Abstract
In female mammals, one of the two X chromosomes becomes genetically silenced to compensate for dosage imbalance of X-linked genes between XX females and XY males. X chromosome inactivation (X-inactivation) is a classical model for epigenetic gene regulation in mammals and has been studied for half a century. In the last two decades, efforts have been focused on the X inactive-specific transcript (Xist) locus, discovered to be the master regulator of X-inactivation. The Xist gene produces a non-coding RNA that functions as the primary switch for X-inactivation, coating the X chromosome from which it is transcribed in cis. Significant progress has been made towards understanding how Xist is regulated at the onset of X-inactivation, but our understanding of the molecular basis of silencing mediated by Xist RNA has progressed more slowly. A picture has, however, begun to emerge, and new tools and resources hold out the promise of further advances to come. Here, we provide an overview of the current state of our knowledge, what is known about Xist RNA and how it may trigger chromosome silencing.
Keywords: X chromosome, Xist RNA, silencing compartment
1. Introduction
The present sex chromosomes in mammals are believed to have evolved from a pair of morphologically identical autosomes. Although this must have directly or indirectly benefited the mechanism for sex determination or efficient reproduction, the advent of two morphologically different sex chromosomes, which generated homogametic and heterogametic animals in the same species, caused an imbalance in the dosage of sex-chromosome-linked genes. To circumvent this, female mammals evolved a mechanism by which one of the two X chromosomes in females is genetically silenced during early development. Since Mary Lyon first described the X chromosome inactivation (X-inactivation) hypothesis in 1961 [1], it has intrigued and occupied many researchers. Significant progress has been made, and X chromosome inactivation now stands as a classical model that illustrates the principles of epigenetic gene regulation in mammals.
The discovery of the X inactive-specific transcript (Xist) gene in the early 1990s [2–6] brought a breakthrough in our understanding of the molecular basis for X-inactivation. Xist was initially identified on the basis of its location in the classically defined master control region for X-inactivation, called the X chromosome inactivation centre (Xic/XIC). The gene was found to be expressed only from the inactive X chromosome and to produce a transcript that does not encode protein, but rather plays a role as a functional RNA that associates in cis with the X chromosome from which it originated. These observations led to the idea that Xist RNA recruits proteins involved in heterochromatinization of the X chromosome. Targeted disruption of Xist unequivocally showed that it is essential for X-inactivation to occur in cis. The X chromosome bearing a null mutation of Xist never undergoes inactivation in the mouse [7] and differentiating female embryonic stem (ES) cells [8], which recapitulate the process of X-inactivation [9,10].
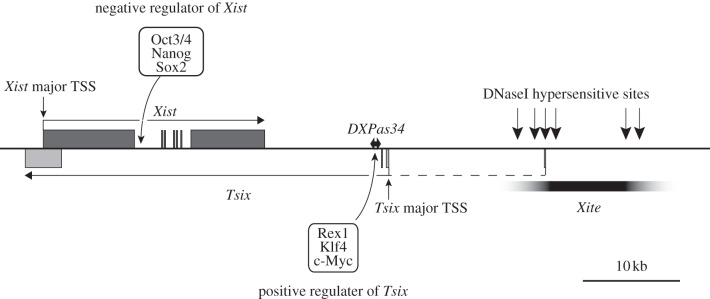
Xist has been at the centre of the studies in X-inactivation during the last two decades. Efforts have been largely directed towards the importance of Xist in X-inactivation and how Xist is differentially regulated between two X chromosomes during development. We have learned that Xist regulation plays a central role in the initiation of X-inactivation [7,8,11,12], and its antisense gene, known as Tsix, negatively regulates Xist in cis through chromatin modifications at the onset of X-inactivation [13–18] (figure 1). Recent studies further propose that the differential expression of Xist is spatio-temporally regulated between two X chromosomes prior to the onset of X-inactivation by a physical association of the Xic region referred to as ‘pairing’, suggesting a means by which two X chromosomes may communicate with one another prior to selecting a single X chromosome for silencing [19,20]. Other studies have suggested that pluripotency factors, which bind their recognition sequences present in potential regulatory regions of Xist and Tsix, balance their expression to suppress or induce X-inactivation in a developmentally regulated manner [21–23]. More recently, an X-linked factor, Rnf12, has been shown to have a role in ensuring that Xist is activated only on a single X chromosome in female cells [24]. A similar function has been attributed to the non-coding RNA (ncRNA) Jpx, produced by a gene located immediately upstream of Xist [25]. These studies have advanced our knowledge about initiation of X-inactivation in early development. On the other hand, although an elegant transgenic approach in ES cells identified functional domains of Xist RNA required for silencing and chromosomal localization [26], the molecular basis of how Xist RNA induces and establishes chromosome-wide silencing has progressed more slowly. This is partly because the extremely long Xist RNA has proved to be relatively intractable to conventional biochemical assays. Additionally, the lack of mutants that express dysfunctional Xist RNA from the endogenous locus has been a factor. Although progress has been slow, a picture has begun to emerge, and new tools and resources hold out the promise of further advances to come. Here we provide an overview of the current state of knowledge, what is known about Xist RNA in terms of functional domains, and how Xist RNA may trigger chromosome silencing. For an overview of progress on regulation of Xist expression, we point readers to other recent reviews [27–29].
