Abstract
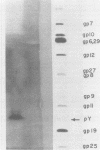
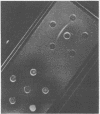
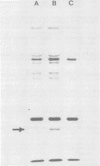
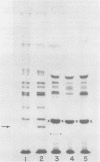
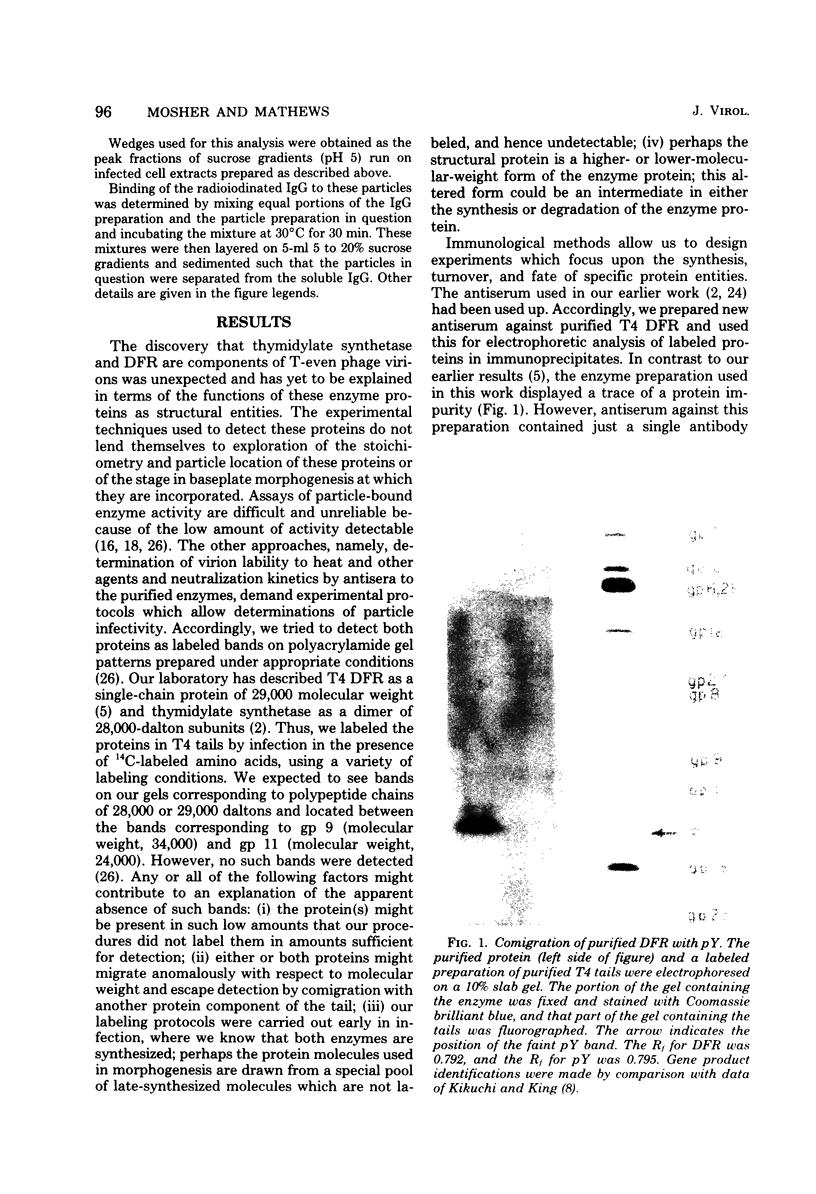
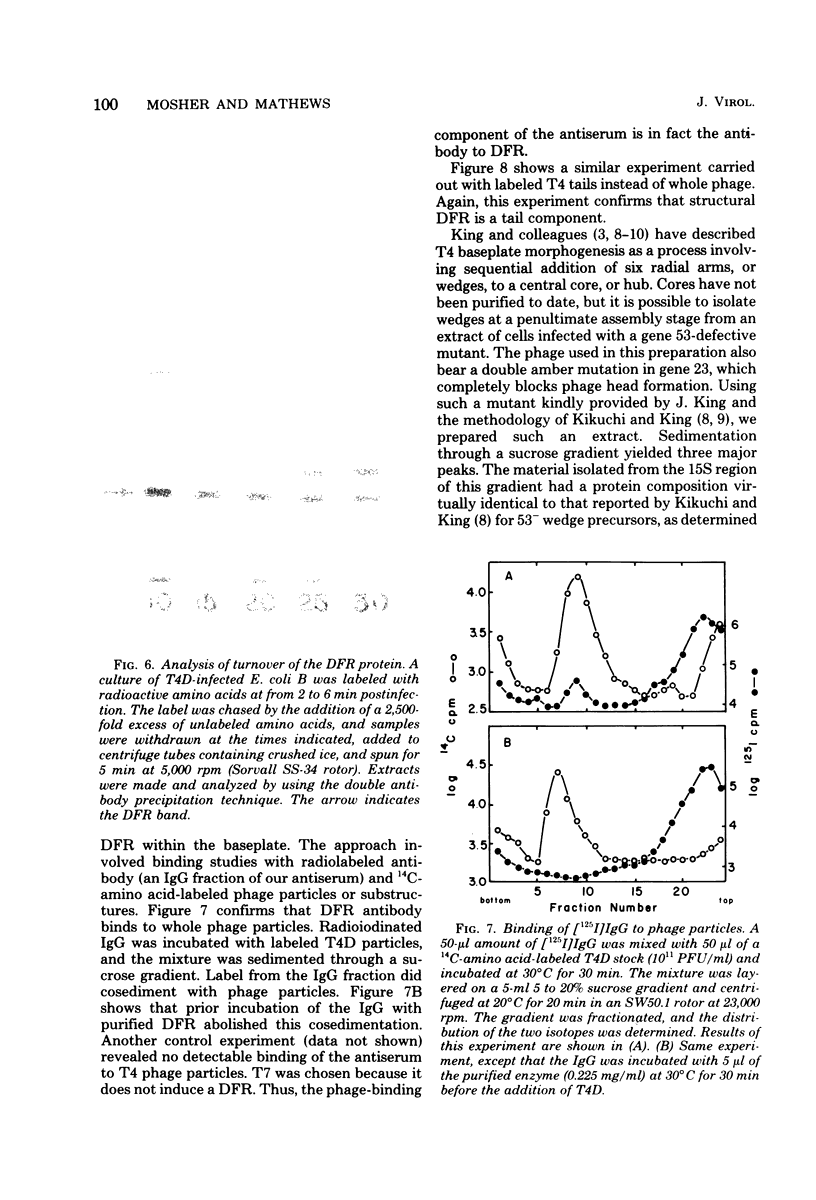
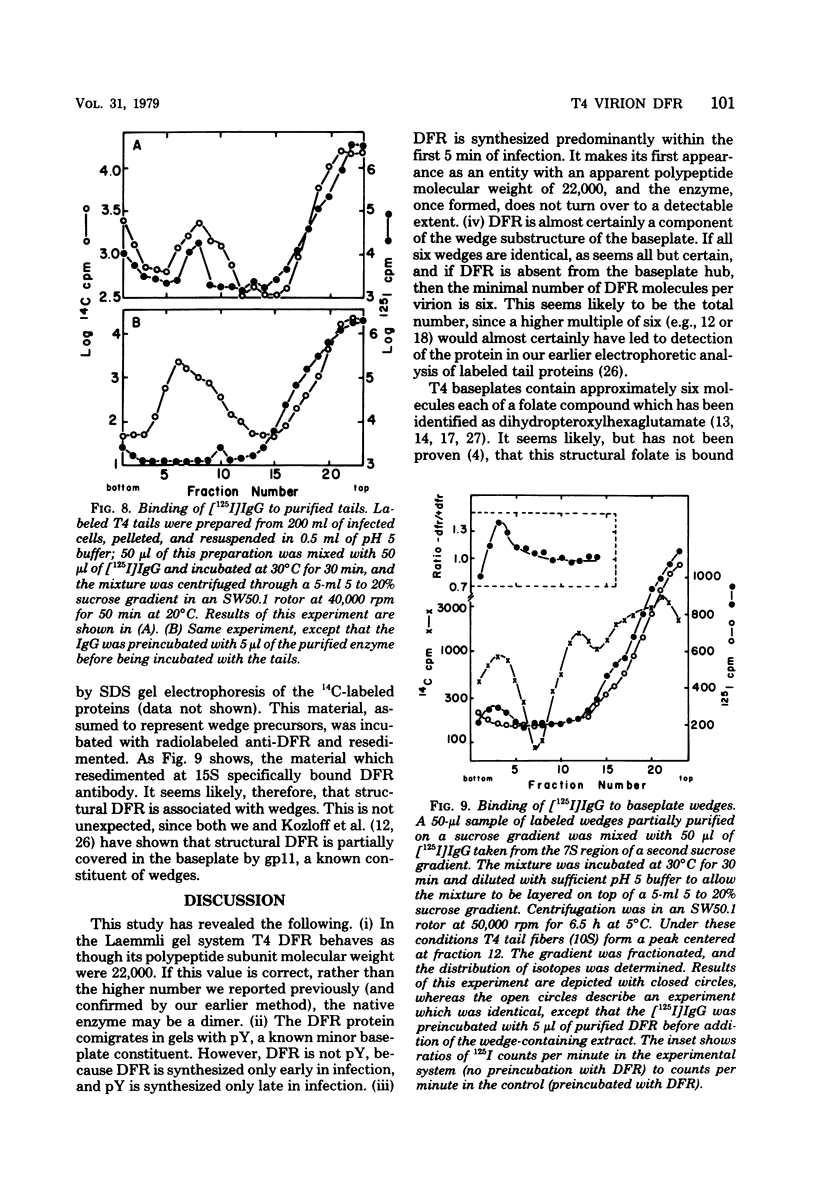
Dihydrofolate reductase plays a dual role in bacteriophage T4, first, as an enzyme of thymidylate metabolism, and second, as a protein component of the tail baseplate. Antibody to the purified enzyme has been used to study its synthesis and intracellular turnover. The antibody specifically precipitates one protein from T4D-infected cell extracts. This has been identified as dihydrofolate reductase, although the polypeptide molecular weight (22,000) is lower than that earlier determined for this enzyme. The protein comigrates on gels with pY, a genetically undefined protein component of the baseplate. However, it is not pY, for pY is synthesized late in infection, whereas virtually no dihydrofolate reductase synthesis occurs later than 10 min after infection at 37 degrees C. Dihydrofolate reductase, once formed, is neither degraded nor converted to proteins of higher or lower molecular weight. Thus, it is probably incorporated into virions at the same molecular weight as that of the soluble enzyme. 125I-radiolabeled antibody binds to the wedge substructure of the baseplate, and this binding is blocked by preincubation with purified T4 dihydrofolate reductase. Thus, the enzyme protein seems to be a component of the wedge.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berget P. B., King J. Isolation and characterization of precursors in T4 baseplate assembly. The complex of gene 10 and gene 11 products. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 25;124(3):469–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capco G. R., Mathews C. K. Bacteriophage-coded thymidylate synthetase. Evidence that the T4 enzyme is a capsid protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):736–743. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90568-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther R. A., Lenk E. V., Kikuchi Y., King J. Molecular reorganization in the hexagon to star transition of the baseplate of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov 5;116(3):489–523. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes J., Goldberg E. B. Functions of baseplate components in bacteriophage T4 infection. I. Dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroylhexaglutamate. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):380–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. S., Mathews C. K. T4 bacteriophage-specific dihydrofolate reductase: purification to homogeneity by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 4;43(5):1164–1170. