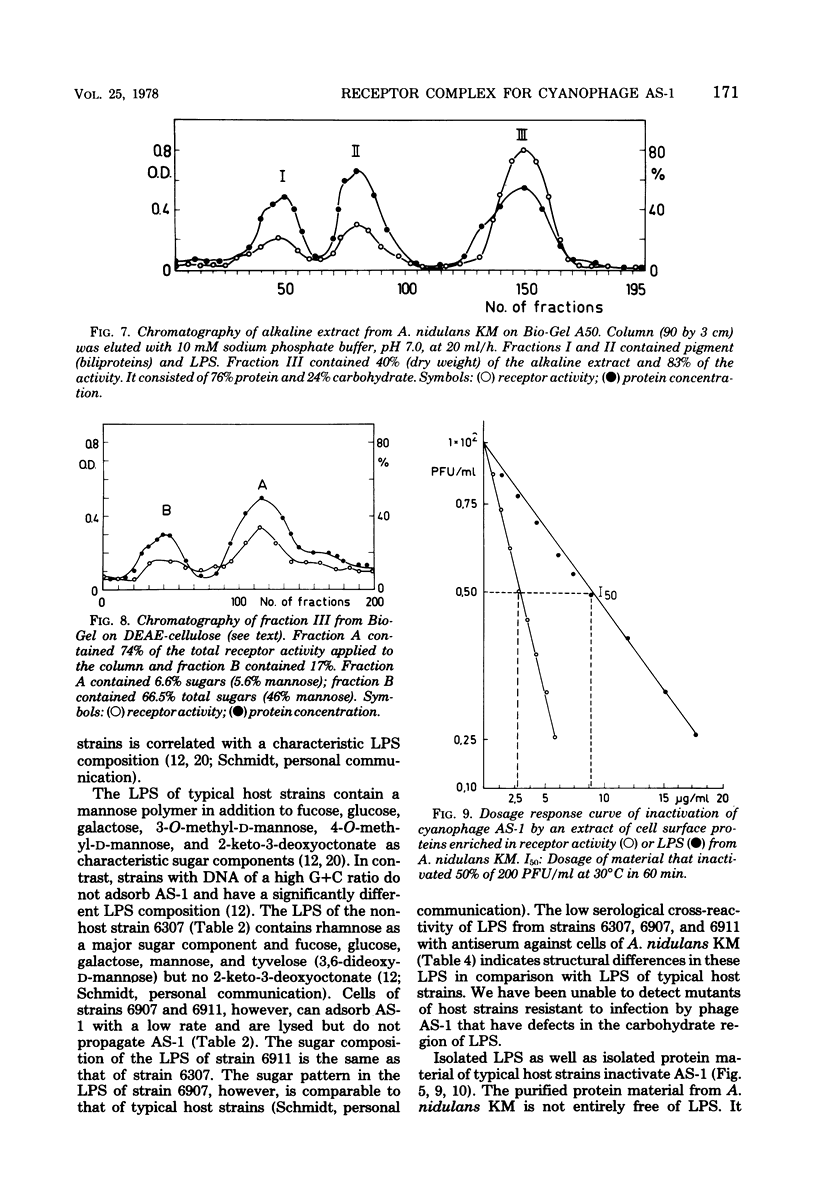
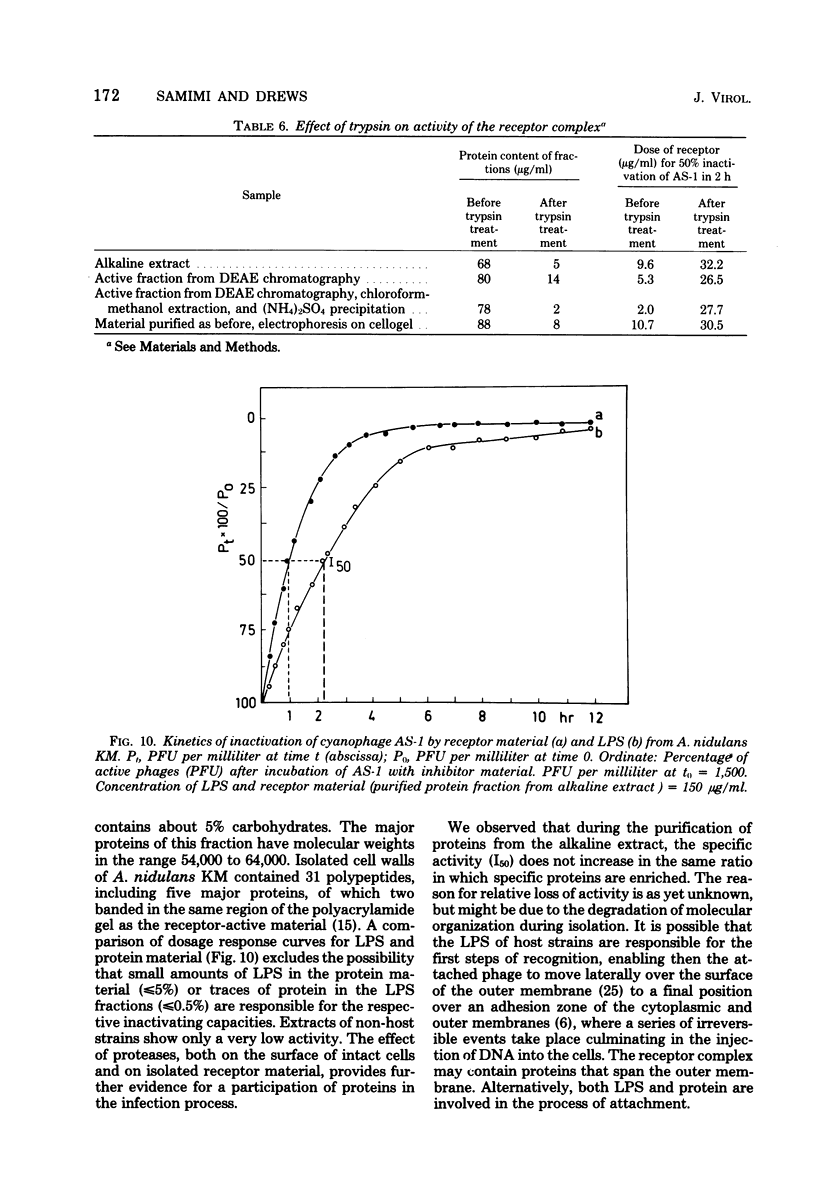
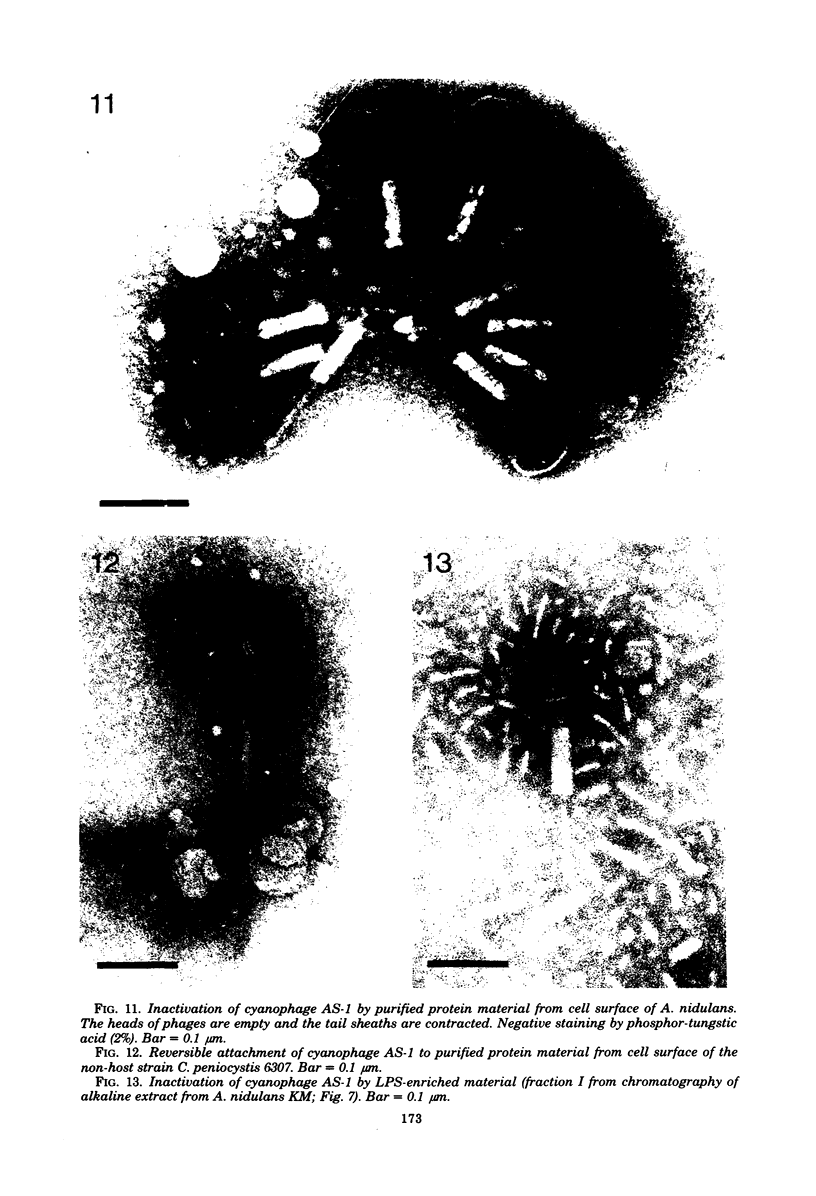
Abstract
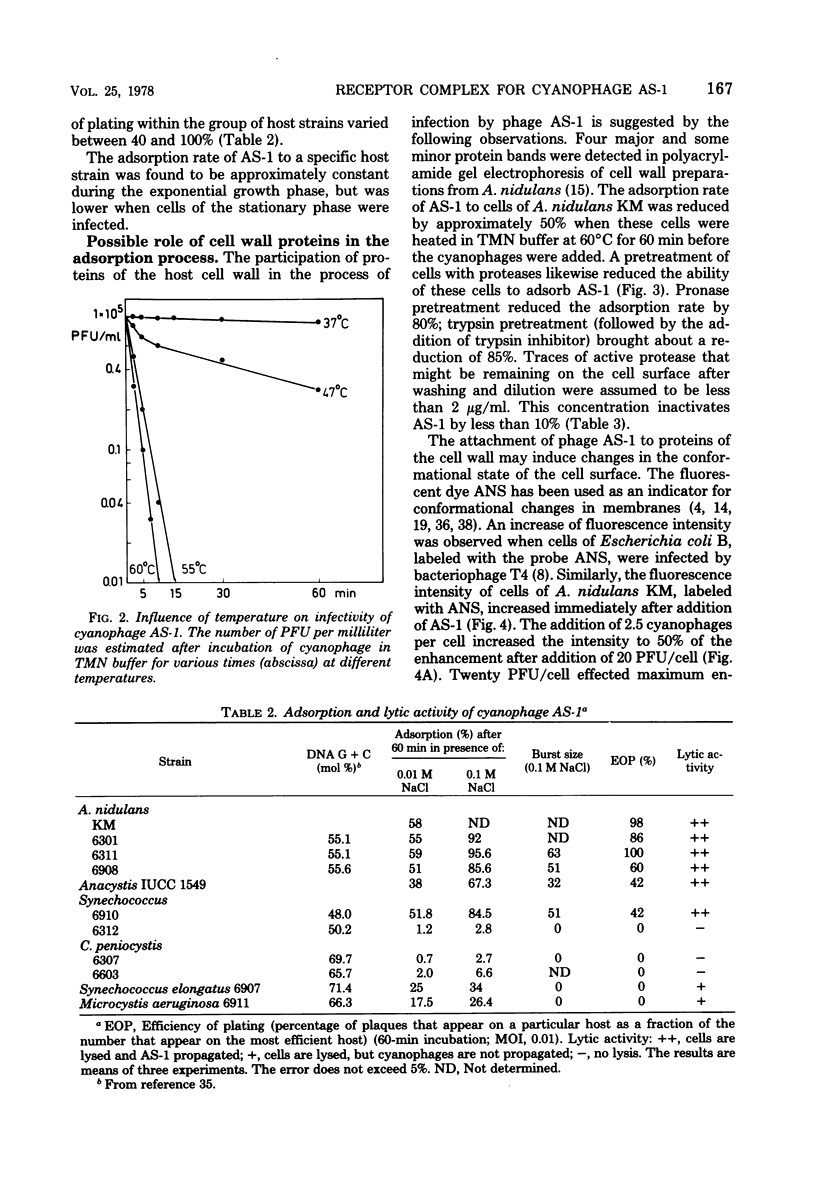
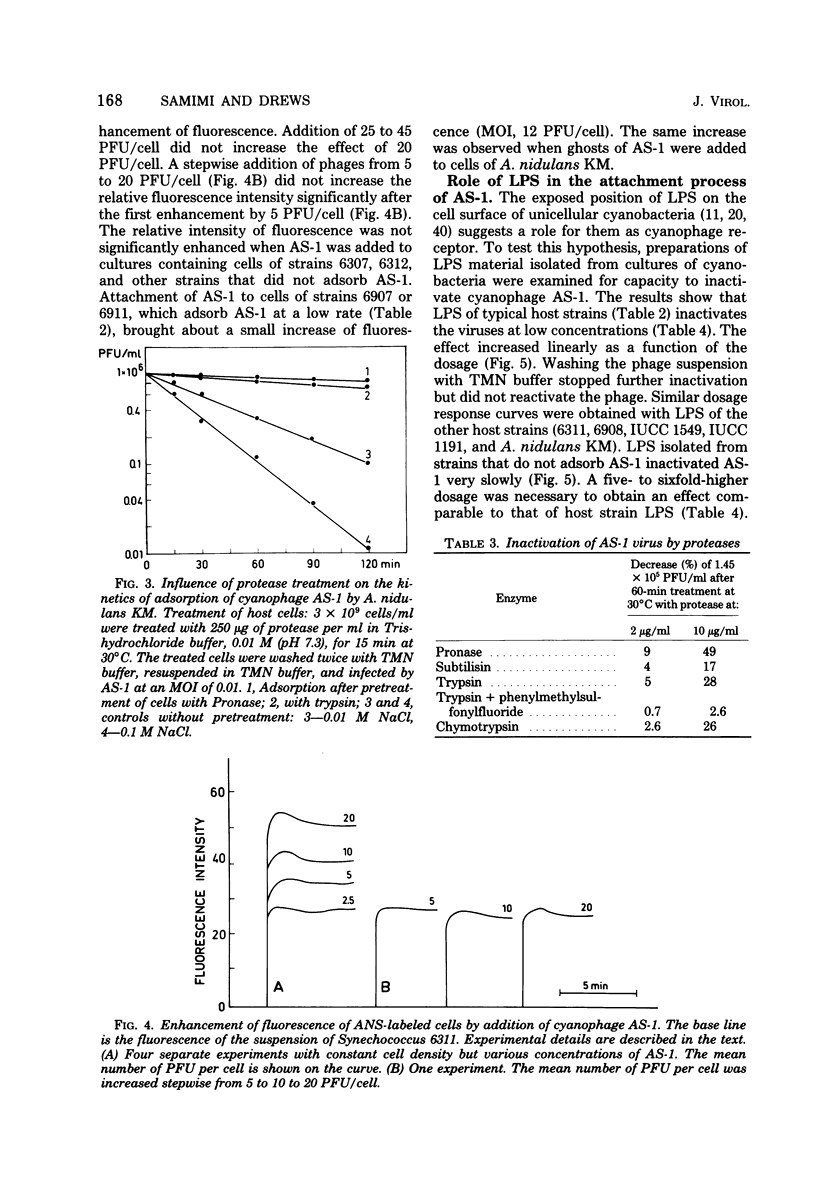
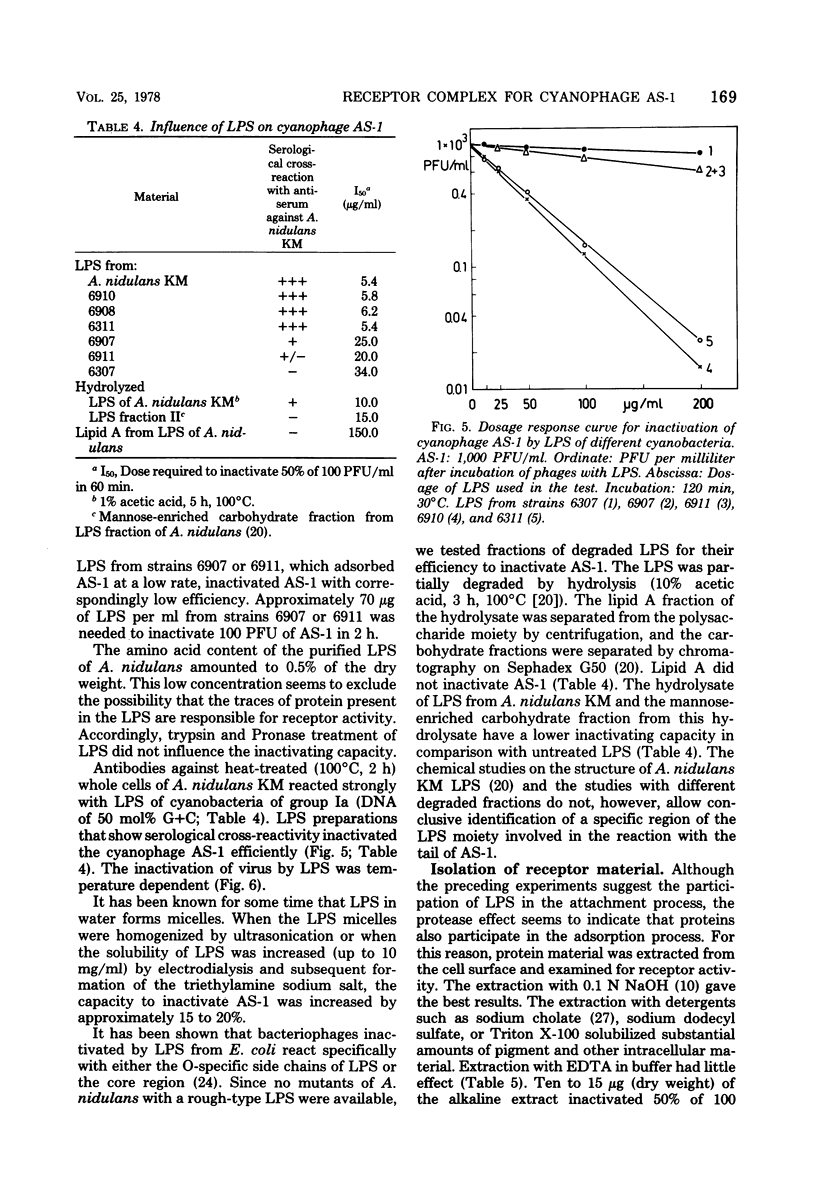
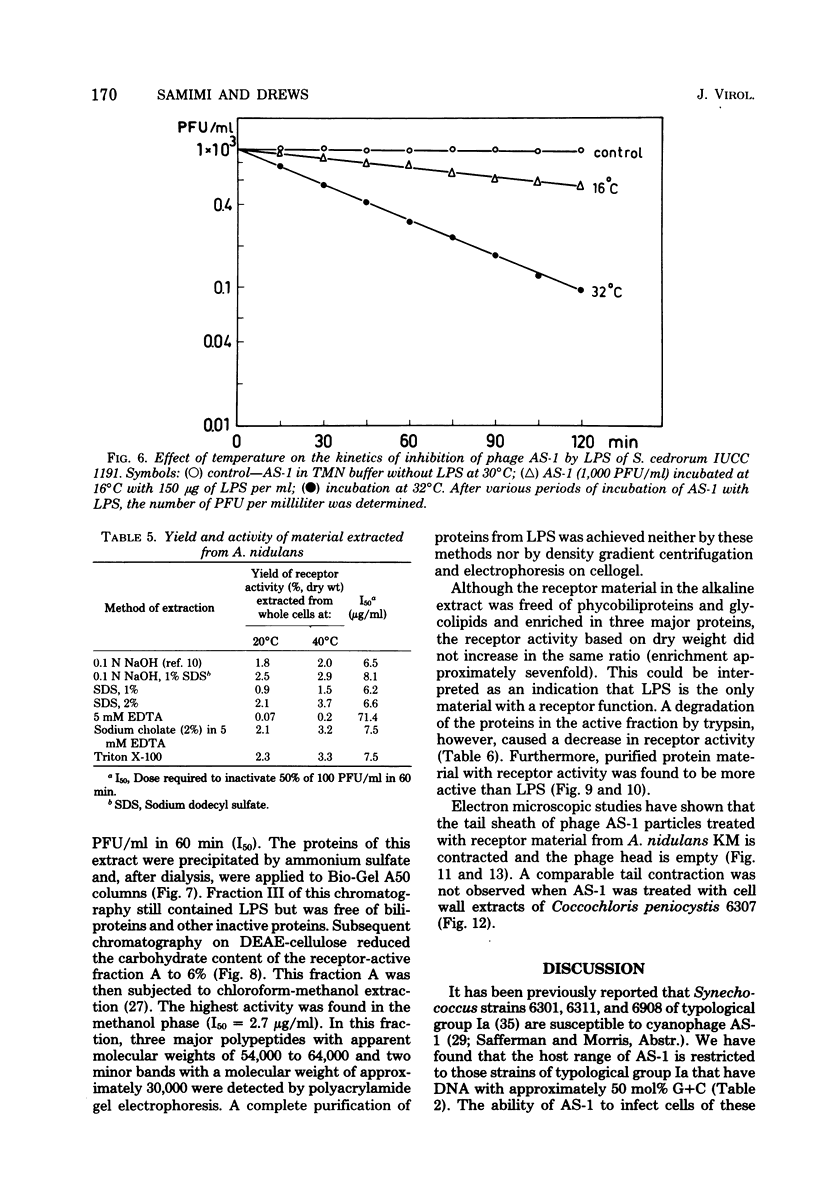
Cells of unicellular cyanobacteria of typological group Ia, containing approximately 50 mol% guanine + cytosine (G+C) in their DNA (R. Y. Stanier, R. Kunisawa, M. Mandel, and G. Cohen-Bazire, Bacteriol. Rev. 35:171-205, 1971), were susceptible to infection by the cyanophage AS-1. Cyanobacteria of the same typological group, containing approximately 65 mol% G+C in their DNA, did not adsorb the cyanophage AS-1 or adsorbed it at a low rate. AS-1 was not propagated by any of the investigated strains with a high G+C content in their DNA. However, cells of strains 6907 and 6911 were lysed by cyanophage AS-1. A comparison of the host range of this phage with the lipopolysaccharide composition of host and non-host cell walls suggests that lipopolysaccharides are involved in the adsorption process. About 8 microgram of lipopolysaccharide per ml from host strains inactivated 