Abstract
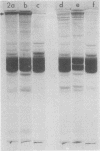
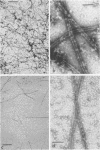
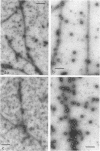
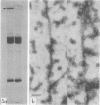
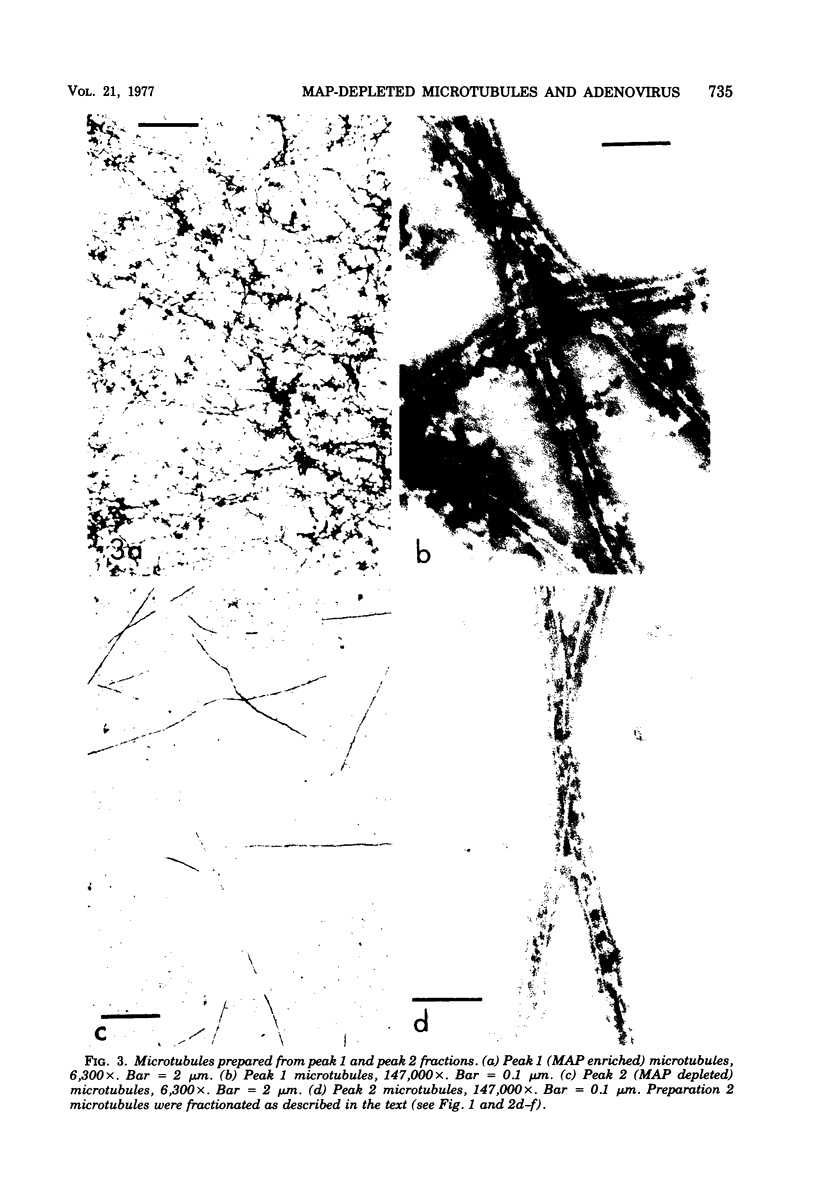
A specific in vitro association between adenovirus and pruified rat brain microtubules has been previously demonstrated (R. B. Luftig and R. R. Weihing, 1975). When examined by negative-staining electron microscopy, approximately 90% of the virus associated with microtubules was edge bound, i.e., associated within +/-4 nm of the microtubule edge. Similar results are now found for the association of adenovirus with purified chick brain microtubules. When the content of the high-molecular-weight proteins (MAPs) normally present as projections on the surface of microtubules is depleted by fractionation of cold-depolymerized microtubules on agarose A-15M columns or by brief treatment of polymerized microtubules with trypsin, the percentage of edge-bound microtubule-associated viruses is reduced to a level close to that found for particles such as reovirus, coliphage f2, or polystyrene latex spheres, which randomly associate with microtubules (54 to 64% for column-fractionated microtubules; 45 to 68% for trypsin-treated microtubules). Counts of adenovirus particles specifically bound to microtubules, corrected for variations in microtubule and virus concentrations, gave values 2.5 to 3.5 times higher for unfractionated microtubules than for microtubule-associated protein-depleted microtubules. These results are consistent with the suggestion that the specific association between adenovirus and microtubules is mediated by microtubule-associated proteins.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhisey A. N., Freed J. J. Altered movement of endosomes in colchicine-treated cultured macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Feb;64(2):430–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90097-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Marcum J. M., Olmsted J. B., Murphy D. B., Johnson K. A. Purification of tubulin and associated high molecular weight proteins from porcine brain and characterization of microtubule assembly in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:107–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S. ASSOCIATION BETWEEN THE SPINDLE APPARATUS AND REOVIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:268–275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S., GOMATOS P. J., HSU K. C. THE UPTAKE AND DEVELOPMENT OF REOVIRUS IN STRAIN L CELLS FOLLOWED WITH LABELED VIRAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND FERRITIN-ANTIBODY CONJUGATES. Virology. 1965 Feb;25:193–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström A., Heiwall P. O., Häggendal J., Saunders N. R. Effect of antimitotic drugs on the intraaxonal transport of neurotransmitters in rat adrenergic and cholinergic nerves. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:507–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S., Chardonnet Y. Early events in the interaction of adenoviruses with HeLa cells. IV. Association with microtubules and the nuclear pore complex during vectorial movement of the inoculum. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Granett S., Rosenbaum J. L. Ultrastructural localization of the high molecular weight proteins associated with in vitro-assembled brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):237–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed J. J., Lebowitz M. M. The association of a class of saltatory movements with microtubules in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):334–354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. G. Presynaptic microtubules and their association with synaptic vesicles. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Aug 19;190(1100):367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Choppin P. W. On the role of microtubules in movement and alignment of nuclei in virus-induced syncytia. J Cell Biol. 1968 Dec;39(3):526–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.39.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James K. A., Bray J. J., Morgan I. G., Austin L. The effect of colchicine on the transport of axonal protein in the chicken. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):767–771. doi: 10.1042/bj1170767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Fulton J. P. An association of plant cell microtubules and virus particles. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):560–565. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R. B., Kilham S. S., Hay A. J., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. An ultrastructural study of virions and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):170–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R. B., Weihing R. R. Adenovirus binds to rat brain microtubules in vitro. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):696–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.696-706.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E. The melanocyte model. Colchicine-like effects of other antimitotic agents. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):848–855. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew D. E., Carrol T. W. Barley stripe mosaic virions assoicated with spindle microtubules. Science. 1974 Sep 13;185(4155):957–958. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4155.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPENDLOVE R. S., LENNETTE E. H., JOHN A. C. THE ROLE OF THE MITOTIC APPARATUS IN THE INTRACELLULAR LOCATION OF REOVIRUS ANTIGEN. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand J., Frizell M., Hasselgren P. O. Effects of colchicine on axonal transport in peripheral nerves. J Neurochem. 1970 Nov;17(11):1563–1570. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. S., Järlfors U., Cameron B. F. Morphological evidence for the participation of microtubules in axonal transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:472–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbings H. Influence of vinblastine sulphate on the deployment of microtubules and ribosomes in telotrophic ovarioles. J Cell Sci. 1971 Jan;8(1):111–125. doi: 10.1242/jcs.8.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]