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. H. Mutants of bacteriophage T4 unable to induce dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):584–591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homyk T., Jr, Weil J. Deletion analysis of two nonessential regions of the T4 genome. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):505–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., King J. Genetic control of bacteriophage T4 baseplate morphogenesis. I. Sequential assembly of the major precursor, in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):645–672. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., King J. Genetic control of bacteriophage T4 baseplate morphogenesis. II. Mutants unable to form the central part of the baseplate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):673–694. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., King J. Genetic control of bacteriophage T4 baseplate morphogenesis. III. Formation of the central plug and overall assembly pathway. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):695–716. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Crosby L. K., Lute M. Bacteriophage T4 baseplate components. III. Location and properties of the bacteriophage structural thymidylate synthetase. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1409–1419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1409-1419.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Crosby L. K., Lute M., Hall D. H. Bacteriophage T4 baseplate components. II. Binding and location of bacteriophage-induced dihydrofolate reductase. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1401–1408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1401-1408.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M. Bacteriophage tail components. IV. Pteroyl polyglutamate synthesis in T4D-infected Escherichia coli B. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):630–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.630-636.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M., Baugh C. M. Bacteriophage tail components. V. Complementation of T4D gene 28 - -infected bacterial extracts with pteroyl hexaglutamate. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):637–641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.637-641.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M., Crosby L. K. Bacteriophage T4 virion baseplate thymidylate synthetase and dihydrofolate reductase. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):637–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.637-644.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M., Crosby L. K., Rao N., Chapman V. A., DeLong S. S. Bacteriophage tail components. I. Pteroyl polyglutamates in T-even bacteriophages. