Abstract
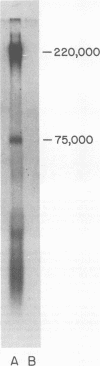
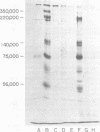
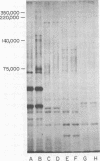
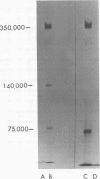
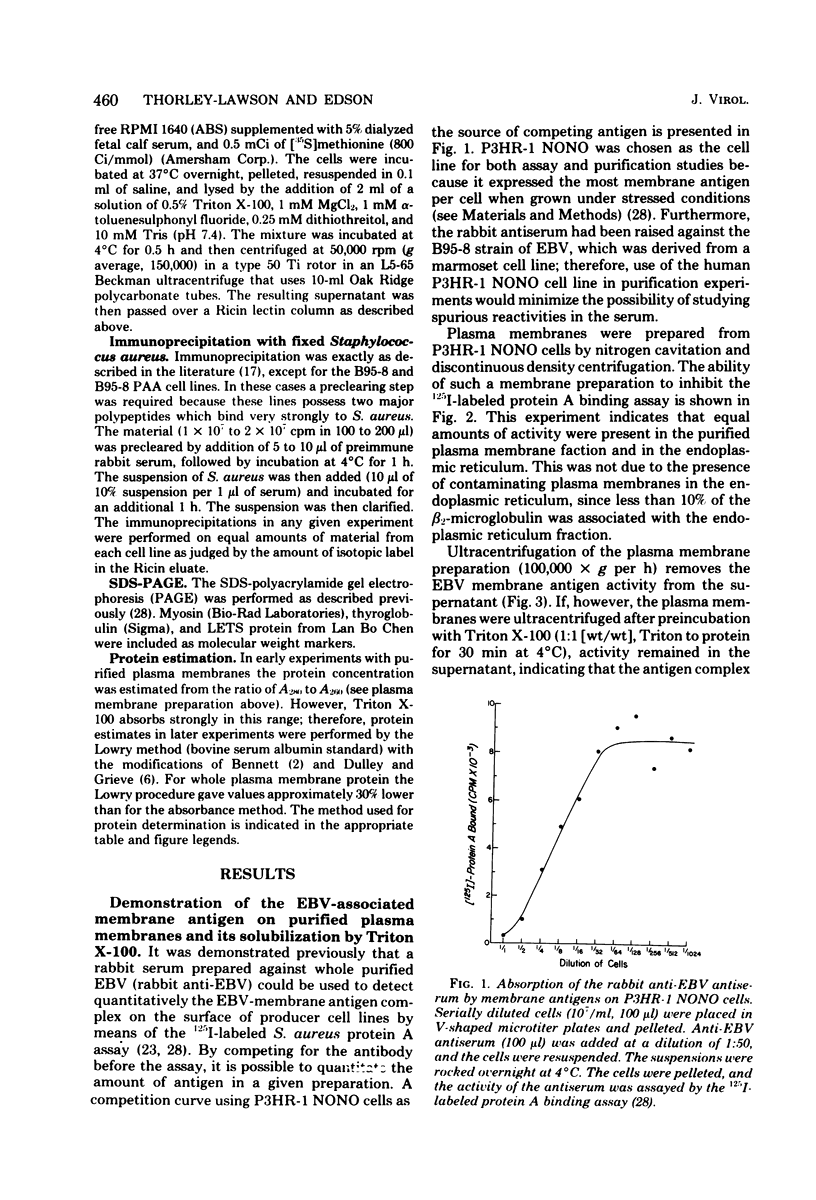
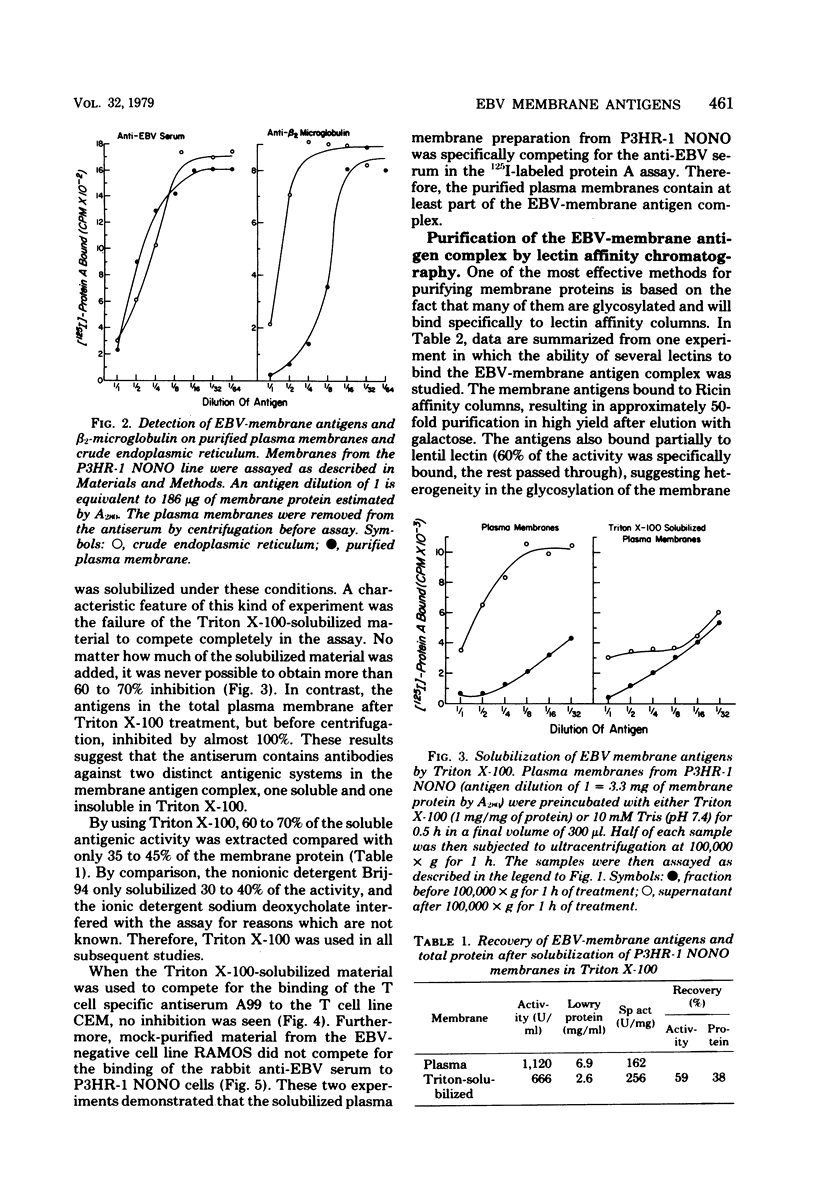
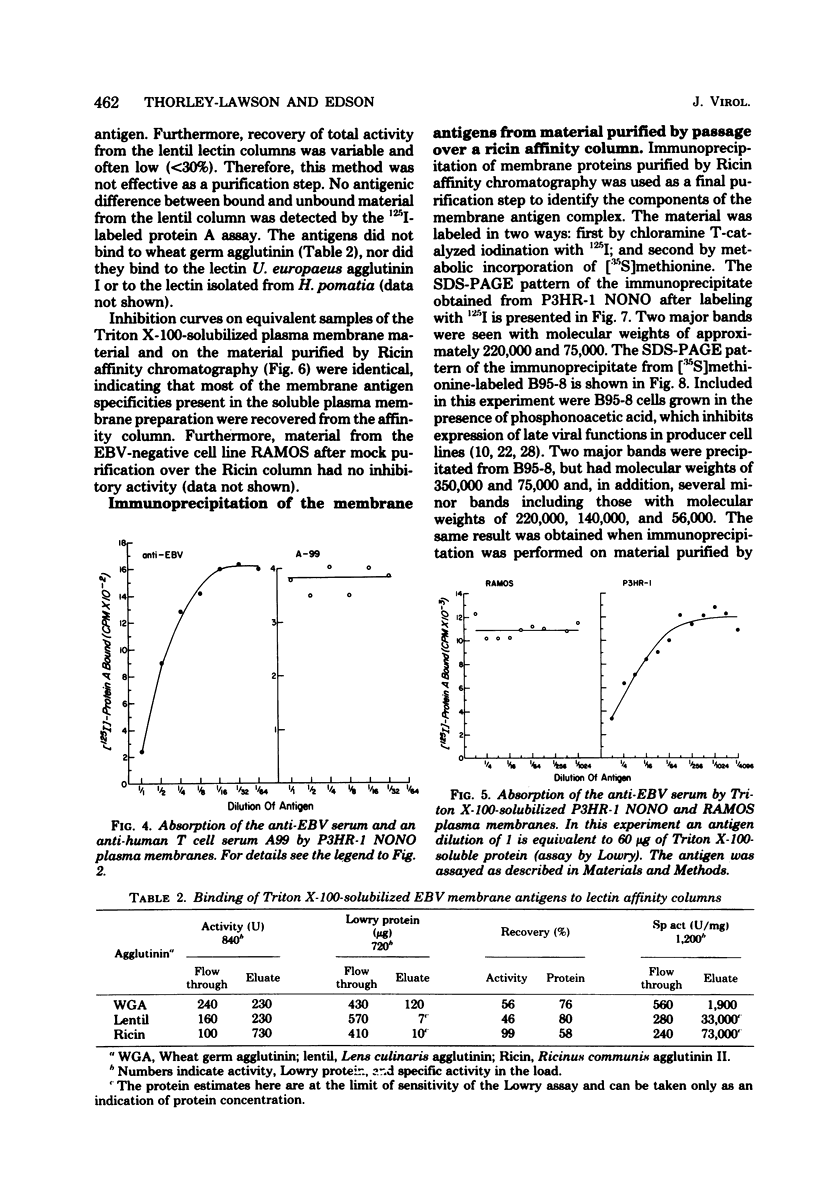
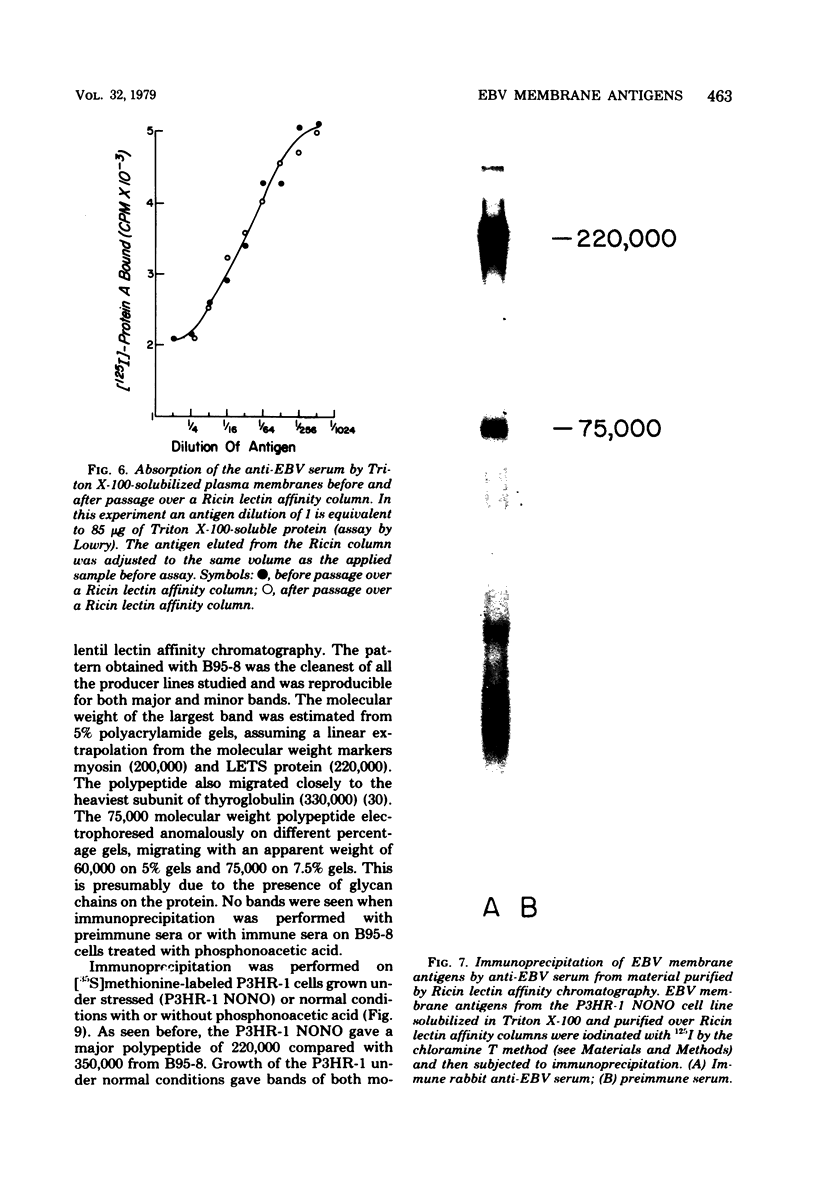
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated membrane antigens have been purified from the plasma membranes of the producer cell line P3HR-1 NONO. The antigens were assayed with a specific rabbit anti-ebv antiserum using an 125I-labeled staphylococcal protein A binding assay. The antigens have been shown to be present on purified plasma membranes. Treatment of the plasma membranes with Triton X-100 allows the separation of two antigenically distinct classes of antigens, one soluble and one insoluble in the detergent. Immunoprecipitates of [125I5- and [35S]methionine-labeled, detergent-soluble antigens contained three major polypeptides of molecular weights of 350,000, 140,000, and 75,003 (on 7.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) and several minor components. These polypeptides were all specifically precipitated from four EBV-producer cell lines, P3HR-1, P3HR-1 NONO, B95-8, and 7744. They could not be precipitated from producer cell lines treated with phosphonoacetic acid, which inhibits late viral functions, nor could they be precipitated from nonproducer cell lines. The 350,000 and 75,000 molecular weight polypeptides bound to Ricin and lentil lectin columns; however, most of the 140,000 molecular weight material did not. A component of molecular weight 220,000 (prominent only in P3HR-1 NONO) was probably a degradation product of the 350,000 molecular weight polypeptide.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron D., Strominger J. L. Partial purification and properties of the Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2875–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett T. P. Membrane filtration for determining protein in the presence of interfering substances. Nature. 