Abstract
Recent findings have implicated the gut microbiota as a contributor of metabolic diseases through the modulation of host metabolism and inflammation. Atherosclerosis is associated with lipid accumulation and inflammation in the arterial wall, and bacteria have been suggested as a causative agent of this disease. Here we use shotgun sequencing of the gut metagenome to demonstrate that the genus Collinsella was enriched in patients with symptomatic atherosclerosis, defined as stenotic atherosclerotic plaques in the carotid artery leading to cerebrovascular events, whereas Roseburia and Eubacterium were enriched in healthy controls. Further characterization of the functional capacity of the metagenomes revealed that patient gut metagenomes were enriched in genes encoding peptidoglycan synthesis and depleted in phytoene dehydrogenase; patients also had reduced serum levels of β-carotene. Our findings suggest that the gut metagenome is associated with the inflammatory status of the host and patients with symptomatic atherosclerosis harbor characteristic changes in the gut metagenome.
 The gut microbiota has emerged as an environmental factor that can influence the development of obesity and diabetes. Here, Karlsson et al. report compositional and functional alterations of the gut metagenome in patients with symptomatic atherosclerosis.
The gut microbiota has emerged as an environmental factor that can influence the development of obesity and diabetes. Here, Karlsson et al. report compositional and functional alterations of the gut metagenome in patients with symptomatic atherosclerosis.
The gut metagenome has been implicated as an environmental factor influencing adiposity and obesity by modulating host lipid metabolism1,2,3,4. The gut microbiota is also a source of inflammatory molecules such as lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan that may contribute to metabolic disease2,5,6. Whole-genome metagenomic sequencing has provided knowledge about the structure of the human gut microbiome and identified a large number of genes and direct links to functional information7,8. Links between the gut metagenome and human diseases have been investigated, showing that obesity is associated with alterations in the gut metagenome and reduced bacterial diversity9. Going beyond traditional comparative analysis of functional components, the integration of metagenomic data with metabolic network analysis provides deeper understanding of metabolic capabilities of the metagenome10, and this approach could be very useful for mechanistically delineating the link between the gut metagenome and human health.
Atherosclerotic disease, with manifestations such as myocardial infarction and stroke, is characterized by accumulation of cholesterol and recruitment of macrophages to the arterial wall. The gut microbiota has been shown to metabolize the dietary lipid phosphatidylcholine to trimethyl amine, which promotes atherosclerosis and inflammation in mice, furthermore levels of choline, trimethylamine N-oxide and betaine have been found to predict cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in humans11. In a recent study, we pyrosequenced the 16S rRNA gene and showed that atherosclerotic plaques contain bacterial DNA with phylotypes common to the gut microbiota and that the amount of bacterial DNA in the plaque correlated with inflammation12. However, it is unclear whether atherosclerosis is associated with alterations in the composition of the gut metagenome.
To address this issue, we sequenced the gut metagenomes of patients with symptomatic atherosclerotic plaques and gender- and age-matched controls without large vulnerable plaques in the carotid arteries. To analyse the data, we developed and used a bioinformatics pipeline, Metagenomic Data Utilization and Analysis, (MEDUSA) that, besides identification of species abundance, also allows for de novo assembly and the identification of enriched metabolic functions in the metagenome. Our data show that patients were enriched in the genus Collinsella whereas controls were enriched in Eubacterium and Roseburia. At the functional level, patient metagenomes were enriched in genes encoding peptidoglycan biosynthesis whereas those of healthy controls were enriched in phytoene dehydrogenase genes.
Results
Taxonomic characterization of the gut microbiota
To address whether the gut metagenome is associated with symptomatic atherosclerosis, we sequenced the fecal metagenome of 12 patients with symptomatic atherosclerotic plaques (who had undergone carotid endarterectomy for minor ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack or amaurosis fugax) and 13 gender- and age-matched controls without large vulnerable plaques in the carotid arteries (Table 1). In total, we generated 337 million 100 bp paired-end reads (12.5±4.7 (s.d.) million reads per sample) that, first, were trimmed and filtered to only contain non-human reads longer than 35 bp (Fig. 1a). To determine the composition of the gut microbiota, we aligned the reads to a catalog of 2,382 non-redundant reference genomes (Supplementary Data 1) collected from National Center for Biological Information (NCBI) and Human Microbiome Project catalog (http://hmpdacc.org). On average, 28% of the reads in a sample could be aligned to any reference genome, which is close to the 31% found in a previous metagenomic study using Illumina reads7. The majority (98±4% (s.d.) of aligned reads were bacterial and dominated by the phyla Firmicutes and Bacteroides, representing 56% and 29% of the microbiota, respectively, followed by Actinobacteria (6%) and Proteobacteria (4%; Supplementary Fig. S1). This distribution is in agreement with previous observations13,14. The archael phylum Euryarchaeota was also present but with a high inter-subject variation (2.0±4.3% (s.d.); Supplementary Fig. S1) and was dominated by the species Methanobrevibacter smithii, which constituted at least 93% of the reads assigned to Euryarchaeota in any individual. Bacteroides, Ruminococcus, Eubacterium and Faecalibacterium were the most abundant genera in our cohort (Supplementary Fig. S2) as found previously7,13. Species and genome level abundances were also calculated (Supplementary Figs S3 and S4), and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii was shown to be the most abundant species. At coverage of at least 1% of aligned reads to reference genomes, we identified 82 species in all 27 subjects making up the core microbiota in our cohort (Supplementary Data 2). By contrast, the MetaHIT study identified 18 species in their total cohort of 124 individuals and 75 in half of the individuals at 1% coverage7. This difference may be explained by the fact that our cohort was smaller and more homogenous (that is, individuals of a similar age living in the same area) than the MetaHIT cohort, which included healthy subjects as well as patients with obesity or inflammatory bowel disease from different countries.