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):726–739. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.726-739.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Lute M. Folic acid, a structural component of T4 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):780–792. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80327-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozloff L. M., Verses C., Lute M., Crosby L. K. Bacteriophage tail components. II. Dihydrofolate reductase in T4D bacteriophage. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):740–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.740-753.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS C. K., SUTHERLAND K. E. COMPARATIVE BIOCHEMISTRY OF BACTERIAL AND PHAGE-INDUCED DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASES. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:2142–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K., Crosby L. K., Kozloff L. M. Inactivation of T4D bacteriophage by antiserum against bacteriophage dihydrofolate reductase. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):74–78. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.74-78.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K. Evidence that bacteriophage-induced dihydrofolate reductase in a viral gene product. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4083–4086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K. Growth of a dihydrofolate reductaseless mutant of bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):963–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.963-967.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K. Identity of genes coding for soluble and structural dihydrofolate reductases in bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):531–533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.531-533.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews C. K. Deoxyribonucleic acid metabolism and virus-induced enzyme synthesis in a thymine-requiring bacterium infected by a thymine-requiring bacteriophage. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):2092–2100. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher R. A., DiRenzo A. B., Mathews C. K. Bacteriophage T4 virion dihydrofolate reductase: approaches to quantitation and assessment of function. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):645–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.645-658.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Kozloff L. M. Folate polyglutamates in T4D bacteriophage and T4D-infected Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 3;540(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W., Roberts C. W. Proteolytic cleavage of bacteriophage lambda repressor in induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]