Abstract
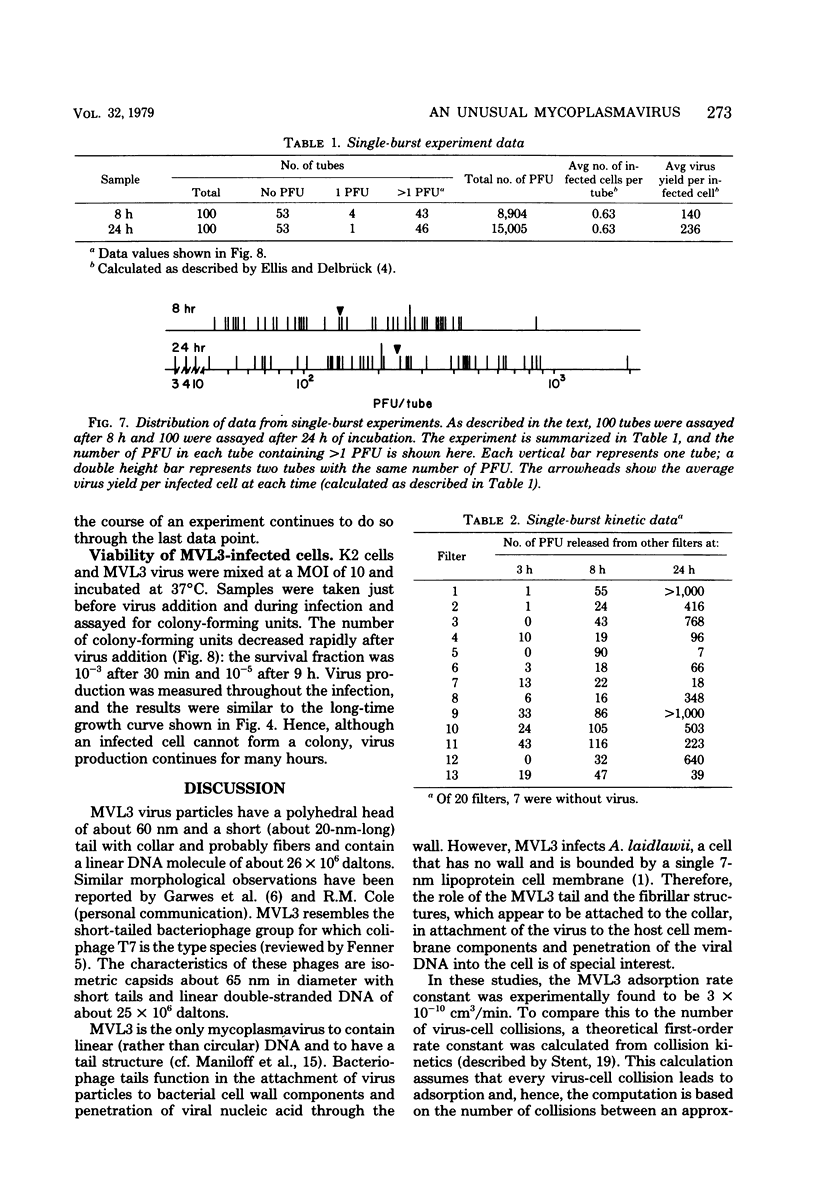
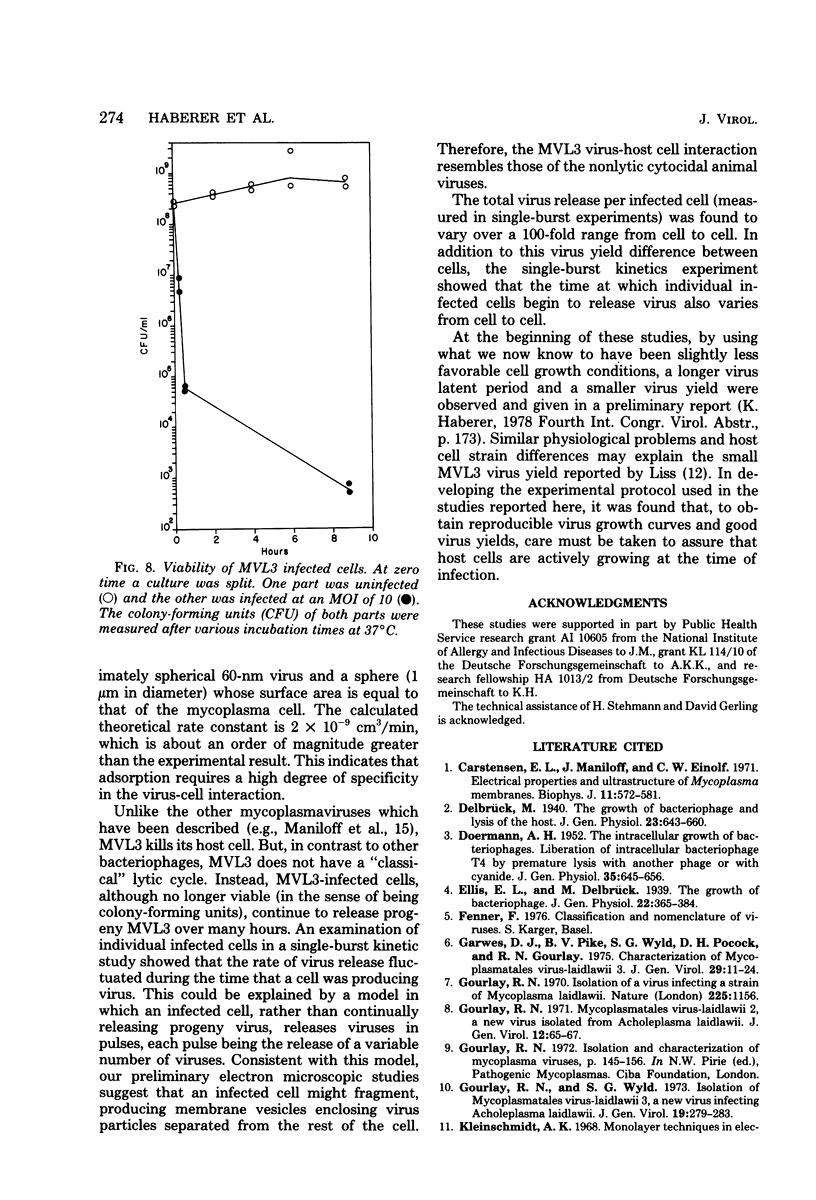
The kinetics of adsorption and growth of mycoplasmavirus MVL3 in Acholeplasma laidlawii 1305/68 host cells have been studied with one-step growth, premature lysis, and single-burst experiments. The virus was found to kill infected host cells. Virus release starts 90 min after infection and continues for about 10 to 15 h. Hence, virus production is unlike the classical lytic bacteriophages and instead resembles nonlytic cytocidal animal viruses. Structural details of the virus are described, and the molecular weight of the viral linear DNA has beenfound to be 26 x 10(6).
Full text
PDF


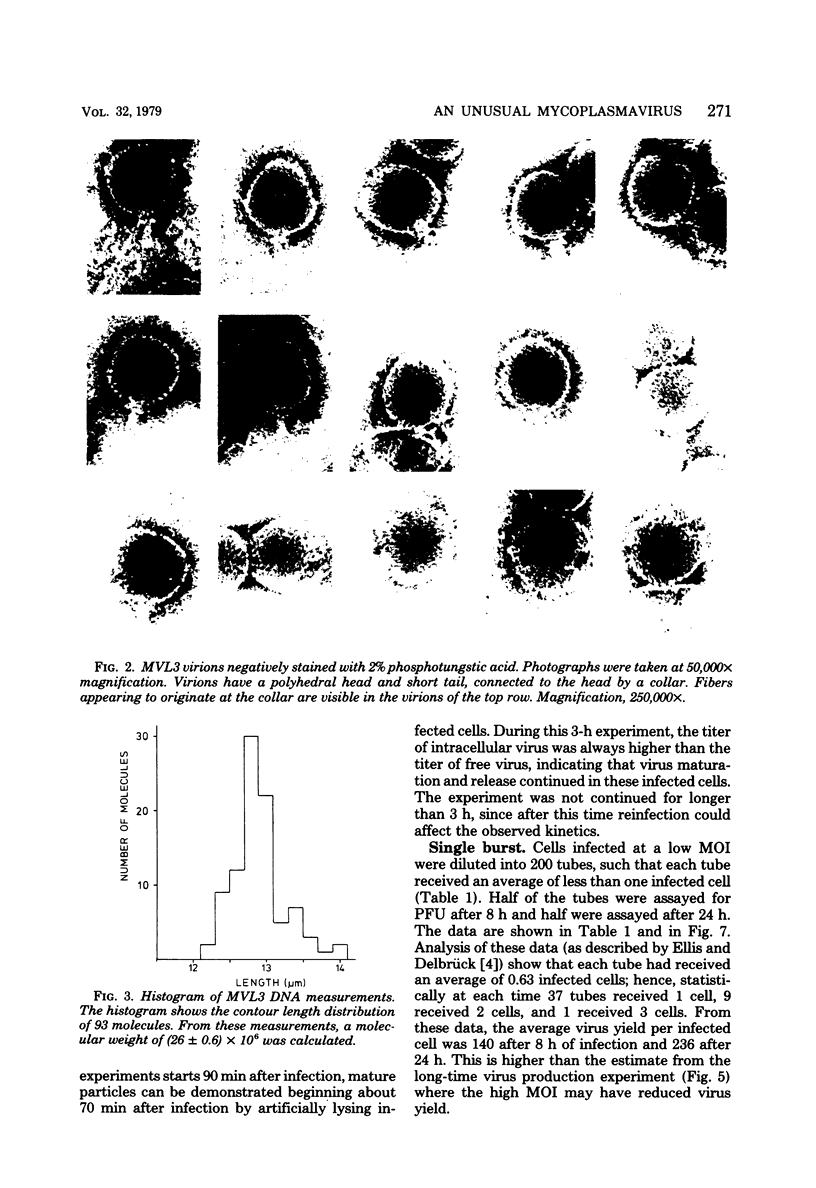
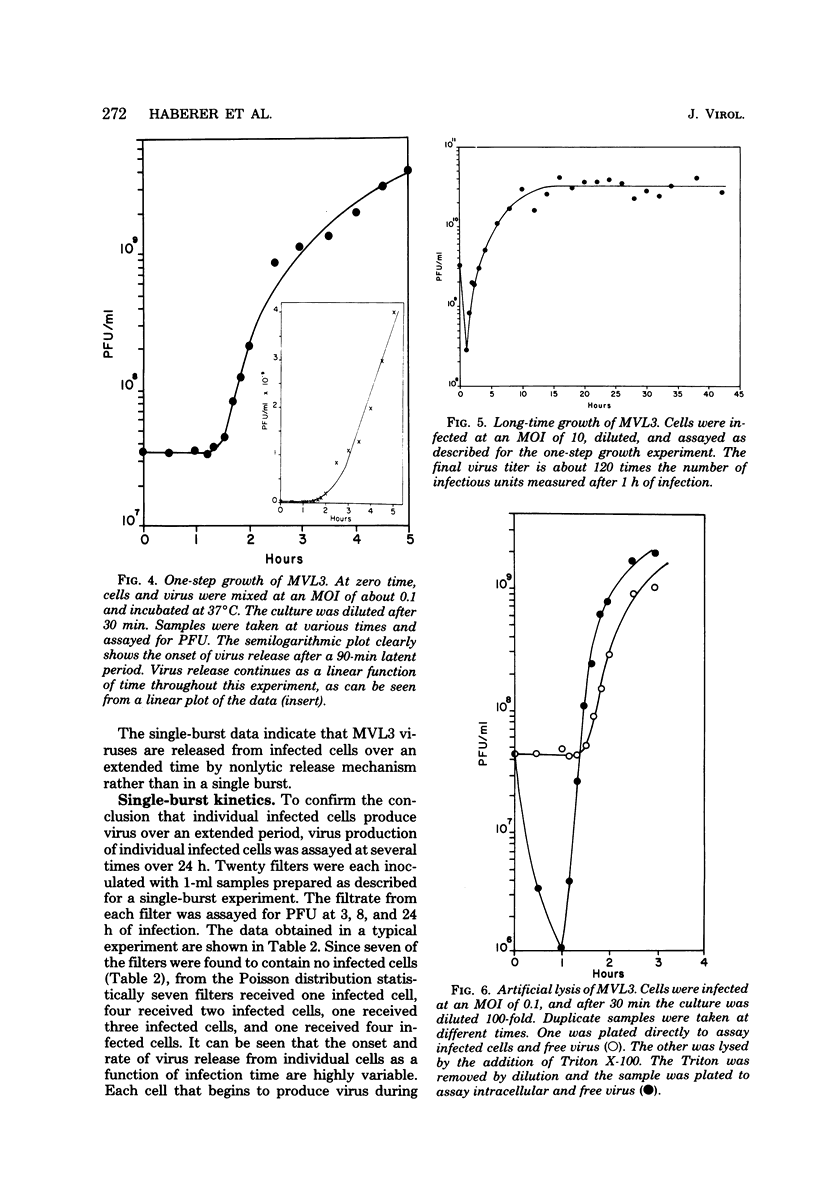

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carstensen E. L., Maniloff J., Einolf C. W., Jr Electrical properties and ultrastructure of Mycoplasma membranes. Biophys J. 1971 Jul;11(7):572–581. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86236-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOERMANN A. H. The intracellular growth of bacteriophages. I. Liberation of intracellular bacteriophage T4 by premature lysis with another phage or with cyanide. J Gen Physiol. 1952 Mar;35(4):645–656. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.4.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garwes D. J., Pike B. V., Wyld S. G., Pocock D. H., Gourlay R. N. Characterization of Mycoplasmatales virus-laidlawii 3. J Gen Virol. 1975 Oct;29(1):11–24. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N. Mycoplasmatales virus-laidlawii 2, a new virus isolated from Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jul;12(1):65–67. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Wyld S. G. Isolation of mycoplasmatales virus-laidlawii 3, a new virus infecting Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Gen Virol. 1973 May;19(2):279–283. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liss A. Acholeplasma laidlawii infection by group 3 mycoplasmavirus. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi P. S., Cole B. C. Characterization of mycoplasmavirus MVL2 DNA. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):381–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.381-384.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Das J., Christensen J. R. Viruses of mycoplasmas and spiroplasmas. Adv Virus Res. 1977;21:343–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60765-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak J. A., Maniloff J. Physical characterization of the superhelical DNA genome of an enveloped mycoplasmavirus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):374–380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.374-380.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan D. C., Liss A., Maniloff J. Eagle's basal medium as a defined medium for Mycoplasma studies. Microbios. 1972 Sep-Oct;6(22):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. J., White R. E., Thorpe W. H. Acoustic basis for individual recognition by voice in the gannet. Nature. 1970 Mar 21;225(5238):1156–1158. doi: 10.1038/2251156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]