Abstract
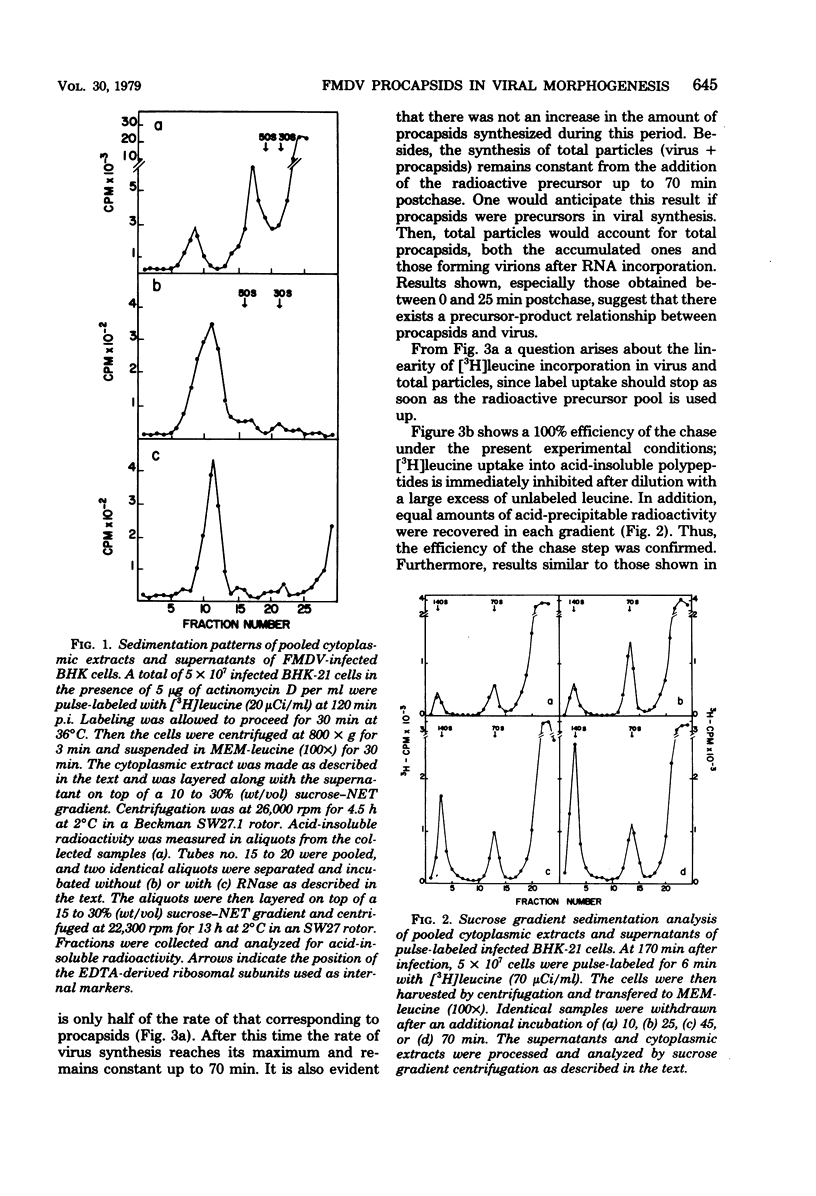
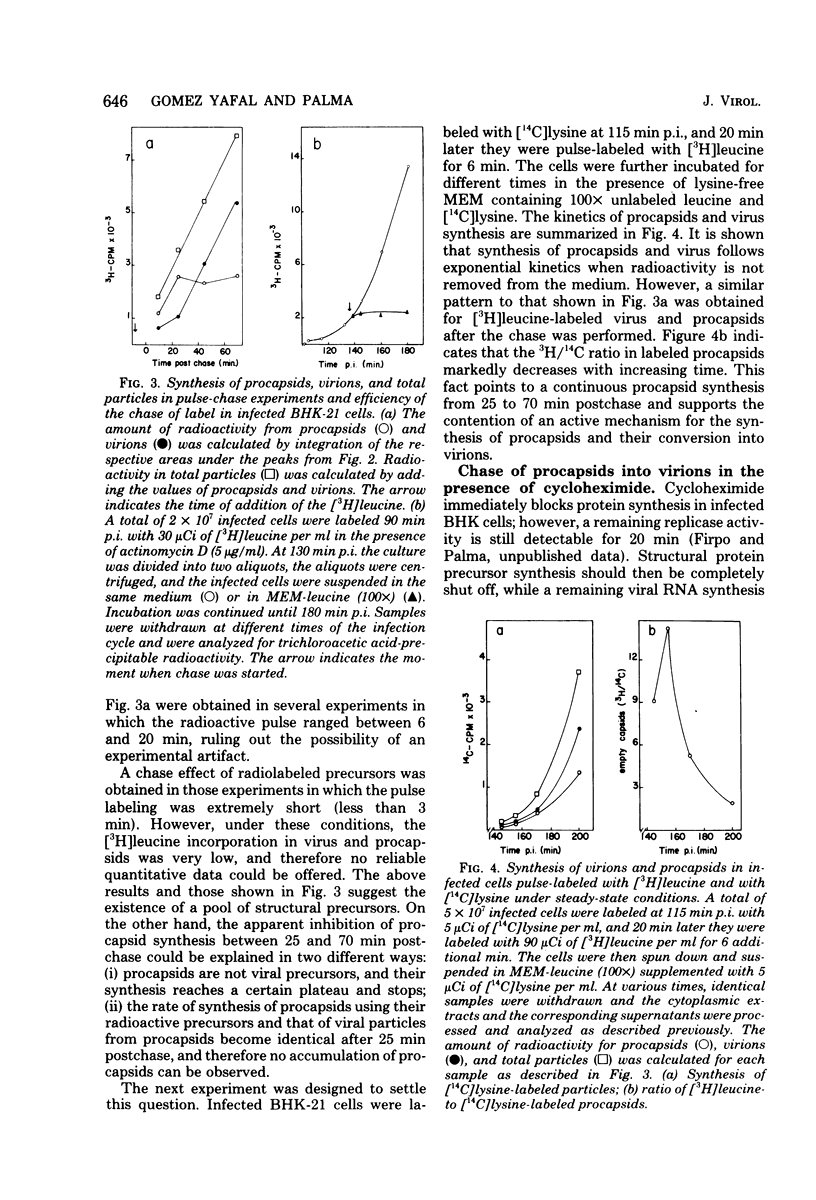
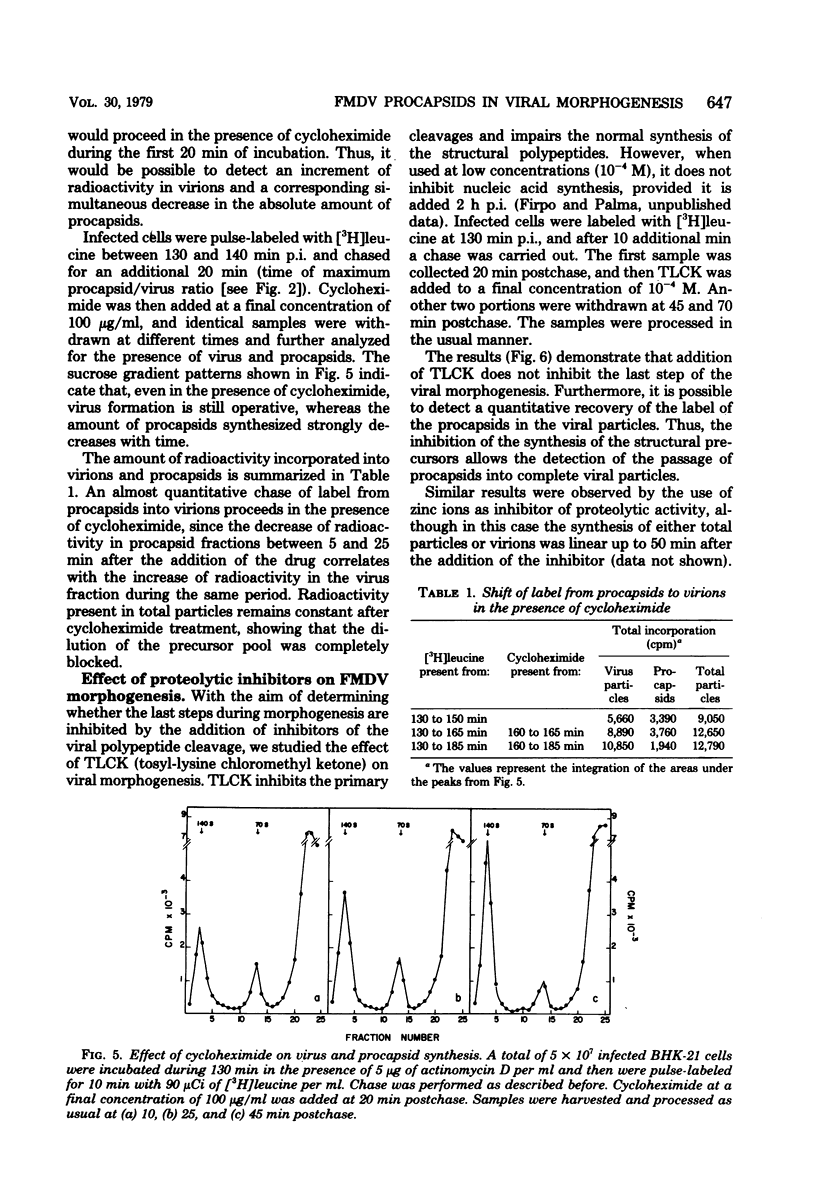
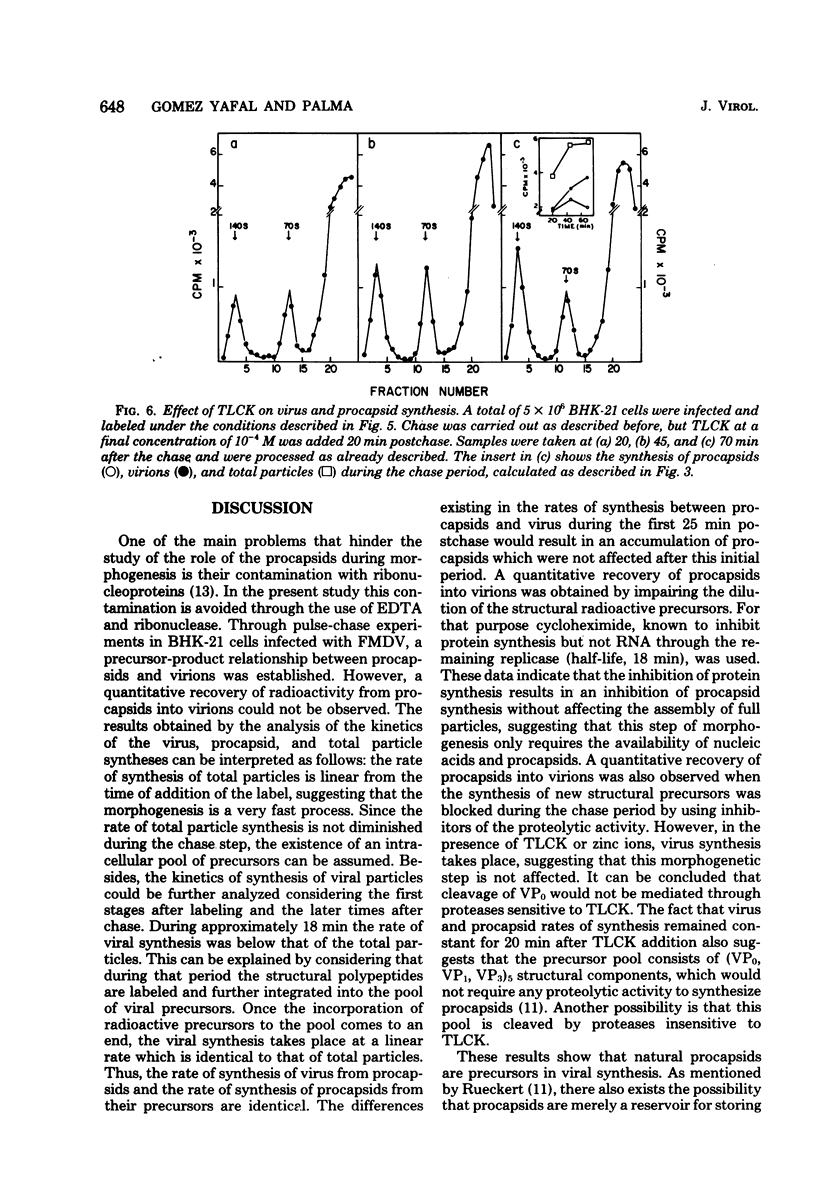
The role of procapsids during foot-and-mouth disease virus multiplication was studied on infected BHK-21 cells. Purified virus and procapsids were obtained by treating the infected cytoplasmic extracts with RNase and EDTA. The synthesis of virus, procapsids, and total particles was determined in pulse-chase experiments. A precursor-product relationship between procapsids and virions was obtained. The results show that the rate of synthesis of total particles (virus + procapsids) was linear from the addition of the label and was identical to that corresponding to virions. Therefore, the speed of the morphogenetic process as well as the existence of a precursor pool of structural proteins was established. Furthermore, the rate of virus synthesis from procapsids was identical to the rate of synthesis of procapsids from their structural precursors. A quantitative recovery of label from procapsids into virions was obtained by the use of cycloheximide or tosyl-lysine chloromethyl ketone. Under these conditions, virus synthesis proceeds, indicating that these drugs do not affect the morphogenetic step studied in this paper.