50% of the particles of a solution containing 100 PFU/ml after 60 min of incubation at 30 degrees C. Material with receptor activity was extracted from the host strain Anacystis nidulans KM. The extract was purified of glycolipids and pigments, and a fraction showing receptor activity was isolated. This fraction contained three polypeptides of molecular weights between 54,000 and 64,000. Heat and protease treatment of whole cells and of isolated receptor material decreased the receptor activity. The fluorescence intensity of A. nidulans cells labeled with 1-anilino-8-naphthalene sulfonate was increased when AS-1 was adsorbed to these cells. The participation of lipopolysaccharides and proteins in the formation of the receptor complex is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. M. Ultrastructure of the cell wall and cell division of unicellular blue-green algae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):842–852. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.842-852.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzi A., Chance B., Radda G. K., Lee C. P. A fluorescence probe of energy-dependent structure changes in fragmented membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):612–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Adsorption of bacteriophages to adhesions between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):346–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.346-356.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Starkey T. W. The adsorption of bacteriophage phi X174 and its interaction with Escherichia coli; a kinetic and morphological study. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):236–256. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Hantke K. Biochemistry of bacterial cell envelopes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V. Murein-Lipoprotein und Rezeptor für den Phagen T 5 und das Colicin M: Definierte Struktur- und Funktionsbereiche der äusseren Membran von Escherichia coli. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974;228(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schaller K., Wolff H. A common receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golecki J. R. Studies on ultrastructure and composition of cell walls of