Abstract
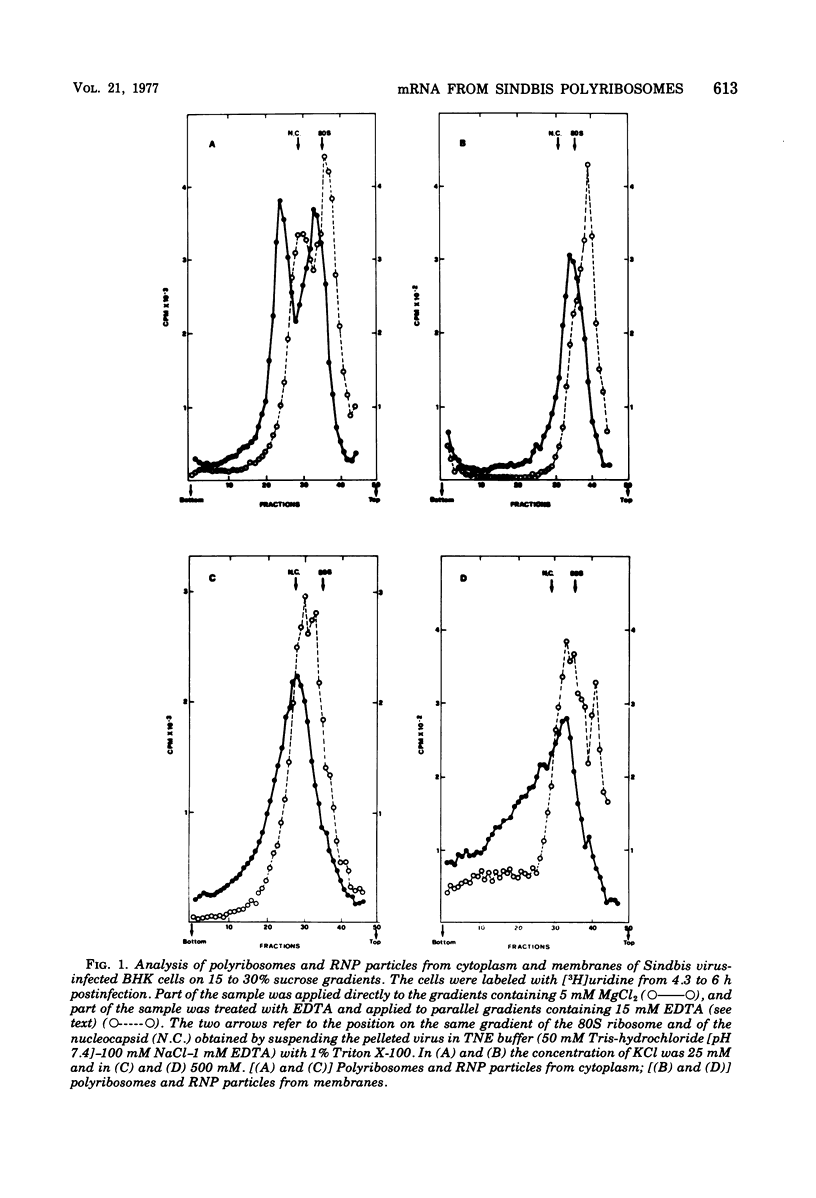
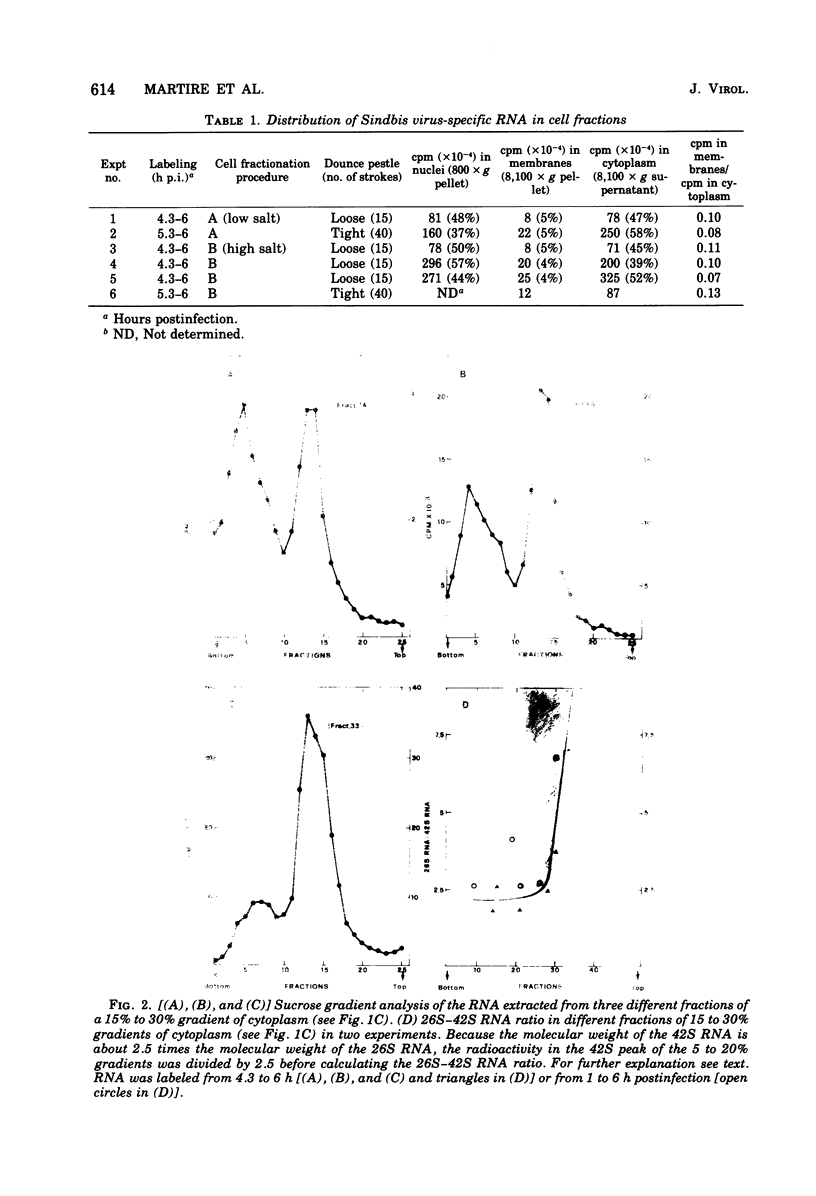
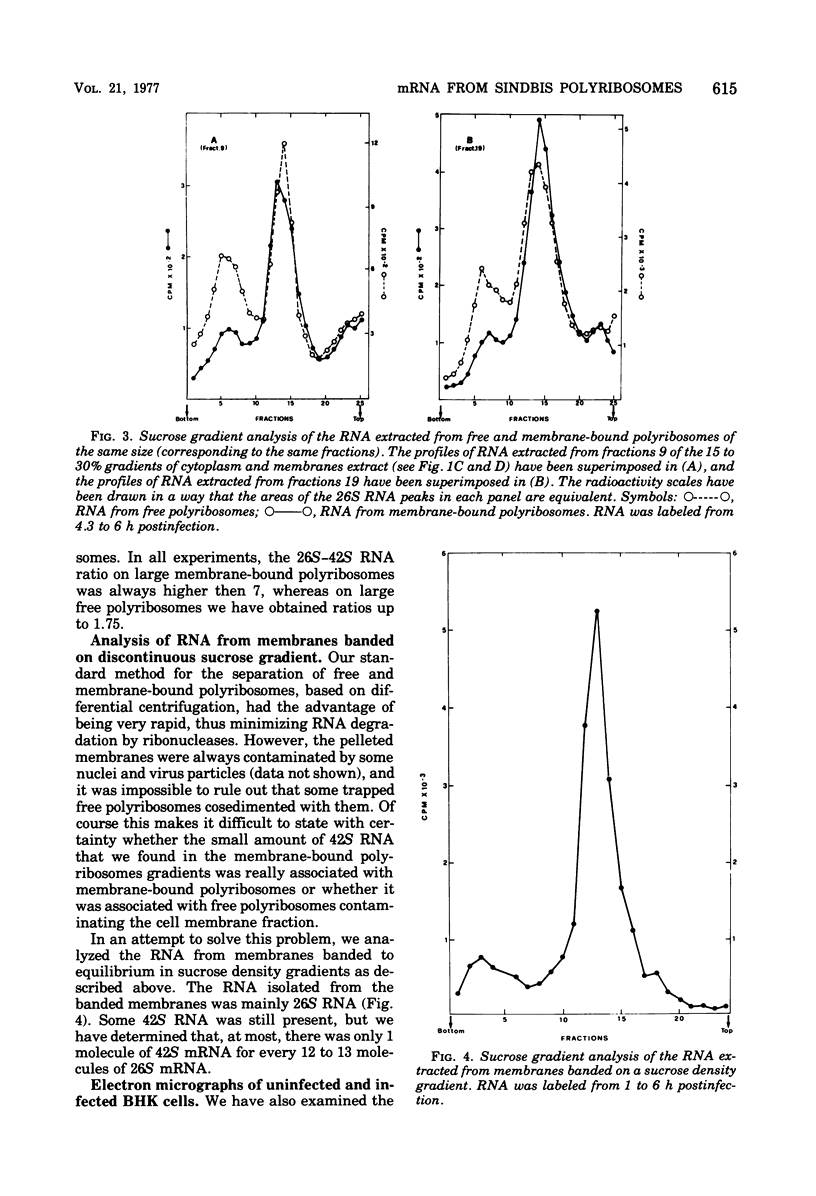
The data presented in the paper demonstrate that in BHK cells infected with Sindbis virus virtually all the 42S mRNA not in nucleocapsid is associated with free polyribosomes, whereas the 26S mRNA is distributed between free and membrane-bound polyribosomes. We suggest that the 26S RNA polyribosomes are bound to the membranes through the nascent chains of the B1 protein and that a large percentage of 26S RNA polyribosomes free in the cytoplasm may be due to the small amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum in BHK cells. In addition, we found that intracellular nucleocapsid is in the nonmembrane fraction of the cytoplasm of infected cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ascione R., Arlinghaus R. B. Characterization and cell-free activity of polyribosomes isolated from baby hamster kidney cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):478–488. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Ribosomes in rat liver: an estimate of the percentage of free and membrane-bound ribosomes interacting with messenger RNA in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1967 Sep 28;28(3):539–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Studies on free and membrane-bound ribosomes in rat liver. I. Distribution as related to total cellular RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha M., Leone A., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of a Sindbis virus nonstructural protein and its relation of 42S mRNA function. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):612–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.612-620.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of Sindbis virus capsid protein in mammalian cell-free extracts programmed with viral messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Swanson R., Schlesinger M. J. Effects of different RNAs and components of the cell-free system on in vitro synthesis of Sindbis viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):652–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.652-663.