Abstract
Filoviruses cause lethal hemorrhagic disease in humans and nonhuman primates. An initial target of filovirus infection is the mononuclear phagocytic cell. Calcium-dependent (C-type) lectins such as dendritic cell- or liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3 grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN or L-SIGN, respectively), as well as the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor, bind to Ebola or Marburg virus glycoprotein (GP) and enhance the infectivity of these viruses in vitro. Here, we demonstrate that a recently identified human macrophage galactose- and N-acetylgalactosamine-specific C-type lectin (hMGL), whose ligand specificity differs from DC-SIGN and L-SIGN, also enhances the infectivity of filoviruses. This enhancement was substantially weaker for the Reston and Marburg viruses than for the highly pathogenic Zaire virus. We also show that the heavily glycosylated, mucin-like domain on the filovirus GP is required for efficient interaction with this lectin. Furthermore, hMGL, like DC-SIGN and L-SIGN, is present on cells known to be major targets of filoviruses (i.e., macrophages and dendritic cells), suggesting a role for these C-type lectins in viral replication in vivo. We propose that filoviruses use different C-type lectins to gain cellular entry, depending on the cell type, and promote efficient viral replication.
Filovirus infection of primates generally presents with severe hemorrhagic manifestations and produces higher mortality rates than seen in any of the other viral hemorrhagic fevers (14, 25, 27). The Filoviridae family comprises two genera, Marburg and Ebola, with the latter consisting of four distinct species: Zaire, Sudan, Ivory Coast, and Reston (14, 27). Among all filoviruses, the Zaire species seems to be most virulent, killing up to 90% of infected persons, while Reston has been less pathogenic than other species in experimentally infected nonhuman primates and has never been associated with symptomatic infection in humans (15, 25, 27). Despite extensive research, the molecular basis for the extreme virulence of the Zaire virus remains elusive.
Filovirus is an enveloped, nonsegmented negative-strand RNA virus that contains at least seven structural proteins, all of which are translated from monocistronic polyadenylated mRNA transcripts (12, 27). The fourth gene from the 3′ end of the filovirus genome encodes envelope glycoprotein (GP) that is responsible for receptor binding and fusion of the virus with host cell membranes (34, 37). Two GPs, the envelope GP and the nonstructural secretory GP, are expressed from the same gene in Ebola viruses (28, 35).
GPs are highly glycosylated and contain both N- and O-linked carbohydrate chains with different terminal sialylation patterns, which seem to depend on the strain and cell line used for virus propagation (12, 13, 18). C-type lectins, such as dendritic cell- or liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN or L-SIGN, respectively), recognize the highly glycosylated Ebola GP and enhance the infectivity of pseudotyped viruses and replication competent Ebola virus when overexpressed on the cell surface (1, 3, 31). High-mannose N-glycans on the GP appear to be important for interaction with these lectins (23). Monocytes and macrophages are the initial targets of filoviruses and are thought to play an important role in viral pathogenesis, since infection of these cells is likely detrimental to host immune functions (9, 11, 17, 29, 33).
Human macrophage C-type lectins specific for galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine (hMGL) have been identified (19, 32). This type II transmembrane protein is expressed by monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells and macrophages and functions as an endocytic receptor for galactosylated GP antigens (19, 20, 32). Because hMGL is the only known macrophage C-type lectin specific for galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine and possesses a ligand specificity distinct from that of DC-SIGN and L-SIGN (32), we embarked on studies to investigate its role as an attachment factor promoting filovirus infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Viruses and cells.
A Zaire virus, strain Mayinga, and a vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), serotype Indiana, were propagated in Vero E6 cells and stored at −80°C until use. VSVΔG* complemented with the GP of Ebola or Marburg virus and expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) was generated as previously described (34). Monkey kidney Vero E6 and human chronic myelogenous leukemia (K562) cells were grown in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium and RPMI 1640, respectively, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, l-glutamine, and antibiotics. All infectious materials involving Ebola virus were handled in a biosafety level 4 facility at the Canadian Science Centre for Human and Animal Health.
Transfection and expression of hMGL cDNA in K562 cells.