Table 1. Characteristics of study participants.
| Controls (n=13) | Patients (n=12) | P-value C vs P | Excluded controls (n=2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males (n) | 10 | 9 | 1* | 2 |
| Age (years) | 70.5 (0.5) | 67.6 (8.6) | 0.27† | 71(0) |
| Current smoker (n) | 0 | 4 | 0.04* | 0 |
| Hypertension (n) | 2 | 10 | 0.001* | 0 |
| Diabetes (n) | 0 | 3 | 0.09* | 0 |
| Previous myocardial infarction (n) | 0 | 3 | 0.09* | 0 |
| Statin treatment (n) | 0 | 9 | <0.001* | 0 |
| Aspirin | 0 | 12 | <0.001* | 0 |
| Cerebrovascular event | <0.001* | |||
| Minor brain infarction (n) | 0 | 5 | 0.01* | 0 |
| Transient ischemic symptoms (n) | 0 | 4 | 0.04* | 0 |
| Retinal artery (n) | 0 | 3 | 0.09* | 0 |
| BMI, kg m−2 | 23.7 (2.9)‡ | 25.8 (2.4)§ | 0.08† | 25.6 (8.8) |
| Cholesterol (mmol l−1) | 5.59 (1.20) | 4.62 (1.59) | 0.10† | 5.38 (0.62) |
| Triglycerides (mmol l−1) | 1.19 (0.74) | 1.72 (1.08) | 0.04|| | 1.8 (0.77) |
| HDL cholesterol (mmol l−1) | 1.67 (0.44) | 1.32 (0.26) | 0.026† | 1.49 (0.63) |
| LDL cholesterol (mmol l−1) | 3.39 (1.05) | 2.53 (1.44) | 0.10† | 3.07 (0.91) |
| ApoA1 | 1.44 (0.20) | 1.33 (0.21) | 0.22† | 1.46 (1.48) |
| ApoB | 1.09 (0.29) | 0.95 (0.34) | 0.27† | 1.16 (0.42) |
| WBC | 5.47 (1.06)§ | 7.78 (1.56)‡ | <0.001† | 5.05 (1.77) |
| hsCRP (mg l−1) | 2.14 (3.35) | 4.81 (5.95) | 0.12|| | 1.81 (2.27) |
BMI, body mass index; hsCRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; WBC, white blood cell count.
Data are mean (s.d.) unless otherwise indicated.
*Fisher’s exact test.
†Welch’s t-test.
‡n=11.
§n=10.
||Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
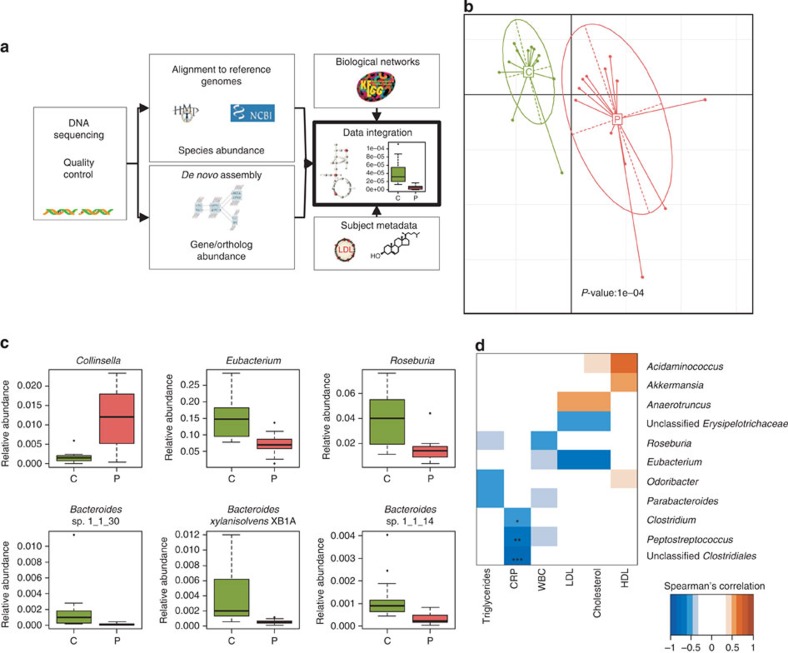
Figure 1. Microbial composition associated with symptomatic atherosclerosis.
(a) Illustration of our bioinformatics pipeline for analysing metagenome data to elucidate its relation to human metabolic disease. Sequence reads from the gut metagenome were generated with high-throughput sequencing technology and subjected to quality control. High-quality reads were used for alignment to reference genomes to estimate species abundance. De novo assembly of the metagenome allows for discovery of new genes not yet found in databases. Annotation of genes to KEGG allows for integration of information at the gene level with the metabolic network. Data on plasma metabolites and proteins together with gut metagenomic data constitute a basis for discovery of mechanisms for gut metagenome association with etiology of complex diseases. (b) Principal component analysis of microbial species abundance using health status as instrumental variable. Red is patients (P, n=12), green controls (C, n=13). The relation between microbial abundance and health status was assessed with Monte Carlo simulations with 10,000 replications by which a P-value was calculated. (c) Abundance of bacterial genera and species that differ between patients (n=12) with symptomatic atherosclerosis (P) and controls (n=13) (C). Adj. P<0.05 for all. (d) Bacterial genera correlating with biomarkers of atherosclerosis, using Spearman’s correlation. All samples, including the two excluded controls (see methods for details), were used for correlations with triglycerides, CRP (n=27, respectively) and white blood cell count (WBC; n=23). Only controls were used for low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and cholesterol correlations to avoid interactions with possible drug effects (n=15). *Adj. P<0.05, **adj. P<0.01 and ***adj. P<0.001. Boxes denote the interquartile range (IQR) between the first and third quartiles and the line within denotes the median; whiskers denote the lowest and highest values within 1.5 times IQR from the first and third quartiles, respectively. Circles denote data points beyond the whiskers.
