Abstract
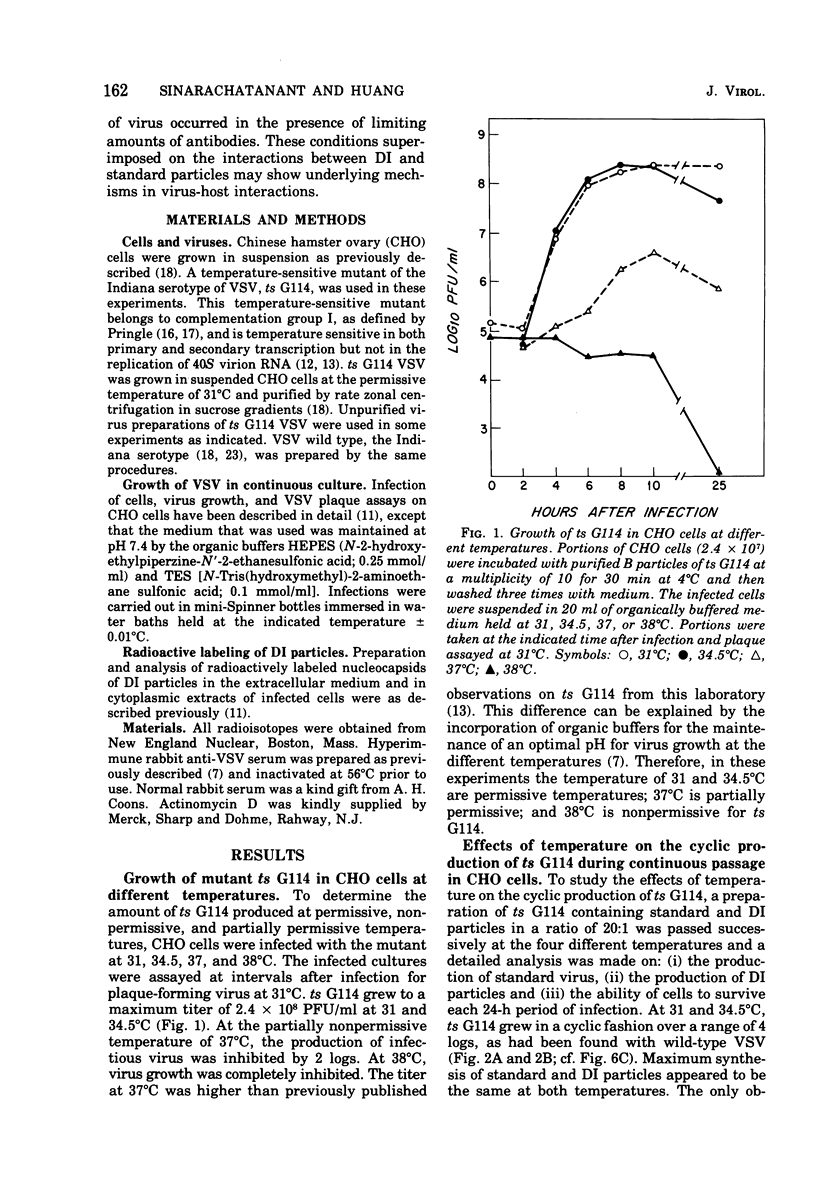
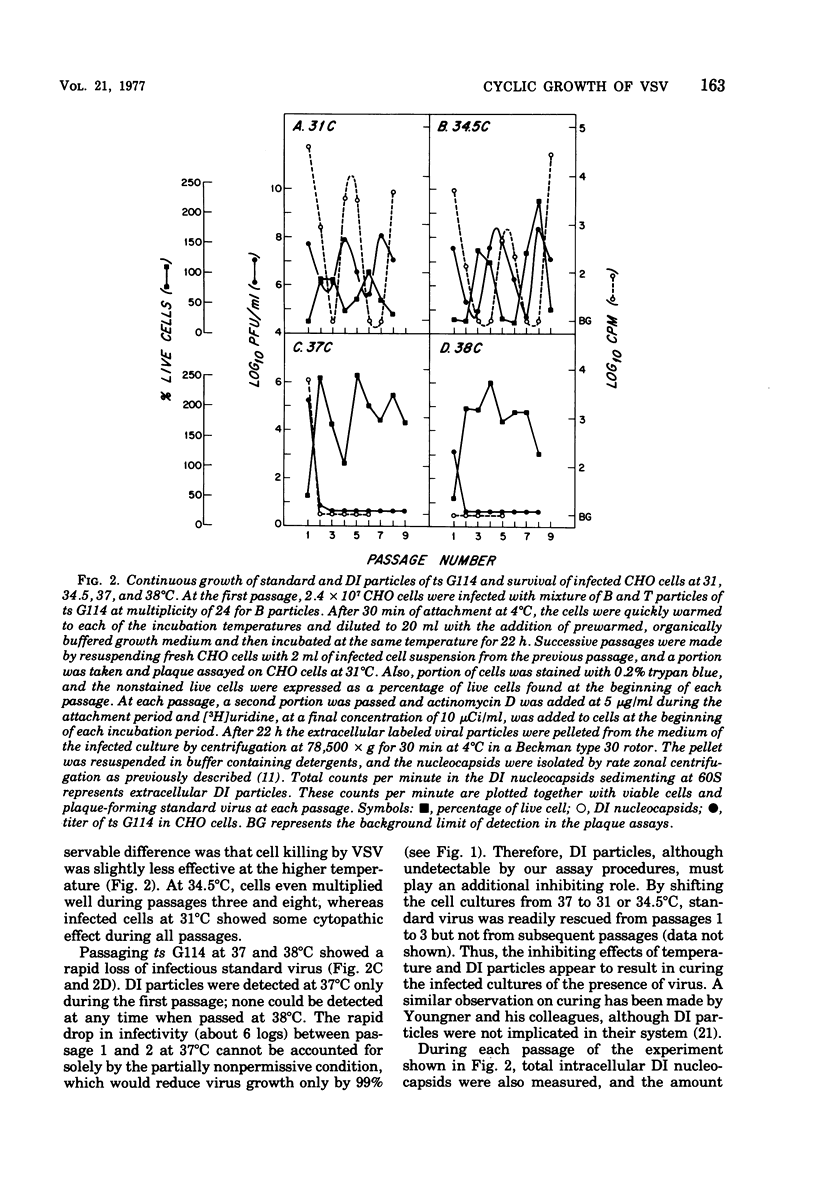
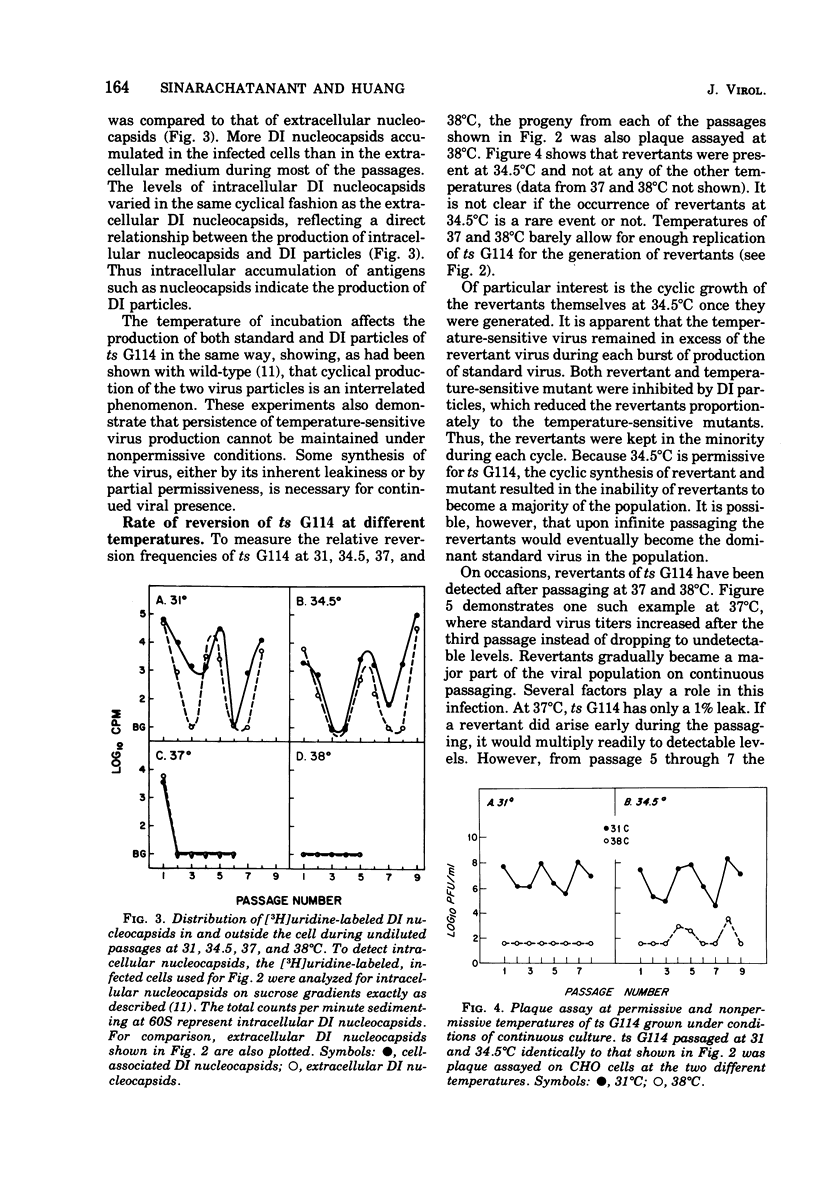
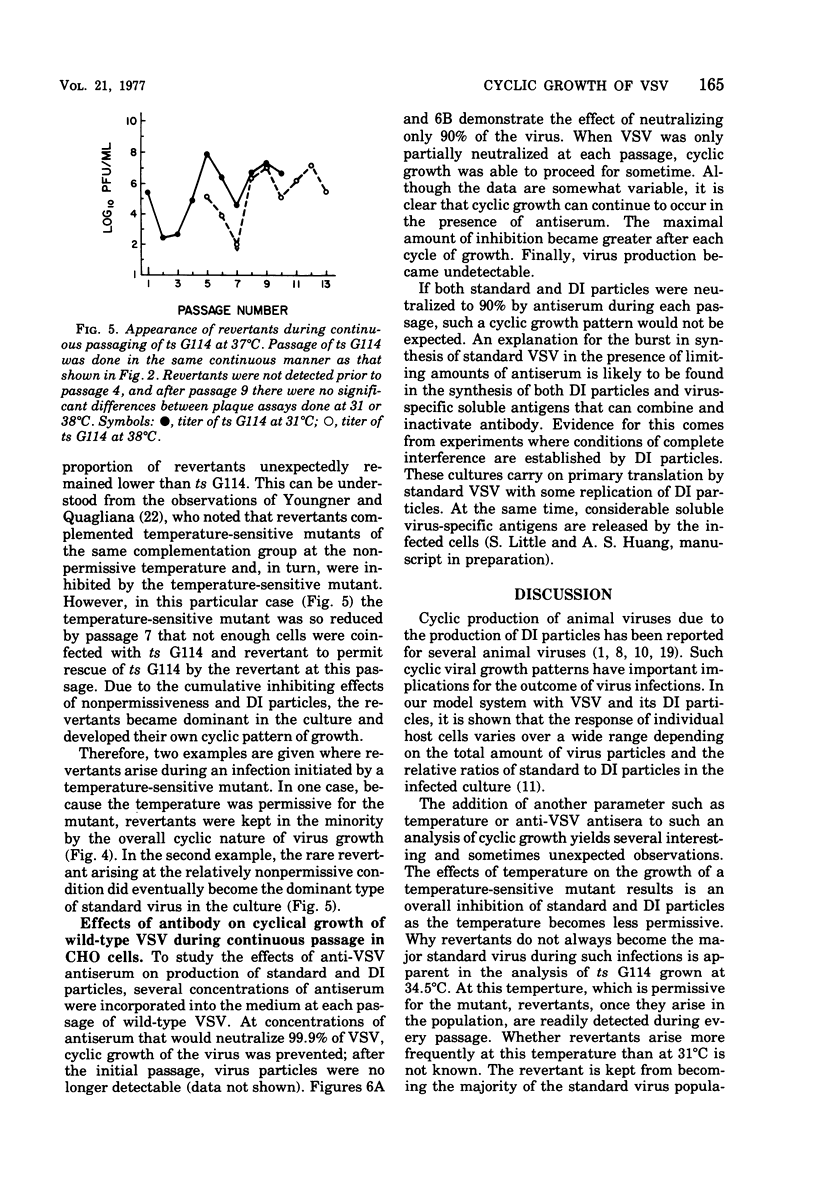
To see the effects of temperature on the interrelated cyclic production of standard and defective interfering (DI) particles of vesicular stomatitis virus, a temperature-sensitive (ts) G114 mutant was passaged successively at different temperatures and the production of the two types of viral particles as well as the ability of Chinese hamster ovary cells to survive each passage was continuously monitored. When the temperature was nonpermissive for standard virus, the synthesis of both standard and defective interfering particles was inhibited. When revertants appeared in the population, their ability to take over the infection depended on the permissiveness of the temperature for the temperature-sensitive mutant. At permissive temperatures periodic inhibition of both types of standard viruses was maintained by the production of defective interfering particles. Reverents did not become a majority of the population due to this periodic inhibition. When the conditions were nonpermissive for the mutant, revertants became the major standard virus in the population within a few passages. These findings can be understood if conditions of high and low multiplicities are dissected out together with a thorough understanding of the individual properties of each of the viral particles and of the result of interactions between them. In the presence of antiserum which neutralized only 90% of the viral particles, cyclic production of standard virus occurred, with a decline in the total amount of virus produced after each cycle. Therefore, in the presence of limiting concentrations of antiserum, the virus appeared to be able to establish a persistent cyclic growth pattern.