A coding sequence of hMGL6A (19, 32) was inserted into a mammalian cell expression vector, pRc/CMV (Invitrogen) in the sense (CR4) and antisense (CR7) orientations. K562 cells were transfected with one of the plasmids by electroporation. After selection with Geneticin (G418 sulfate; Gibco), hMGL6A-positive cells were enriched with immunomagnetic beads by using an anti-hMGL monoclonal antibody (MAb) MLD-1 (20), which does not bind to K562 cells. Cloning of transfectant cells was performed by the limiting dilution method. Flow cytometric analysis with MAb MLD-1 (1:100-diluted ascitic fluid) and fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled F(ab′)2 of anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (Zymed) was performed to determine the levels of MGL(hMGL6A) expression on these cell clones.
Virus titration.
The infectivities of VSVΔG* complemented with the various GPs were determined by counting GFP-positive cells by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Cells were infected with each virus at a multiplicity of infection (as titrated with CR7 cells) of 0.002 to 0.005. The relative percentage of infected cells was determined by setting the number of infected K562 cells (CR7) to 100. The 50% tissue culture infective doses of wild-type Ebola virus and VSV were determined with Vero cells.
RESULTS
Effects of hMGL expression on the infectivity of VSV pseudotyped with Ebola GP.
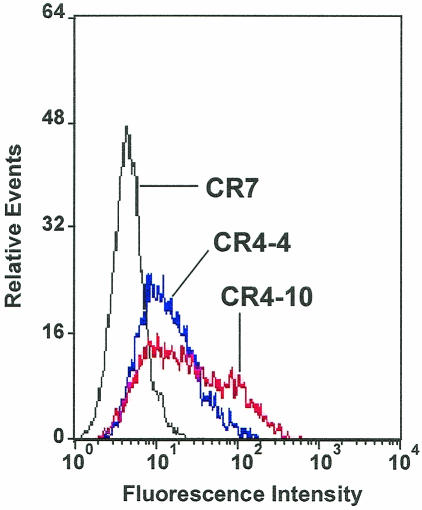
To investigate the role of hMGL in Ebola virus entry, we generated stable K562 transfectants expressing hMGL. A plasmid vector containing a cDNA corresponding to one of the most common splicing variants of human MGL (hMGL6A) (19, 32) was transfected into K562 cells, selected, and cloned. Flow cytometric profiles of these clones were investigated by the cell surface binding of MAb MLD-1 (Fig. 1). Two clonal populations of these cells, CR4-4 and CR4-10, expressing intermediate and high levels of cell surface MGL were chosen for further studies.
FIG. 1.
Expression of hMGL on K562 cell clones. One hundred thousand cells were incubated with MAb MLD-1 (anti-hMGL, ascitic fluid diluted at 1:100) on ice, washed, and incubated with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled F(ab′)2 of anti-mouse immunoglobulin G. The cells were analyzed with an Epics XL flow cytometer. These experiments were performed five times, and representative profiles are shown. CR4-4 and CR4-10 cells express hMGL at different levels, whereas control CR7 cells do not.
Two clones representing hMGL (CR4-4 and CR4-10) and a control transfectant clone (CR7) were infected with VSVΔG* complemented with the GP of Ebola Zaire (VSVΔG*-ZaireGP) or with VSV G protein (VSVΔG*-VSVG) and compared for infectivity. A striking increase in VSVΔG*-ZaireGP infectivity was found in all of the cell clones expressing hMGL, whereas VSVΔG*-VSVG infectivity was not affected by expression of the lectins (Fig. 2A). Anti-hMGL MAb greatly reduced the infectivity of VSVΔG*-ZaireGP (Fig. 2B), confirming the contribution of hMGL to this process.
FIG. 2.
Increased infectivity by VSV pseudotyped with Ebola Zaire GP of K562 cells expressing hMGL. (A) K562 transfectants (105 cells per clone), including the CR7 control, were infected with VSVΔG* complemented with the wild-type Ebola Zaire GP, Zaire GP lacking the mucin-like domain (Zaire GPΔmuc), or VSV G. (B) Cells were incubated with anti-hMGL mouse MAb (MLD-1; 1:200 diluted ascites) or control antibody (1:200-diluted normal mouse ascites) for 30 min and infected with VSVΔG* complemented with Zaire GP or VSV G in the presence of the antibody. The infected cells were counted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting, and background infectivity was subtracted from each data set. The relative percentages of infectivity were determined by setting the number of infected CR7 cells to 100. All experiments were done three times, and the means and standard deviations are shown.