PCA and enterotypes in the cohort
An instrumental principal component analysis with the health status as instrumental variable revealed that the microbial species abundance separated patients and healthy controls (Fig. 1b, P=1e−4, Monte Carlo simulation). The genus Collinsella was enriched in patients whereas Eubacterium and Roseburia and three species of Bacteroides were enriched in control subjects ((adjusted) adj. P<0.05, Wilcoxon rank-sum test; Fig. 1c). Several bacterial groups correlated with cardiovascular risk factors (Fig. 1d); in particular, genera of Clostridiales, Clostridium sp. SS2/1 and the poorly characterized butyrate-producing bacterium SSC/2 negatively correlated with the inflammatory marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP; Fig. 1d and Supplementary Fig. S5).
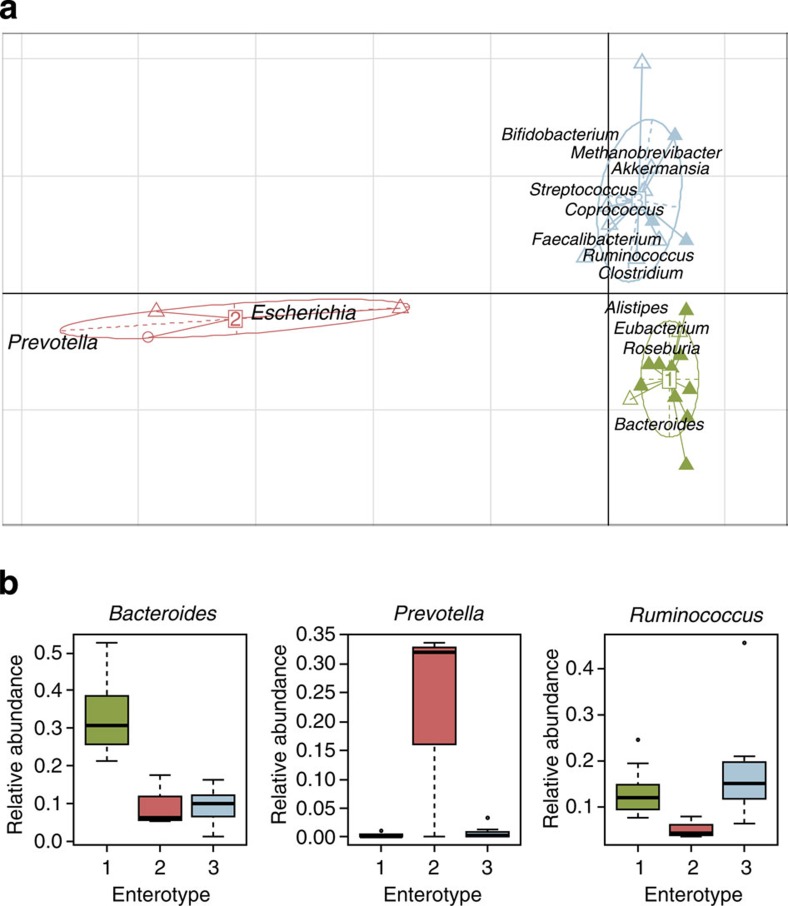
A recent study suggests that the human gut microbiota can be stratified into three enterotypes of distinct microbial compositions13. We analysed our samples according to this earlier study13, calculated the Jensen–Shannon distance of the genus abundance and clustered samples with partitioning around mediods. The Calinski–Harabasz index indicated that the optimal number of clusters was three (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Fig. S6). However, when the average silhouette index was used to assess the quality of the clusters, we saw the highest silhouette index with two clusters (Supplementary Figs S6–7), which has also been observed previously15. We chose, however, to use three clusters as proposed in the publication by Arumugam et al.13, which is the largest enterotypes study to date. The three enterotypes that we observed were characterized by the same contributors at the genus level as shown previously13: Bacteroides contributed to enterotype 1, Prevotella contributed to entrotype 2 and Ruminococcus contributed to enterotype 3 (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. S8). However, as described previously13, the third enterotype may be identified by different contributors depending on the source of sequence data and we found this cluster to be characterized by low levels of Bacteroides and Prevotella rather than a dominant genus (Supplementary Fig. S8). To test whether the enterotypes were associated with disease status, we used Fisher’s exact test and showed that patients were underrepresented in enterotype 1 (P=0.0048, Fisher’s exact test) and overrepresented in enterotype 3 (P=0.047, Fisher’s exact test; Supplementary Table S1).
Figure 2. Symptomatic atherosclerosis correlates with gut enterotypes.
(a) Three enterotypes in our cohort based on the abundance of genera. Controls and patients are denoted by filled triangles and empty triangles, respectively. Two subjects not included in the comparison are represented by empty circles. Green is enterotype 1, red is enterotype 2 and blue is enterotype 3. (b) Abundance of Bacteroides, Prevotella and Ruminococcus, proposed drivers of the three enterotypes. Boxes denote the interquartile range (IQR) between the first and third quartiles and the line within denotes the median; whiskers denote the lowest and highest values within 1.5 times IQR from the first and third quartiles, respectively. Circles denote data points beyond the whiskers.