Figure 1.
Schematic of the Xist/Tsix locus and the regions known to be bound by pluripotency factors. TSS, transcription start site.
2. Functional domains of Xist RNA
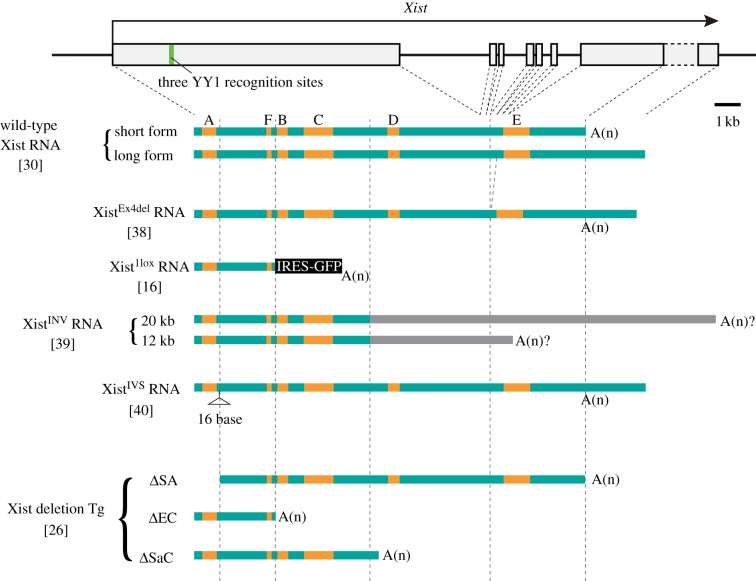
Xist RNA has been generally described as a spliced polyadenylated ncRNA around 17 kb in length. There are two major forms produced through use of alternative termination signals [30]. Xist RNA includes six regions composed of short tandemly arranged repeat sequences, termed A to F, some of which are conserved among species (figure 2). Strauss and co-workers [31] showed that Xist RNA domains or ‘clouds’ seen in the interphase nucleus of female mouse fibroblasts disappear when cells are administered antisense peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) against the C-repeat, but not against the B- and D-repeat. Because steady-state levels of Xist RNA were not affected by PNA treatment, the effect of PNAs appears to be distinct from the transcriptional or posttranscriptional gene silencing caused by siRNA. In addition, the C-repeat PNAs compromise accumulation of Xist RNA on the X chromosome in differentiating female ES cells with an accompanying failure of X-linked gene silencing. A similar effect of locked nucleic acids (LNAs) against the C-repeat was also recently reported [32]. Interestingly, nucleofection of the LNAs against the C-repeat in female embryonic fibroblasts caused a loss of Xist RNA within 1 h, but the effect did not last for long and Xist RNA clouds were reestablished in 8 h. Because there is no change in steady-stated levels of Xist RNA upon LNA treatment, as is the case with PNAs, the antisense LNAs, and also probably PNAs, may displace Xist RNA from the X chromosome. It has not, however, been confirmed by northern blotting whether the RNA stripped off from the X chromosome remains intact. A more recent study using ES cells found that YY1—a multifunctional protein that has been implicated in both activation and repression, probably depending on the context of the complex—bound to the C-repeat of Xist RNA and tethered it to YY1 recognition sites present in exon 1 of the Xist gene (figure 2), creating nucleation sites for Xist RNA [33]. Taken together, these results suggest that the C-repeat is a domain involved in the association of Xist RNA with the X chromosome.