Role of the mucin-like domain of the GP in its interaction with hMGL.
Ebola virus GP contains an O-glycan-rich mucin-like domain. To elucidate the role of this domain in the enhanced infection of hMGL-expressing cells, we generated VSVΔG* complemented with GP lacking this domain (VSVΔG*-ZaireGPΔmuc). In agreement with a previous report by Simmons et al. (30), deletion of the mucin-like domain (amino acid positions 311 to 462) did not affect viral infectivity on Vero cells (data not shown). When we tested the infectivity of VSVΔG*-ZaireGPΔmuc in hMGL-expressing cells, it was enhanced, but not as much as that of VSVΔG*-ZaireGP (Fig. 2A). These results indicate that the mucin-like domain may play a role in the interactions of Zaire GP with hMGL.
Increased infectivity by filoviruses of cells expressing hMGL.
To investigate whether our findings on hMGL-mediated infectivity-enhancement extend to other Ebola virus species and Marburg virus, we compared the infectivities of VSVΔG* complemented with their respective GPs in K562 transfectants (Fig. 3). In each instance, the pseudotyped viruses infected hMGL-expressing cells (CR4-10) more efficiently than control CR7 cells. However, the enhancement seen with the Reston or Marburg GP was significantly lower (P < 0.05) than corresponding results for the Zaire, Sudan, and Ivory Coast GPs.
FIG. 3.
Increased infectivity by VSV pseudotyped with filovirus GPs of K562 cells expressing hMGL. K562 transfectants (105 cells per clone) were infected with VSVΔG* complemented with the GP of the Zaire, Sudan, Ivory Coast, or Reston species of Ebola virus or with Marburg virus GP. Other experimental conditions were the same as those described in the legend for Fig. 2. The results are shown as the means and standard deviations of five independent experiments. The infectivity of viruses pseudotyped with the Reston and Marburg GPs were significantly lower than results for all remaining viruses (P < 0.05 [Student t test]).
Effects of hMGL expression on the infectivity of wild-type Ebola virus.
Finally, to determine the effect of hMGL on authentic Ebola virus infection, we compared viral replication in the transfectant cells. As with the pseudotyped viruses, hMGL expression resulted in an appreciable increase in the infectivity of Ebola virus but not VSV (Fig. 4). Notably, control cells did not produce detectable levels of infectious Ebola virus in the supernatants when infected at a low multiplicity of infection, suggesting that hMGL apparently serves as a receptor to mediate virus entry. However, cells infected with the virus at a high multiplicity of infection produced progeny virus in the supernatants, indicating that K562 cells are naturally permissive for Ebola Zaire virus, allowing the virus to undergo multiple cycles of replication. These results suggest that the expression of hMGL increases the infectivity of Ebola virus, most likely by promoting virus attachment to the natural cellular receptors in certain cell types.
FIG. 4.
Increased infectivity by wild-type Ebola virus of K562 cells expressing hMGL. K562 transfectants (107 cells per clone) were infected with VSV (A) or Ebola Zaire virus (B) (either a 105 [low MOI] or a 107 [high MOI] 50% tissue culture infective dose on Vero cells), and the supernatants were collected on days 1, 2, and 3 after infection. Symbols: ⧫, CR7 (control); ▪, CR4-10.
DISCUSSION
Although lectins on antigen-presenting cells potentially function as an endocytic receptor for antigen uptake, DC-SIGN, originally identified as an attachment factor for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) gp120 (8), has been thought to facilitate HIV entry into susceptible cells and to play a role in transferring infectious virus particles from dendritic cells to CD4/CCR5 type T cells (2, 3, 4, 6, 16, 21, 22, 23, 26). L-SIGN, which is expressed on the sinusoidal endothelial cells in the human liver and lymph nodes, also promotes HIV entry (4, 26). These lectins preferentially bind to endogenous high-mannose oligosaccharides (10, 24). DC-SIGN and L-SIGN were recently shown to enhance the infectivity of viruses pseudotyped with the Ebola GP (1, 3, 31), suggesting the involvement of these lectins in the pathogenesis of Ebola virus infection. We demonstrate here that another C-type lectin, hMGL, whose ligand specificity is distinct from that of DC-SIGN, and L-SIGN (32) also functions as an attachment factor to promote filovirus entry, suggesting that filoviruses rely on several different C-type lectins for efficient entry into antigen-presenting cells.
