Abstract
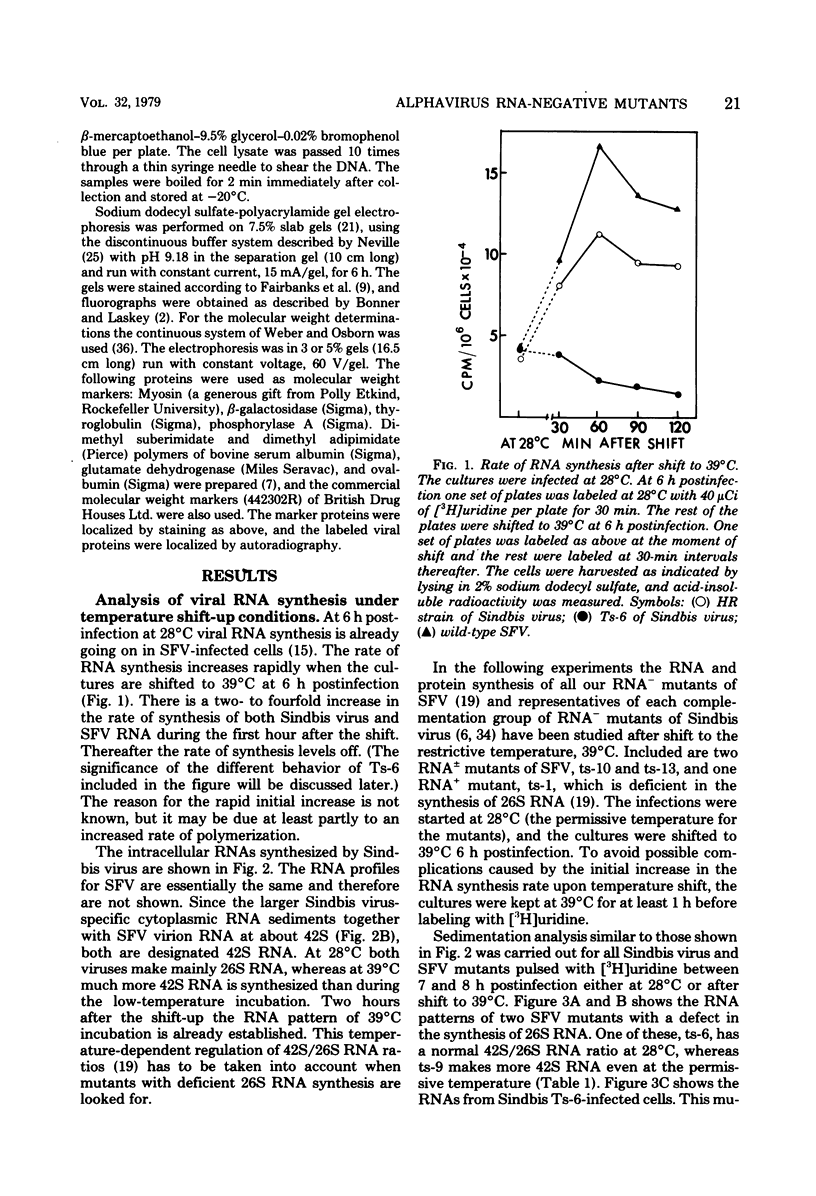
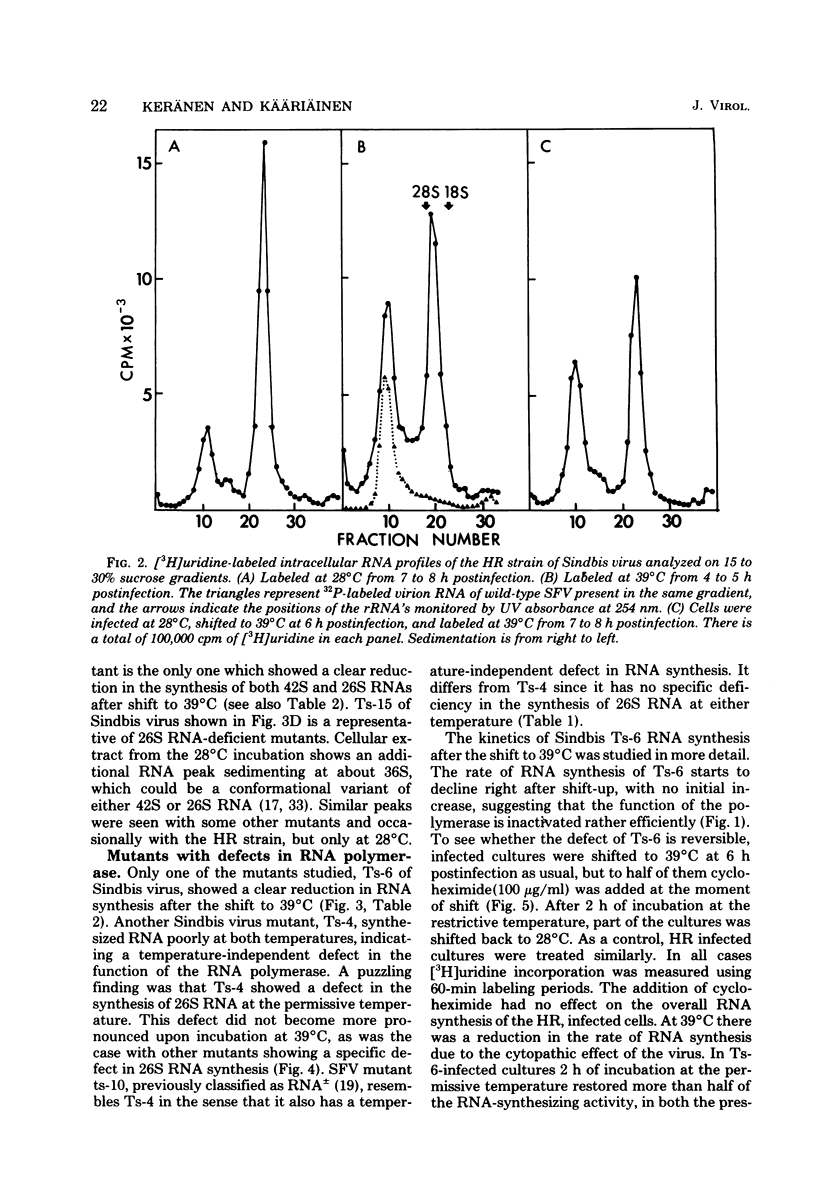
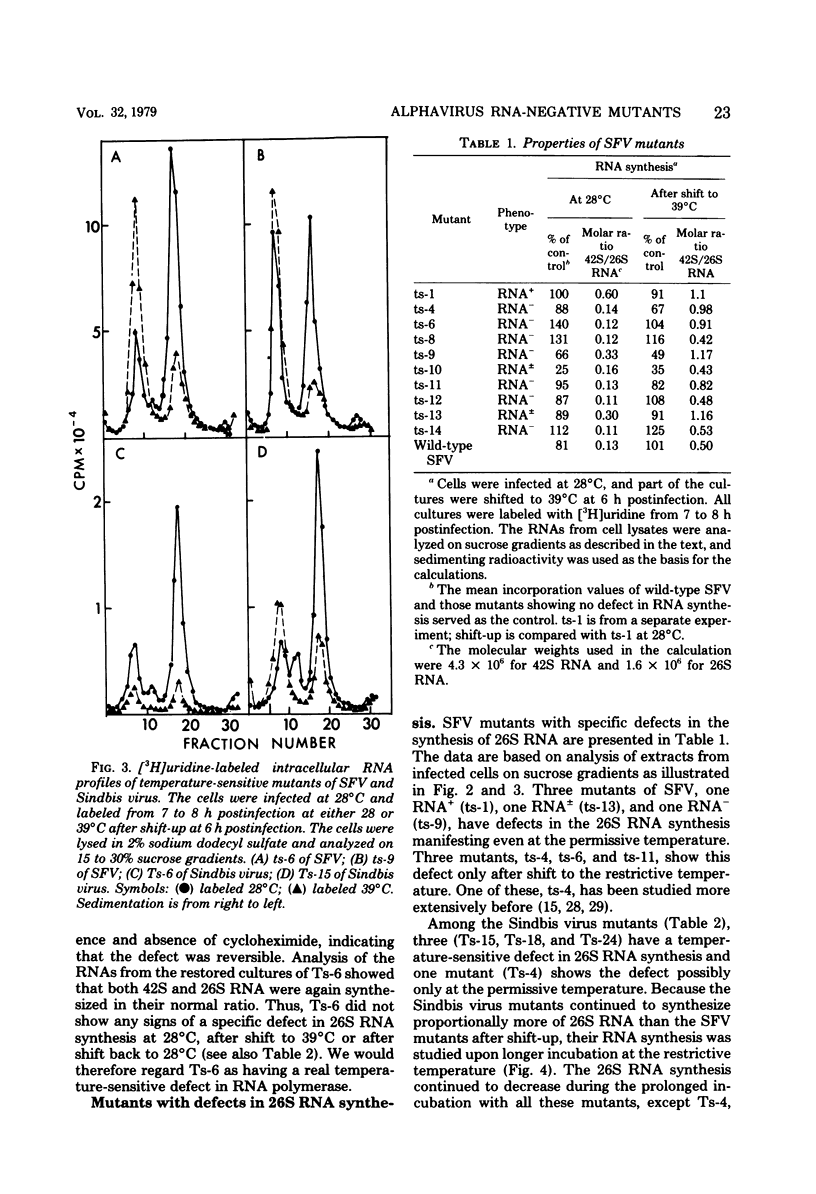
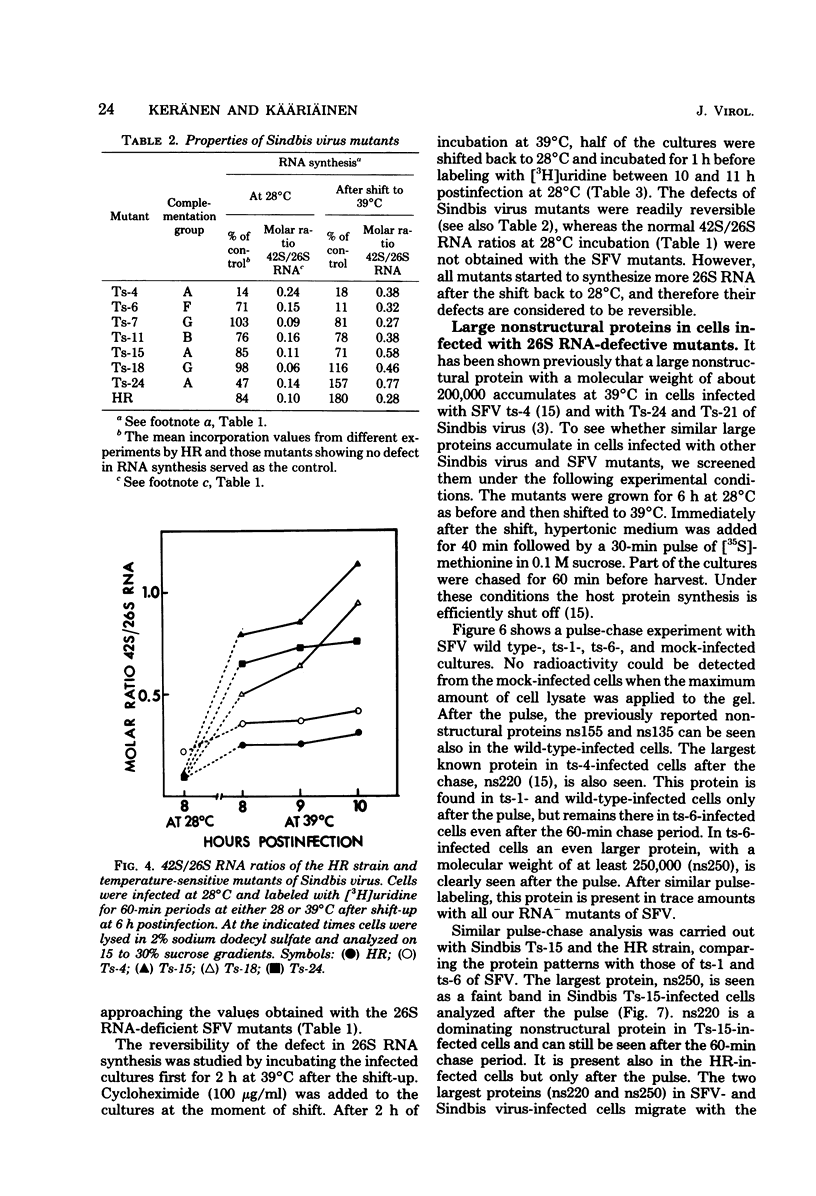
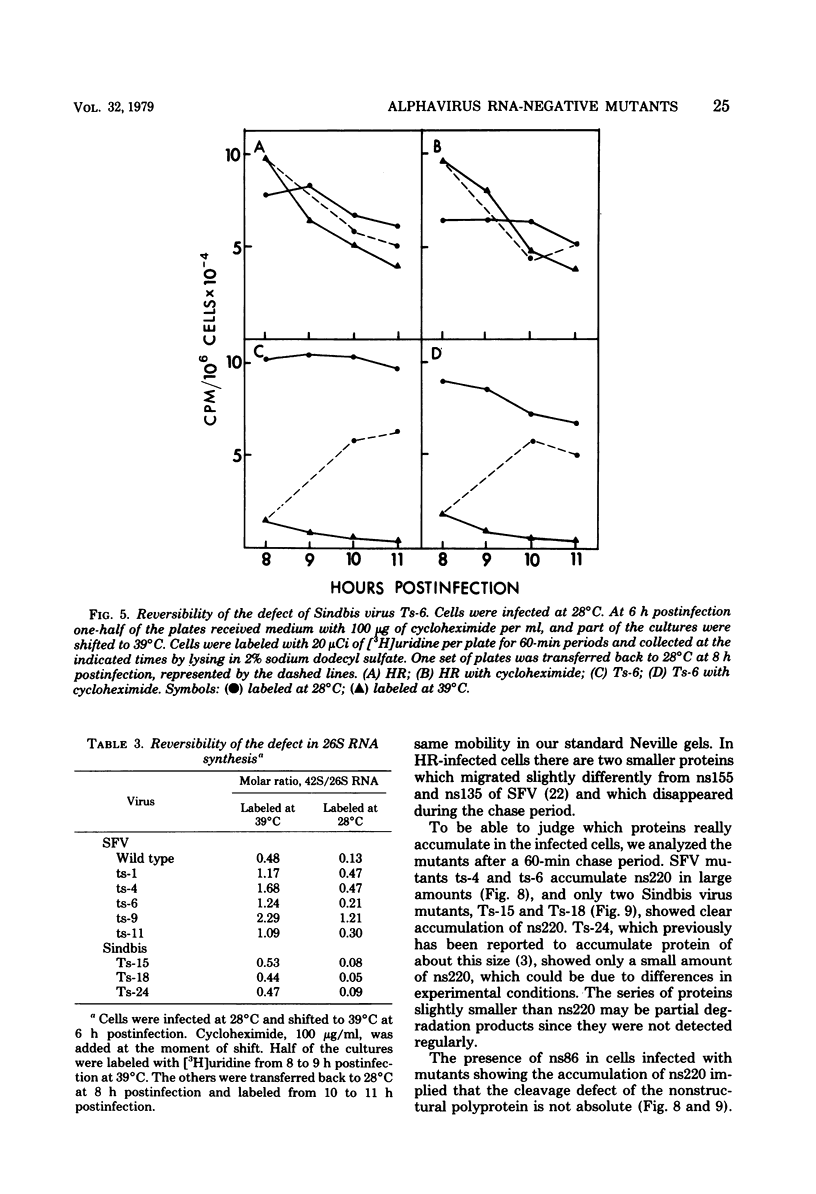
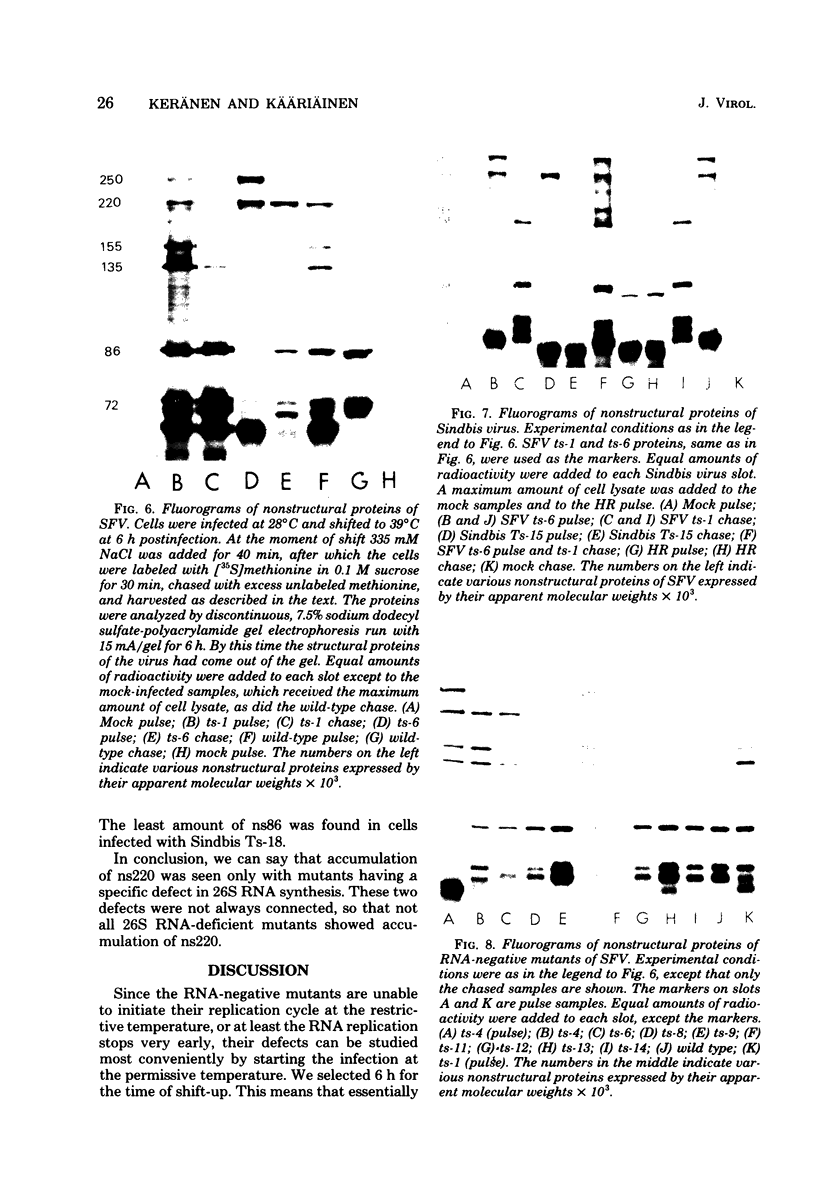
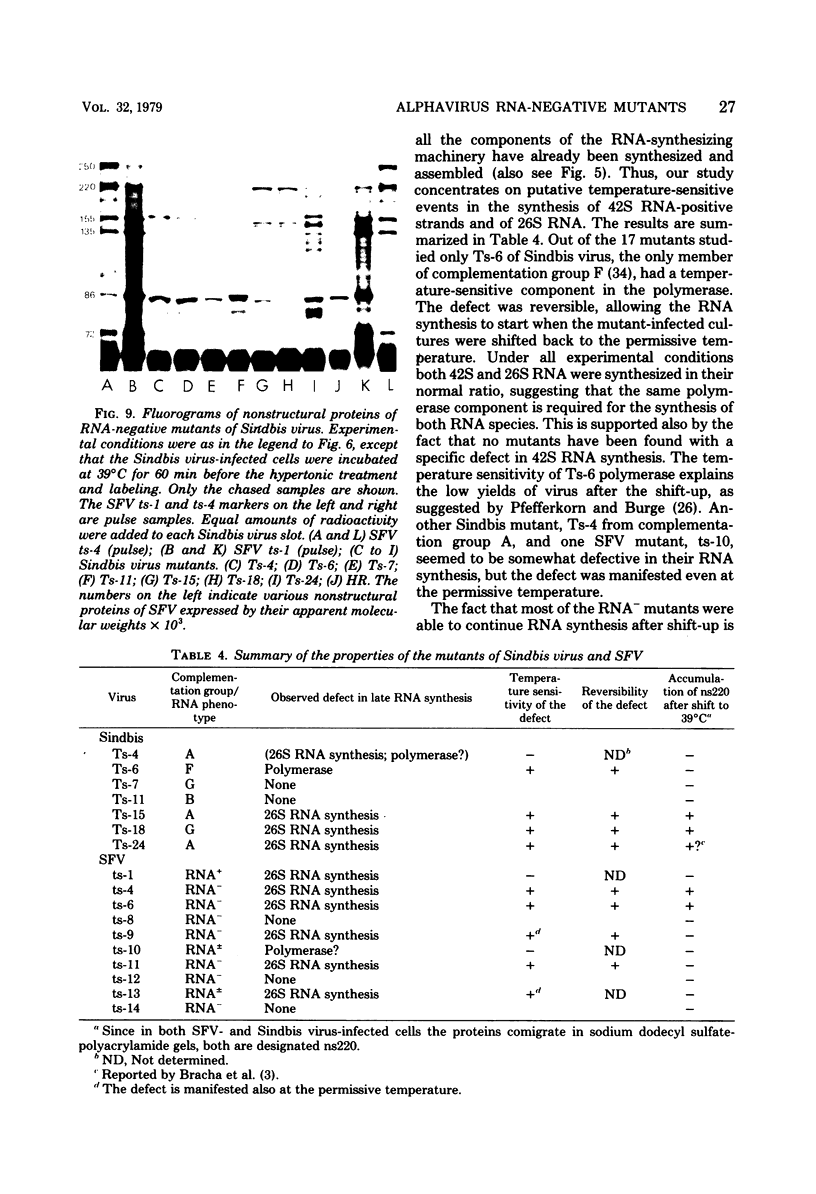
Defects in RNA and protein synthesis of seven Sindbis virus and seven Semliki Forest virus RNA-negative, temperature-sensitive mutants were studied after shift to the restrictive temperature (39 degrees C) in the middle of the growth cycle. Only one of the mutants, Ts-6 of Sindbis virus, a representative of complementation group F, was clearly unable to continue RNA synthesis at 39 degrees C, apparently due to temperature-sensitive polymerase. The defect was reversible and affected the synthesis of both 42S and 26S RNA equally, suggesting that the same polymerase component(s) is required for the synthesis of both RNA species. One of the three Sindbis virus mutants of complementation group A, Ts-4, and one RNA +/- mutant of Semliki Forest virus, ts-10, showed a polymerase defect even at the permissive temperature. Seven of the 14 RNA-negative mutants showed a preferential reduction in 26S RNA synthesis. The 26S RNA-defective mutants of Sindbis virus were from two different complementation groups, A and