Metabolic functions of the gut microbiota
To discover new genes in the metagenome, we performed de novo assembly of the sequence data, first for each individual sample separately and subsequently for a pool of all the non-assembled data from the individual samples to create one global gene catalog of our cohort. A total of 1.7 Gbp of contigs longer than 500 bp could be assembled and with a N50 value of 1.8 kbp using 3 as coverage cutoff and kmer of 31. MetaGeneMark16 was used to predict genes from the contig set and 2.6 million open reading frames representing 1.4 million non-redundant genes were found. The genes were functionally annotated to KEGG, Pfam and carbohydrate active enzyme (CAZy) databases and their relative abundance was assessed. On average, 60% of the reads could be aligned to the set of contigs, which is substantially more than the percentage of reads (28%) that could be aligned to the reference genomes. This indicates that our gene catalog contains a majority of the sequenced microbiome.
A global analysis of the abundance of KEGG orthologies (KO) resulted in separation of the patient group from the control group (Supplementary Fig. S9). In total, 225 KOs were differentially abundant (adj. P<0.05, Wilcoxon rank-sum test), illustrating that there were functional aspects of the gut metagenome associated with symptomatic atherosclerosis. Enriched metabolic functions in the metagenomes of patients and controls can be assessed by integrating the relative gene abundance with metabolic networks. We used the reporter feature algorithm17,18, and based on the KEGG metabolic network and the pathway associations for the KOs together with the corrected P-values, we identified first, reporter pathways (for example, pathways containing several significantly differentially abundant KOs; Supplementary Table S2) and second reporter metabolites (for example, metabolites around which there are enzymatic reactions with associated KO differentially abundant; Supplementary Table S3).
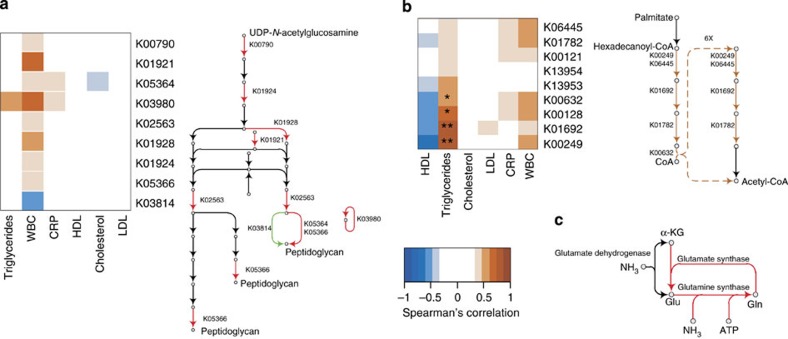
The peptidoglycan biosynthesis pathway was the highest scoring reporter pathway; eight peptidoglycan biosynthetic KOs were enriched in the gut metagenomes of patients and one was enriched in controls (adj. P<0.05, Wilcoxon rank-sum test, Fig. 3a). Consequently, we also found several of the metabolites in the peptidoglycan pathway to be reporter metabolites, for example, UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, which is a key precursor for peptidoglycan, indicating significant changes in KOs linked to these metabolites. There were also features of the metagenome that correlated negatively with inflammation, the highest scoring association being butyrate-acetoacetate CoA-transferase (K01036) with hsCRP (Spearman’s ρ=−0.73, adj. P=0.04). These findings are in agreement with a previous study showing that butyrate is an important negative regulator of inflammation19. To investigate the origin of the butyrate-acetoacetate CoA-transferase genes, we performed a BLASTP search and identified the source as Clostridium sp. SS2/1; as discussed above, this species also negatively correlated with hsCRP (Fig. 1d and Supplementary Fig. S5).
Figure 3. KOs are associated with symptomatic atherosclerosis.
(a) Peptidoglycan KOs were enriched in patients and eight out of nine KOs correlated positively with white blood cell levels. (b) β-Oxidation KOs correlate with plasma triglyceride levels. (c) The glutamine synthetase—glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase system (K00265, K00266 and K01915) with high affinity for ammonium is enriched in patients. In all panels, red indicates enriched in patients (P), green indicates enriched in controls (C). *Adj. P<0.05, **adj. P<0.01 and ***adj. P<0.001. All samples were used for correlations with triglycerides, CRP (n=27, respectively) and white blood cell count (WBC; n=23). Only controls were used for low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and cholesterol correlations to avoid interactions with possible drug effects (n=15). Adj., adjusted.
A recent metabolomics study showed that three microbially modulated metabolites of dietary phosphatidylcholine metabolism (choline, trimethylamine N-oxide and betaine) correlate with CVD in humans11. We reconstructed the metabolic pathway from phosphatidylcholine to trimethylamine (Supplementary Fig. S10) but did not observe any significant association of gene abundance in this pathway with atherosclerosis. However, we observed a positive correlation between plasma triglycerides and the abundance of several KOs in the pathway for fatty acid metabolism, specifically β-oxidation (Fig. 3b, Supplementary Fig. S11), which suggests a strong interaction between the gut microbiota and dietary components. We also observed that the GS-GOGAT system, which the microbiota uses for assimilation of nitrogen into amino acids, was significantly enriched in the patient group (Fig. 3c). In particular, the ATP-dependent reaction carried out by glutamine synthase (adj. P=0.035, Wilcoxon rank-sum test) and the glutamate synthase large and small subunits (adj. P=0.013 and adj. P=0.0074, Wilcoxon rank-sum test, respectively) were enriched in patient microbiota. The ATP-independent glutamate dehydrogenase was not found to be different between the groups.
