Abstract
Nucleotide variants, especially those related to epigenetic functions, provide critical regulatory information beyond simple genomic sequence, and they define cell status in higher organisms. 5-methylcytosine, which is found in DNA, was until recently the only nucleotide variant studied in terms of epigenetics in eukaryotes. However, 5-methylcytosine has turned out to be just one component of a dynamic DNA epigenetic regulatory network that also includes 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-formylcytosine, and 5-carboxycytosine. Reversible methylation of N6-methyladenosine in RNA has also been demonstrated. The discovery of new nucleotide variants triggered an explosion of new information in the epigenetics field. This rapid research progress has benefited significantly from timely developments of new technologies that specifically recognize, enrich, and sequence nucleotide modifications, as evidenced by the wide application of the bisulfite sequencing of 5-methylcytosine and very recent modifications of bisulfite sequencing to revolve 5-hydroxymethylcytosine from 5-methylcytosine with base-resolution information.
The mammalian genome possesses much more information than a sequence of nucleotides. Each adult human body contains over 200 distinct cell types; yet despite their marked differences in phenotype and function, these cell types share an almost identical genome sequence. Epigenetic modifications play a major role in this diversity. An important epigenetic modification in mammalian genomic DNA is the nucleotide variant 5-methylcytosine (5mC); 5mC regulates gene expression, determines cell development, and affects disease pathogenesis1,2. But 5mC is not the only nucleotide variant.
During the past three years, three additional cytosine variants were identified in the mammalian genome. In 2009, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) was shown to exist in relatively high abundance in certain mammalian cells and tissues3,4. Following this discovery, 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC) were revealed in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and mouse tissues5-7. These cytosine derivatives are produced from a stepwise oxidation of 5mC by the ten-eleven translocation (TET) family dioxygenases (Fig. 1, Table 1)4,6-8. These new DNA base modifications immediately drew broad attention from the research community and have been extensively reviewed9-13.
Figure 1.
New DNA nucleotide variants, including 5hmC, 5fC, and 5caC. The pattern of DNA methylation is established and maintained by DNA methyltransferases. Demethylation can be passive (e.g. during replication) or active. TET family proteins can oxidize 5mC to 5hmC, 5hmC to 5fC, and then 5fC to 5caC. The oxidation products 5fC and 5caC can be removed by TDG to generate an abasic site. This abasic site can be repaired to a cytosine by the base excision repair (BER) pathway. Alternatively, 5hmC may be deaminated by AID or APOBEC to 5hmU, which can subsequently be removed and repaired by TDG or SMUG1 and then BER, respectively. 5caC may also be removed in a decarboxylation pathway. Solid arrows indicate biochemically validated pathways whereas dotted arrows are pathways yet to be confirmed biochemically. 5hmU has not been detected in the mammalian genome so far.
Table 1.
Proteins that deposit, bind to, modify or remove nucleotide variants, and the known genomic locations of some of these nucleotide variants.
| Modification | Proteins that deposit the modification | Proteins that modify, remove or bind the modification | Genomic or transcriptomic location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5hmC | TET1-34,8 | TET1-36,7 | With affinity-based profiling, it is shown to be enriched at TSSs, promoters, exons, CTCF-binding sites and enhancers18-20,22,61,62,65,66. With single-base resolution sequencing, it shows highest enrichment at distal regulatory regions, near but not on transcription factor-binding sites69. |
| 5fC | TET1-36 | TET1-36, TDG23,24 | Unknown |
| 5caC | TET1-36,7 | TDG7,23,24 | Unknown |
| m6A in mRNA | MT-A70 (A 70 kD subunit protein in a 200 kD protein complex)120 | FTO37, YTHDF2-3 and ELAVL1 (binding proteins)101 | Enriched around stop codons, in 3′ UTRs and within long internal exons101,102 |
| 5mC in RNA | NSUN292 | Unknown | Enriched in untranslated regions (both 5′ and 3′ UTRs) and near Argonaute-binding regions within mRNA92 |
5mC is generally viewed as a ‘silencing’ epigenetic mark because of the hydrophobic recruitment of methylCpG-binding proteins2. 5hmC, although carrying a hydrophilic modification, is not simply an ‘activating’ epigenetic mark; it is regarded as an intermediate in an active demethylation pathway4,6,7,14-16 (Fig. 1) and appears to play complex roles in gene regulation17-22. In certain cells or tissues in which 5hmC accumulates to relative high abundance, it may also have unique functions of its own that directly affect gene expression. Currently, 5fC and 5caC are thought to be strictly demethylation intermediates for two reasons. First, they exist in much lower abundance compared with 5hmC in mouse ESCs. Second, they are recognized and removed by DNA glycosylase TDG to yield abasic sites, which are subsequently converted to cytosine through base excision repair (BER) (Fig. 1)7,23,24. However, the generation and removal of these further oxidized cytosine derivatives could be regulated to affect gene expression. Box 1 summarizes our current knowledge of the biological functions of these new DNA epigenetic nucleotide variants.
The availability of next-generation sequencing technologies that allow for high-throughput and affordable sequencing significantly accelerated research on nucleic acid modifications25. In less than three years tremendous progress has been made in understanding the biological function of 5hmC as a direct result of the rapid development of 5hmC-detection and sequencing methods26. In this review, we discuss methods for detecting nucleotide modifications of potential functional importance, such as 5hmC, 5fC and 5caC in DNA, and we briefly summarize other interesting modifications, such as m6A and 5mC in RNA. To fully describe new technologies and the biological insights revealed through their application to the study of a single nucleotide variant, we focus on 5hmC. This review will not cover 5mC in DNA, which is the subject of many other articles27,28. Although 5-hydroxymethyluracil (5hmU) is a suggested intermediate in active demethylation mediated through deamination and then BER (Fig. 1)29,30, it is essentially undetectable in the mammalian genome15, and a recent biochemistry and cell-based investigation raised questions about the feasibility of the deamination step31. Nevertheless, 5hmU behaves similarly to 5hmC in certain aspects. Therefore, many 5hmC detection/profiling methods that we discuss can potentially be applied to future 5hmU detection and profiling, if it does indeed play functional roles in certain biological pathways32,33.
New nucleotide variants bring technological challenges
The nucleotide variants discussed here generally exist in very low abundance in the genome, ranging from several ppm (parts per million, equal to 0.0001%) to less than 1% compared to regular nucleotides (A, T, C, G) (Table 2). Therefore, highly selective and sensitive methods with low background noise are required to detect, profile, and sequence these variants. While antibody-based immunoprecipitation approaches typically show bias towards densely populated regions, an ideal method would recognize or enrich every single modification in the genome without bias, thus achieving high sensitivity for scarce modifications.
Table 2.
