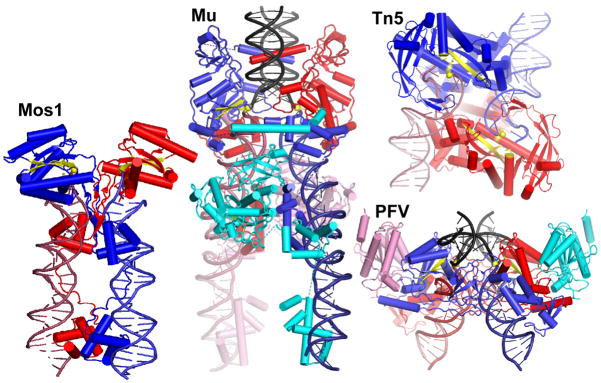
Figure 5.
Comparison of DDE recombinase-DNA complexes. The mobile element ends are red and blue and target DNA (where included) is black. Subunits that carry out the chemical reactions are red and blue; additional subunits pink and cyan. Active site residues, scissile phosphate groups, and the two β strands of the conserved catalytic domain that carry the catalytic D’s are in yellow. Mos1 is a Tc1/mariner family eukaryotic DNA transposon; Tn5 is a bacterial DNA transposon, and Prototype Foamy Virus (PFV) is a mammalian retrovirus5–7. Mos1 and Tn5 require only a dimer for activity, whereas Mu transposase and PFV integrase require tetramers. In the PFV structure, only the catalytic domains of the additional subunits were visible (pink and cyan).