Abstract
Sialolipoma is a relatively rare and fairly recently described as a variant of lipoma with salivary elements. Any site within the oral and maxillofacial region may be involved with the parotid gland being the most common location. Herein, we present a case of silaolipoma in lower lip. The clinical and histological features and differential diagnosis are discussed.
Keywords: Lipoma, Salivary gland, Oral cavity.
INTRODUCTION
Sialolipoma is a new histological variant of salivary gland lipoma, which is composed of adipose and glandular tissues. It was first described by Nagao et al., in 2001 [1]. The etiology of sialolipoma is not completely understood. It typically arises within the major salivary glands and the minor salivary gland of oral cavity. To the best of our knowledge only 35 cases of sialolipoma have been reported in English literature (Table1 [1-21]) including the present case.
Table 1.
Clinical Features of 36 Cases of Sialolipoma
| Author | Age (years) | Sex | Location | Size in cm | Duration | Treatment | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Walts and Perzik, [2] | 48 | M | Parotid gland | 3.5x2.5x1 | NA | Superficial parotidectomy | NED |
| Walts and Perzik, [2] | 65 | M | Parotid gland | 2.6 diameter | 2 months | Superficial parotidectomy | NED |
| Baker et al., [3] | 44 | M | Parotid gland | 1.0 diameter | 2 months | Superficial parotidectomy | 30 mo; NED |
| Nagao et al., [1] | 20 | M | Parotid gland | 3.5x3.0x2.2 | 4 months | Superficial parotidectomy | 7 yr, 7 mo;NED |
| Nagao et al., [1] | 45 | F | Parotid gland | 6.0x3.0x2.0 | 10 years | Superficial parotidectomy | 7 yr, 1 mo;NED |
| Nagao et al., [1] | 67 | M | Parotid gland | 1.7diameter | 2 months | Superficial parotidectomy | 3 yr,1mo; NED |
| Nagao et al., [1] | 66 | F | Parotid gland | 6.0 diameter | 5 months | Superficial parotidectomy | 2 yr,11mo;NED |
| Nagao et al., [1] | 42 | M | Parotid gland | 6.0 diameter | 10 years | Superficial parotidectomy | 1 yr 8 mo; NED |
| Nagao et al., [1] | 66 | M | Soft palate | 2.2x1.5x1.5 | 6 years | Surgical excision | 11 mo; NED |
| Nagao et al., [1] | 75 | M | Hard palate | 1.0 diameter | 3 years | Surgical excision | NA |
| Fregnani et al., [4] | NA | NA | Tongue | NA | NA | Surgical excision | NED |
| Fregnani et al., [4] | NA | NA | Buccal sulcus | NA | NA | Surgical excision | NED |
| Lin et al., [5] | 67 | F | Floor of the mouth | 3.0x2.0 | 1 year | Surgical excision | 2 yr; NED |
| Hornigold et al., [6] | 7 wk | F | Parotid gland | 2.0x1.7x1.1 | 10 weeks | Surgical excision | 2 yr; NED |
| Michaelidis et al., [7] | 44 | M | Parotid gland | 3.5 diameter | 1 .5 years | Total parotidectomy | 2 yr; NED |
| Sakai et al., [8] | 60 | F | Hard palate | 1.8x1.2x1.0 | 10 years | Surgical excision | NED |
| Kadivar et al., [9] | 3 | F | Parotid gland | 3.0 diameter | 8 months | Superficial parotidectomy | NA |
| Ramer et al., [10] | 84 | F | Buccal mucosa | 1.0x1.0 | NA | Surgical excision | 11 mo; NED |
| Ramer et al., [10] | 43 | F | Soft palate | 2.0x2.0 | NA | Surgical excision | NA |
| Ponniah et al., [11] | 70 | M | Floor of mouth | 2.0 diameter | NA | Surgical excision | 2 yr; NED |
| De Freitas et al., [12] | 38 | M | Lower lip | 1.0 diameter | NA | Surgical excision | NA |
| Parente et al., [13] | 77 | F | Submandibular gland | 3.0x2.0x1.8 | NA | Surgical excision | 22mo; NED |