Relative abundance and known tissue locations of new nucleotide modifications.
| Modification | Tissues and cell lines | Relative abundance | Genome- or transcriptome-wide profiling methods applied | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5hmC in DNA | Mouse ESC | 0.1% of cytosine6 | hMeDIP18-20,61 | |
| GLIB22 | ||||
| anti-CMS22 | ||||
| TAB-Seq69 (single-base resolution) | ||||
|
| ||||
| Human ESC | Not available | hMeDIP62 | ||
| hMe-Seal 66 | ||||
| TAB-Seq69 (single-base resolution) | ||||
|
| ||||
| Mouse brain tissue | 0.4∼0.7% of cytosine6,15 | hMe-Seal39,65 | ||
|
| ||||
| Human brain tissue | Not available | hMeDIP35 | ||
| hMe-Seal39 | ||||
|
| ||||
| Other mouse tissue | 0.02∼0.3% of cytosine6,15 | Not available | ||
|
| ||||
| Human cancer cells | 0.03∼0.1% of guanine116 | Not available | ||
|
| ||||
| mouse P19 and 3T3-L1 cells | Not available | hMeDIP63 | ||
|
| ||||
| 5fC in DNA | Mouse ESC | 20 ppm of cytosine6 | Not available | |
|
| ||||
| Mouse tissues | 3-20 ppm of cytosine6 | Not available | ||
|
|
||||
| 5caC in DNA | Mouse ESC | 3 ppm of cytosine6 | Not available | |
|
|
||||
| m6A in mRNA | Human HepG2 cells | Not available | anti-m6A antibody101 | |
|
| ||||
| Mouse liver | Not available | anti-m6A antibody101 | ||
|
| ||||
| Mouse brain | Not available | anti-m6A antibody102 | ||
|
| ||||
| Human HEK293T cells | Not available | anti-m6A antibody102 | ||
|
| ||||
| 5mC in RNA | HeLa cell | Not available | Bisulfite sequencing92 | |
Since discovering the potential epigenetic role of 5hmC3,4, the field has progressed through three stages of technology development and implementation. When 5hmC was first discovered, methods to accurately detect and quantify this base variant in the genome were required. Next, genome-wide affinity-based profiling methods to enrich 5hmC-containing genomic regions, which could then be subjected to next-generation sequencing, were required to determine the genomic distribution of 5hmC. Although powerful enough to reveal initial biological insights into 5hmC, the sequencing data obtained from these methods does not provide single-base resolution maps with the relative abundance at each modification site; this quantitative information is crucial to the understanding of the biology associated with 5hmC. Just recently, we have seen the emergence of single-base resolution sequencing technologies that are capable of quantifying the relative abundance of 5hmC at each modification site. In addition, these methods can further refine base-resolution maps of 5mC both genome-wide and at specific loci in combination with the conventional bisulfite sequencing approach, which by itself could not differentiate 5hmC from 5mC and gives the sum of 5mC+5hmC. Therefore, these new methods are expected to have a transformative impact on DNA epigenetic research in general.
Detection and quantification
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis of hydrolyzed nucleotides is perhaps the oldest method for studying DNA or RNA modifications34. Combined with radioactive labeling, TLC can be quite sensitive; in fact many new nucleotide variants, such as 5hmC3,4 and 5caC6,7 were initially discovered by TLC with genomic samples isolated from mammalian cells. TLC can be performed in either one or two dimensions, with the latter providing more resolution power6. A chemical reaction with the base modification can change the physical properties of the base and thus induce a shift of its migration on TLC for enhanced separation or validation of the chemical properties of the modification. For instance, 5fC and 5caC can react with O-ethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC), respectively, thus resulting in dramatic shifts of their migrations on TLC for easy detection and validation6. The TLC method, however, can be tedious and its overall sensitivity is limited by radioactive labeling.
Antibody-based detection has also been implemented17,35-37. However, as a result of its nonlinear and density-biased response, this approach tends to be limited to semiquantitative information22,38. Nevertheless, antibodies can directly stain nucleotide modifications inside cells for cell-based visualization8,38-42. The chemical properties of a modification can also be varied in order to achieve much enhanced antibody-based recognition. Rao, Agarwal and colleagues demonstrated this by treating 5hmC with sodium bisulfite to generate cytosine 5-methylenesulfonate (CMS), a chemically modified 5hmC derivative that is highly immunogenic (Fig. 2a)38. The resulting anti-CMS antibody is very specific with much less density bias compared with anti-5hmC antibodies22,38.
Figure 2.
Summary of genome-wide affinity-based 5hmC-profiling methods. (a) 5hmC in genomic DNA can be enriched by anti-5hmC antibodies or, after treatment with sodium bisulfite, by anti-CMS antibody. (b) 5hmC can be labeled with glucose by βGT. The resulting glucosylated 5hmC can be enriched with JBP-1. Alternatively, βGT-treated 5hmC can undergo glucosylation, periodate oxidation, biotinylation (GLIB); in this reaction sodium periodate cleaves the vicinal hydroxyl groups in the glucose to generate reactive aldehyde groups, which can be biotinylated using an aldehyde-reactive hydroxylamine-biotin probe. Alternatively, an azide-modified glucose can be introduced to 5hmC by βGT and subsequently biotinylated via click chemistry in selective chemical labeling (hMe-Seal). Biotinylated 5hmC residues can be enriched using streptavidin beads, and all the affinity-enriched 5hmC DNA can be subjected to high-throughput sequencing, or to SMRT sequencing in the case of hMe-Seal, to determine the genomic distribution of 5hmC.
Besides antibodies, enzymes that specifically recognize and react with the nucleotide of interest have proved to be extremely valuable. In this regard, the T4 bacteriophage enzyme β-glucosyltransferase (βGT) has become a critical tool for specifically modifying 5hmC for subsequent detection and sequencing (Fig. 2b)43. This bacteriophage enzyme has long been known to transfer a glucose moiety from UDP-glucose to 5hmC, which also exists in the T4 phage genome44. Since the glucosylation reaction is specific to 5hmC, it was used to transfer a radioactively labeled glucose to 5hmC for quantification, which is more sensitive and accurate than the antibody-based detection32,45.
Restriction endonucleases sensitive to methylation have long been used to detect DNA methylation46. Recently, several restriction endonucleases including MspI47,48, TaqαI49, MspJI50,51, PvuRts1I52,53, and SauUSI54 have been employed to detect 5hmC at specific loci and potentially for genome-wide analysis as well. These enzymes are either selective to 5hmC or blocked by glucose-modified 5hmC (from βGT-catalyzed glucosylation), thus providing a sequence-dependent interrogation of 5hmC. Methyltransferase55 and exonuclease56 have also been used for the detection of 5hmC. Equivalent methods have yet to be reported for 5fC and 5caC.
For a more accurate method, researchers turn to the gold standard in quantifying low levels of modified nucleotides: liquid chromatography (LC)-mass spectroscopy (MS), which separates and identifies hydrolyzed nucleotides. Carell and colleagues coupled LC with high-resolution MS and used isotope-labeled internal standard to achieve accurate quantification of 5hmC57. Later, they applied the same approach to the detection of 5fC in genomic DNA isolated from mouse ESCs5. They reacted the formyl group of 5fC with biotin-hydroxylamine for enhanced signal and validation5. Recent advances in applying triple quadrupole mass spectrometer for LC–tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) detection of rare base modifications, such as 5hmC58, 5fC6, 5caC6,7, m6A37 and other nucleotide variants59, further improve the detection limits and allow for the quantification. In fact, LC-MS/MS is the only reported method so far that can quantify 5caC, the scarcest cytosine derivative in ESC genomic DNA, at the level of ∼3 ppm of that of cytosine6. The relative abundance of these new nucleotide variants determined by LC-MS are summarized in Table 2.