the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00429627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heil A., Zillig W. Reconstitution of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase from isolated subunits as a tool for the elucidation of the role of the subunits in transcription. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80519-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Changeux J. P., Monnerie L. In vitro interaction of 1-anilino 8 naphthalene sulfonate with excitable membranes isolated from the electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 7;36(3):420–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90581-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Weckesser J., Drews G., Mayer H. Chemical and biological studies on the lipopolysaccharide (O-antigen) of Anacystis nidulans. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jun 20;113(3):247–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00492032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Bacteriophage receptors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:205–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Menzel J., Golecki J. R., Speth V. Lateral mobility and surface density of lipopolysaccharide in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson N. J., Small E. A., Allen M. M. Electron microscopic study of the infection of Anacystis nidulans by the cyanophage AS-1. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall-Hazelbauer L., Schwartz M. Isolation of the bacteriophage lambda receptor from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1436–1446. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1436-1446.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAFFERMAN R. S., MORRIS M. E. GROWTH CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BLUE-GREEN ALGAL VIRUS LPP-1. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:771–775. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.771-775.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safferman R. S., Diener T. O., Desjardins P. R., Morris M. E. Isolation and characterization of AS-1, a phycovirus infecting the blue-green algae, Anacystis nidulans and Synechococcus cedrorum. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer R., Hinnen R., Franklin R. M. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. Properties of the structural proteins and distribution of the phospholipid. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):15–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Connelly M., Sherman D. M. Infection of Synechococcus cedrorum by the cyanophage AS-1M. I. Ultrastructure of infection and phage assembly. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A. Infection of Synechococcus cedrorum by the cyanophage AS-1M. III. Cellular metabolism and phage development. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Pauw P. Infection of Synechococcus cedrorum by the cyanophage AS-1M. II. Protein and DNA synthesis. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):17–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Kunisawa R., Mandel M., Cohen-Bazire G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):171–205. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.171-205.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. The interaction of a naphthalene dye with apomyoglobin and apohemoglobin. A fluorescent probe of non-polar binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):482–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W. Bacterial viruses; with particular reference to adsorption/penetration. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1958;12:27–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.12.100158.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Katz A., Drews G., Mayer H., Fromme I. Lipopolysaccharide containing L-acofriose in the filamentous blue-green alga Anabaena variabilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):672–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.672-678.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidekamm E., Wallach D. F., Fischer H. The effect of phospholipase A upon the interaction of I-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonate with erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 14;241(3):770–778. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weise G., Drews G., Jann B., Jann K. Identification and analysis of a lipopolysaccharide in cell walls of the blue-green alga Anacystis nidulans. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;71(1):89–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00412238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]