Figure 2.
Structure of mutant Xist RNAs defective in silencing. Mutant Xist RNAs defective in silencing, which are expressed from the endogenous locus in the mouse, are compared with two major forms of wild-type Xist RNA and relevant mutant forms of Xist RNA (ΔSA, ΔEC and ΔSaC) expressed from single copy transgenes in the study by Wutz et al. [26]. Positions of the six regions composed of short tandemly arranged repeat sequences, A to F, are indicated in orange.
To identify regions in the Xist RNA sequence required for chromosome silencing and coating, Wutz et al. [26] developed a way to measure the competency of mutant Xist RNA harbouring various deletions to cause chromosome silencing by doxycycline-induced expression from a single copy transgene on a single X chromosome in male ES cells. The most striking finding in this work was that chromosome silencing is severely compromised by deletion of the A-repeat located in the 5′ region of the RNA (figure 2, ΔSA), suggesting that the A-repeat is a domain critical for Xist RNA-mediated silencing. The A-repeat consists of 7.5–8.5 copies of 26-mer tandem repeats separated by U-rich spacers. Although the mechanism of A-repeat function is currently unknown, possible conformational structures of the A-repeat have been suggested to form a module interacting with proteins required for chromosome silencing [34,35]. An Xist transgene containing a mutation that disrupts the predicted conformation of the A-repeat in vitro has, in fact, been shown to abrogate the silencing in differentiating ES cells [34]. Another study found that a splicing factor, ASF/SF2, binds to the A-repeat in ES cells and that deletion of the repeat compromises proper splicing of Xist RNA and precludes its accumulation, resulting in non-random inactivation of the wild-type X chromosome [36].
The importance of the A-repeat in the endogenous locus has been examined in the mouse. A mutant allele, XistΔA, was produced by gene targeting [37]. Males and females hemizygous and heterozygous, respectively, for XistΔA, which is maternal in origin, were produced but intercrosses between those males hemizygous for XistΔA and wild-type females revealed that the majority of female offspring, all of which should have inherited the XistΔA allele, were lost soon after implantation. Female-specific loss upon paternal transmission of XistΔA was indicative of the failure of imprinted X-inactivation in the extraembryonic tissues, which gives rise to the future placenta and some extraembryonic membranes, suggesting that XistΔA was dysfunctional, similar to null mutation of Xist. Although it was anticipated that this would be attributable to defective silencing by XistΔA RNA, RNA-fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) revealed that expression of Xist RNA from the mutated paternal X was severely compromised and no Xist RNA cloud was observed, not only in the trophoblast of developmentally stunted postimplantation embryos, but also in the preimplantation stage embryos. Although this result was apparently consistent with the study in ES cells described earlier, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) failed to detect expression of Xist per se from the mutated X, suggesting that the genomic sequence encompassing the A-repeat plays an essential role as a cis-element required for proper upregulation of Xist at the onset of X-inactivation. The effect was not observed by Wutz et al. [26] because in those experiments, expression of mutant Xist RNA was driven by a heterologous inducible promoter. Thus, to date, it has not been possible to assess the silencing function of the A-repeat in the mouse embryo. To achieve this, it would be necessary to modify the endogenous gene such that expression of the A-repeat deleted allele could be forced, for example using knock-in of an inducible promoter.
Wutz et al. [26] also reported that deletion of the C-repeat compromises neither the association of the mutant Xist RNA with the X chromosome nor the silencing function of the RNA. This is at variance with the effect of the antisense PNAs and LNAs against the C-repeat. It seems that the antisense PNAs and LNAs have a more severe impact than the deletion of the C-repeat on the association of Xist RNA with the X chromosome. It will be of interest to see what happens to Xist RNA coating and X-inactivation in the mouse embryo if the C-repeat in the endogenous Xist gene is deleted, and also if the antisense RNA against the C-repeat is expressed from an ectopic site. However, it should be commented that the Wutz et al. [26] study indicated that association of Xist RNA with the X chromosome is not mediated by a single domain, but by functionally redundant sequences dispersed along the transcript length.