Genome-wide profiling methods
Compared to simple detection and quantification, genome-wide profiling methods that combine affinity-based enrichment and high-throughput sequencing to yield a genome-wide distribution map of the modified base can provide much-needed biological insights. Figure 2 and Table 3 summarize and compare all reported profiling methods for 5hmC. Antibody is usually the first method came to mind (Fig. 2a). Traditional antibody-based captures, such as methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-sequencing (MeDIP-seq) and the related methyl-binding protein-sequencing (MBD-seq), have been used extensively to map methylomes60. Similarly, several groups have simultaneously developed hydroxymethyl-DNA immunoprecipitation-sequencing (hMeDIP)18-20,35,61-63 using antibodies raised against 5hmC. However, careful analyses reveal the tendency of these anti-5hmC antibodies to recognize modification-dense regions22 as well as CA repeats64. Such biases, together with the high background noise and inferior reproducibility when using antibodies from different lots can pose problems in data analysis22,38,64. Nevertheless, valuable information on the genome-wide distribution of 5hmC has been gained11-13. As mentioned above, the anti-CMS antibody showed substantially improved performance over anti-5hmC antibody in genome-wide pull-down and sequencing with less bias and lower background noise22. Based on this body of work, 5hmC has been shown to be enriched at transcription start sites (TSSs), promoters, gene bodies (exons), CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF)-binding sites and enhancers in ESCs, thus suggesting potential roles for 5hmC in DNA methylation fidelity, pluripotency and lineage commitment balance11-13 (Table 1).
Table 3. Advantages and disadvantages of current 5hmC sequencing methods.
| Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Affinity-based methods | ||
| hMeDIP18-20,35,61-63 | Antibody readily available; relatively straightforward procedure | Biased to heavily modified regions and CA-repeats; high background; antibody lot-to-lot inconsistency |
| Anti-CMS22 | Less bias and lower background compared to anti-5hmC antibody | Prolonged procedure; PCR bias after bisulfite treatment |
| hMe-Seal39,65-67 | Highly efficient, specific and unbiased labeling; built-in disulfide bond for easy pull-down | Requires synthesis of azide-modified glucose (now commercially available) |
| GLIB22 | Highly specific biotin-based pull-down; readily available materials | Sodium periodate oxidation introduces high background; comparison to a non-trivial negative control is necessary |
| JBP-133,68 | Highly efficient one-step βGT labeling; readily available materials | Takes one week to prepare the JBP-1 beads; no published genome-wide profiling data for comparison |
| Single-base resolution methods | ||
| SMRT67 | Single molecular sequencing, no PCR amplification required; strand-specific 5hmC sequencing | Loss of quantitative information due to prior enrichment; higher sequencing capacity needed |
| oxBS-Seq78 | Low-cost and readily available materials; simple procedure. | Oxidation degradation of DNA; repeated bisulfite treatments to fully deaminate 5fC; potentially increased error owing to the comparitive nature of the method. |
| TAB-Seq69 | Measure 5hmC directly; readily deamination of 5caC under traditional bisulfite treatment | Requires highly active TET enzymes for high conversion rate of 5mC to 5caC. |
We took advantage of the βGT-catalyzed 5hmC glucosylation reaction and developed a selective chemical labeling-based method we named hMe-Seal (Fig. 2b)65. Like unmodified glucose, azide-modified glucose is well tolerated by βGT and efficiently transferred to 5hmC. A biotin can be subsequently installed onto the azido group. Relying on the extremely tight and specific binding between biotin and streptavidin, which has virtually no modification density bias22, we can in principle label every 5hmC and perform selective pull-down for genome-wide profiling or loci-specific analysis of 5hmC distribution39,65,66. Thanks to use of a disulfide linker, the enriched product can be readily released from streptavidin via reduction with dithiothreitol (DTT)67. hMe-Seal is robust with extremely low background and no bias64. It should also be noted that the glucose modification on the enriched DNA fragments does not interfere with polymerases employed regularly for library preparation in Illumina sequencing. Only in rare cases do we observe pausing with Taq polymerase at modification sites65. Using hMe-Seal, we have performed whole-genome profiling of 5hmC in mouse and human brain tissues. We found distinct age-dependent distribution of 5hmC in brain tissues as compared with ESCs. Specifically, we saw enrichment within gene bodies of expressed genes and upstream of the TSS, but we observed depletion at the TSS, suggesting a unique function of 5hmC in neurodevelopment39,65.
A related biotin-based 5hmC-profiling method is referred to as glucosylation, periodate oxidation, biotinylation (GLIB). It utilizes βGT to transfer an unmodified glucose to 5hmC, followed by cleavage of the vicinal hydroxyl groups in the glucose by sodium periodate to generate reactive aldehyde groups, which can then be biotinylated using an aldehyde-reactive hydroxylamine-biotin probe for further enrichment22. However, the sodium periodate oxidation may cause DNA damage and introduce high background. Nevertheless, with appropriate controls the GLIB method provides an alternative approach. Applying this method and the anti-CMS antibody-based enrichment, the Rao group revealed the distribution of 5hmC in ESCs as described above22.
After treating 5hmC with βGT, Klungland and colleagues showed that the J-binding protein 1 (JBP-1), which is known to interact with glucosylated 5hmU in certain kinetoplastids, can also bind and therefore enrich glucosylated 5hmC for specific 5hmC profiling33,68. Thus, JBP-1 works as a naturally existing ‘antibody’ for glucosylated 5hmC.
Single-base resolution sequencing methods
Although valuable, affinity-based genome-wide profiling methods have several disadvantages. First, these methods generate distribution maps with poor resolution as a result of the size limitation of the nucleic acid fragmentation and capture technology. Second, enrichment renders it impossible to measure the absolute abundance of the nucleotide modification. Third, the affinity-based methods' propensity to amplify frequent but weak signals may impose biases69. In contrast, a single-base resolution mapping method, especially a whole-genome sequencing method without prior enrichment, could provide the most accurate and quantitative information regarding the modification.
The simplest way to achieve single-base resolution sequencing of a nucleotide variant would be to recognize its physical size or properties directly during sequencing. Unfortunately, the current second-generation sequencing technologies involve sample pre-amplification, which leads to the loss of base modification information. Third-generation sequencing technologies that feature single-molecule sequencing and do not require sample pre-amplification may pose a solution70. The single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing developed by Pacific Biosciences records the incorporation of phospholinked nucleotides by individual DNA polymerase in real time71. By further monitoring the polymerase kinetics during replication, SMRT can directly detect DNA base modifications including 5mC and 5hmC, albeit with low confidence72. Through collaboration with Pacific Biosciences we have successfully integrated hMe-Seal (Fig. 2) and SMRT sequencing to improve the polymerase kinetics for confident detection of 5hmC at single-base resolution67. Further technological advances are needed before this approach can be applied to whole mammalian genome 5hmC sequencing. Other third-generation sequencing approaches, such as nanopore sequencing73, also have the potential to detect 5mC74 and 5hmC75,76 at the single-base level, but these applications are still in the early stages of development.