1967 Mar 18;213(5081):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/2131131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. E., Brown W. C. Isolation of membrane associated immunoglobulins from T lymphocytes by non-ionic detergents. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jul;13(7):571–579. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulley J. R., Grieve P. A. A simple technique for eliminating interference by detergents in the Lowry method of protein determination. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):136–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN M. A., ACHONG B. G., BARR Y. M. VIRUS PARTICLES IN CULTURED LYMPHOBLASTS FROM BURKITT'S LYMPHOMA. Lancet. 1964 Mar 28;1(7335):702–703. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91524-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A. Implications of a vaccine for the prevention of Epstein-Barr virus infection: ethical and logistic considerations. Cancer Res. 1976 Feb;36(2 Pt 2):711–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Klein G., Kourilsky F. M., Silvestre D. Differentiation between early and late membrane antigen on human lymphoblastoid cell lines infected with Epstein-Barr virus. I. Immunofluorescence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jul;53(1):61–65. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Clifford P., Diehl V., Kafuko G. W., Kirya B. G., Klein G., Morrow R. H., Munube G. M., Pike P. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt's lymphoma and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Nov;43(5):1147–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt's tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):94–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Klein G., Gunven P., Clifford P., Morrow R. H., Ziegler J. L. Antibodies to early Epstein-Barr virus-induced antigens in Burkitt's lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Apr;46(4):861–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Grace J. T., Jr Cloning of immunoglobulin-producing human leukemic and lymphoma cells in long-term cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):107–111. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Lindahl T., Klein G. Purification of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen from Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoid cell lines. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.604-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Hibi N., Nishi S., Hirai H., Osato T. Studies on Epstein-Barr virus-related antigens. III. Purification of the virus-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA) from non-producer Raji cells. Int J Cancer. 1978 Dec;22(6):747–752. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Niederman J. C., Andrews L. L. Prolonged oropharyngeal excretion of Epstein-Barr virus after infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):229–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Shope T., Lisco H., Stitt D., Lipman M. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation, cytopathic changes, and viral antigens in squirrel monkey and marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyormoi O., Thorley-Lawson D. A., Elkington J., Strominger J. L. Differential effect of phosphonoacetic acid on the expression of Epstein-Barr viral antigens and virus production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1745–1748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Qualtiere L. F. Papain solubilization of the Epstein-Barr virus-induced membrane antigen. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):344–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.344-351.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H. Establishment of cell lines from Australian leukaemic patients: presence of a herpes-like virus. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1968 Oct;46(5):643–645. doi: 10.1038/icb.1968.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Klein G. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus DNA synthesis and late gene expression by phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.151-155.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr A., Demissie A., Klein G., Clifford P. Antibody patterns in different human sera against intracellular and membrane-antigen complexes associated with Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Mar;44(3):595–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A. Characterization of cross-reacting antigens on the Epstein-Barr virus envelope and plasma membranes of producer cells. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Green N. M. Separation and characterisation of tryptic fragments from the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):193–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg A., Becker Y. Studies on EB virus of Burkitt's lymphoblasts. Virology. 1969 Oct;39(2):312–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Geser A., Day N. E., Tukei P. M., Williams E. H., Beri D. P., Smith P. G., Dean A. G., Bronkamm G. W., Feorino P. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Walt B., Kotzé B., van Jaarsveld P. P., Edelhoch H. Evidence that thyroglobulin contains nonidentical half molecule subunits. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1853–1858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hansen H., Diehl V., Wolf H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Schneider U. Occurrence of Epstein-Barr virus genomes in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 7;237(75):189–190. doi: 10.1038/newbio237189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]