Four alleles that express mutant forms of Xist RNA from the endogenous locus have been described, and these have furthered our understanding of functional domains in Xist RNA; Caparros et al. [38] deleted exon 4 of Xist because its primary sequence is highly conserved and is potentially able to form a stable RNA stem-loop structure. However, the mutant allele, XistEx4del, was transmitted from the father to female pups at the expected ratio, indicating that the XistEx4del allele is competent to establish imprinted inactivation of the paternal X chromosome in the extraembryonic tissues. In the female pups thus obtained, which are heterozygous for XistEx4del, either the wild-type or the mutated X was inactivated in an essentially random fashion, and in fact no allelic bias was observed in expression at the X-linked loci examined. The results, therefore, demonstrate that exon 4 is dispensable for the function of Xist RNA and the mutant RNA produced by the XistEx4del allele is competent to establish both imprinted and random X-inactivation in the extraembryonic and embryonic lineages, respectively. Steady-state levels of the mutant RNA were, however, diminished, and Xist RNA clouds detected by RNA-FISH were less intense than those formed by the wild-type Xist RNA. Because stability of the mutant RNA did not show significant difference from that of the wild-type RNA, it is likely that the deletion of exon 4 affects transcription rate or processing of Xist RNA. That lower expression of XistEx4del when compared with the wild-type does not seem to affect silencing is consistent with an early study that showed considerable variation in steady-state levels of Xist RNA in different mouse strains. Notably, levels in the wild-derived Mus spretus strain were significantly lower than in laboratory strains [3].
The second mutant allele that produces an aberrant Xist transcript is the Xist1lox allele. Here, a chimeric transcript is produced, consisting of an IRES-EGFP sequence with the proximal 2.3-kb sequence of Xist exon1 under the control of the endogenous Xist promoter [16]. This allele behaves like the null mutant reported by Marahrens et al. [7]. Xist1lox, when paternally transmitted, results in female-specific embryo lethality occurring soon after implantation, indicating a failure of imprinted paternal X-inactivation in the extraembryonic lineages. By contrast, there is no phenotypic defect upon maternal transmission of the mutation and both hemizygous males and heterozygous females for Xist1lox are recovered at the expected ratio.
Several studies have demonstrated that Tsix plays a role in establishing the repressive chromatin modifications at the Xist promoter and represses Xist on the X that stays active at the onset of X-inactivation [16–18]. When the allele Xist1lox was introduced onto an X chromosome deficient for Tsix [16], the Xist1lox allele on the Tsix-deficient X (Xdc) expressed the chimeric RNA at a significant level in both male and female mouse foetuses, despite the fact that Xdc is active. Interestingly, although these foetuses express the chimeric RNA containing the IRES-EGFP sequence, they do not exhibit green fluorescent protein (GFP) fluorescence. The chimeric RNA may fail to be exported to the cytoplasm for translation, possibly due to the intrinsic property of Xist RNA to be retained in the nucleus. In fact, preliminary results suggest that the chimeric transcript expressed from a single X chromosome in mutant male ES cells is found predominantly in the nucleus but not in the cytoplasm (T. Sado 2005, unpublished result). It is tempting to speculate that any RNA transcribed from the Xist locus or RNA containing an Xist sequence is somehow diverted from the mRNA export pathway. Although this chimeric transcript probably stays in the nucleus and harbours the A-repeat, it is defective in silencing. This is most probably due to the fact that the RNA, which contains only the proximal 2.3-kb sequence of Xist RNA and lacks the rest of it, cannot accumulate on the X chromosome. This is consistent with the finding by Wutz et al. [26], who showed that the same 2.3-kb fragment of Xist RNA (figure 1, ΔEC) does not correctly localize on the X chromosome.
Two other mutations that give rise to modified Xist RNA are hypomorphic alleles, XistINV and XistIVS, recently reported by Senner et al. [39] and Hoki et al. [40], respectively. XistINV was generated from XistEx4del by a targeted inversion disrupting conserved sequences beginning 6 kb into exon 1 and extending to intron 5. XistIVS was originally generated for the study of Tsix-mediated antisense regulation of Xist by Ohhata et al. [41]. It contains an exogenously introduced 1 kb intron at 0.9 kb from the major transcription start site. These two mutant alleles are quite distinct from the null mutant alleles previously generated by gene targeting in that they produce RNA that coats the X chromosome in cis and is competent to initiate the inactivation process. Also, these hypomorphic alleles, upon paternal transmission, do not cause severe developmental defects in the extraembryonic lineages until some time after implantation.