Bisulfite sequencing, the gold standard for single-base resolution sequencing of 5mC, can be adapted to essentially any sequencing platform. In this approach the distinct chemical reactions of cytosine and 5mC with sodium bisulfite (NaHSO3) (cytosine deaminates to uracil, whereas 5mC remains intact), are explored to achieve single base resolution differentiation of cytosine from 5mC77. Complications arise, however, with all of the newly discovered cytosine derivatives. Under bisulfite conditions, cytosine, 5fC (which requires harsher conditions to achieve complete deamination)78, and 5caC7,69 undergo deamination to read as thymine, whereas 5mC and 5hmC resist deamination and thus will read as cytosine79-81. Therefore, traditional bisulfite sequencing cannot differentiate 5hmC from 5mC, nor can it differentiate 5fC or 5caC from unmodified cytosine.
Two groups independently designed modified bisulfite sequencing for quantitative single-nucleotide resolution mapping of 5hmC and 5mC in mammalian DNA by taking advantage of different properties of modified cytosines69,78. In the first approach, termed oxidative bisulfite sequencing (oxBS-Seq), Balasubramanian, Reik and colleagues explored the chemical property of 5hmC and discovered that potassium perruthenate (KRuO4) specifically oxidizes 5hmC to 5fC, which subsequently deaminates under repeated bisulfite treatments (Fig. 3a)78. Therefore, in a KRuO4- and bisulfite-treated DNA sample, 5hmC would read as thymine while 5mC still reads as cytosine. This method directly reads out 5mC. To reveal base-resolution information of 5hmC, traditional bisulfite sequencing of the KRuO4-untreated DNA sample can be performed to reveal both 5mC and 5hmC as cytosine. A subtraction yields the abundance of 5hmC (Fig. 3a). The authors then applied oxBS-Seq to reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS, which selects a fraction of restriction enzyme digested fragments to generate a ‘reduced representation’ of the genome) in order to sequence a subset of genomic regions enriched with CpG islands (CGIs) in mouse ESCs78. Potential limitations of this method include that genomic DNA can be damaged and degraded by chemical oxidation conditions and by the repeated bisulfite treatments needed to fully deaminate 5fC (generated from 5hmC). However, this simple method, with further optimization to avoid extensive DNA degradation and achieve high yields of 5fC deamination, could be very attractive in practical sequencing of 5hmC in genomic samples.
Figure 3.
OxBS-Seq and TAB-seq for single-base resolution sequencing of 5hmC. (a) OxBS-Seq requires two bisulfite sequencings. In the first sequencing, 5hmC in genomic DNA is oxidized to 5fC by KRuO4, and subsequently converted into T by bisulfilte treatment and PCR. In the second sequencing, genomic DNA is subjected to bisulfite treatment and PCR without KRuO4 treatment. The first sequencing provides genuine sites of 5mC; this information is subtracted from the 5mC plus 5hmC sites provided by the second traditional bisulfite sequencing. (b) TAB-Seq directly reads out 5hmC in one bisulfite sequencing. 5hmC is protected from TET-mediated oxidation and bisulfite conversion by βGT-catalyzed glucosylation. Next, 5mC is oxidized by TET to 5caC, and subsequently converted into T after bisulfite treatment and PCR. Therefore, TAB-Seq provides genuine sites of 5hmC in genomic DNA with absolute abundance at each modification site.
As an approach to directly read out 5hmC, we and our collaborators developed TET-assisted bisulfite sequencing, which we have termed TAB-Seq (Fig. 3b)69. In TAB-Seq, we first protect 5hmC from TET-mediated oxidation by blocking it with glucose using βGT. Next, all the 5mC are oxidized by the mTet1 enzyme to 5caC, which subsequently undergo deamination in bisulfite treatment. When the DNA is sequenced, these bases are read as thymine. The only remaining cytosine signals after TAB-Seq stem from the protected 5hmCs (Fig. 3b). To obtain base-resolution information of 5mC, the results of TAB-Seq can be compared with those of traditional bisulfite sequencing, which reveals the sum of 5mC+5hmC. A subtraction yields the base-resolution map of 5mC. A current limitation to this method is the requirement of highly active TET enzymes. An oxidation conversion rate over 96% of 5mC to 5caC is desirable to reduce sequencing costs69. Currently, only mTet1 expressed from insect cells and carefully purified can achieve this level of activity69.
Neither oxBS-Seq nor TAB-Seq requires an enrichment step. Therefore, quantitative information of 5mC and 5hmC within the genome can be obtained. The availability of base-resolution methods for 5hmC sequencing is potentially transformative for studies of 5hmC biology. We have applied TAB-Seq to provide the first full maps of 5hmC in human and mouse ESCs and uncovered new features of 5hmC, including its significant enrichment at distal functional regulatory elements such as enhancers, its distribution near but not on transcription factor–binding sites, and the sequence bias and strand asymmetry associated with 5hmC sites, suggesting that active demethylation occurs at regulatory elements through 5hmC69. However, the depletion of 5hmC at transcription factor binding sites could also be attributed to less methylation and/or the steric exclusion of TET proteins by transcription factors at these sites.
RNA modifications
Chemical modifications (e.g. methylation) on DNA and histones have been widely accepted as key processes that regulate gene expression. In contrast to the limited types of modifications found in DNA, cellular RNAs, including mRNA and non-coding RNA, contain more than a hundred structurally distinct post-transcriptional modifications at thousands of sites (http://rna-mdb.cas.albany.edu/RNAmods/)82. We have hypothesized that some of these RNA modifications can also be dynamic and reversible and may play regulatory roles analogous to reversible DNA and protein modifications83,84. Traditional methods to determine the localization of RNA modifications such as TLC85, primer extension86, ligation87, microarray88, or mass spectrometry89 are low-throughput, laborious, time-consuming, and especially difficult for low abundant cellular RNAs such as mRNA. As a result, the functions of potential dynamic RNA modifications, especially those on low abundant mRNA and non-coding RNA that will be discussed in this review, remained largely unexplored due to the lack of large scale sequencing methods and lack of RNA demodification enzymes84. In fact, prior to 2011, there were no known reversible chemical modifications on RNA that could affect gene expression.