| Dogan et al., [14] | 33 | M | Parotid gland | 2.0x2.0 | 1year | Superficial parotidectomy | NED |
| Jang et al., [15] | 62 | F | Submandibular gland | 5.0 diameter | 2-3years | Surgical excision | 17mo,NED |
| Okada et al., [16] | 66 | F | Hard palate | 0.8 diameter | 10 years | NA | NA |
| De Moraes et al., [17] | 72 | F | Hard palate | 2.0 diameter | 2 weeks | Surgical excision | 8 mo; NED |
| Sato et al., [18] | 3 | M | Submandibular gland | 4.0x3.0 | NA | Surgical excision | 3 yr; NED |
| Akrish et al., [19] | 52 | M | Submandibular gland | 3.5x2.0x1.5 | NA | Surgical excision | 1yr; NED |
| Akrish et al., [19] | 67 | F | Hard Palate | 5.0x4.0x4.0 | NA | Surgical excision | 1yr; NED |
| Nonaka et al., [20] | 27 | F | Tongue | 1.0x1.0 | 5 years | Surgical excision | NA |
| Nonaka et al., [20] | 73 | F | Floor of mouth | 4.0x1.0 | NA | Surgical excision | NA |
| Nonaka et al., [20] | 65 | F | Buccal Mucosa | 2.0 diameter | 2 years | Surgical excision | NA |
| Nonaka et al., [20] | 68 | F | Retromolar pad | 0.9 diameter | NA | Surgical excision | 14mo; NED |
| Kidambi et al., [21] | 6 wk | M | Parotid gland | 4.7x4.5x3.0 | 4 wk | Total parotidectomy with facial nerve dissection | 3 mo; NED |
| Case report*, | 54 | F | Lower lip | 0.6 diameter | NA | Surgical excision | 3 yr; NED |
| Total number of cases=35 | Avg: 47.6 | M:F 15:18 | Parotid gland:13, Hard palate:5, Soft palate:2, Tongue :2, Floor of mouth:3, Buccal mucosa:3,Lower lip :2,submandibular gland:4, retromolar pad: 1 | Avg:2.74 | Avg: 3.04 years | ||
Present case report; NA, not available; NED, no evidence of disease.
CASE REPORT
A 54-year-old Caucasian female was seen by her general dentist for evaluation of a painless swelling in her lower lip. There was no history of trauma or infection and the patient’s medical history was unremarkable. An intra-oral examination revealed a 0.6x0.6cm soft tissue mass with normal overlying mucosa in her left lower lip, while an extra-oral examination revealed a normal facial morphology. The clinical differential diagnosis included mucocele, fibroma, lipoma, and salivary gland neoplasm. An excisional biopsy was performed and submitted to the Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Department at University of Maryland, Baltimore. On gross examination, the mass was well-circumscribed, tan in color, soft in consistency and measured 0.6cm at its largest diameter. The histological examination revealed a mass of mature adipose tissue completely encapsulated by a fibrous band. Islands of salivary gland acini and ducts were located within the tumor. Neither atypia nor mitotic figures were observed in either the salivary glandular type tissue or the adipocytes. Mild lymphocytic infiltration and ductal dilation were seen (Fig. 1). Consequently, the lesion was diagnosed as sialolipoma and no further treatment was required. The patient has been followed for 3 years without evidence of recurrence.
Fig. (1).
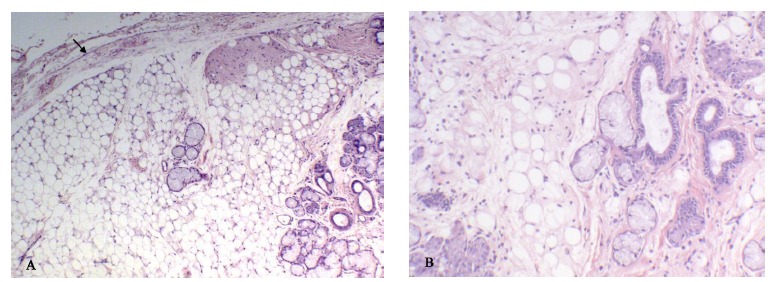
(A) Photomicrograph showing islands of salivary gland tissue present within an adipose tissue tumor encapsulated by thin fibrous tissue (arrow) (hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification 4x); (B) Higher magnification revealing mild ductal dilatation with fibrosis within the tumor mass (hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification 10x).