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capstick P. B., Garland A. J., Chapman W. G., Masters R. C. Factors affecting the production of foot-and-mouth disease virus in deep suspension cultures of BHK21 clone 13 cells. J Hyg (Lond) 1967 Sep;65(3):273–280. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400045794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Tomas C. B., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. II. Demonstration of a new intermediate, the proviron. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1122–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1122-1130.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Tomas C. B., Guttman N., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus 3. Formation of provirion in cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1181–1183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1181-1183.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghendon Y., Yakobson E., Mikhejeva A. Study of some stages of poliovirus morphogenesis in MiO cells. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):261–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.261-266.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. H., Cowan K. M., Trautman R. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. II. Characterization of RNA-free viruslike particles. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman N., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. IV. existence of particles sedimenting at 150S and having the properties of provirion. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):363–367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.363-367.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey E. M., Martin S. J. A possible precursor containing RNA of a bovine enterovirus: the provirion 11. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):515–524. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S. Evidence for the existence of protomers in the assembly of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1107–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1107-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Sangar D. V., Brown F. A comparative chemical and serological study of the full and empty particles of foot-and mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):227–238. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKER M., MACPHERSON I. SYRIAN HAMSTER FIBROBLAST CELL LINE BHK21 AND ITS DERIVATIVES. Nature. 1964 Sep 26;203:1355–1357. doi: 10.1038/2031355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. J., Cooper P. D. Poliovirus proteins associated with ribosomal structures in infected cells. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