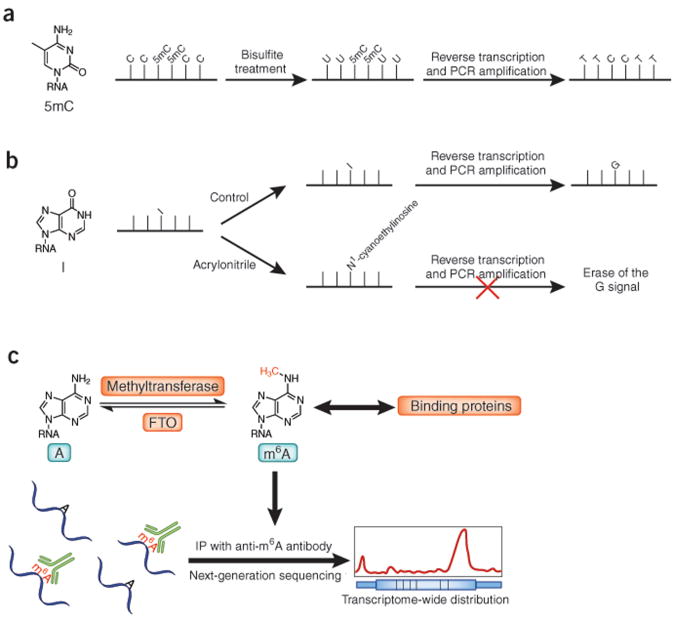
Several recently developed high-throughput sequencing methods specific for RNA modifications have rekindled interest in functional dynamics of RNA modifications, in particular those in mRNA and non-coding RNA. For example, bisulfite sequencing was applied to map transcriptome-wide 5mC in RNA and reveal that 5mC exists not only in tRNA and rRNA as previously known90,91, but also in mRNA and certain non-coding RNAs92 (Fig. 4a, Tables 1,2). A chemical method, termed inosine chemical erasing (ICE), which involves cyanoethylation combined with reverse transcription, was developed to sequence inosine (I) in mammalian transcriptomes93 (Fig. 4b). RNA editing converts A to I and C to U, and I may play regulatory roles94. Although sequencing of RNA editing events is straightforward using current RNA-Seq technology, caution should be exercised when analyzing sequencing data95 so as to avoid errors that arise from copy number variants or sequencing errors96-99. More comprehensive analyses and orthogonal approaches such as ICE should facilitate the discovery of additional RNA-editing events93,100.
Figure 4.
New sequencing methods for RNA modifications. (a) Bisulfite sequencing can be used to map transcriptome-wide 5mC in RNA. (b) Inosine chemical erasing (ICE) can be used to sequence inosine (I) in mammalian transcriptome. In the control group, inosine is converted into G by reverse transcription and PCR amplification. In the acrylonitrile treatment group, reverse transcription is blocked at the modified inosine site, which leads to identification of inosines on RNA. (c) m6A as a reversible RNA modification. m6A is generated by RNA methyltransferase(s) and removed by demethylases such as FTO. It further interacts with binding-proteins and may regulate various biological functions. Its genomic distribution can be determined by antibody-based immunoprecipitation.
In 2011, our laboratory showed that m6A, the most prevalent internal mRNA modification, is a major substrate of the fat mass and obesity-associated protein FTO both in vitro and inside cells (mRNA was isolated by poly(T) oligo with subsequent removal of rRNA)37, raising the possibility that this reversible RNA nucleotide modification could serve as an epigenetic mark to tune gene expression analogous to methylated nucleotides observed in DNA83. Recently, antibodies raised against m6A were used to enrich m6A-containing RNA fragments for high-throughput sequencing (Fig. 4c). This m6A-Seq approach was applied to human and mouse samples, and revealed that the transcriptome-wide m6A distribution was dynamically modulated and preferentially enriched around stop codons, in 3′-UTR, and within long internal exons101,102 (Table 1,2). In addition, several m6A-binding proteins have been identified, suggesting a function for m6A in regulating cellular dynamics. This field of reversible RNA modifications holds great promise in uncovering new biology associated with RNA metabolism, localization, and translation.
Perspective
The rapid progress of research on 5hmC has benefited from the rapid development of methods for 5 hmC detection, profiling, and now quantitative base-resolution mapping. These advances may guide studies of other nucleotide variants, especially the recently discovered 5fC and 5caC in mammalian DNA. The current lack of methods to reliably profile and quantitatively assess the location and abundance of these further oxidized 5mC derivatives substantially limits further research on these nucleotide variants. Antibodies against 5fC and 5caC are available for immunostaining42, but given the low levels of 5fC and 5caC in mammalian genomic DNA (only ppm levels compared to cytosine in mouse ESC6; comparable to the levels of DNA damage), it can be very challenging to apply an antibody-based capture strategy, which tends to favor densely populated modifications. Even if the antibodies can pull down certain genomic regions, such an approach will still have very limited coverage. One potential solution to this problem is to selectively label 5fC or 5caC with biotin. The high-affinity interaction between biotin and streptavidin can in principle capture every modification with no density or sequence-dependent bias, which is extremely important for reliable enrichment of scarce modifications. Chemical transformations are available for the aldehyde group in 5fC and the carboxylate group in 5caC, such as hydroxylamine–aldehyde condensation for 5fC5,6,22 (right at the time this paper was accepted a method describing the hydroxylamine-based profiling of 5fC was published on-line, which showed the enrichment of 5fC in CGIs of promoters and exons103) and EDC-mediated coupling for 5caC6, which can be used to introduce a biotin group. However, both approaches can introduce high background noise as a result of side reactions of hydroxylamine and EDC with other functionalities on DNA22,104,105. Therefore, careful tuning of the reaction conditions and appropriate controls are necessary.Besides chemical transformation, enzymatic approaches are also attractive if selective 5fC and 5caC enzymes can be developed. TDG is a good starting point because it can remove 5fC and 5caC and generate abasic sites for further labeling. TDG also recognizes T/G and U/G mismatches23,24, which have to be repaired first. Another possibility is to evolve an engineered βGT that can selectively label these modifications, especially 5caC106.
Compared to limited DNA modifications, hundreds of RNA modifications present an even greater technological challenge owing to the huge pool of structural and functional diversity. For instance, although m6A has been known for decades as an internal mRNA modification107, it has only recently been recognized as another reversible nucleotide modification37. Although distribution of m6A has been determined by the antibody-based affinity enrichment approach, high-resolution sequencing to assess the exact location and relative abundance at each modification site is highly desired. For other RNA modifications, antibody-based approaches can be a good start towards revealing their distributions.
Quantitative mapping of 5fC, 5caC, and m6A (and many other modifications in RNA) at single-base resolution remains challenging. The application of third-generation sequencing to 5fC and 5caC in DNA and m6A in RNA may seem feasible but has yet to be adequately exploited. Future innovations in sequencing technology, such as SMTR and nanopore analysis, to generate truly high-throughput, high-capacity platforms that can discern modifications are highly desirable. On the other hand, base-resolution sequencing for 5fC and 5caC analogous to TAB-Seq and oxBS-Seq can be developed if specific chemical transformations alter the behavior of these nucleotides in bisulfite sequencing. Similarly, chemical or enzymatic transformations for m6A or other RNA modifications108 that can affect base reading in PCR followed by sequencing would be required to develop base-resolution sequencing methods.
In addition to high-resolution sequencing, methods are needed to analyze nucleotide variants in rare cells and in living cells. 5hmC and related nucleotide variants may play roles in the development of cancer38,109,110 and early zygotes111-113, where sample amounts can be very limited. Therefore, sequencing methods that can deal with hundreds to thousands of cells or even single-cell sequencing will have a profound impact on fundamental biological understanding as well as diagnostics. Understanding the dynamics of these modifications in living biological systems would benefit from methods for high-resolution, single-molecule imaging.
