Abstract
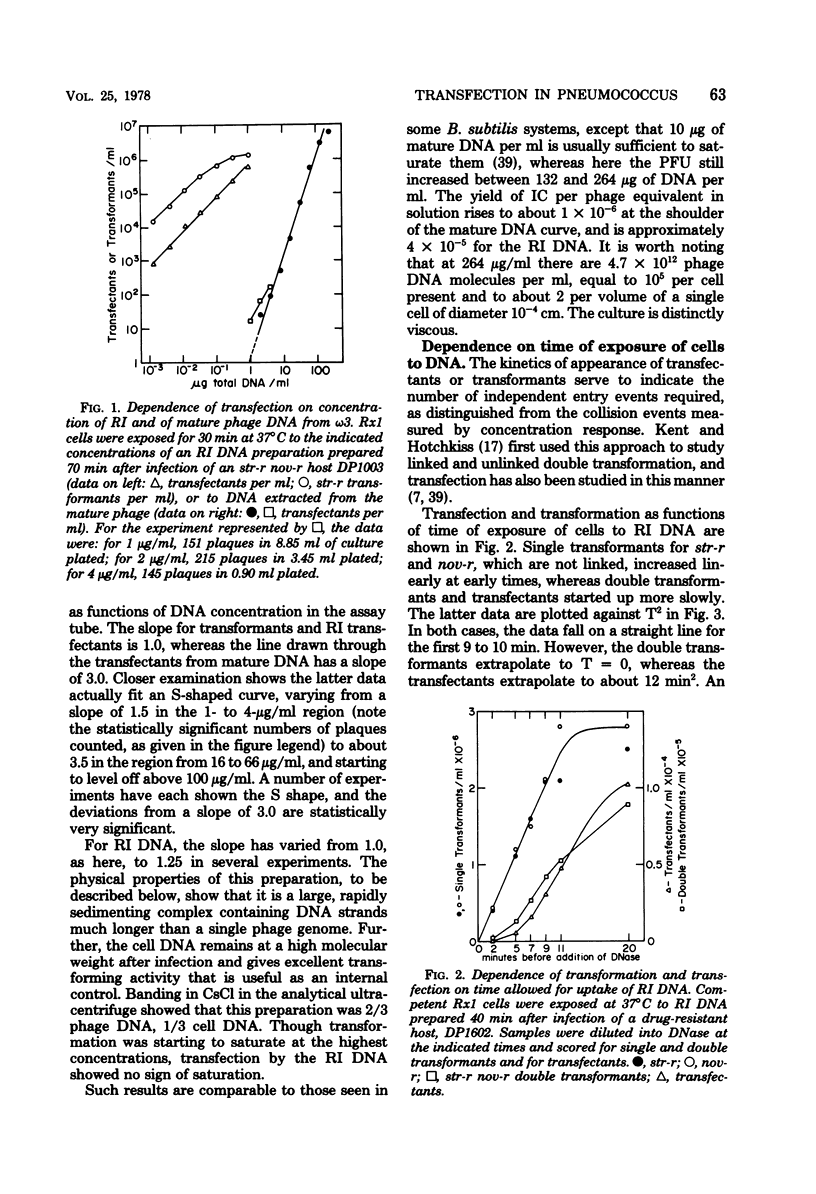
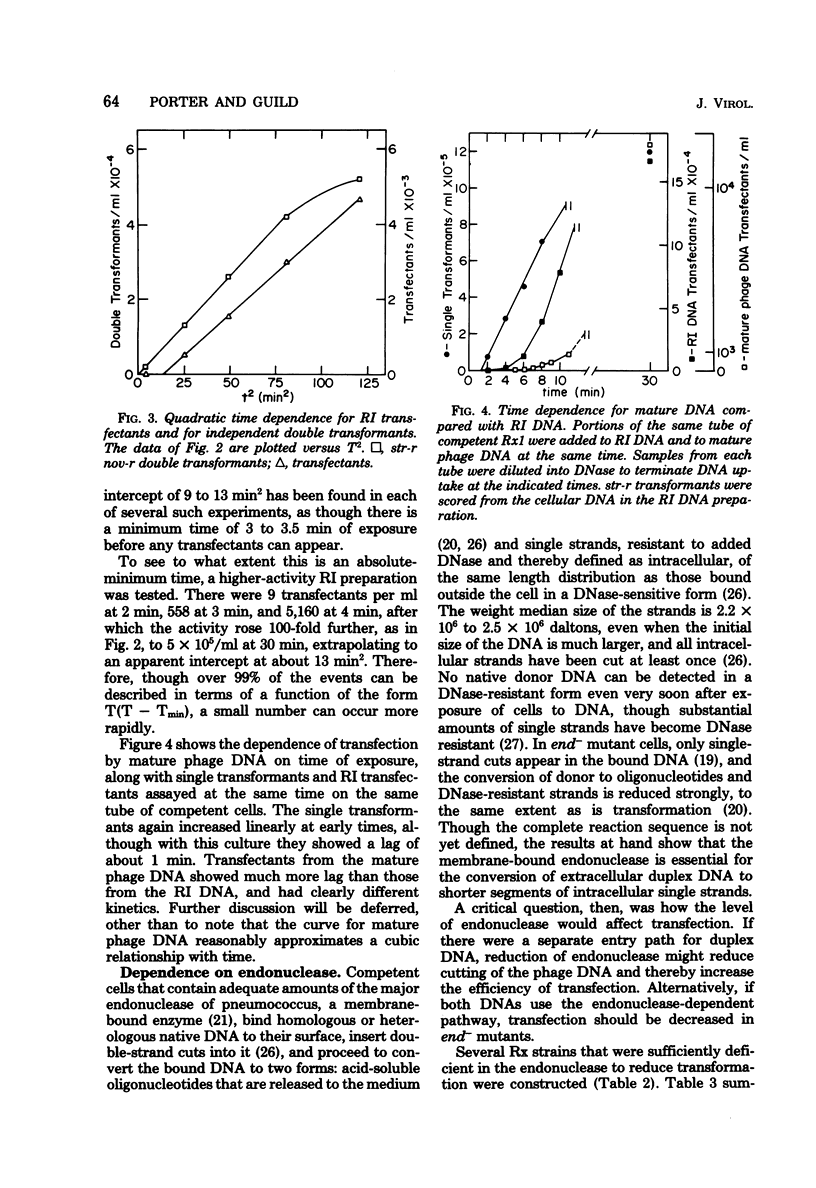
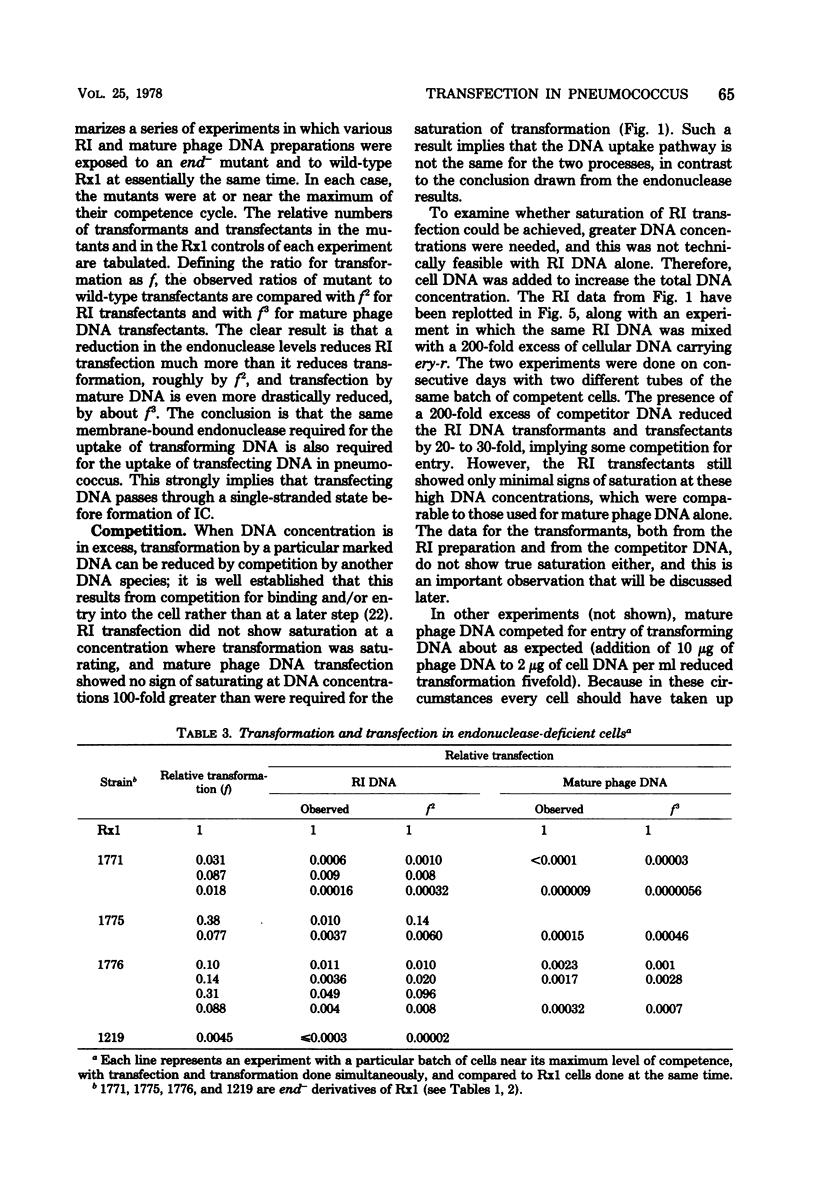
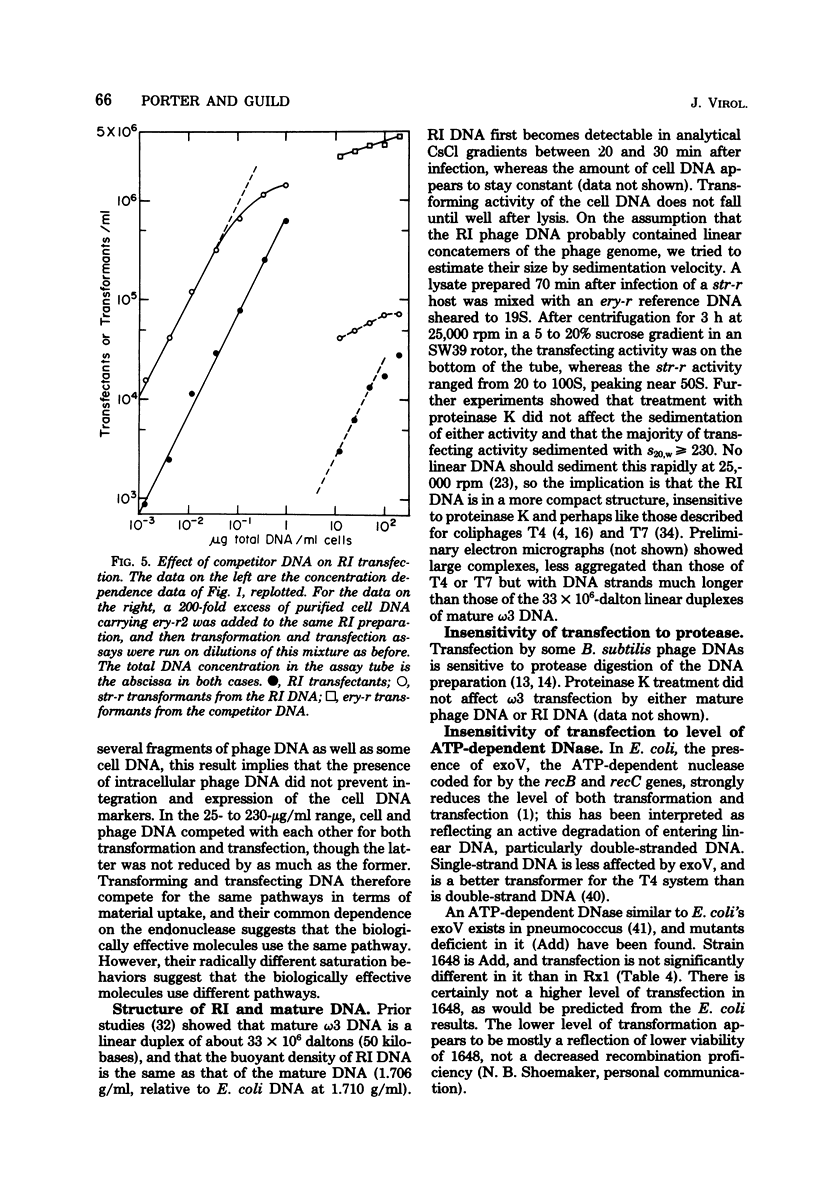
Transfection has been found and characterized in pneumococcus. For replicating ω3 phage DNA extracted from infected cells, transfection was relatively efficient and rose linearly with DNA concentration and quadratically with time, according to T(T - 3.5) min2. For mature DNA extracted from phage particles, transfection was hardly detectable below 1 μg/ml but increased about as the cube of the DNA concentration up to 100 μg/ml, and was still rising at concentrations over 200 μg/ml. The kinetics suggest a dependence on a mixed cubic function of the time of exposure of cells to mature DNA. Cell and phage DNAs competed with each other for transformation and transfection. Transfection was reduced much more strongly than transformation in cells that were deficient in the membrane-bound endonuclease required for conversion of donor duplex DNA to intracellular single strands; these data agree with the kinetic data in implying that independent entry of segments of two strands is necessary for transfection by replicating ω3 phage DNA and entry of at least three strands is necessary for transfection by mature DNA. To reconcile differing DNA concentration dependences of transfection and transformation with a common entry path, it was necessary to reexamine data on transformation and to recognize that this process continued to rise slowly through the concentration region usually described as “plateau.” These results and the transfection data reflect multiple binding and nicking events that occurred on the cell