The inability of patients infected with Ebola virus to develop adequate immune responses can be partly attributed to infection of the mononuclear phagocyte and fibroblastic reticular systems. Infection of these cells could disrupt antigen trafficking and appropriate cytokine production, resulting in inadequate immune responses. Like DC-SIGN, hMGL is expressed in limited types of myeloid lineage cells (i.e., immature dendritic cells and intermediate precursors of macrophages) but not in monocytes (19). Enhanced infection of antigen-presenting cells that express C-type lectins such as hMGL and DC-SIGN may play an important role in the pathogenesis of filovirus infections. However, since the oligosaccharide composition of GP molecules may depend on the type of virus-producing cells and may affect GP specificity for a given lectin (23), further studies are needed to directly show the association between lectin-mediated tropism and pathogenicity in filovirus infection.
Another C-type lectin, the hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor found exclusively in hepatocytes, recognizes GPs displaying N-linked sugar chains with terminal galactose residues and was initially identified as a receptor for Marburg virus (5). However, since filoviruses are pantropic and cells lacking this receptor (e.g., human endothelial cells and epithelial cells) are susceptible to these viruses, other ubiquitous cellular receptors must exist. Similarly, although the human folate receptor alpha was identified as a cofactor that mediates infection by both Marburg and Ebola viruses (7), other molecules must also mediate filovirus entry, since not all cell types that are naturally permissive for filoviruses express this protein (36).
Whether C-type lectins directly serve as a primary receptor to mediate filovirus natural entry is controversial (1, 31), although the available data suggest that C-type lectins, including hepatic asialoglycoprotein receptor, DC-SIGN, L-SIGN, and hMGL, function as an attachment factor to promote virus infection. The mucin-like domain on the GP appears important for interaction with these lectins. It should also be noted that the tissue tropism of filoviruses is associated with the tissue distribution of these lectins, which may explain why filoviruses preferentially infect monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, endothelial cells, and hepatocytes. One way to test this hypothesis in future investigations would be to use the reverse genetics approach to generate recombinant Ebola viruses lacking the ability to interact with lectins (e.g., mutants with a deletion of the GP mucin-like domain).
Acknowledgments
We thank Michael Whitt for VSVΔG*; Daryl Dick, Michael Garbutt, and Allen Grolla for excellent technical assistance; and John Gilbert for editing the manuscript.
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas from the Ministries of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan to A.T.; by National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Public Health Service research grants to Y.K.; by CREST (Japan Science and Technology Corp.) to A.T. and Y.K.; and by a research grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to H.F. (MOP-43921).
