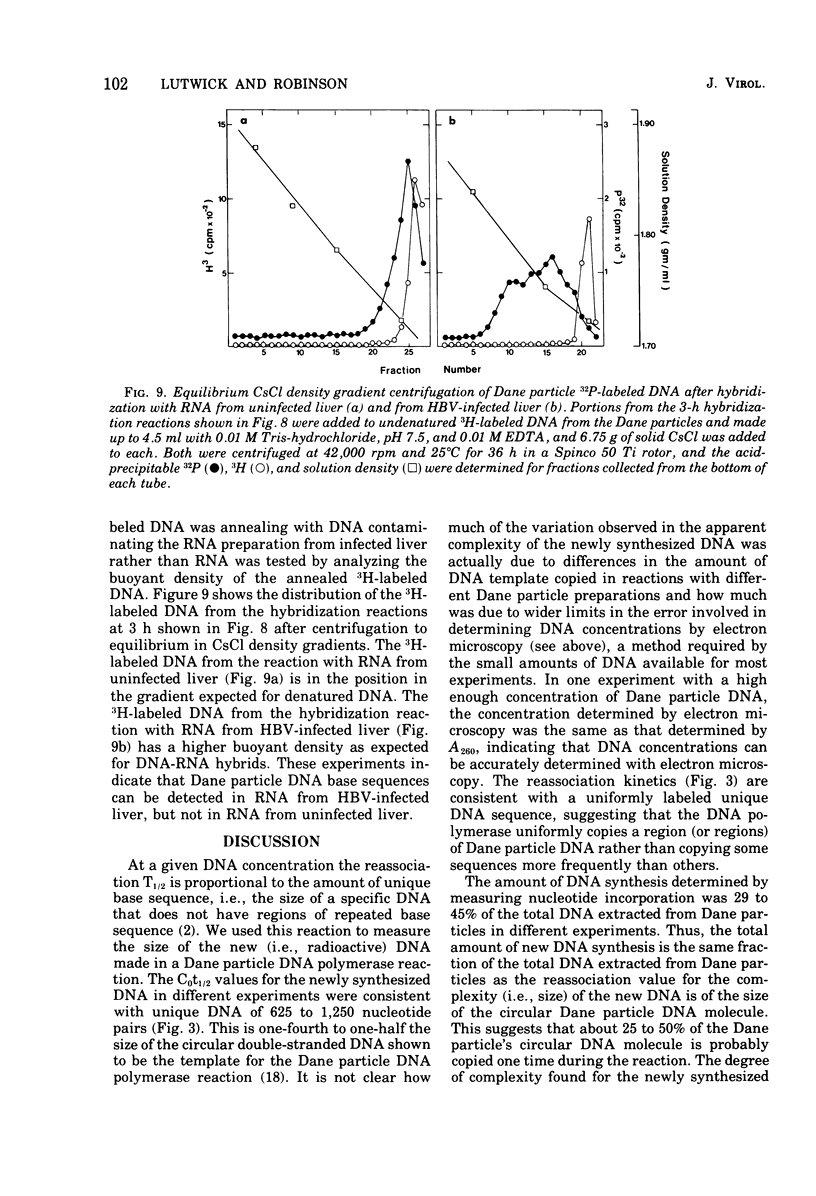
Abstract
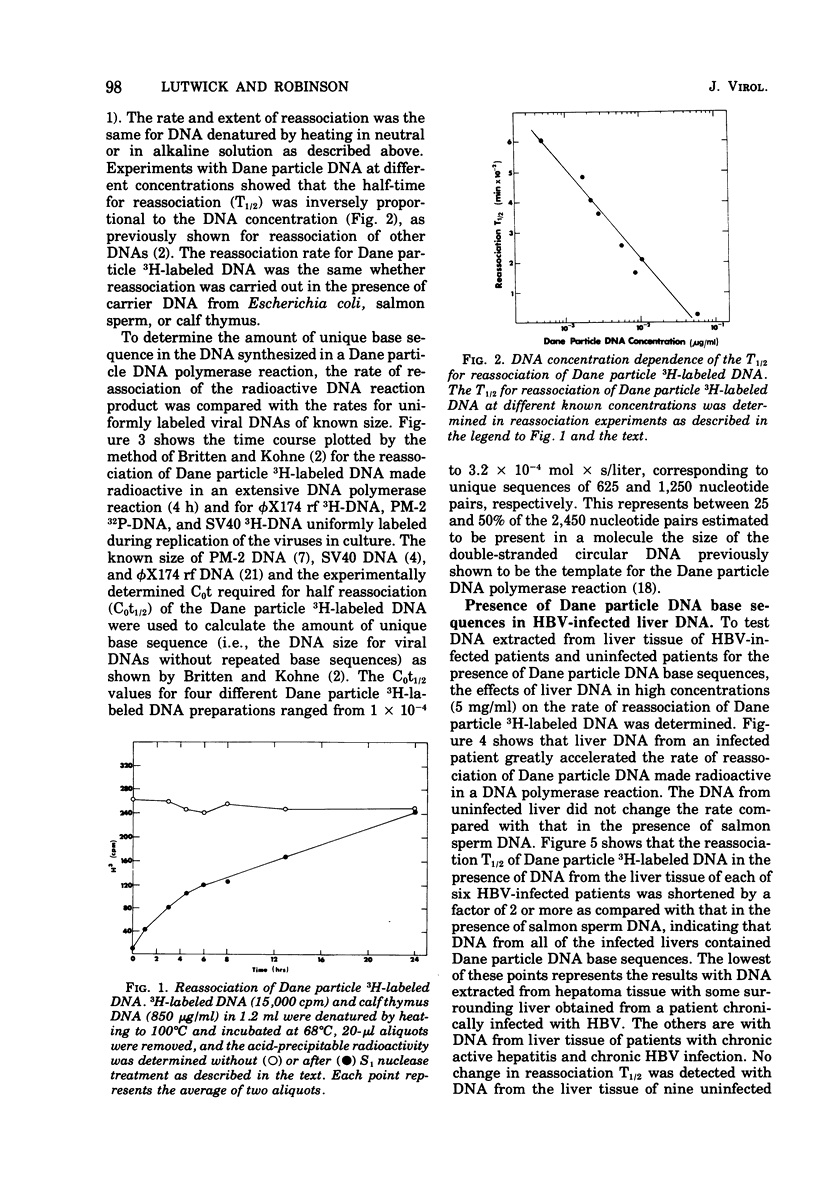
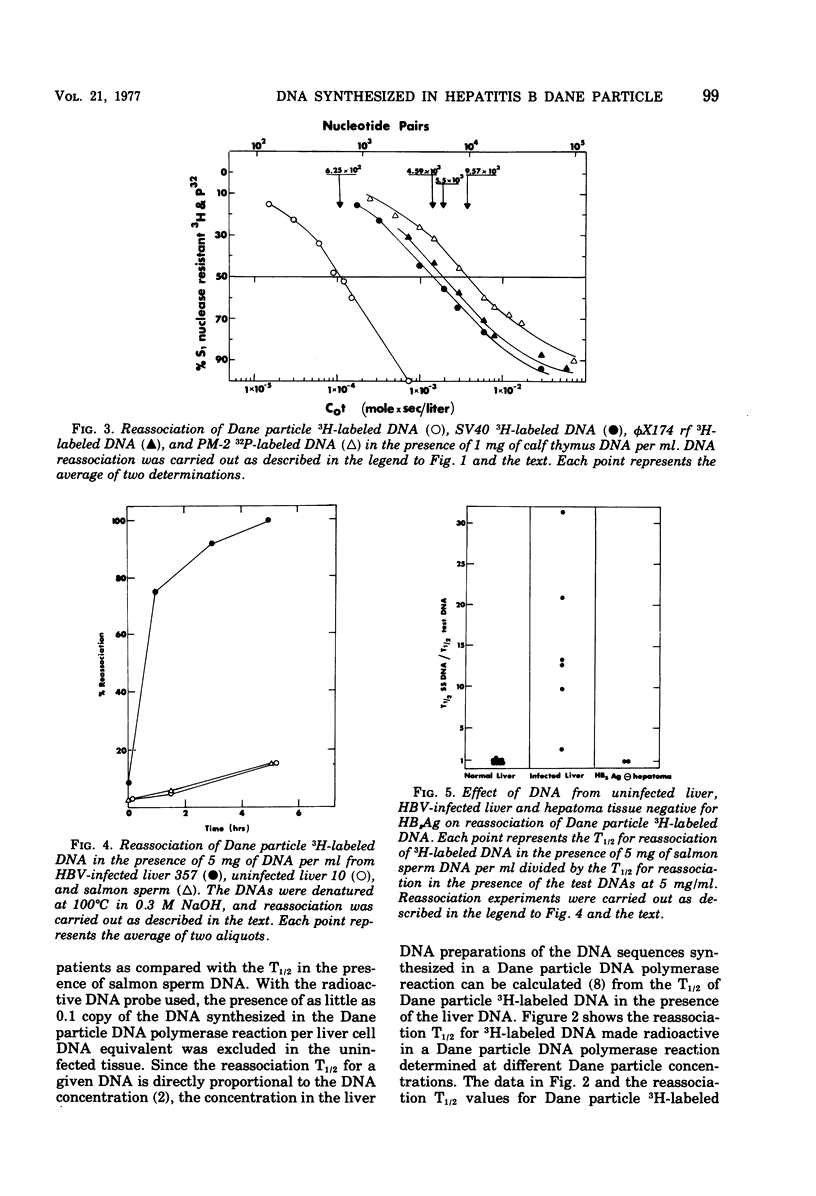
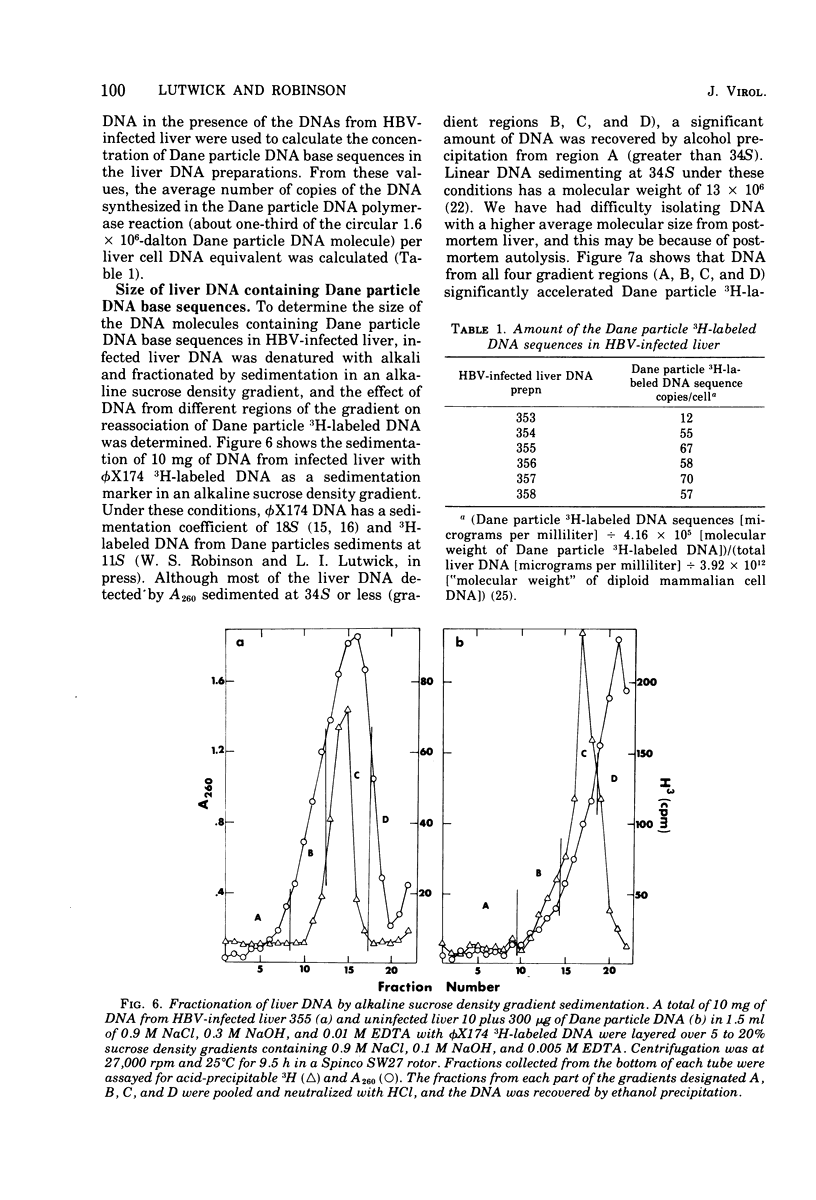
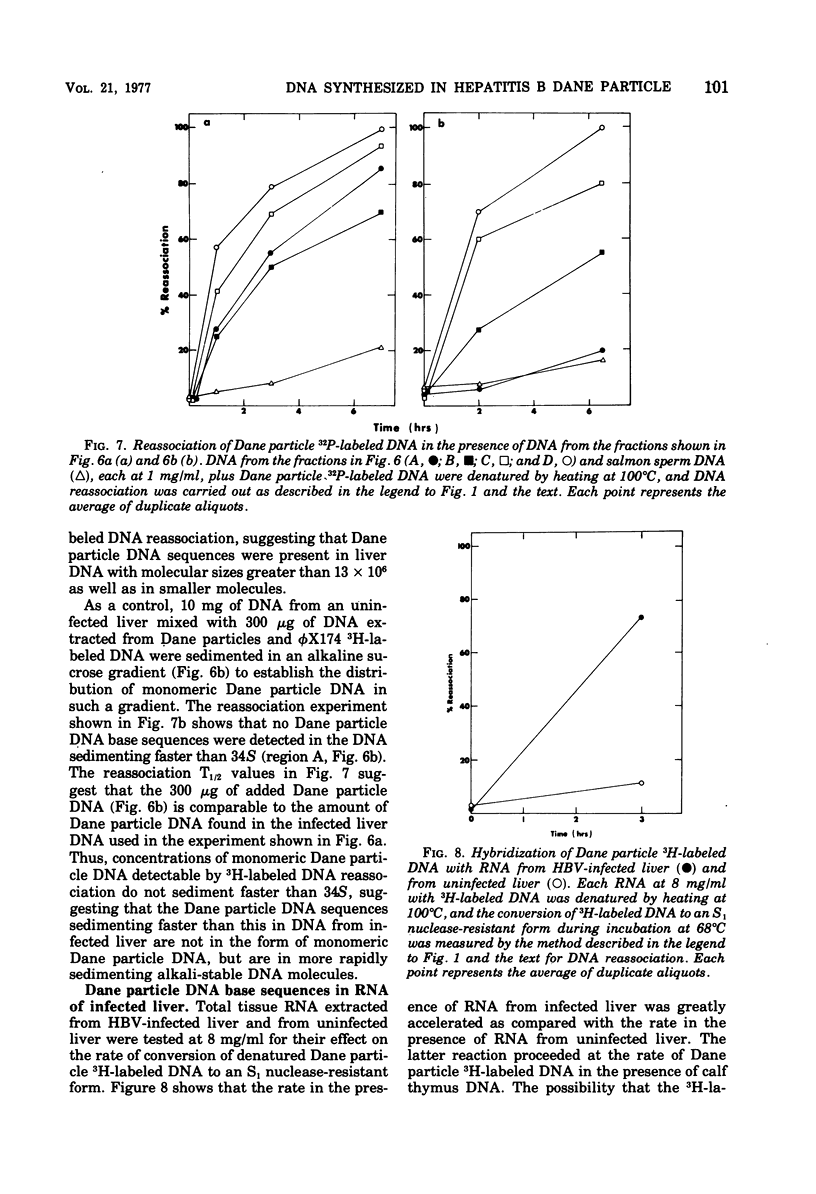
Radioactive DNA was prepared in extensive (4 h) Dane particle DNA polymerase reactions. In different experiments the amount of new DNA, determined by the amount of nucleotide incorporation into an acid-insoluble form, was between 29 and 45% of the total circular DNA isolated from Dane particle preparations after the reaction. DNA reassociation kinetics were used to determine the complexity of the newly synthesized DNA. In different experiments COt1/2 values, corresponding to between 625 and 1,250 nucleotide pairs, were obtained for the radioactive Dane particle DNA. These results suggest that a unique region (or regions), corresponsing to approximately one-fourth to one-half of the circular Dane particle DNA template, was copied one time during the reaction. DNA and RNA extracted from hepatitis B virus-infected