DISCUSSION
Sialolipoma, an uncommon variant of head and neck lipoma, is composed of proliferative adipocytes with entrapped normal salivary gland islands [1]. Almost any site within the oral and maxillofacial region may be involved with the parotid gland being the most frequently reported location [1-3, 6, 7, 9, 14, 21]. To our knowledge, 34 cases of sialolipoma have previously been reported in the English literature and eighteen of them were found in minor salivary glands [seven on the palate [1, 8, 10, 16, 17, 19], three in buccal mucosa [4, 10, 20], three on floor of the mouth [5, 11, 20], two on the tongue [4, 20], two in lower lip [12,the present case], and one on retromolar pad [20].
Clinically, sialolipomas usually present as a solitary painless palpable mass with an average size of 2.74 cm in diameter. Females are affected slightly more than males (with ratio 1.1:2). Patient’s ages range from 6 weeks to 84 years, with average of 47.6 years. The duration of the lesion range from two months to ten years, with average of three years. In the present report, the lesion is in the lower lip and the diameter is 0.6 cm. Because lower lip is a preferable site of mucocele, it is probable that superficially located sialolipoma might be misdiagnosed clinically as mucocele. The other most common preoperative diagnoses are fibroma and salivary gland tumor. There is no distinguishable radiographic sign for sialolipoma in either computed tomography scan (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) compared to a typical fatty lesion in the head and neck region [14].
Histological findings of haematoxylin and eosin staining in previous studies include a well circumscribed mass surrounded by a delicate fibrous tissue. The tumors are composed of mature adipose elements mixed with salivary gland tissues. The glandular components, consisting of acinar cells and ductal components, may be scattered through out the tumor or located in the periphery of the tumor [1, 5]. The 80 % of sialolipomas in major salivary gland are composed of adipose tissue while in minor salivary gland the glandular elements are clustered and evenly distributed around fat tissue [10,11]. No mitosis is seen in adipocytes or acinar and ductal cells [5]. The glandular components may be showed ductal dilation, oncocytic changes and squamous ductal metaplasia [1, 5-10]. In some cases areas of fibrosis are seen while myxoid changes are reported only in one case [9, 15]. Additionally, lymphocyte infiltration and enlarged congested vessels are reported [1, 10, 15].
The pathogenesis of the sialolipoma is not completely understood. However, immunohistological and ultrastructural studies confirmed that the glandular elements of the lesion could arise from entrapment of minor salivary gland during lipomatous proliferation rather than representing neoplastic process [1, 4, 5].
The morphologic differential diagnosis includes a variety of entities. Adenolipoma has histologic characteristic similar to sialolipoma; but it is composed of adipocytes and duct elements without acinar cells. Adenolipoma also differs from sialolipoma by the lack of organoid arrangement of the ductal type tissue [1, 5, 8]. Lipomatosis which typically occurs in older patients can be excluded by the microscopic lack of the fibrous capsule in addition to the absence of any medical condition associated with lipomatosis, for instance diabetes mellitus, malnutrition, chronic alcoholism and liver cirrhosis [1, 7, 9]. The distinction from pleomorphic adenoma is made by the presence of extensive fatty elements within the normal salivary gland tissue and lack of ducts and strands of dark-staining myoepithelial cells in sialolipoma [1, 5, 10].