REFERENCES
- 1.Alvarez, C. P., F. Lasala, J. Carrillo, O. Muniz, A. L. Corbi, and R. Delgado. 2002. C-type lectins DC-SIGN and L-SIGN mediate cellular entry by Ebola virus in cis and in trans. J. Virol. 76:6841-6844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baribaud, F., S. Pohlmann, and R. W. Doms. 2001. The role of DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR in HIV and SIV attachment, infection, and transmission. Virology 286:1-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baribaud, F., S. Pohlmann, G. Leslie, F. Mortari, and R. W. Doms. 2002. Quantitative expression and virus transmission analysis of DC-SIGN on monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Virol. 76:9135-9142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bashirova, A. A., T. B. Geijtenbeek, G. C. van Duijnhoven, S. J. van Vliet, J. B. Eilering, M. P. Martin, L. Wu, T. D. Martin, N. Viebig, P. A. Knolle, V. N. KewalRamani, Y. van Kooyk, and M. Carrington. 2001. A dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN)-related protein is highly expressed on human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and promotes HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 193:671-678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Becker, S., M. Spiess, and H.-D. Klenk. 1995. The asialoglycoprotein receptor is a potential liver-specific receptor for Marburg virus. J. Gen. Virol. 76:393-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cameron, P. U., P. S. Freudenthal, J. M. Barker, S. Gezelter, K. Inaba, and R. M. Steinman. 1992. Dendritic cells exposed to human immunodeficiency virus type-1 transmit a vigorous cytopathic infection to CD4+ T cells. Science 257:383-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chan, S. Y., C. J. Empig, F. J. Welte, R. F. Speck, A. Schmaljohn, J. F. Kreisberg, and M. A. Goldsmith. 2001. Folate receptor-alpha is a cofactor for cellular entry by Marburg and Ebola viruses. Cell 106:117-126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Curtis, B. M., S. Scharnowske, and A. J. Watson. 1992. Sequence and expression of a membrane-associated C-type lectin that exhibits CD4-independent binding of human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:8356-8360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Davis, K. J., A. O. Anderson, T. W. Geisbert, K. E. Steele, J. B. Geisbert, P. Vogel, B. M. Connolly, J. W. Huggins, P. B. Jahring, and N. K. Jaax. 1997. Pathology of experimental Ebola virus infection in African green monkeys. Involvement of fibroblastic reticular cells. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 121:805-819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Feinberg, H., D. A. Mitchell, K. Drickamer, and W. I. Weis. 2001. Structural basis for selective recognition of oligosaccharides by DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR. Science 294:2163-2166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Feldmann, H., H. Bugany, F. Mahner, H.-D. Klenk, D. Drenckhahn, and H. J. Schnittler. 1996. Filovirus-induced endothelial leakage triggered by infected monocytes/macrophages. J. Virol. 70:2208-2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Feldmann, H., and M. P. Kiley. 1999. Classification, structure, and replication of filoviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 235:1-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Feldmann, H., S. T. Nichol, H.-D. Klenk, C. J. Peters, and A. Sanchez. 1994. Characterization of filoviruses based on differences in structure and antigenicity of the virion glycoprotein. Virology 199:469-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Feldmann, H., A. Sanchez, and H.-D. Klenk. 1998. Filoviruses, p. 651-664. In H. D. Collier (ed.), Topley and Wilson's microbiology and microbial infections, 9th ed. Edward Arnold, London, England.
- 15.Fisher-Hoch, S. P., and J. B. McCormick. 1999. Experimental filovirus infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 235:117-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Geijtenbeek, T. B., D. S. Kwon, R. Torensma, S. J. van Vliet, G. C. van Duijnhoven, J. Middel, I. L. Cornelissen, H. S. Nottet, V. N. KewalRamani, D. R. Littman, C. G. Figdor, and Y. van Kooyk. 2000. DC-SIGN, a dendritic cell-specific HIV-1-binding protein that enhances trans-infection of T cells. Cell 100:587-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Geisbert, T. W., P. B. Jahrling, M. A. Hanes, and P. M. Zack. 1992. Association of Ebola-related Reston virus particles and antigen with tissue lesions of monkeys imported to the United States. J. Comp. Pathol. 106:137-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Geyer, H., C. Will, H. Feldmann, H.-D. Klenk, and R. Geyer. 1992. Carbohydrate structure of Marburg virus glycoprotein. Glycobiology 2:299-312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Higashi, N., K. Fujioka, K. Denda-Nagai, S. Hashimoto, S. Nagai, T. Sato, Y. Fujita, A. Morikawa, M. Tsuiji, M. Miyata-Takeuchi, Y. Sano, N. Suzuki, K. Yamamoto, K. Matsushima, and T. Irimura. 2002. The macrophage C-type lectin specific for galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine is an endocytic receptor expressed on monocyte-derived immature dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277:20686-20693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Higashi, N., A. Morikawa, K. Fujioka, Y. Fujita, Y. Sano, M. Miyata-Takeuchi, N. Suzuki, and T. Irimura. 