Abstract
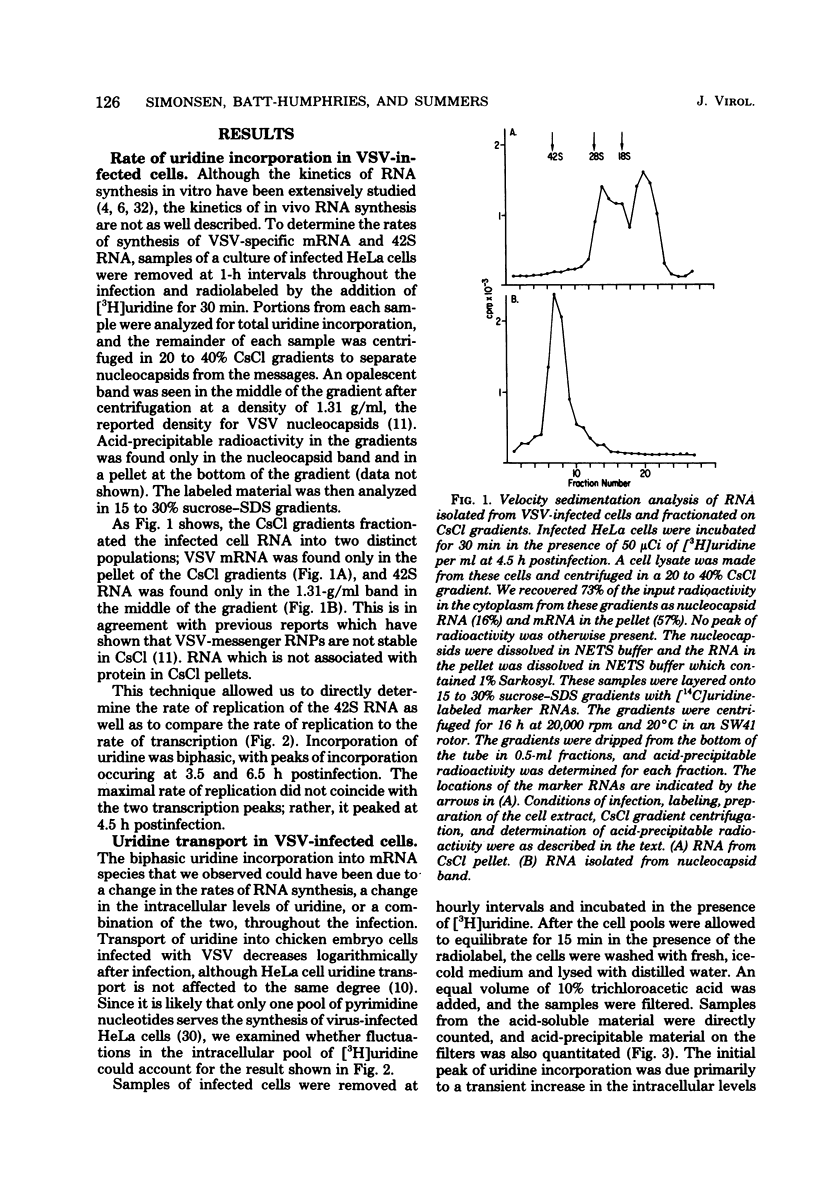
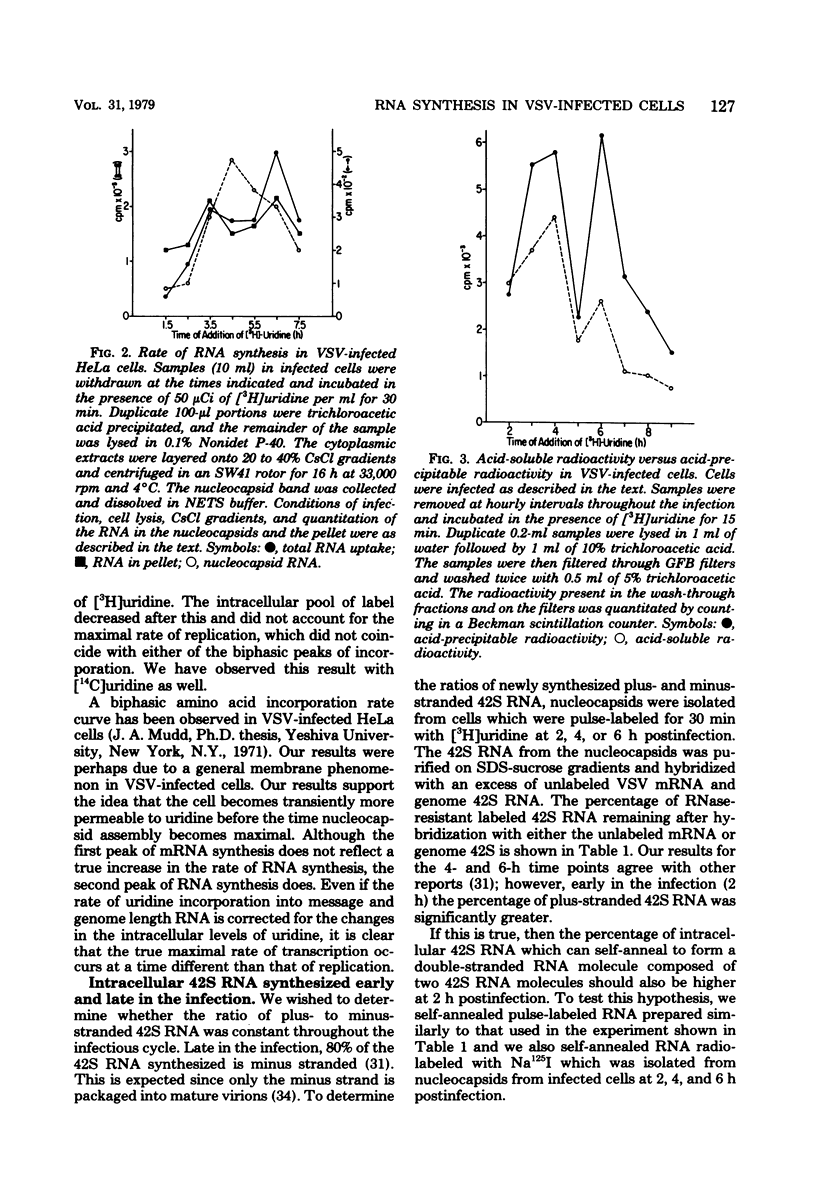
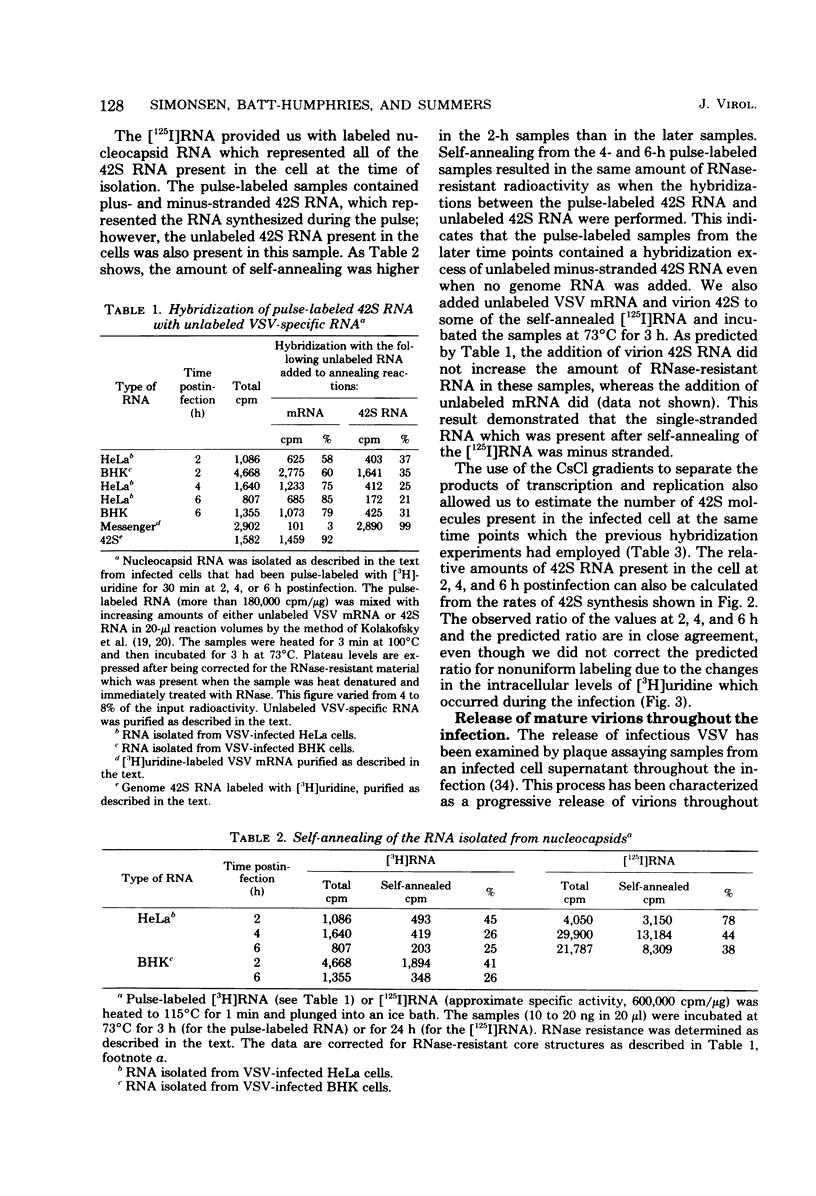
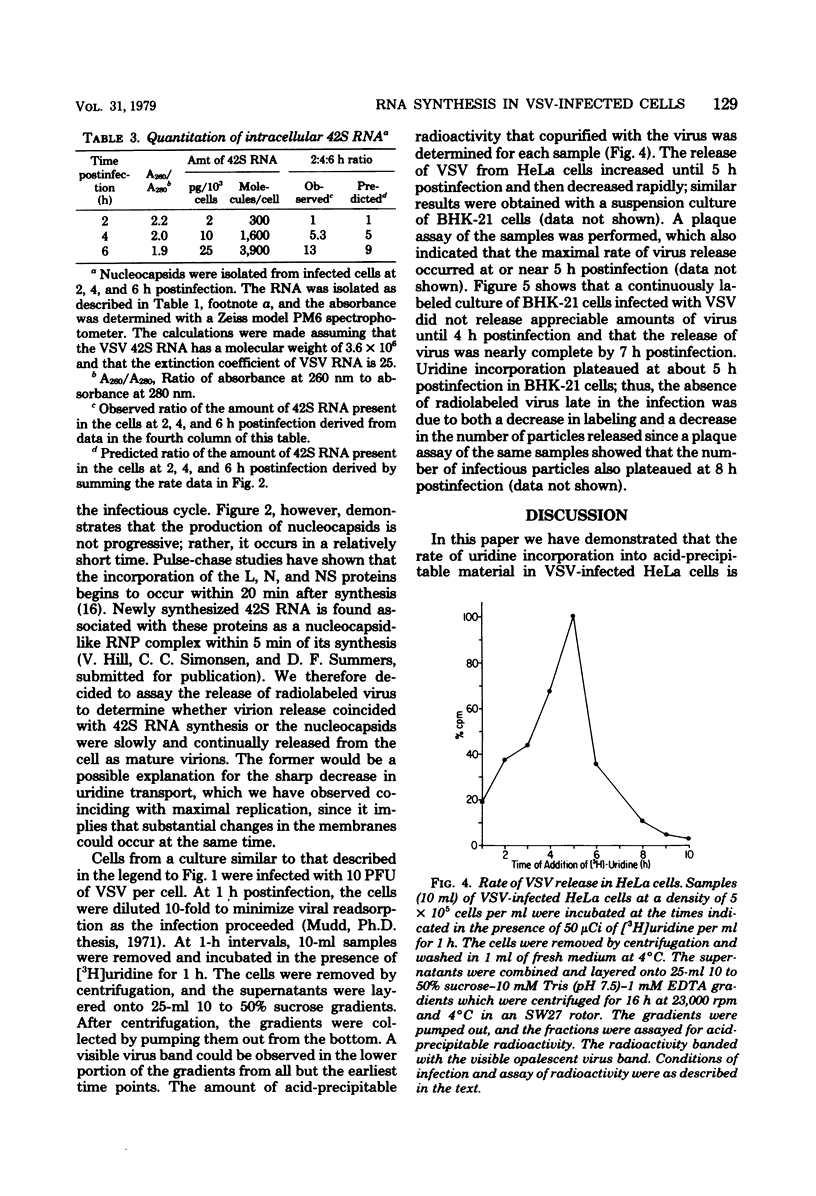
Pulse-labeling of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa and BHK cells with [3H]uridine throughout the infectious cycle demonstrated two peaks of uridine incorporation into virus-specific RNA molecules. By separating total RNA synthesis into replication and transcription products, we showed that replication occurs over a shorter period of time in one peak synthesis. The biphasic nature of uridine incorporation is in part due to a general membrane phenomenon of reduced metabolite transport during vesicular stomatis virus infection and in part due to the apparent uncoupling of replication and transcription. A change in the ratio of newly synthesized plus and minus strands of the genome length (42S) RNA was found as the infection proceeded. Early in the infection, plus-stranded 42S RNA comprised 40% of the total genome length RNA synthesis, whereas late in infection, only 15 to 20% of the 42S RNA synthesized was complementary to the virion minus strand. Our data suggest that the rate of synthesis of plus-stranded 42S RNA was constant throughout the infection. The rate of virus release was determined by monitoring the uptake of [3H]uridine into released virus particles. Virus maturation and release are closely associated with the assembly of 42S RNA-containing nucleocapsids.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Rhodes D. P., Banerjee A. K. The 5' terminal structure of the methylated mRNA synthesized in vitro by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson P. H., Moyer S. A., Summers D. F. Assembly of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and matrix protein into HeLa cell plasma membranes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):613–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson P. H. Synthesis and assembly of HeLa cell plasma membrane glycoproteins and proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2123–2134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Rhodes D. P. In vitro synthesis of RNA that contains polyadenylate by virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3566–3570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Roy P. Kinetics of RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus particles. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):513–527. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Anderson P. J., Bauer W. R. Resolution of single- and double-stranded RNAs in buoyant cesium trichloroacetate. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Yu Y. Both NS and L proteins are required for in vitro RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1348–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1348-1356.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Pringle C. R., Wunner W. H., Skehel J. J. Virus replication in enucleate cells: vesicular stomatitis virus and influenza virus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.394-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genty N. Analysis of uridine incorporation in chicken embryo cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus and its temperature-sensitive mutants: uridine transport. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.8-15.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Shafritz D. A. Identification and characterization of messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes from vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Summers D. F. In vitro protein-synthesizing activity of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cell extracts. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.265-274.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Adler S., Lazzarini R. A., Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K., Westphal H. Intervening polyadenylate sequences in RNA transcripts of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. 3. Multiple complementary messenger RNA molecules. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):946–957. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. M., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. RNA- temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: L-protein thermosensitivity accounts for transcriptase restriction of group I mutants. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):596–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.596-603.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. A., Summers D. F. Association of vesicular stomatitis virus proteins with HeLa cell membranes and released virus. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):637–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.637-645.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. R., Lazzarini R. A. The relationship between autointerference and the replication of defective interfering particle. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley M. P., Wagner R. R. Ribonucleic acid species of intracellular nucleocapsids and released virions of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):244–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.244-255.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolakofsky D. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Kort L., Kolakofsky D. Further characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs: a model for their generation. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):539–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Maizel J. V., Jr In vivo regulation of the poliovirus RNA polymerase. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):484–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. Messenger RNA species synthesized in vitro by the virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Polysomal ribonucleic acid of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):958–968. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90344-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito S., Ishihama A. Function and structure of RNA polymerase from vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4307–4314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg B., Philipson L. Replicative structures of poliovirus RNA in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S. M., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. V. Interactions between transcription and replication. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1395–1400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1395-1400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Flamand A., Bishop D. H. Synthesis of RNA by mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) and the ability of wild-type VSV New Jersey to complement the VSV Indiana ts G I-114 transcription defect. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):157–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.157-169.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. P., Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. In vitro synthesis of methylated messenger RNA by the virion-associated RNA polymerase of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E., Manning J. Strand-specific attachment of avidin-spheres to double-stranded poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):676–680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Ehrenfeld E. Cytoplasmic and nuclear pyrimidine ribonucleotide pools in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jun 15;77(1):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90371-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria M., Little S. P., Huang A. S. Characterization of vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsids. I. Complementary 40 S RNA molecules in nucleocapsids. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):270–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi J. F., Pringle C. R. Effect of temperature-sensitive mutations on the virion-associated RNA transcriptase of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., Holland J. J. Synthesis of poly(A) in vitro by purified virions of vesicular stomatitis virus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 7;246(149):17–19. doi: 10.1038/newbio246017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W. Isolation of possible replicative intermediate structures from vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. Virology. 1978 Mar;85(1):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Levine M. RNA synthesis by vesicular stomatitis virus and a small plaque mutant: effects of cycloheximide. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):253–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.253-264.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