In summary, recent discoveries of new nucleotide variants with epigenetic functions have stimulated the development of methods to detect, profile, and sequence these base modifications in the genome and transcriptome. In turn, the technological advances accelerate research to understand the biology of these nucleotide variants. This trend will continue as refined or completely new methods are developed.
Box 1. Biological functions of new DNA nucleotide variants.
Emerging data depict 5hmC as an intermediate involved in DNA 5mC demethylation7,10,29,41 as well as a potentially functional epigenetic mark involved in gene regulation17-22,114,115. 5hmC is oxidized from 5mC by TET family iron(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases4,8 (Fig. 1), which play important roles in ESC maintenance and differentiation11-13,17, normal hematopoiesis and malignancies38,109,110, and zygote development111-113. The level of 5hmC varies significantly in different tissues and cells (Table 2). 5hmC accumulates with age and is most enriched in brain tissues (0.4∼0.7% of cytosine)6,15, where it is suspected to play regulatory roles in neurodevelopment and aging, as well as in neurological diseases39,57,65. It exists in intermediate amounts (0.1% of cytosine) in mouse ESCs6 where it may have dual roles of being an DNA demethylation intermediate as well as exhibiting gene regulation functions11-13,17. Proteins that bind 5hmC have been reported, although they are not specific to 5hmC114,115. The exact mechanisms of 5hmC-mediated regulation still require further investigation, in particular to identify and characterize potential 5hmC-specific binding proteins. 5hmC is strongly depleted in human cancer cells compared with normal tissue (0.03–0.1% of guanine), which indicates its potential roles in aberrant DNA demethylation in oncogenic processes40,116,117.
5fC and 5caC are continuous products of TET protein-mediated oxidation of 5hmC and they can be removed by TDG (Fig. 1a). The level of 5fC is about 10-fold lower than that of 5hmC in mouse ESCs, and the level of 5caC is about 10-fold lower than 5fC (Table 2)5,6. In contrast to 5hmC, 5fC and 5caC have not been found to accumulate in brain tissues. In fact, 5caC has been detected in mouse ESCs, but not yet in other tissues.5,6,15 Currently, 5fC and 5caC are thought to be intermediates of active 5mC demethylation, either in a replication-dependent manner in zygotic development41,42, or in a replication-independent manner through TDG-mediate BER in specific loci (Fig. 1)7,23,30, although other pathways such as decarboxylation are possible118. However, 5fC and 5caC may also have regulatory roles, which will be confirmed if specific binding proteins can be identified. For example, 5fC and 5caC were recently shown to slow down RNA polymerase II transcription, which may suggest potential functional interplay between transcription and these epigenetic modifications119.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health (GM071440 to C.H.). We thank S.F. Reichard, MA for editing the manuscript.
References
- 1.Klose RJ, Bird AP. Genomic DNA methylation: the mark and its mediators. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31:89–97. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2005.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jones PA. Functions of DNA methylation: islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:484–492. doi: 10.1038/nrg3230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kriaucionis S, Heintz N. The nuclear DNA base 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is present in Purkinje neurons and the brain. Science. 2009;324:929–930. doi: 10.1126/science.1169786. This paper discovered that 5hmC is present in high levels in Purkinje cells. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tahiliani M, et al. Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science. 2009;324:930–935. doi: 10.1126/science.1170116. This paper showed that 5hmC is present in ESCs, and discovered the TET1-mediated oxidation of 5mC to 5hmC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pfaffeneder T, et al. The discovery of 5-formylcytosine in embryonic stem cell DNA. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2011;50:7008–7012. doi: 10.1002/anie.201103899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ito S, et al. Tet proteins can convert 5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine. Science. 2011;333:1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.1210597. This paper discovered 5fC and 5caC produced through TET-calayzed oxidation of 5mC in mammalian cells and quantified these modified bases using LC-MS/MS. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.He YF, et al. Tet-mediated formation of 5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA. Science. 2011;333:1303–1307. doi: 10.1126/science.1210944. This paper discovered 5caC as a product of TET-catalyzed oxidation of 5mC. It also showed 5caC removal by TDG in mammalian cells. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ito S, et al. Role of Tet proteins in 5mC to 5hmC conversion, ES-cell self-renewal and inner cell mass specification. Nature. 2010;466:1129–1133. doi: 10.1038/nature09303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Munzel M, Globisch D, Carell T. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine, the sixth base of the genome. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2011;50:6460–6468. doi: 10.1002/anie.201101547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bhutani N, Burns DM, Blau HM. DNA demethylation dynamics. Cell. 2011;146:866–872. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Williams K, Christensen J, Helin K. DNA methylation: TET proteins-guardians of CpG islands? EMBO Rep. 2012;13:28–35. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Branco MR, Ficz G, Reik W. Uncovering the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the epigenome. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:7–13. doi: 10.1038/nrg3080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu H, Zhang Y. Mechanisms and functions of Tet protein-mediated 5-methylcytosine oxidation. Genes Dev. 2011;25:2436–2452. doi: 10.1101/gad.179184.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wu SC, Zhang Y. Active DNA demethylation: many roads lead to Rome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:607–620. doi: 10.1038/nrm2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Globisch D, et al. Tissue distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and search for active demethylation intermediates. PLoS One. 2010;5:e15367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Loenarz C, Schofield CJ. Oxygenase catalyzed 5-methylcytosine hydroxylation. Chem Biol. 2009;16:580–583. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Koh KP, et al. Tet1 and Tet2 regulate 5-hydroxymethylcytosine production and cell lineage specification in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8:200–213. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.01.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Williams K, et al. TET1 and hydroxymethylcytosine in transcription and DNA methylation fidelity. Nature. 2011;473:343–348. doi: 10.1038/nature10066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ficz G, et al. Dynamic regulation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mouse ES cells and during differentiation. Nature. 2011;473:398–402. doi: 10.1038/nature10008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wu H, et al. Genome-wide analysis of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine distribution reveals its dual function in transcriptional regulation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Genes Dev. 2011;25:679–684. doi: 10.1101/gad.2036011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wu H, et al. Dual functions of Tet1 in transcriptional regulation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2011;473:389–393. doi: 10.1038/nature09934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pastor WA, et al. Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2011;473:394–397. doi: 10.1038/nature10102. This paper developed anti-CMS and GLIB for genome-wide 5hmC profiling. It also demonstrated advantages of the biotin-based enrichment methods. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Maiti A, Drohat AC. Thymine DNA glycosylase can rapidly excise 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine: potential implications for active demethylation of CpG sites. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:35334–35338. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C111.284620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang L, et al. Thymine DNA glycosylase specifically recognizes 5-carboxylcytosine-modified DNA. Nat Chem Biol. 2012;8:328–330. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Metzker ML. Sequencing technologies - the next generation. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:31–46. doi: 10.1038/nrg2626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Song CX, He C. The hunt for 5-hydroxymethylcytosine: the sixth base. Epigenomics. 2011;3:521–523. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sulewska A, et al. Detection of DNA methylation in eucaryotic cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2007;45:315–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fouse SD, Nagarajan RO, Costello JF. Genome-scale DNA methylation analysis. Epigenomics. 2010;2:105–117. doi: 10.2217/epi.09.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Guo Junjie U, Su Y, Zhong C, Ming Gl, Song H. Hydroxylation of 5-methylcytosine by TET1 promotes active DNA demethylation in the adult brain. Cell. 2011;145:423–434. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cortellino S, et al. Thymine DNA glycosylase is essential for active DNA demethylation by linked deamination-base excision repair. Cell. 2011;146:67–79. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nabel CS, et al. AID/APOBEC deaminases disfavor modified cytosines implicated in DNA demethylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2012 doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1042. advance online publication. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Terragni J, Bitinaite J, Zheng Y, Pradhan S. Biochemical characterization of recombinant beta-glucosyltransferase and analysis of global 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in unique genomes. Biochemistry. 2012;51:1009–1019. doi: 10.1021/bi2014739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Robertson AB, et al. A novel method for the efficient and selective identification of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:e55. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Grippo P, Iaccarino M, Rossi M, Scarano E. Thin-layer chromatography of nucleotides, nucleosides and nucleic acid bases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965;95:1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jin SG, Wu X, Li AX, Pfeifer GP. Genomic mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the human brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:5015–5024. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li W, Liu M. Distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in different human tissues. J Nucleic Acids. 2011;2011:870726. doi: 10.4061/2011/870726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jia G, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:885–887. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.687. This paper reported FTO as the first RNA demethylase that catalyzes demethylation of m6A on RNA. It also quantified m6A by antibody and LC-MS/MS. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ko M, et al. Impaired hydroxylation of 5-methylcytosine in myeloid cancers with mutant TET2. Nature. 2010;468:839–843. doi: 10.1038/nature09586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Szulwach KE, et al. 5-hmC-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:1607–1616. doi: 10.1038/nn.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Haffner MC, et al. Global 5-hydroxymethylcytosine content is significantly reduced in tissue stem/progenitor cell compartments and in human cancers. Oncotarget. 2011;2:627–637. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Inoue A, Zhang Y. Replication-dependent loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mouse preimplantation embryos. Science. 2011;334:194. doi: 10.1126/science.1212483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Inoue A, Shen L, Dai Q, He C, Zhang Y. Generation and replication-dependent dilution of 5fC and 5caC during mouse preimplantation development. Cell Res. 2011;21:1670–1676. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Höbartner C. Enzymatic labeling of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2011;50:4268–4270. doi: 10.1002/anie.201100350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Josse J, Kornberg A. Glucosylation of deoxyribonucleic acid .3. Alpha and beta-glucosyl transferases from T4-infected Escherichia Coli. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:1968–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Szwagierczak A, Bultmann S, Schmidt CS, Spada F, Leonhardt H. Sensitive enzymatic quantification of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e181. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Singer-Sam J, LeBon JM, Tanguay RL, Riggs AD. A quantitative HpaII-PCR assay to measure methylation of DNA from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990;18:687. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Davis T, Vaisvila R. High sensitivity 5-hydroxymethylcytosine detection in Balb/C brain tissue. J Vis Exp. 2011 doi: 10.3791/2661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kinney SM, et al. Tissue-specific distribution and dynamic changes of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian genomes. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:24685–24693. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.217083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Song CX, Yu M, Dai Q, He C. Detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in a combined glycosylation restriction analysis (CGRA) using restriction enzyme Taq(α)I. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21:5075–5077. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.03.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zheng Y, et al. A unique family of Mrr-like modification-dependent restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:5527–5534. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Cohen-Karni D, et al. The MspJI family of modification-dependent restriction endonucleases for epigenetic studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:11040–11045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018448108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Szwagierczak A, et al. Characterization of PvuRts1I endonuclease as a tool to investigate genomic 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:5149–5156. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang H, et al. Comparative characterization of the PvuRts1I family of restriction enzymes and their application in mapping genomic 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:9294–9305. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Xu SY, Corvaglia AR, Chan SH, Zheng Y, Linder P. A type IV modification-dependent restriction enzyme SauUSI from Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus USA300. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:5597–5610. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Liutkevičiūtė Z, Kriukienė E, Grigaitytė I, Masevičius V, Klimašauskas S. Methyltransferase-directed derivatization of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2011;50:2090–2093. doi: 10.1002/anie.201007169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Song CX, et al. Detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA by transferring a keto-glucose by using T4 phage β-glucosyltransferase. ChemBioChem. 2011;12:1682–1685. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201100278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Munzel M, et al. Quantification of the sixth DNA base hydroxymethylcytosine in the brain. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2010;49:5375–5377. doi: 10.1002/anie.201002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Le T, Kim KP, Fan G, Faull KF. A sensitive mass spectrometry method for simultaneous quantification of DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation levels in biological samples. Anal Biochem. 2011;412:203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2011.01.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chan CT, et al. A quantitative systems approach reveals dynamic control of tRNA modifications during cellular stress. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1001247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Beck S, Rakyan VK. The methylome: approaches for global DNA methylation profiling. Trends Genet. 2008;24:231–237. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Xu Y, et al. Genome-wide regulation of 5hmC, 5mC, and gene expression by Tet1 hydroxylase in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell. 2011;42:451–464. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Stroud H, Feng S, Morey Kinney S, Pradhan S, Jacobsen S. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine is associated with enhancers and gene bodies in human embryonic stem cells. Genome Biol. 2011;12:R54. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Serandour AA, et al. Dynamic hydroxymethylation of deoxyribonucleic acid marks differentiation-associated enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 doi: 10.1093/nar/gks595. advance online publication. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Matarese F, Carrillo-de Santa Pau E, Stunnenberg HG. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine: a new kid on the epigenetic block? Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7:562. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Song CX, et al. Selective chemical labeling reveals the genome-wide distribution of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:68–72. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1732. This paper reported the first genome-wide 5hmC profiling using hMe-Seal. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Szulwach KE, et al. Integrating 5-hydroxymethylcytosine into the epigenomic landscape of human embryonic stem cells. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Song CX, et al. Sensitive and specific single-molecule sequencing of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat Methods. 2012;9:75–77. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Robertson AB, Dahl JA, Ougland R, Klungland A. Pull-down of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine DNA using JBP1-coated magnetic beads. Nat Protoc. 2012;7:340–350. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Yu M, et al. Base-resolution analysis of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the mammalian genome. Cell. 2012;149:1368–1380. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.027. This paper developed TAB-Seq for single-base resolution 5hmC sequencing and performed the first whole-genome mapping of 5hmC sites in mouse and human ESCs. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Korlach J, Turner SW. Going beyond five bases in DNA sequencing. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.04.002. advance online publication. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Eid J, et al. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science. 2009;323:133–138. doi: 10.1126/science.1162986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Flusberg BA, et al. Direct detection of DNA methylation during single-molecule, real-time sequencing. Nat Methods. 2010;7:461–465. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Venkatesan BM, Bashir R. Nanopore sensors for nucleic acid analysis. Nat Nanotechnol. 2011;6:615–624. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Mirsaidov U, et al. Nanoelectromechanics of methylated DNA in a synthetic nanopore. Biophys J. 2009;96:L32–34. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.12.3760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Wanunu M, et al. Discrimination of methylcytosine from hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA molecules. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;133:486–492. doi: 10.1021/ja107836t. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Wallace EV, et al. Identification of epigenetic DNA modifications with a protein nanopore. Chem Commun. 2010;46:8195–8197. doi: 10.1039/c0cc02864a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Hayatsu H. The bisulfite genomic sequencing used in the analysis of epigenetic states, a technique in the emerging environmental genotoxicology research. Mutat Res. 2008;659:77–82. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2008.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Booth MJ, et al. Quantitative sequencing of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine at single-base resolution. Science. 2012;336:934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.1220671. This paper developed oxBS-Seq for single-base resolution 5hmC sequencing and performed 5hmC mapping in CGIs. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Huang Y, et al. The behaviour of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in bisulfite sequencing. PLoS One. 2010;5:e8888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Jin SG, Kadam S, Pfeifer GP. Examination of the specificity of DNA methylation profiling techniques towards 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e125. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Nestor C, Ruzov A, Meehan RR, Dunican DS. Enzymatic approaches and bisulfite sequencing cannot distinguish between 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA. BioTechniques. 2010;48:317–319. doi: 10.2144/000113403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Grosjean H. Fine-tuning of RNA functions by modification and editing. Springer, Berlin; New York; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 83.He C. Grand challenge commentary: RNA epigenetics? Nat Chem Biol. 2010;6:863–865. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yi C, Pan T. Cellular dynamics of RNA modification. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44:1380–1388. doi: 10.1021/ar200057m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Zhao X, Yu YT. Detection and quantitation of RNA base modifications. RNA. 2004;10:996–1002. doi: 10.1261/rna.7110804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Motorin Y, Muller S, Behm-Ansmant I, Branlant C. Identification of modified residues in RNAs by reverse transcription-based methods. Methods Enzymol. 2007;425:21–53. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)25002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Dai Q, et al. Identification of recognition residues for ligation-based detection and quantitation of pseudouridine and N6-methyladenosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:6322–6329. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Saikia M, Fu Y, Pavon-Eternod M, He C, Pan T. Genome-wide analysis of N1-methyl-adenosine modification in human tRNAs. RNA. 2010;16:1317–1327. doi: 10.1261/rna.2057810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Durairaj A, Limbach PA. Improving CMC-derivatization of pseudouridine in RNA for mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chim Acta. 2008;612:173–181. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.02.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Schaefer M, Pollex T, Hanna K, Lyko F. RNA cytosine methylation analysis by bisulfite sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:e12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Motorin Y, Lyko F, Helm M. 5-methylcytosine in RNA: detection, enzymatic formation and biological functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:1415–1430. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Squires JE, et al. Widespread occurrence of 5-methylcytosine in human coding and non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:5023–5033. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sakurai M, Yano T, Kawabata H, Ueda H, Suzuki T. Inosine cyanoethylation identifies A-to-I RNA editing sites in the human transcriptome. Nat Chem Biol. 2010;6:733–740. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Jepson JE, Reenan RA. RNA editing in regulating gene expression in the brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1779:459–470. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Li M, et al. Widespread RNA and DNA sequence differences in the human transcriptome. Science. 2011;333:53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.1207018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Pickrell JK, Gilad Y, Pritchard JK. Comment on “Widespread RNA and DNA sequence differences in the human transcriptome”. Science. 2012;335:1302. doi: 10.1126/science.1210484. author reply 1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Lin W, Piskol R, Tan MH, Li JB. Comment on “Widespread RNA and DNA sequence differences in the human transcriptome”. Science. 2012;335:1302. doi: 10.1126/science.1210419. author reply 1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kleinman CL, Majewski J. Comment on “Widespread RNA DNA sequence differences in the human transcriptome”. Science. 2012;335:1302. doi: 10.1126/science.1209658. author reply 1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Schrider DR, Gout JF, Hahn MW. Very few RNA and DNA sequence differences in the human transcriptome. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Peng Z, et al. Comprehensive analysis of RNA-Seq data reveals extensive RNA editing in a human transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30:253–260. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Dominissini D, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–206. doi: 10.1038/nature11112. This is one of the first two papers reporting transcriptome-wide m6A distribution by using the antibody-based enrichment. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Meyer Kate D, et al. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3′ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–1646. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.003. This is one of the first two papers reporting transcriptome-wide m6A distribution by using the antibody-based enrichment. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Raiber EA, et al. Genome-wide distribution of 5-formylcytosine in ES cells is associated with transcription and depends on thymine DNA glycosylase. Genome Biol. 2012;13:R69. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-8-r69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Münzel M, Lercher L, Müller M, Carell T. Chemical discrimination between dC and 5MedC via their hydroxylamine adducts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e192. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Chu BC, Wahl GM, Orgel LE. Derivatization of unprotected polynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983;11:6513–6529. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Matsuo K, Nishikawa K, Shindo M. Stereoselective synthesis of beta-glycosyl esters of cis-cinnamic acid and its derivatives using unprotected glycosyl donors. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011;52:5688–5692. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Horowitz S, Horowitz A, Nilsen TW, Munns TW, Rottman FM. Mapping of N6-methyladenosine residues in bovine prolactin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81:5667–5671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Behm-Ansmant I, Helm M, Motorin Y. Use of Specific Chemical Reagents for Detection of Modified Nucleotides in RNA. Journal of Nucleic Acids. 2011;2011 doi: 10.4061/2011/408053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Moran-Crusio K, et al. Tet2 loss leads to increased hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and myeloid transformation. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Quivoron C, et al. TET2 inactivation results in pleiotropic hematopoietic abnormalities in mouse and is a recurrent event during human lymphomagenesis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:25–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Iqbal K, Jin SG, Pfeifer GP, Szabo PE. Reprogramming of the paternal genome upon fertilization involves genome-wide oxidation of 5-methylcytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:3642–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014033108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Wossidlo M, et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the mammalian zygote is linked with epigenetic reprogramming. Nat Commun. 2011;2:241. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Gu TP, et al. The role of Tet3 DNA dioxygenase in epigenetic reprogramming by oocytes. Nature. 2011;477:606–610. doi: 10.1038/nature10443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Frauer C, et al. Recognition of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by the Uhrf1 SRA domain. PLoS One. 2011;6:e21306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Yildirim O, et al. Mbd3/NURD complex regulates expression of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine marked genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2011;147:1498–1510. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Jin SG, et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine is strongly depleted in human cancers but its levels do not correlate with IDH1 mutations. Cancer Res. 2011;71:7360–7365. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Kudo Y, et al. Loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is accompanied with malignant cellular transformation. Cancer Sci. 2012;103:670–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Schiesser S, et al. Mechanism and stem-cell activity of 5-carboxycytosine decarboxylation determined by isotope tracing. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2012;51:6516–6520. doi: 10.1002/anie.201202583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Kellinger MW, et al. 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine reduce the rate and substrate specificity of RNA polymerase II transcription. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19:831–833. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Bokar JA, Shambaugh ME, Polayes D, Matera AG, Rottman FM. Purification and cDNA cloning of the AdoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA (N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase. RNA. 1997;3:1233–1247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]