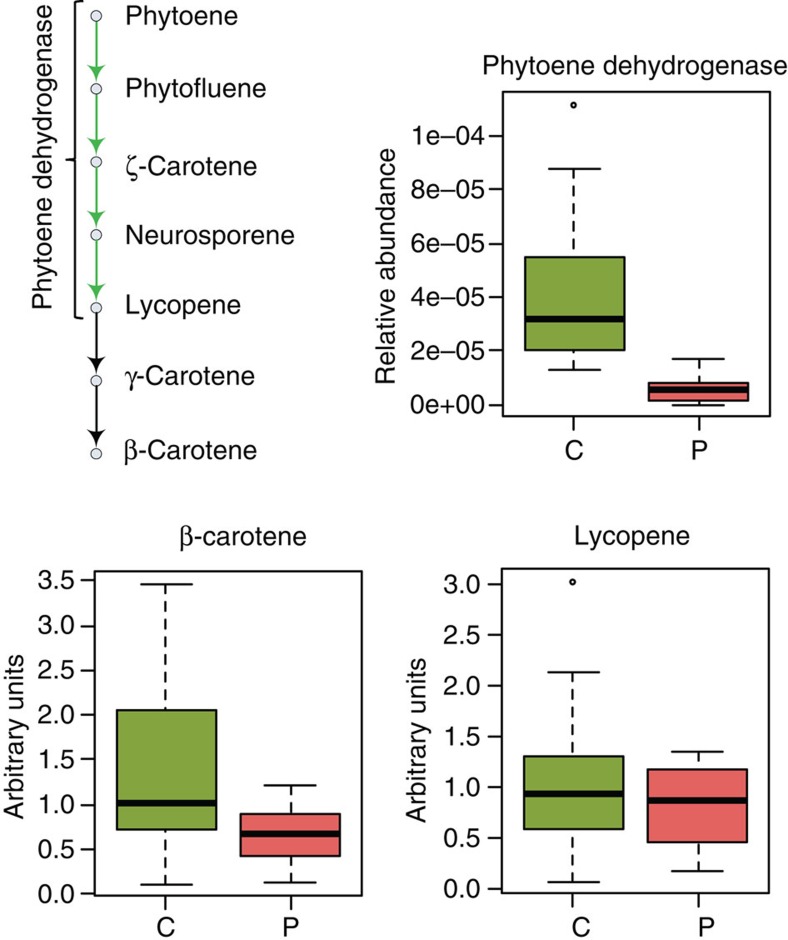
Interestingly, phytoene dehydrogenase (K10027), which is involved in the metabolism of lipid-soluble antioxidants (such as the carotenoids lycopene and β-carotene), was the KO most significantly enriched in controls in our study (adj. P=0.0046, Wilcoxon rank-sum test, Fig. 4). To determine the phylogenetic origin of the 13 genes annotated as phytoene dehydrogenases in this study, we used BLASTP to search for related sequences in the NCBI nr database. Seven of the genes matched to Bacteroides, two to Clostridia, two to Prevotella and the remaining two to Actinobacteria and various Bacteroidetes. We evaluated whether the enrichment of phytoene dehydrogenase was accompanied by increased levels of carotenoids, and found increased levels of β-carotene (P=0.05, Student’s t-test), but not lycopene, in serum of healthy controls compared with patients (Fig. 4, Supplementary Figs S12–13).
Figure 4. Phytoene dehydrogenase K10027 is enriched in the gut metagenome of healthy controls.
β-Carotene (P=0.05, Student’s t-test) but not lycopene (P=0.35, Student’s t-test) was enriched in serum of healthy controls. Red is patients (P), green controls (C). Boxes denote the interquartile range (IQR) between the first and third quartiles and the line within denotes the median; whiskers denote the lowest and highest values within 1.5 times IQR from the first and third quartiles, respectively. Circles denote data points beyond the whiskers.
Discussion
In this study, we identified several compositional and functional alterations of the gut metagenome that may be related to symptomatic atherosclerosis. The differences in the metagenome between patients and controls did not seem to be related to smoking, diabetes or body mass index (Supplementary Figs S14–S19), but these factors and the potentially modifying effects of different types of medication and diet that may be different between patients and controls require further investigation. Interestingly, we observed enrichment of patients within the Ruminococcus enterotype.
The metagenomes of patients were enriched in genes associated with peptidoglycan biosynthesis, which suggests that increased peptidoglycan production by the gut metagenome may contribute to symptomatic atherosclerosis by priming the innate immune system and enhancing neutrophil function. Indeed, inflammation has been identified as an important contributor to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis20. The increased abundance of genes in this pathway cannot be explained solely by a general increase in Gram-positive bacteria because both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria have peptidoglycan and even more, abundant Gram-positive groups of bacteria such as Eubacterium and Roseburia were enriched in controls.
