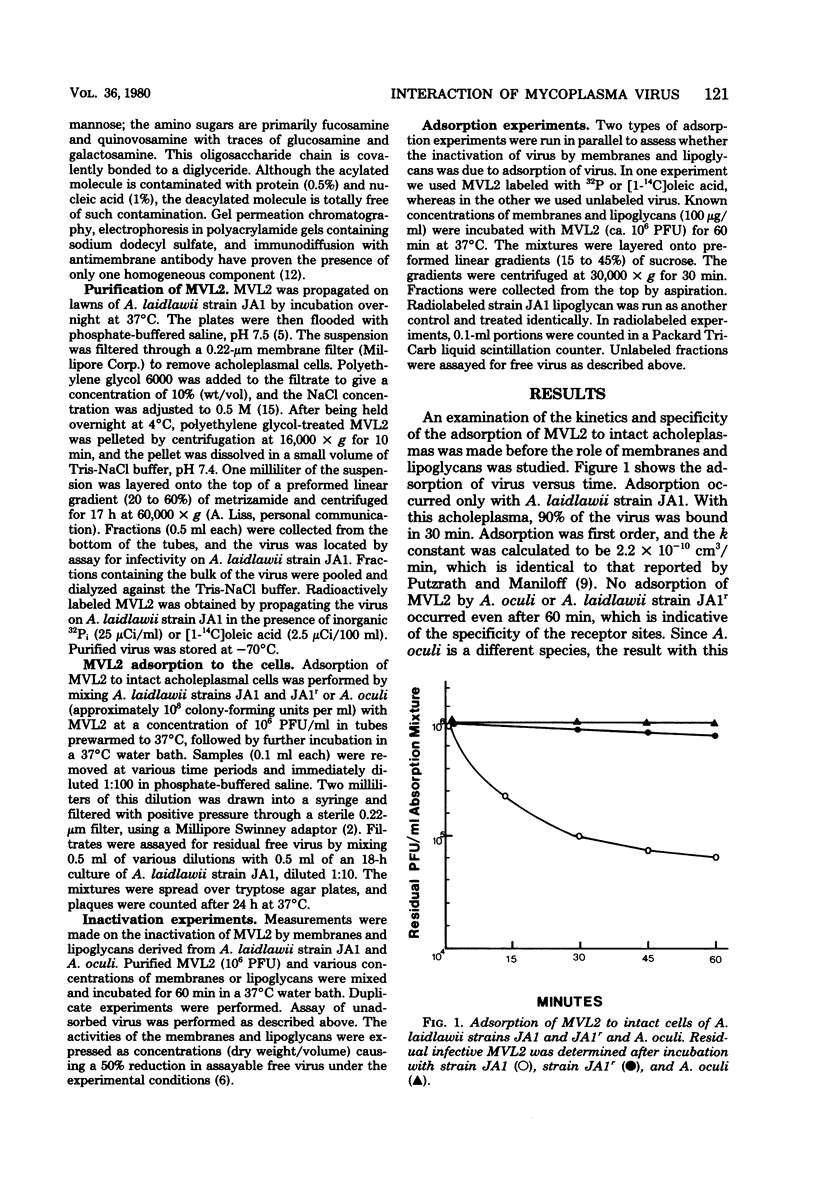
Abstract
Mycoplasma virus type 2 was shown to adsorb specifically to intact cells, membranes, and lipoglycan of Acholeplasma laidlawii strain JA1 but not to these components of Acholeplasma oculi. The oligosaccharide chain of the lipoglycan defined the specificity of the receptor site since deacylation not only did not reduce adsorption but increased it threefold. Actual adsorption of virus to lipoglycan was demonstrated by sucrose density gradient separation of the virus-lipoglycan complex. A strain of A. laidlawii, JA1r, resistant to infection with mycoplasma virus type 2, was incapable of adsorbing the virus and was devoid of lipoglycan.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Shammari A. J., Smith P. F. Lipid and lipopolysaccharide composition of Acholeplasma oculi. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):356–361. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.356-361.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D., Fleischmann C. Interaction of mycoplasma with viruses. I. Primary adsorption of virus is ionic in mechanism. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1067–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1067-1074.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N., Garwes D. J., Bruce J., Wyld S. G. Further studies on the morphology and composition of Mycoplasmatales virus-laidlawii 2. J Gen Virol. 1973 Feb;18(2):127–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N. Mycoplasmatales virus-laidlawii 2, a new virus isolated from Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jul;12(1):65–67. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Studies of a receptor for felix O-1 phage in Salmonella minnesota. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):225–233. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Das J., Christensen J. R. Viruses of mycoplasmas and spiroplasmas. Adv Virus Res. 1977;21:343–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60765-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak J. A., Maniloff J. Physical characterization of the superhelical DNA genome of an enveloped mycoplasmavirus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):374–380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.374-380.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putzrath R. M., Maniloff J. Growth of an enveloped mycoplasmavirus and establishment of a carrier state. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.308-314.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putzrath R. M., Maniloff J. Properties of a persistent viral infection: possible lysogeny by an enveloped nonlytic mycoplasmavirus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):254–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.254-261.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The cell membrane of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):115–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F. Homogeneity of lipopolysaccharides from Acholeplasma. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):393–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.393-398.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R. Distribution and composition of lipopolysaccharides from mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):916–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.916-922.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Smith P. F., Langworthy T. A., Mayberry W. R. Immunological analysis of glycolipids and lipopolysaccharides derived from various mycoplasmas. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1273–1279. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1273-1279.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