G, indicating that functions of two viral nonstructural proteins ("A" and "G") are required in the regulation of the synthesis of 26S RNA. Since the synthesis of 42S RNA continued, these functions of proteins A and G are not needed for the polymerization of RNA late in infection. The RNA-negative phenotype of 26S RNA-deficient mutants implies that proteins regulating the synthesis of this subgenomic RNA must have another function vital for RNA synthesis early in infection or in the assembly of functional polymerase. Several of the mutants having a specific defect in the synthesis of 26S RNA showed an accumulation of a large nonstructural precursor protein with a molecular weight of about 200,000. One even larger protein was demonstrated in both Semliki Forest virus- and Sindbis virus-infected cells which probably represents the entire nonstructural polyprotein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins G. J., Samuels J., Kennedy S. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus strain AR339. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):371–380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha M., Leone A., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of a Sindbis virus nonstructural protein and its relation of 42S mRNA function. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):612–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.612-620.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski H., Kennedy S. I. Synthesis of alphavirus-specified RNA. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):630–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.630-640.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge B. W., Pfefferkorn E. R. Complementation between temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):214–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge B. W., Pfefferkorn E. R. Isolation and characterization of conditional-lethal mutants of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):204–213. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter F. H., Harrington K. T. Intermolecular cross-linking of monomeric proteins and cross-linking of oligomeric proteins as a probe of quaternary structure. Application to leucine aminopeptidase (bovine lens). J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5580–5586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Griffith J., Kornberg A. phiX174 cistron A protein is a multifunctional enzyme in DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Lachmi B. E., Smith A. E., Käriäinen L. Tryptic peptide mapping of the nonstructural proteins