Female embryos heterozygous for XistINV of paternal origin are indistinguishable from wild-type male littermates when recovered at E6.5. Growth retardation, however, becomes discernible as early as E7.5, and the further developmental delay is evident by E9.5. Remarkably, these female embryos show no sign of developing a placenta and, as a result, are resorbed by E10.5. Similarly, those female embryos that inherit XistIVS from the father are apparently normal during the early postimplantation stages, and the majority are still essentially indistinguishable from the wild-type male littermates even at E9.5. A subset of the heterozygous females start to show developmental anomalies from E10.5 onwards and many are lost by E13.5. Some, however, continue to develop and can even survive to term. Histological analysis demonstrated that the trophoblast giant cells are the major tissue affected in +/XistIVS females. Thus, lethality caused by paternal transmission of the XistIVS and XistINV mutations is apparently ascribed to aberrant inactivation of the paternal X chromosome in the extraembryonic lineages. However, because the effects of mutation become apparent earlier in +/XistINV females than +/XistIVS, it is likely that effects of the respective mutations are more severe in the former than in the latter.
The XistINV allele produces two distinct transcripts of 12 and 20 kb in length. In both, only the proximal 6-kb sequences are shared with wild-type Xist RNA (figure 2). Expression levels of the respective transcripts, when compared by northern blotting, are lower than those of wild-type Xist in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). XistINV RNA clouds, although detectable by RNA-FISH in the extraembryonic and embryonic tissues, are significantly diminished when compared with the wild-type Xist RNA clouds. This, however, is also the case for XistEx4del RNA, which silences the X chromosome quite efficiently. Analysis of Xist RNA on metaphase chromosomes is, however, needed to determine whether or not binding occurs strictly in cis with the X chromosome, and here there was a clear difference with XistEx4del RNA binding being similar to wild-type Xist RNA and XistINV RNA being barely detectable. This observation suggests that XistINV RNA is in some way defective in localizing on the X chromosome in cis, and this is probably the underlying basis of aberrant X-inactivation. Consistent with this interpretation, H2A monoubiquitylated at lysine 119 (H2AK119u1), deposition of which on the inactive X is dependent on Xist RNA, was strongly reduced in cells expressing XistINV RNA.
XistINV RNA may be viewed to be a chimeric RNA composed of a proximal 6-kb fragment of Xist connected to an unrelated 6-kb or 14-kb fragment, although the additional linked sequences actually correspond to the antisense strand of Xist genomic sequence. Assuming that the exogenous sequences do not impact on the function of the chimeric RNA, it can be concluded that the proximal 6-kb fragment of Xist RNA is responsible for the partial silencing function of XistINV. This would be consistent with a previous observation that truncated Xist RNA, which corresponds to a sequence similar to but not exactly the same as the distal 6-kb fragment of XistINV RNA, was less efficient in not only silencing but also chromosomal association when compared with the full length Xist RNA [26] (figure 2, ΔSaC). It will be interesting in the future to determine if chromatin markers other than H2AK119u1 are affected when the chromosome is coated with XistINV RNA and also to examine their distribution relative to a normal inactive X chromosome.
In contrast to the XistINV allele, the XistIVS allele produces essentially the same RNA as wild-type Xist except for an insertion of an unrelated 16-base sequence at 0.9 kb from the 5′ end associated with introduction of an exogenous intron. Expression levels and stability of the RNA arising from the XistIVS allele is comparable to the wild-type Xist RNA in trophoblast stem (TS) cells. XistIVS RNA coats the X chromosome in cis with an intensity similar to wild-type Xist RNA and apparently can recruit the machinery responsible for histone H3 trimethylated at lysine 27 (H3K27me3) in TS cells. In addition, these TS cells contain an asynchronously replicating X chromosome, a cytogenetic correlate of the inactive X chromosome. Presumably this corresponds to the chromosome bearing the expressed XistIVS allele. Collectively these observations indicate that the mutated X chromosome carrying XistIVS has undergone proper inactivation in TS cells. A subset of cells, however, lose XistIVS RNA and the inactive X associated histone modification H3K27me3 when TS cells are induced to differentiate. Furthermore, microarray analysis revealed that expression levels of X-linked genes become widely misregulated upon differentiation. Although the global misregulation became evident only after induction of differentiation, a small fraction of X-linked genes were not properly repressed even in the undifferentiated state. These results suggest that XistIVS can initiate X-inactivation but is deficient in maintaining the inactivated state. Given that the H3K27me3 domain excludes active chromatin modifications such as H3K4me2 and H4Ac, the silent domain has apparently formed in response to the accumulation of XistIVS RNA in the nucleus of undifferentiated mutant TS cells.