2002. Human macrophage lectin specific for galactose/N-acetylgalactosamine is a marker for cells at an intermediate stage in their differentiation from monocytes into macrophages. Int. Immunol. 14:545-554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kwon, D. S., G. Gregorio, N. Bitton, W. A. Hendrickson, and D. R. Littman. 2002. DC-SIGN-mediated internalization of HIV is required for trans-enhancement of T-cell infection. Immunity 16:135-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee, B., G. Leslie, E. Soilleux, U. O'Doherty, S. Baik, E. Levroney, K. Flummerfelt, W. Swiggard, N. Coleman, M. Malim, and R. W. Doms. 2001. cis expression of DC-SIGN allows for more efficient entry of human and simian immunodeficiency viruses via CD4 and a coreceptor. J. Virol. 75:12028-12038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lin, G., G. Simmons, S. Pohlmann, F. Baribaud, H. Ni, G. J. Leslie, B. S. Haggarty, P. Bates, D. Weissman, J. A. Hoxie, and R. W. Doms. 2003. Differential N-linked glycosylation of human immunodeficiency virus and Ebola virus envelope glycoproteins modulates interactions with DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR. J. Virol. 77:1337-1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mitchell, D. A., A. J. Fadden, and K. Drickamer. 2001. A novel mechanism of carbohydrate recognition by the C-type lectins DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR. Subunit organization and binding to multivalent ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 276:28939-28945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Peters, C. J., and A. S. Khan. 1999. Filovirus diseases. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 235:85-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pohlmann, S., E. J. Soilleux, F. Baribaud, G. J. Leslie, L. S. Morris, J. Trowsdale, B. Lee, N. Coleman, and R. W. Doms. 2001. DC-SIGNR, a DC-SIGN homologue expressed in endothelial cells, binds to human and simian immunodeficiency viruses and activates infection in trans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:2670-2675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sanchez, A., A. S. Khan, S. R. Zaki, G. J. Nabel, T. G. Ksiazek, and C. J. Peters. 2001. Filoviridae: Marburg and Ebola viruses, p. 1279-1304. In D. M. Knipe and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed. Lippincott/The Williams & Wilkins Co., Philadelphia, Pa.
- 28.Sanchez, A., S. G. Trappier, B. W. Mahy, C. J. Peters, and S. T. Nichol. 1996. The virion glycoproteins of Ebola viruses are encoded in two reading frames and are expressed through transcriptional editing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:3602-3607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schnittler, H. J., and H. Feldmann. 1999. Molecular pathogenesis of filovirus infections: role of macrophages and endothelial cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 235:175-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Simmons, G., R. J. Wool-Lewis, F. Baribaud, R. C. Netter, and P. Bates. 2002. Ebola virus glycoproteins induce global surface protein down-modulation and loss of cell adherence. J. Virol. 76:2518-2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Simmons, G., J. D. Reeves, C. C. Grogan, L. H. Vandenberghe, F. Baribaud, J. C. Whitbeck, E. Burke, M. J. Buchmeier, E. J. Soilleux, L. J. Riley, R. W. Doms, P. Bates, and S. Pohlmann. 2003. DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR bind Ebola glycoproteins and enhance infection of macrophages and endothelial cells. Virology 305:115-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Suzuki, N., K. Yamamoto, S. Toyoshima, T. Osawa, and T. Irimura. 1996. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding human macrophage C-type lectin: its unique carbohydrate binding specificity for Tn antigen. J. Immunol. 156:128-135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Takada, A., and Y. Kawaoka. 2001. The pathogenesis of Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Trends Microbiol. 9:506-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Takada, A., C. Robison, H. Goto, A. Sanchez, K. G. Murti, M. A. Whitt, and Y. Kawaoka. 1997. A system for functional analysis of Ebola virus glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:14764-14769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Volchkov, V. E., S. Becker, V. A. Volchkova, V. A. Ternovoj, A. N. Kotov, S. V. Netesov, and H.-D. Klenk. 1995. GP mRNA of Ebola virus is edited by the Ebola virus polymerase and by T7 and vaccinia virus polymerases. Virology 214:421-430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Weitman, S. D., R. H. Lark, L. R. Coney, D. W. Fort, V. Frasca, V. R. Zurawski, Jr., and B. A. Kamen. 1992. Distribution of the folate receptor GP38 in normal and malignant cell lines and tissues. Cancer Res. 52:3396-3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wool-Lewis, R. J., and P. Bates. 1998. Characterization of Ebola virus entry by using pseudotyped viruses: identification of receptor-deficient cell lines. J. Virol. 72:3155-3160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]