Our finding of enriched levels of phytoene dehydrogenase in the metagenomes of healthy controls and its association with elevated levels of β-carotene in the serum may indicate that the possible production of this anti-oxidant by the gut microbiota may have a positive health benefit. Lycopene and β-carotene adipose levels are associated with a reduced risk of CVD in epidemiological studies21,22, but several large randomized, placebo-controlled studies with durations up to 12 years have failed to show that supplementation of pure β-carotene reduces CVD risk23,24. However, lycopene has been related to intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery25 and suggested to have a role in the early stage and prevention of atherosclerosis26. A previous study encompassing >500 participants failed to observe an association between lycopene intake and plasma lycopene levels27, indicating that other mechanisms might be more important in determining plasma levels than oral intake of lycopene. Together with evidence that bacterial species from the human gut can synthesize carotenoids28,29, we propose that our findings of increased prevalence of phytoene dehydrogenase, and increased levels of β-carotene in plasma of control subjects represent an important step towards elucidating the importance of carotenoids in the development of atherosclerosis. It is worth noting that peptidoglycan and phytoene dehydrogenase genes were not linked to obesity as there was no significant difference in abundance of these genes between lean and overweight/obese subjects in our study (Supplementary Fig. S14), or in the meta-analysis of an independent study13 (Supplementary Fig. S17).
In conclusion, here we observed associations between enterotypes, genera and species and symptomatic atherosclerosis at the taxonomical level. Within the metagenome, genes in the peptidoglycan pathway were enriched in patients, whereas genes involved in synthesis of anti-inflammatory molecules (for example, butyrate) and antioxidants were enriched in controls, suggesting that the metagenome may contribute to the development of symptomatic atherosclerosis by acting as a regulator of host inflammatory pathways. Even though our study cannot provide evidence for direct causal effects, these findings indicate that the gut metagenome may have a role in the development of symptomatic atherosclerosis.
Methods
Study design and recruitment
The patient samples were from the Göteborg Atheroma Study Group Biobank, which includes samples from patients who had undergone surgery to excise an atherosclerotic plaque30. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee in Gothenburg. All subjects gave written informed consent to participate after receiving oral and written information. All patients had severely stenotic plaques in the carotid artery with ipsilateral manifestations of emboli to either the brain, as minor brain infarction or transient ischemic symptoms, or to the retinal artery (Table 1). The clinical definition of minor brain infarction corresponds to a patient who has mild and no severe functional deficits without any need of prolonged hospital care. Hence, the underlying etiology in all these patients was a vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque with plaque rupture and embolism leading to operations with excision of the plaque30. It is not likely that the clinical events per se directly influenced the gut metagenome, as minor stroke has no acute effects on CRP and white blood cell count31 and because the patients only had transient or minor tissue-damaging effects in the brain or eye.
The control group was selected to represent an age- and sex-matched group with no cardiovascular health problems and was recruited from two on-going population-based cohorts that have been described previously32,33. The investigations of the control group included repeated ultrasound examinations of the carotid and femoral arteries, and no large, potentially vulnerable plaques were detected. Further inclusion criteria in the control group were no history of CVD, no smoking, no diabetes and no treated hyperlipidemia. The underlying rationale was to avoid subjects with vulnerable plaques defined as echo-thin plaques with stenosis >50% of vessel lumen34,35. Analysis of updated health records showed that one control subject had a dilation of ascending aorta as the initial recruitment as ‘healthy control’ and a second had white matter disease in the brain, possibly due to a small artery disease. As these diagnoses may have atherosclerosis as underlying cause, we excluded these subjects from analyses of differences between patients and controls, although they were included in specified analyses of the total cohort.
Blood samples were drawn before surgery and plasma and serum samples were prepared and immediately frozen at −70 °C. The subjects were given material and instructions for providing fecal samples at home. Methods for processing fecal samples and isolation of metagenomic DNA have been described previously36.
Sequencing
All samples were sequenced in the Illumina HiSeq2000 instrument at SciLifeLab in Stockholm, Sweden, with up to ten samples pooled in one lane. Libraries were prepared with a fragment length of ~300 bp. Paired-end reads were generated with 100 bp in the forward and reverse direction.
Data quality control
Sequencing adapter sequences were removed with cutadapt (http://code.google.com/p/cutadapt/). The length of each read was trimmed with SolexaQA with the options ‘-b –p 0.05’37. Read pairs with either reads shorter than 35 bp were removed with a custom Python script. The high-quality reads were then aligned to the human genome (NCBI version 37) with Bowtie38 using ‘-n 2 -l 35 -e 200 –best -p 8 –chunkmbs 1024 -X 600 –tryhard’. This set of high-quality reads were then used for further analysis.
Alignment to reference genomes and taxonomical analysis
A set of 2,382 microbial reference genomes were obtained from the NCBI and Human Microbiome Project on 02 August 2011. The reference genomes were combined into two Bowtie indexes and the metagenomic sequence reads were aligned to the reference genomes using Bowtie with parameters ‘-n 2 -l 35 -e 200 –best -p 8 –chunkmbs 1024 -X 600 –tryhard’. Mapping results were merged by selecting the alignment with fewest mismatches; if a read was aligned to a reference genome with the same number of mismatches, each genome was assigned half to each genome. The relative abundance of each genome was calculated by summing the number of reads aligned to that genome divided by the genome size. In each subject, the relative abundance was scaled to sum to one. The taxonomic rank for every genome was downloaded from NCBI taxonomy to assign each genome to a species, genus and phyla. The relative abundance for each taxonomical rank was calculated buy summing the relative abundance of all its members.
De novo assembly and gene calling
The high-quality reads were used for de novo assembly with Velvet39 into contigs of at least 500-bp length using 3 as coverage cutoff and kmer length of 31. To obtain long contigs with high specificity, we iteratively explored parameter values for the kmer length and coverage cutoff to balance the total assembly length and the N50 value to be used in the final de novo assembly. Reads from each subject were used in separate assemblies and unassembled reads were then used in a global final assembly. Genes were predicted on the contigs with MetaGeneMark16. All genes were then aligned on the contigset with Bowtie using the same parameters as above. The abundance of a gene was calculated by counting the number of reads that align to the gene normalizing by the gene length and the total number of reads aligned to any contig.