A loss of XistIVS clouds seen in a subset of differentiated TS cells could be due to either dissociation of the RNA from the X chromosome or transcriptional repression of the XistIVS allele. Since qRT-PCR showed that relative expression levels of Xist were reduced after differentiation of TS cells carrying the paternal XistIVS but unchanged in wild-type, it is unlikely that XistIVS RNA simply dissociates from the chromosome. Assuming that the observed effect is due to transcriptional inhibition of XistIVS, the presence of an exogenously introduced intron in exon 1 could be causal. In this scenario, the XistIVS phenotype may not reflect defective silencing by the mutant RNA but rather failure to maintain Xist RNA expression in a subset of cells. It may be relevant that the extra intron in the XistIVS allele is inserted at 0.3 kb upstream of the three potential YY1 binding sites, which have been suggested to function as an enhancer [42]. More recently, these YY1 sites were found to be the sites for touchdown of Xist RNA bound by YY1 [33]. However, it is also possible that the XistIVS deficiencies are attributable to loss of function of the RNA product. The insertion of the 16-base sequence may directly or indirectly compromise an interaction between XistIVS RNA and factors that are critical for the stable association of Xist RNA on the X chromosome. Alternatively, the insertion may partially compromise the function of the A-repeat that contributes both to silencing and localization on the X chromosome. Finally, it is possible that the 16-base insertion disrupts a previously unidentified silencing element in Xist RNA.
3. Role of Xist RNA in X chromosome silencing
The inactive X chromosome coated with Xist RNA is often found to reside at the periphery of the interphase nucleus to form the Barr body. An early study showed that Xist RNA remains with the nuclear scaffold or matrix fraction after removal of chromatin by DNaseI digestion and salt extraction [43]. This implied that the association of Xist RNA with chromatin of the X chromosome was not mediated by hybridization of DNA and RNA, but probably by an interaction with a protein(s). The finding that scaffold attachment factor-A (SAF-A), also termed hnRNP U, one of the major components of the nuclear scaffold, is enriched on the inactive X chromosome in human and mouse female cells [44,45] suggested a potential role for this protein in targeting of the inactive X to the nuclear periphery via association with Xist RNA. In fact, SAF-A contains two distinct domains, a SAF box and RGG domain, that have been shown to mediate SAF-A binding to DNA and RNA, respectively [44,46]. A more recent study showed that knockdown of SAF-A in mouse tissue culture cells breaks up the Xist cloud, resulting in a more dispersed nuclear signal, suggesting that SAF-A is responsible for the retention of Xist RNA on the inactive X chromosome [47]. Interestingly, of the long and short forms of Xist RNA (figure 2) detected on a northern blot, only the former is selectively diminished after a depletion of SAF-A, suggesting that while the long form is unstable and readily degraded after dissociation from the inactive X, the short form is relatively stable and thereby detectable as dispersed signals in the nucleus. Given that Xist RNA is polyadenylated only in the short form but not in the long form [30], stability of the dissociated Xist RNA appears to depend on the presence or absence of a poly(A) tail. It should be commented that the functional difference between the long and short form is unknown. While it appears that the association of Xist RNA with the inactive X chromosome depends on the presence of SAF-A, another study showed that the loss of Xist RNA resulted in loss of SAF-A from the inactive X and, therefore, localization of SAF-A is apparently dependent on the presence of Xist RNA [45]. Thus, although a potential role of SAF-A in compartmentalization of the inactive X chromosome is attractive, the picture is currently complicated and further studies are required.