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Swanson R., Schlesinger M. J. Viral proteins formed in a cell-free rabbit reticulocyte system programmed with RNA from a temperature-sensitive mutant of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.664-671.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancedda R., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F., Schlesinger M. Initiation sites for translation of sindbis virus 42S and 26S messenger RNAs. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Kennedy S. I. In vitro synthesis of structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus directed by isolated 26 S RNA from infected cells. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80757-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Kennedy S. I. Initiation of synthesis of the structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):401–411. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobos P., Faulkner P. Properties of 42S and 26S Sindbis viral ribonucleic acid species. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):429–438. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.429-438.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton B. T., Donaghue T. P., Faulkner P. Presence of poly (A) in the polyribosome-associated RNA of Sindbis-infected BHK cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):109–111. doi: 10.1038/newbio238109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I. Isolation and identification of the virus-specified RNA species found on membrane-bound polyribosomes of chick embryo cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1254–1258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90846-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Friedman R. M. Analysis of arbovirus ribonucleic acid forms by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1971 Apr;7(4):504–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.4.504-514.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowshowitz D. Identification of polysomal RNA in BHK cells infected by sindbis virus. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):535–543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.535-543.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Boyle M. K. Selective inhibition of the synthesis of Sindbis virion proteins by an inhibitor of chymotrypsin. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):187–188. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.187-188.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Synthesis and transfer of amylase in pigeon pancreatic micromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 10;241(5):1150–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemond H., Sreevalsan T. Viral RNAs associated with ribosomes in Sindbis virus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1973 Mar;11(3):399–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.3.399-415.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Schlesinger S. Large-molecular-weight precursors of sindbis virus proteins. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):1013–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.1013-1016.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Replication of Sindbis virus. I. Relative size and genetic content of 26 s and 49 s RNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):599–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Strauss J. H. Translation of Sindbis virus 26 S RNA and 49 S RNA in lysates of rabbit reticulocytes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Wheeler T., Glanville N., Käriäinen Translation of Semliki-Forest-virus 42-S RNA in a mouse cell free system to give virus-coat proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):101–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Simons K. Studies on the amphipathic nature of the membrane proteins in Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):569–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Beato M., Hackemack B. A. Translation of 26 S virus-specific RNA from Semliki Forest virus-infected cells in vitro. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Studies on the polyribosome-associated RNA in BHK21 cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):21–35. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]