Gene annotation
The genes were annotated to the KEGG database with hidden Markov models (HMMs). Protein sequences for microbial orthologs were downloaded and aligned with MUSCLE40. HMMs were generated with HMMer3 (ref. 41) for each KO. Each gene was queried on the 4,283 HMMs and annotated the KO with lowest scoring E-value below 10−20. Out of the 2,645,414 genes, 848,353 (32%) were annotated to KOs. The genes were also annotated to CAZy42. The CAZy proteins of bacterial and archaeal origin were downloaded and HMMs were built and genes annotated as described above. The feature abundance (KOs and CAZy) was calculated by summing the abundance of genes annotated to a feature.
Genes for betaine reductase were collected from two species, Clostridium difficile 630 (Entrez protein accession codes Gi: 126699967 and GI: 126699969) and Carboxydothermus hydrogenoformans Z-2901 (Entrez protein accession codes Gi: 78044558 and GI: 78044225). The gene catalogue was searched against these four genes with USEARCH43 using an E-value cutoff of 10−30.
Statistical analysis
To determine differential abundance of metagenomic features (that is, taxonomic and functional features between patients and controls) Wilcoxon rank-sum test was applied. Strains and genera with a relative abundance in any subject above 10−5 and 10−3, respectively, were included in the analysis. Correlations were done between serum biomarkers and metagenomic features with Spearman’s correlation. P-values were adjusted with false discovery rate with the method from Benjamini and Hochberg44 when multiple hypotheses were considered simultaneously and are denoted adj. P. The R package ade4 using instrumental principal component analysis45 was used to determine the global analysis of species abundance between patients and controls (in Fig. 1b and Supplementary Figs S7,S9,S18,S19). Monte Carlo test on the between-groups inertia percentage was performed 10,000 permutations to calculate a P-value in Fig. 1b.
Testing the association between microbial genes and obesity
We analysed data from Arumugam et al.13 to investigate whether the abundance of peptidoglycan and phytoene dehydrogenase genes in the gut metagenome differed between obese and lean subjects. The corresponding clusters of orthologous groups was identified to the KOs involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis and phytoene dehydrogenase. The results are presented in Supplementary Figs S14–S17. There was no significant differential abundance of the studied corresponding clusters of orthologous groups between healthy lean and obese subjects (Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
Measurement of β-carotene and lycopene
β-Carotene and lycopene were measured in the serum from healthy controls and patients using a modified protocol from46. Briefly, 200 μl of serum was mixed with 200 μl of ethanol and 8 μl of 0.191 mmol l−1 retinyl propionate in ethanol. Samples were vortexed gently and then 1 ml hexane was added; the samples were again vortexed (for 30 s). The phases were separated by centrifugation at 1,500g for 5 min and 900 μl of the upper phase was then transferred to a new tube. The samples were dried under low pressure at room temperature in a Speedvac concentrator, not to complete dryness. The residue was dissolved in 100 μl ethanol followed by addition of 100 μl acetonitrile. Samples were protected from light during handling and preparation.
The compounds were measured using a Dionex HPLC system with a C18 column, maintained at 29 °C. The mobile phase was ethanol and acetonitrile (1:1) with 0.1 ml l−1 diethylamine and was kept at a flow rate of 0.9 ml min−1. Samples were stored at 4 °C before injection of 50 μl. Chromatograms for absorbance at the wavelengths 300, 325 and 450 nm were collected simultaneously for 20 min. Peaks were identified by comparing retention time with a standard solution of β-carotene and lycopene. Quantification was based on the area under the curve.
Author contributions
J.N., F.B., D.P. and B.F. conceived and designed the project. F.H.K., F.F., and V.T., performed the experiments. F.H.K. and I.N. analysed the sequence data. All authors contributed writing and editing the manuscript. F.B. and J.N. contributed equally to the study.
Accession codes: Gut metagenome sequences have been deposited in the Sequence Read Archive under accession code SRA059451.
Additional information
How to cite this article: Karlsson F. H. et al. Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Nat. Commun. 3:1245 doi: 10.1038/ncomms2266 (2012).
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Figures S1-S19 and Supplementary Tables S1-S3
Reference genomes included in the database for taxonomic assignment of metagenomic reads.
Core microbiota in our cohort. Genomes with a coverage of more than 1% in all 27 subjects.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Rosie Perkins for critically reading and editing the manuscript, Suwanee Jansa-Ard for technical assistance with HPLC measurements, Swedish National Infrastructure for large-scale sequencing for performing the Illumina sequencing and our colleagues of the Göteborg Atheroma Study Group (Sahlgrenska University Hospital and University of Gothenburg) and Marie Louise Ekholm for providing clinical specimens. The bioinformatic computations were performed on resources provided by the Swedish National Infrastructure for Computing (SNIC) at C3SE. This study was funded by Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Chalmers Foundation, Swedish Heart Lung Foundation, Torsten Söderberg’s Foundation, IngaBritt och Arne Lundbergs foundation, AFA Insurances, the Swedish Research Council and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research.