surface before entry. Our conclusion is that transfection in pneumococcus occurs by association inside the cell of segments of single strands of phage DNA that have entered independently, creating gapped structures that need repair synthesis to create infective centers. Physical recombination is therefore automatically a prerequisite to transfection.
Full text
PDF



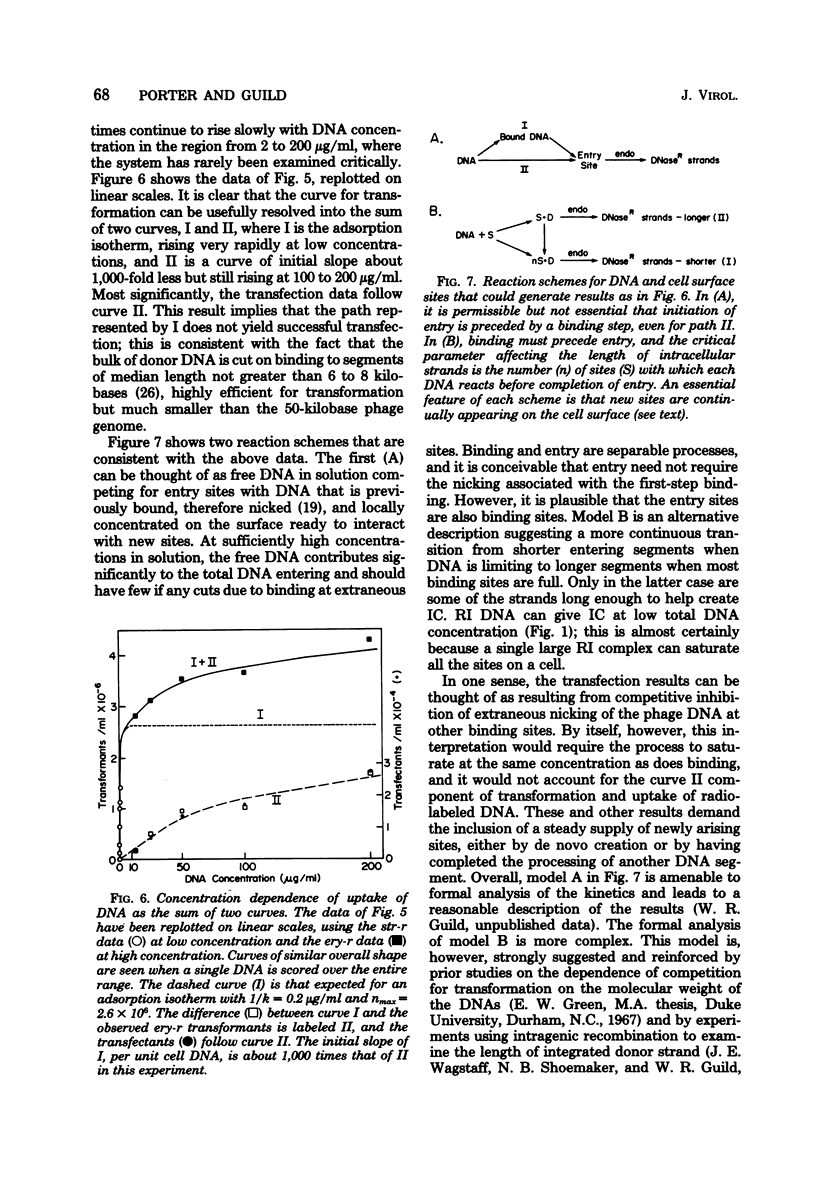
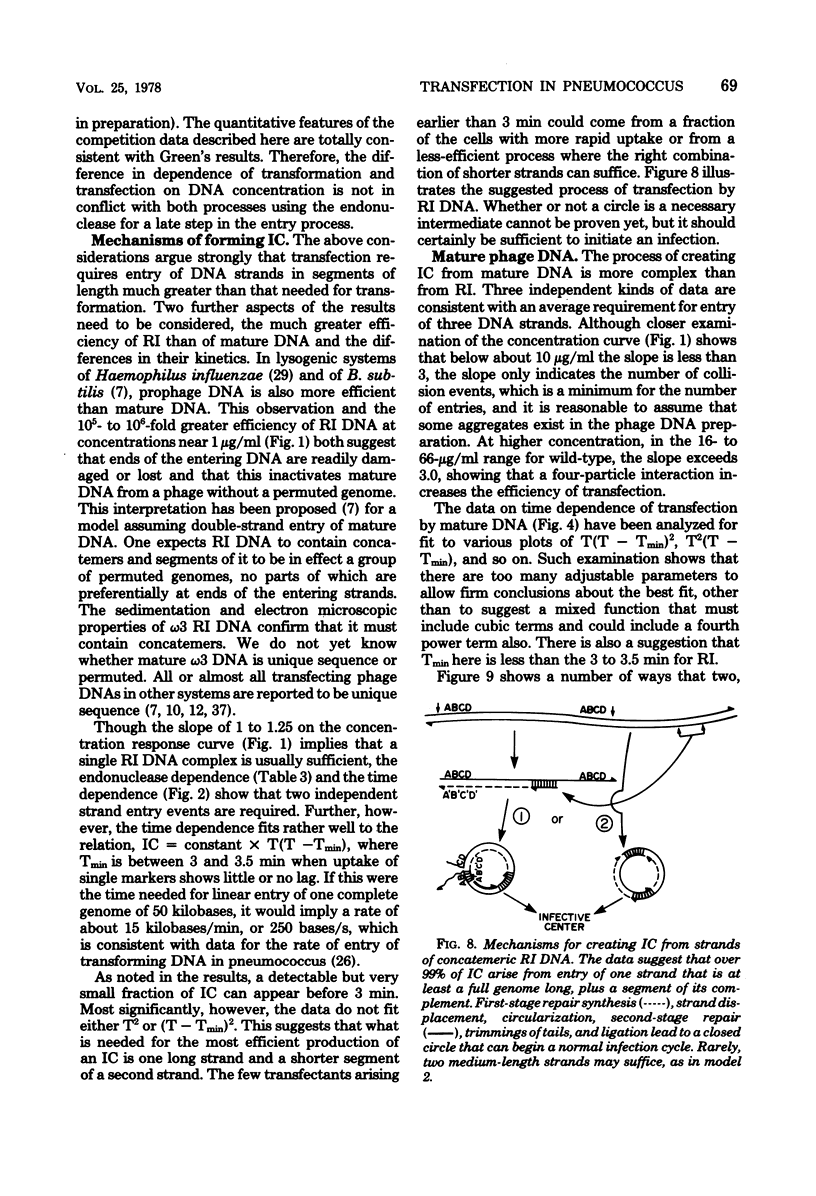



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benzinger R., Enquist L. W., Skalka A. Transfection of Escherichia coli spheroplasts. V. Activity of recBC nuclease in rec+ and rec minus spheroplasts measured with different forms of bacteriophage DNA. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):861–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.861-871.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A., Jr, Guild W. R. Transformation and DNA size. I. Activity of fragments of defined size and a fit to a random double cross-over model. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):157–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. J., Guild W. R. Events occurring near the time of synapsis during transformation in Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):266–275. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.266-275.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis M. J., Alberts B. Studies on the structure of intracellular bacteriophage T4 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 25;102(4):793–816. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff-Abelson R., Dubnau D. Conditions affecting the isolation from transformed cells of Bacillus subtilis of high-molecular-weight single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid of donor origin. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):146–153. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.146-153.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Cirigliano C. Fate of transforming DNA following uptake by competent Bacillus subtilis. Formation and properties of products isolated from transformed cells which are derived entirely from donor DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):9–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOELDES J., TRAUTNER T. A. INFECTIOUS DNA FROM A NEWLY ISOLATED B. SUBTILIS PHAGE. Z Vererbungsl. 1964 Apr 10;95:57–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00898184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flock J. I., Rutberg L. Mature DNA from temperate bacillusphage phi105 requires primary recombination to be infectious in transfection. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;131(4):301–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00264861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN D. M. INFECTIVITY OF DNA ISOLATED FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS BACTERIOPHAGE, SP82. J Mol Biol. 1964 Dec;10:438–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild W. R., Shoemaker N. B. Mismatch correction in pneumococcal transformation: donor length and hex-dependent marker efficiency. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):125–135. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.125-135.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa H. Transfecting deoxyribonucleic acid of Bacillus bacteriophage phi 29 that is protease sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1555–1559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A. Visualization of replicating mammalian and T4 bacteriophage DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:509–524. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. L., HOTCHKISS R. D. KINETIC ANALYSIS OF MULTIPLE, LINKED RECOMBINATIONS IN PNEUMOCOCCAL TRANSFORMATION. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:308–322. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S., TOLMACH L. J. Genetic transformation. I. Cellular incorporation of DNA accompanying transformation in Pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):68–82. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Identification of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):222–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.222-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. Single-strand breakage on binding of DNA to cells in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 25;101(2):255–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Mutants of Diplococcus pneumoniae that lack deoxyribonucleases and other activities possibly pertinent to genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.373-383.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Neuberger M. Membrane location of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1321–1329. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1321-1329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., Hutchinson F. Neutral sucrose sedimentation of very large DNA from Bacillus subtilis. I. Effect of random double-strand breaks and centrifuge speed on sedimentation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):455–478. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonnell M., Lain R., Tomasz A. "Diplophage": a bacteriophage of Diplococcus pneumoniae. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):577–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Breakage prior to entry of donor DNA in Pneumococcus transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Structure of deoxyribonucleic acid on the cell surface during uptake by pneumococcus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1055-1062.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTER E. W., STOCKER B. A. BIOSYNTHETIC LATENCY IN EARLY STAGES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDTRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:785–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.785-796.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notani N. K., Setlow J. K. Mechanism of bacterial transformation and transfection. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1974;14(0):39–100. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUBO S., STRAUSS B., STODOLSKY M. THE POSSIBLE ROLE OF RECOMBINATION IN THE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. Virology. 1964 Dec;24:552–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechowska M., Fox M. S. Fate of transforming deoxyribonucleate in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):680–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.680-689.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. D., Guild W. R. Characterization of some pneumococcal bacteriophages. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):659–667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.659-667.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwer P. Fast sedimenting bacteriophage T7 DNA from T7-infected Escherichia coli. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):70–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90207-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guild W. R. Destruction of low efficiency markers is a slow process occurring at a heteroduplex stage of transformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(4):283–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00268516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker N. B., Guild W. R. Kinetics of integration of transforming DNA in pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. One way to do experiments on gene conversion? Transfection with heteroduplex SPP1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(1):84–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00334048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiraby J. G., Tiraby E., Fox M. S. Pneumococcal bacteriophages. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):566–569. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90300-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vovis G. F. Adenosine triphosphate-dependent deoxyribonuclease from Diplococcus pneumoniae: fate of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid in a strain deficient in the enzymatic activity. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):718–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.718-723.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