of Semliki Forest virus and their precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 23;518(3):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Lachmi B. E. Translation of proteins accounting for the full coding capacity of the Semliki Forest virus 42 S RNA genome. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80563-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville N., Ranki M., Morser J., Käriäinen L., Smith A. E. Initiation of translation directed by 42S and 26S RNAs from Semliki Forest virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3059–3063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazwinski S. M., Lindberg A. A., Kornberg A. The gene H spike protein of bacteriophages phiX174 and S13. I. Functions in phage-receptor recognition and in transfection. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):283–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazwinski S. M., Marco R., Kornberg A. The gene H spike protein of bacteriophages phiX174 and S13. II. Relation to synthesis of the parenteral replicative form. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):294–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species of standard and defective-interfering Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec;108(2):491–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen S. Complementation in 26 S RNA synthesis between temperature-sensitive mutants of Semliki Forest virus. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keränen S., Käriäinen L. Isolation and basic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants from Semliki Forest virus;. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):810–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad E. B., Lehman I. R. A conditional lethal mutant of Escherichia coli K12 defective in the 5' leads to 3' exonuclease associated with DNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2048–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Sawicki D., Gomatos P. J. Cleavage defect in the non-structural polyprotein of Semliki Forest virus has two separate effects on virus RNA synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jun;39(3):463–473. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-3-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Söderlund H. Structure and replication of alpha-viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;82:15–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46388-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Glanville N., Keränen S., Läriäinen L. Tryptic peptide analysis on nonstructural and structural precursor proteins from Semliki Forest virus mutant-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1615–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1615-1629.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmi B. E., Käriäinen L. Sequential translation of nonstructural proteins in cells infected with a Semliki Forest virus mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1936–1940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. M. Studies on the RNA polymrase of some temperature-sensitive mutants of Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1969 Sep;39(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90352-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzyczka N., Poland R. L., Bessman M. J. Studies on the biochemical basis of spontaneous mutation. I. A comparison of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases of mutator, antimutator, and wild type strains of bacteriophage T4. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7116–7122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Käiäinen L., Söderlund H., Keränen S. RNA synthesis directed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):399–406. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki D. L., Kaariainen L., Lambek C., Gomatos P. J. Mechanism for control of synthesis of Semliki Forest virus 26S and 42s RNA. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):19–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.19-27.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele C. M., Pfefferkorn E. R. Inhibition of interjacent ribonucleic acid (26S) synthesis in cells infected by Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):117–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.117-122.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. I. Relative size and genetic content of 26 s and 49 s RNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):599–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. II. Multiple forms of double-stranded RNA isolated from infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):615–631. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. V. Polyribosomes and mRNA in infected cells. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):552–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.552-559.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Lenches E. M., Strauss J. H. Mutants of sindbis virus. I. Isolation and partial characterization of 89 new temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):154–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]