Footnotes
J.N and F.B. are shareholders in MetaboGen AB. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Bäckhed F., Ley R. E., Sonnenburg J. L., Peterson D. A., Gordon J. I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307, 1915–1920 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cani P. D. et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 56, 1761–1772 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäckhed F. et al. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 15718–15723 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley R. E., Turnbaugh P. J., Klein S., Gordon J. I. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444, 1022–1023 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erridge C., Attina T., Spickett C. M., Webb D. J. A high-fat meal induces low-grade endotoxemia: evidence of a novel mechanism of postprandial inflammation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 86, 1286–1292 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schertzer J. D. et al. NOD1 activators link innate immunity to insulin resistance. Diabetes 60, 2206–2215 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin J. et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 464, 59–65 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 486, 207–214 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbaugh P. J. et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457, 480–484 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblum S., Turnbaugh P. J., Borenstein E. Metagenomic systems biology of the human gut microbiome reveals topological shifts associated with obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 594–599 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 472, 57–63 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren O. et al. Human oral, gut, and plaque microbiota in patients with atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, Suppl 14592–4598 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arumugam M. et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 473, 174–180 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tap J. et al. Towards the human intestinal microbiota phylogenetic core. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 2574–2584 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. D. et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 334, 105–8 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W., Lomsadze A., Borodovsky M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, e132 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira A. P., Patil K. R., Nielsen J. Architecture of transcriptional regulatory circuits is knitted over the topology of bio-molecular interaction networks. BMC Syst. Biol. 2, 17 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil K. R., Nielsen J. Uncovering transcriptional regulation of metabolism by using metabolic network topology. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 2685–2689 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maslowski K. M. et al. Regulation of inflammatory responses by gut microbiota and chemoattractant receptor GPR43. Nature 461, 1282–1286 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1685–1695 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardinaal A. F. et al. Antioxidants in adipose tissue and risk of myocardial infarction: the EURAMIC Study. Lancet 342, 1379–1384 (1993). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlmeier L. et al. Lycopene and myocardial infarction risk in the EURAMIC study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 146, 618–626 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennekens C. H. et al. Lack of effect of long-term supplementation with beta carotene on the incidence of malignant neoplasms and cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 334, 1145–1149 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kritchevsky S. B. beta-Carotene, carotenoids and the prevention of coronary heart disease. J. Nutr. 129, 5–8 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rissanen T. H. et al. Serum lycopene concentrations and carotid atherosclerosis: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 77, 133–138 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sesso H. D., Buring J. E., Norkus E. P., Gaziano J. M. Plasma lycopene, other carotenoids, and retinol and the risk of cardiovascular disease in women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 79, 47–53 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermudez O. I., Ribaya-Mercado J. D., Talegawkar S. A., Tucker K. L. Hispanic and non-Hispanic white elders from Massachusetts have different patterns of carotenoid intake and plasma concentrations. J. Nutr. 135, 1496–1502 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaneja R. et al. Carotenoids found in Bacillus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 108, 1889–1902 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Fons L. et al. Identification and the developmental formation of carotenoid pigments in the yellow/orange Bacillus spore-formers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1811, 177–185 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagerberg B. et al. Differences in lesion severity and cellular composition between in vivo assessed upstream and downstream sides of human symptomatic carotid atherosclerotic plaques. J. Vasc. Res. 47, 221–230 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H., Boysen G. C-reactive protein and white blood cell count increases in the first 24 hours after acute stroke. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 18, 214–219 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagerberg B., Kellis D., Bergstrom G., Behre C. J. Adiponectin in relation to insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in the development of type 2 diabetes: a prospective study in 64-year-old women. J. Intern. Med. 269, 636–643 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C., Wikstrand J. High apoB/apoA-I ratio is associated with increased progression rate of carotid artery intima-media thickness in clinically healthy 58-year-old men: experiences from very long-term follow-up in the AIR study. Atherosclerosis 205, 284–289 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen E. B., Bonaa K. H., Joakimsen O. Echolucent plaques are associated with high risk of ischemic cerebrovascular events in carotid stenosis: the tromso study. Circulation 103, 2171–2175 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl U. et al. Percentage white: a new feature for ultrasound classification of plaque echogenicity in carotid artery atherosclerosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 36, 218–226 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen A. et al. Comparative analysis of fecal DNA extraction methods with phylogenetic microarray: effective recovery of bacterial and archaeal DNA using mechanical cell lysis. J. Microbiol. Methods 81, 127–134 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. P., Peterson D. A., Biggs P. J. SolexaQA: At-a-glance quality assessment of Illumina second-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinformatics 11, 485 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langmead B., Trapnell C., Pop M., Salzberg S. L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10, R25 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino D. R., Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 18, 821–829 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. C. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1792–1797 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy S. R. Profile hidden Markov models. Bioinformatics 14, 755–763 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantarel B. L. et al. The carbohydrate-active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D233–238 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26, 2460–2461 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate—a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B Met. 57, 289–300 (1995). [Google Scholar]
- Dray S., Dufour A. B. The ade4 package: Implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. J. Stat. Softw. 22, 1–20 (2007). [Google Scholar]
- Sowell A. L., Huff D. L., Yeager P. R., Caudill S. P., Gunter E. W. Retinol, alpha-tocopherol, lutein/zeaxanthin, beta-cryptoxanthin, lycopene, alpha-carotene, trans-beta-carotene, and four retinyl esters in serum determined simultaneously by reversed-phase HPLC with multiwavelength detection. Clin. Chem. 40, 411–416 (1994). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Figures S1-S19 and Supplementary Tables S1-S3
Reference genomes included in the database for taxonomic assignment of metagenomic reads.
Core microbiota in our cohort. Genomes with a coverage of more than 1% in all 27 subjects.