Sialolipoma in the minor salivary glands is treated by complete surgical excision. However, most of tumors in parotid glands are treated with superficial parotidectomy. A complete parotidectomy with preservation of the facial nerve has been reported in two cases [7, 21] (Table 1). Malignant transformation of sialolipoma has not been reported yet in the literature [5]. The follow up period ranged from 2 months to 10 years and there is no evidence of recurrent sialolipoma.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Declared none.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Nagao T, Sugano I, Ishida Y, et al. Sialolipoma: a report of seven cases of a new variant of salivary gland lipoma. Histopathology. 2001;38(1):30–6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2001.01054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Walts AE, Perzik SL. Lipomatous lesions of the parotid area. Arch Otolaryngol. 1976;102(4):230–2. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1976.00780090072010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baker SE, Jensen JL, Correll RW. Lipomas of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981;52(2):167–71. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(81)90315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fregnani ER, Pires FR, Falzoni R, Lopes MA, Vargas PA. Lipomas of the oral cavity: clinical findings, histological classification and proliferative activity of 46 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;32(1):49–53. doi: 10.1054/ijom.2002.0317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lin YJ, Lin LM, Chen YK, et al. Sialolipoma of the floor of the mouth: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2004;20(8):410–4. doi: 10.1016/S1607-551X(09)70178-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hornigold R, Morgan PR, Pearce A, Gleeson MJ. Congenital sialolipoma of the parotid gland first reported case and review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005;69(3):429–34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2004.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Michaelidis IG, Stefanopoulos PK, Sambaziotis D, Zahos MA, Papadimitriou GA. Sialolipoma of the parotid gland. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2006;34(1):43–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2005.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sakai T, Iida S, Kishino M, Okura M, Kogo M. Sialolipoma of the hard palate. J Oral Pathol Med. 2006;35(6):376–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2006.00409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kadivar M, Shahzadi SZ, Javadi M. Sialolipoma of the parotid gland with diffuse sebaceous differentiation in a female child. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2007;10(2):138–41. doi: 10.2350/06-05-0091.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ramer N, Lumerman HS, Ramer Y. Sialolipoma: report of two cases and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;104(6):809–13. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ponniah I, Lavanya N, Suresh Kumar P. Island of salivary gland in adipose tissue: a report of three cases. J Oral Pathol Med. 2007;36(9):558–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2007.00544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.de Freitas MA, Freitas VS, de Lima AA, Pereira FB, Jr, dos Santos JN. Intraoral lipomas: a study of 26 cases in a Brazilian population. Quintessence Int. 2009 Jan;40(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Parente P, Longobardi G, Bigotti G. Hamartomatous sialolipoma of the submandibular gland: case report. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(7):599–600. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2008.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Doğan S, Can IH, Unlü I, Süngü N, Gönültas MA, Samim EE. Sialolipoma of the parotid gland. J Craniofac Surg. 2009;20(3):847–8. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181a2ef7d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jang YW, Kim SG, Pai H, Park JW, Lee YC, Rotaru H. Sialolipoma: case report and review of 27 cases. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;13(2):109–13. doi: 10.1007/s10006-009-0153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Okada H, Yokoyama M, Hara M, Akimoto Y, Kaneda T, Yamamoto H. Sialolipoma of the palate: a rare case and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108(4):571–6. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.05.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.de Moraes M, de Matos FR, de Carvalho CP, de Medeiros AM, de Souza LB. Sialolipoma in minor salivary gland: case report and review of the literature. Head Neck Pathol. 2010;4(3):249–52. doi: 10.1007/s12105-010-0187-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sato K, Gotoh C, Uchida H, et al. Sialolipoma of the submandibular gland in a child. J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46(2):408–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2010.09.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Akrish S, Leiser Y, Shamira D, Peled M. Sialolipoma of the Salivary Gland: two new cases, literature review, and histogenetic hypothesis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;69(5):1380–4. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2010.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nonaka CF, Pereira KM, de Andrade Santos PP, de Almeida Freitas R, da Costa Miguel MC. Sialolipoma of minor salivary glands. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2011;15(1):6–11. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2009.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kidambi T, Been MJ, Maddalozzo J. Congenital sialolipoma of the parotid gland: presentation, diagnosis, and management. Am J Otolaryngol. 2012;33(2):279–81. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2011.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