liver but not from uninfected liver accelerated the rate of reassociation of radioactive DNA from Dane particles. These Dane particle DNA base sequences were found in alkali-stable, rapidly sedimenting DNA from infected liver as well as in DNA sedimenting at a rate similar to the DNA extracted from Dane particles. These findings are consistent with Dane particle DNA being hepatitis B virus DNA that is integrated into high-molecular-weight cellular DNA and transcribed into RNA in infected liver.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V., BLACK P. H. THE NUCLEIC ACID OF SIMIAN VIRUS 40. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:388–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A., Vinograd J. Circular dimer and catenate forms of mitochondrial DNA in human leukaemic leucocytes. Nature. 1967 Nov 18;216(5116):652–657. doi: 10.1038/216652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Ritt D. J. Intrahepatic expression of serum hepatitis virus-associated antigens. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):871–885. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Canelo E. S., Sinsheimer R. L. DNA of bacteriophage PM2: a closed circular double-stranded molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1164–1168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Kohne D. E., Martin M. A. Quantitation of Simian virus 40 sequences in African green monkey, mouse and virus-transformed cell genomes. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudat F., Bianchi L., Sonnabend W., Thiel G., Aenishaenslin W., Stalder G. A. Pattern of core and surface expression in liver tissue reflects state of specific immune response in hepatitis B. Lab Invest. 1975 Jan;32(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S. Viral hepatitis type B: prospects for active immunization. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Sep-Oct;270(2):391–393. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197509000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley J. W., Edwards V. M., Meihaus J. E., Redeker A. G. Subdeterminants d and y of hepatitis B antigen as epidemiologic markers. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Jun;95(6):529–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulwels P. H., Jansz H. S., van Rotterdam J., Cohen J. A. Structure of the replicative form of bacteriophage phi-X-174. Physico-chemical studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 May 19;119(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90187-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouwels P. H., Knijnenburg C. M., van Rotterdam J., Cohen J. A. Structure of the replicative form of bacteriphage phi X174. VI. Studies on alkali-denatured double-stranded phi X DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Clayton D. A., Greenman R. L. DNA of a human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.384-391.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S. DNA and DNA polymerase in the core of the Dane particle of hepatitis B. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):151–159. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Greenman R. L. DNA polymerase in the core of the human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1231–1236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1231-1236.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Westphal H., Srinivasan P. R., Dulbecco R. The integrated state of viral DNA in SV40-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1288–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., O'Connell A., Millman I. Genome of hepatitis B virus: restriction enzyme cleavage and structure of DNA extracted from Dane particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Ogawa T. Replication of phage lambda DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:533–551. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J., Radloff R., Watson R., Laipis P. The twisted circular form of polyoma viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1104–1111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



