Abstract
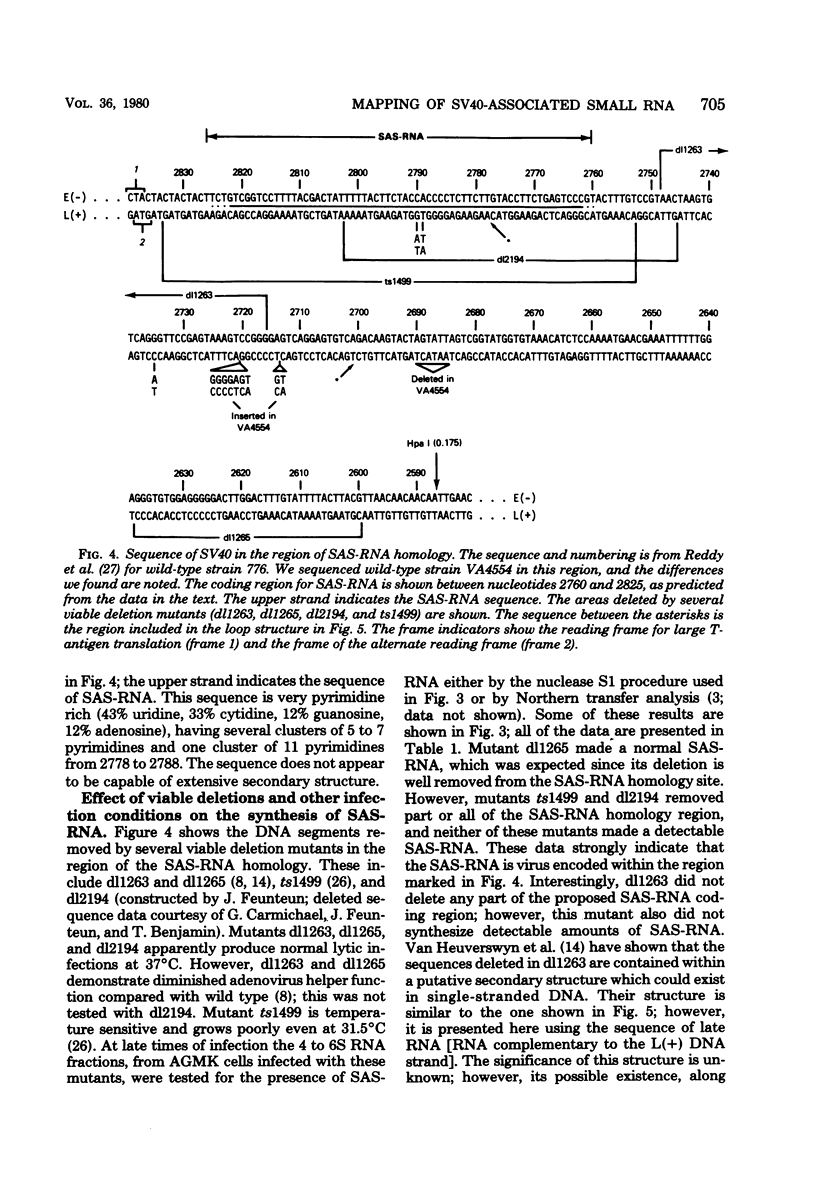
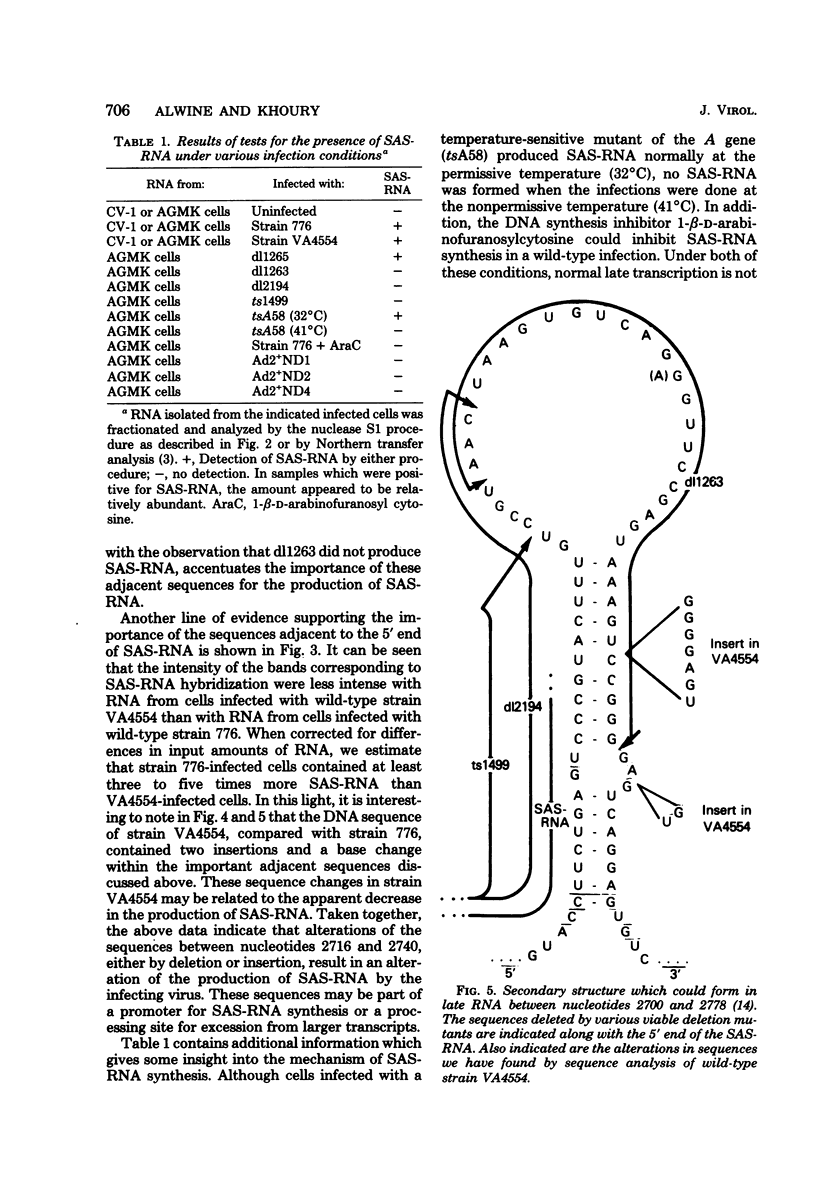
The simian virus 40 (SV40)-associated small RNA (SAS-RNA) has previously been shown to arise late in SV40 lytic infection and to bear homology with the SV40 early mRNA's, or the SV40 genome, at map position 0.21. By using hybridization analysis, we determined that the SAS-RNA is between 62 and 65 nucleotides in length and its homology region lies between nucleotides 2760 and 2825 of the SV40 late(+) DNA strand. Viable deletion mutants which lacked part or all of this region made no SAS-RNA, strongly indicating that this is the coding region of the SAS-RNA. The expected sequence for the SAS-RNA, determined from the DNA sequence between nucleotides 2760 and 2825, appeared to be very pyrimidine rich (76% uridine and cytidine). Deletion or alteration of sequences immediately preceding the SAS-RNA coding region (approximately nucleotides 2716 to 2748) resulted in the loss of SAS-RNA production. These sequences may be part of a promotor for SAS-RNA synthesis or a processing site for its excision from long nuclear late transcripts. Under growth conditions where late transcription was not fully initiated (tsA58 at 41 degrees C; wild-type SV40 in the presence of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine), no SAS-RNA was produced, indicating that the expression of the SAS-RNA is regulated by a mechanism related to the control of late transcription.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Alwine J. C., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Use of recombinant plasmids to characterize collagen RNAs in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4935–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Dhar R., Khoury G. A small RNA induced late in simian virus 40 infection can associate with early viral mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1379–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Reed S. I., Stark G. R. Characterization of the autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):22–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.22-27.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecke B. J., Penman S. A new class of small nuclear RNA molecules synthesized by a type I RNA polymerase in HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90158-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Crawford L. V., Berg P. Simian virus 40 mutants with deletions at the 3' end of the early region are defective in adenovirus helper function. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):683–691. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.683-691.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K., Tegtmeyer P., Anthony D. D. Relationship of replication and transcription of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1927–1930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S. Gel electrophoretic separation of the complementary strands of bacteriophage DNA. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellung-Larsen P., Frederiksen S. Occurrence and properties of low molecular weight RNA components from cells at different taxonomic levels. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1977;58(3):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(77)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Leinwand L. Low molecular weight RNAs hydrogen-bonded to nuclear and cytoplasmic poly(A)-terminated RNA from cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Carter B. J., Ferdinand F. J., Howley P. M., Brown M., Martin M. A. Genome localization of simian virus 40 RNA species. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):832–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.832-840.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Dhar R., Khoury G. Mapping the spliced and unspliced late lytic SV40 RNAs. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):971–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. S., Levin M. J., Oxman M. N., Lewis A. M., Jr Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. VII. Characterization of the simian virus 40 RNA species induced by five nondefective hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):672–681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.672-681.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark D. F., Berg P. A third splice site in SV40 early mRNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):55–62. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohe K., Weissman S. M., Cooke N. R. Studies on the origin of a low molecular weight ribonucleic acid from human cells infected with adenoviruses. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5320–5332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Philipson L. Location of sequences on the adenovirus genome coding for the 5.5S RNA. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintel D., Bouck N., di Mayorca G., Thimmappaya B., Swerdlow B., Shenk T. SV40 mutant tsA1499 is heat-sensitive for lytic growth but generates cold-sensitive rat-cell transformants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):305–309. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
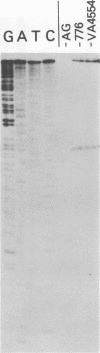
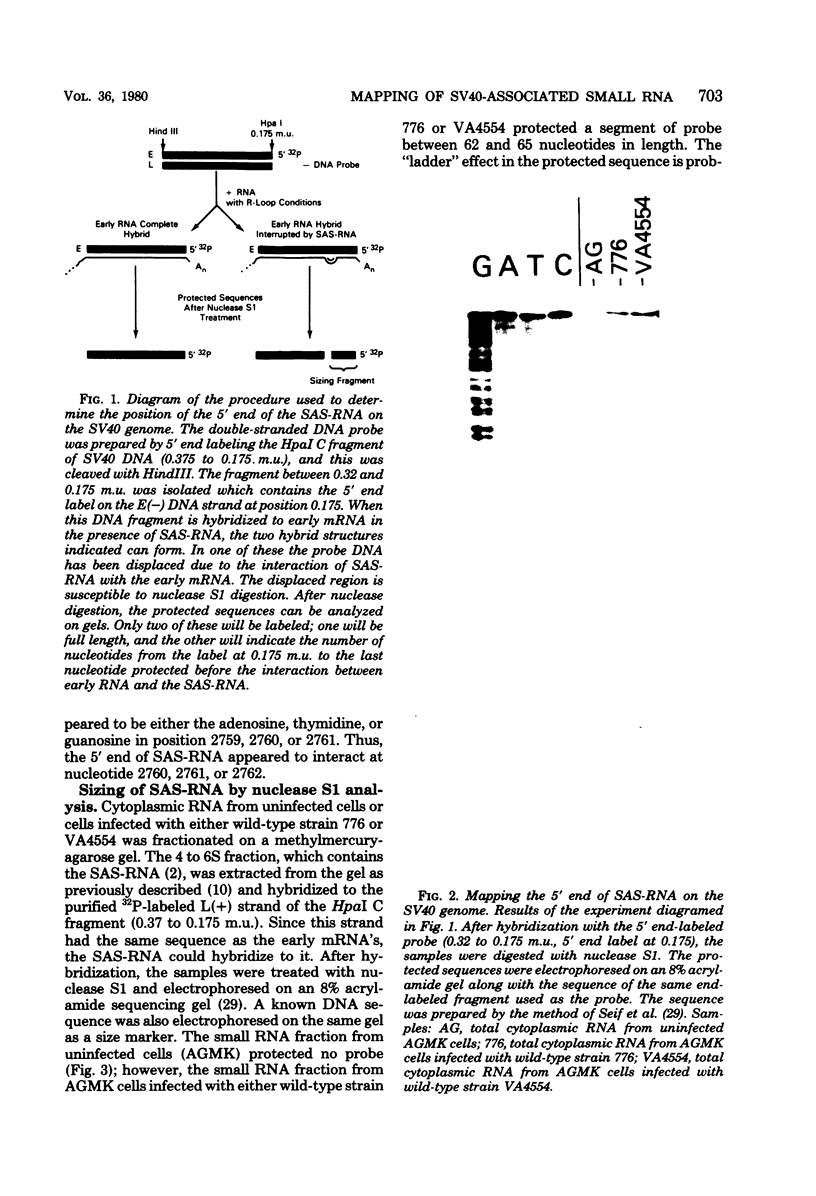
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. A rapid enzymatic DNA sequencing technique: determination of sequence alterations in early simian virus 40 temperature sensitive and deletion mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2225–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Altered patterns of protein synthesis in infection by SV40 mutants. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):9–15. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Zain B. S., Dhar R., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of DNA template for the 3' ends of SV40 mRNA. II. The sequence of the DNA fragment EcorII-F and a part of EcorII-H. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1613–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heuverswyn H., Cole C., Berg P., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence analysis of two simian virus 40 mutants with deletions in the region coding for the carboxyl terminus of the T antigen. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):936–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.936-941.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Penman S. Small molecular weight monodisperse nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):289–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain S., Gingeras T. R., Bullock P., Wong G., Gelinas R. E. Determination and analysis of adenovirus-2 DNA sequences which may include signals for late messenger RNA processing. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):413–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Penman S. Small RNA species of the HeLa cell: metabolism and subcellular localization. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]