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doyle M., Holland J. J. Prophylaxis and immunization in mice by use of virus-free defective T particles to protect against intracerebral infection by vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2105–2108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Jacob R. J., Honess R. W., Hayward G. S., Locker H., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. III. Characterization of defective DNA molecules and biological properties of virus populations containing them. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):153–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.153-167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Persistent noncytocidal vesicular stomatitis virus infections mediated by defective T particles that suppress virion transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Purification of defective interfering T particles of vesicular stomatitis and rabies viruses generated in vivo in brains of newborn mice. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):438–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S. Defective interfering viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:101–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. E., Tovell D. R., Brown D. T., Faulkner P. Interfering passages of Sindbis virus: concomitant appearance of interference, morphological variants, and trucated viral RNA. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):951–958. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.951-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Leavitt R. W., Kingsbury D. T., Holland J. J. Natural selection of mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus by cultured cells of Drosophila melanogaster. J Gen Virol. 1973 Sep;20(3):341–351. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. K., Biswal N., Bookout J. B., Lanford R. E., Courtney R. J., Melnick J. L. Cyclic appearance of defective interfering particles of herpes simplex virus and the concomitant accumulation of early polypeptide VP175. Intervirology. 1975;5(3-4):173–184. doi: 10.1159/000149894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palma E. L., Huang A. Cyclic production of vesicular stomatitis virus caused by defective interfering particles. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):402–410. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S. M., Huang A. S. RNA synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. V. Interactions between transcription and replication. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1395–1400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1395-1400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Youngner J. S. Temperature-sensitive mutants isolated from L cells persistently infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):200–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.200-206.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Youngner J. S. Temperature-sensitive viruses and the etiology of chronic and inapparent infections. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):467–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Conditional lethal mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:85–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Genetic characteristics of conditional lethal mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus induced by 5-fluorouracil, 5-azacytidine, and ethyl methane sulfonate. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):559–567. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.559-567.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneck L. D., Trowbridge R. S., Welsh R. M., Wright E. A., Pfau C. J. Arenaviruses: cellular response to long-term in vitro infection with parana and lymphocytic choriomeningitis viruses. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):444–450. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.444-450.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVEY A. H., SNYDER R. M., RATCLIFF G. A., Jr, HYATT D. F. BIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF TWO PLAQUE VARIANTS OF VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS (INDIANA SEROTYPE). J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:112–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Dubovi E. J., Quagliana D. O., Kelly M., Preble O. T. Role of temperature-sensitive mutants in persistent infections initiated with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):90–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.90-101.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngner J. S., Quagliana D. O. Temperature-sensitive mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus are conditionally defective particles that interfere with and are rescued by wild-type virus. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):102–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.102-107.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



