DNA binding protein: in vivo phosphorylation and modification. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):402–411. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.402-411.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Lai S. P., Westphal H. Loop structures in hybrids of early RNA and the separated strands of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4392–4395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassam N. J., Bayley S. T., Graham F. L. Synthesis of DNA, late polypeptides, and infectious virus by host-range mutants of adenovirus 5 in nonpermissive cells. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Levine A. J. The group C adenovirus tumor antigens: identification in infected and transformed cells and a peptide map analysis. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):871–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Postel E. H., Levine A. J. In vivo and in vitro phosphorylation of the adenovirus type 5 single strand-specific DNA-binding protein. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):144–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90341-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A., Levine A. J. The isolation and identification of the adenovirus group C tumor antigens. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Baum P. R., Solem R., Gesteland R. F., Anderson C. W. Location and identification of the genes for adenovirus type 2 early polypeptides. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90264-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linné T., Jörnvall H., Philipson L. Purification and characterization of the phosphorylated DNA-binding protein from adenovirus-type-2-infected cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 15;76(2):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwald P. D., Meyer J., Maizel J. V., Jr, Westpahl H. Early gene expression of adenovirus type 2: R-loop mapping of mRNA and time course of viral DNA, mRNA, and protein synthesis. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1019–1030. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1019-1030.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuss D. L., Oppermann H., Koch G. Selective blockage of initiation of host protein synthesis in RNA-virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Mathews M. B. The gene and messenger RNA for adenovirus polypeptide IX. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):741–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90274-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Tibbetts C., Philipson L. Hybridization maps of early and late messenger RNA sequences on the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):479–501. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Pettersson U., Lindberg U. Molecular biology of adenoviruses. Virol Monogr. 1975;14:1–115. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-8391-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D. M., Russell W. C., Bellet A. J., Robinson A. J. Identification of a protein linked to the ends of adenovirus DNA. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rho H. M., Jeng Y. H., Wold W. S., Green M. Association of adenovirus type 2 early proteins with a soluble complex that synthesizes adenovirus DNA in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 21;79(2):422–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwirth B., Anderson C., Levine A. J. Tryptic fingerprint analysis of adenovirus types 2, 5 and 12 DNA-Binding proteins. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90490-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Blair G. E. Polypeptide phosphorylation in adenovirus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):19–35. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Skehel J. J. The polypeptides of adenovirus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1972 Apr;15(1):45–57. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Oberg B. In vivo and in vitro synthesis of adenovirus type 2 early proteins. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):865–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.865-875.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Pong S. S., Koch G. Selective and reversible inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam G., Bhaduri S., Arens M., Green M. DNA binding proteins in the cytoplasm and in a nuclear membrane complex isolated from uninfected and adenovirus 2 infected cells. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 28;14(2):332–337. doi: 10.1021/bi00673a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K., Gilead Z., Green M. Purification and molecular characterization of adenovirus type 2 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.338-346.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K., Gilead Z., Wold W. S., Green M. Immunofluorescence study of the adenovirus type 2 single-stranded DNA binding protein in infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):527–539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.527-539.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Vliet P. C., Levine A. J., Ensinger M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Thermolabile DNA binding proteins from cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant of adenovrius defective in viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):348–354. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.348-354.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Eb A. J., Houweling A. Transformation with specific fragments of adenovirus DNAs. II. Analysis of the viral DNA sequences present in cells transformed with a 7% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Eb A. J., Mulder C., Graham F. L., Houweling A. Transformation with specific fragments of adenovirus DNAs. I. Isolation of specific fragments with transforming activity of adenovirus 2 and 5 DNA. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):115–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Vliet P. C., Zandberg J., Jansz H. S. Evidence for a function of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein in initiation in DNA synthesis as well as in elongation of nascent DNA chains. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):98–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. IV. Detection of early and late virus-induced polypeptides and their distribution in subcellular fractions. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willians J. F., Young C. S., Austin P. E. Genetic analysis of human adenovirus type 5 in permissive and nonpermissive cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):427–437. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Green M., Brackmann K. H., Devine C., Cartas M. A. Adenovirus type 2 early nuclear and mRNA: kinetic estimation of l anf r DNA strand fractions complementary to different abundance classes of viral RNA. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):616–625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.616-625.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet P. C., Levine A. J. DNA-binding proteins specific for cells infected by adenovirus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 12;246(154):170–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio246170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]