Several lines of evidence suggest that Xist RNA recruits epigenetic modifiers to the inactive X chromosome, among which Polycomb group (PcG) proteins have been most intensively studied. The importance of PcG proteins in X-inactivation is suggested by the fact that the inactive X chromosome is enriched with H3K27me3 and H2AK119u1, which are posttranslational modifications mediated by Polycomb repressive complex (PRC) 2 and 1, respectively [48–51]. The recruitment of PRC2 complex in X-inactivation has been attributed to direct biochemical interaction of the catalytic subunit of the complex, Ezh2, with the A-repeats of Xist RNA [52] Mapping of the candidate RNA interaction domain of Ezh2 suggested that RNA binding requires site specific phosphorylation of Ezh2 [53]. Further to this, others have described an interaction between a different subunit of PRC2, Suz12, and Xist A-repeats [54]. To date these interactions have been demonstrated largely using in vitro assays, and given that none of the PRC2 subunits have a classical RNA binding domain, it will be important in the future to rule out non-specific interactions of Xist A-repeat with charged patches on the surface of either Ezh2 or Suz12 proteins. A key experiment will be to identify amino acids required for interaction with A-repeat RNA in vitro and then test mutant proteins for their ability to associate with the inactive X chromosome in XX cells in vivo.
It was initially thought that recruitment of PRC1 complex to the inactive X is solely attributable to binding of the chromodomain of the core PRC1 subunit, CBX2/4/7/8, to H3K27me3 mediated by PRC2 [50,51]. However, it has been shown that PRC1 complexes and associated H2AK119u1 are enriched on the inactive X in the absence of PRC2 and H3K27me3 [55]. In a recent study, H3K27me3 independent recruitment of PRC1 has been shown to be attributable to distinct PRC1 like complexes, RYBP-PRC1, in which the protein RYBP is included [56]. Both CBX family proteins and another core PRC1 subunit, MPH1/2/3, are excluded from RYBP-PRC1. The existence of an H3K27me3 independent pathway for PRC1 recruitment to the inactive X raises further challenges in terms of understanding interactions between Xist RNA and PcG proteins.
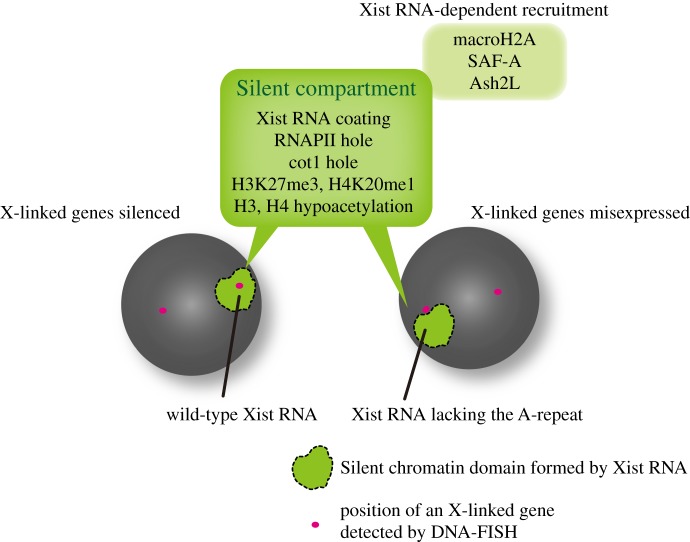
Interestingly, the X chromosome coated with Xist RNA lacking the A-repeat, which is defective in silencing, manifests the enrichment of H3K27me3 and H2AK119u1in differentiating ES cells, albeit at a reduced level [52,55]. This implies that PcG recruitment is not synonymous with gene silencing on the inactive X [57]. This may indicate that elements in Xist RNA other than the A-repeats have the capacity to recruit PcG complexes. Alternatively, PcG recruitment may be secondary to other changes on the inactive X that are conferred both by wild-type and by A-repeat deficient Xist RNA. The domain corresponding to the Xist cloud has also been shown to exclude active epigenetic modifications such as acetylation of core histones and also RNA polymerase II (RNAPII), suggesting that a transcriptionally silent domain or compartment is formed by the accumulation of Xist RNA (figure 3). Interestingly, RNAPII exclusion is also observed in response to expression of Xist RNA lacking the A-repeat [58], suggesting that a transcriptionally silent domain is still formed. Consistent with this, a more recent study demonstrated that expression of Xist RNA lacking the A-repeat is associated with a reduction in the active chromatin modifications H4 acetylation and H3K4 methylation, as detected at the cytogenetic level [45].
Figure 3.
Silencing-defective Xist RNA lacking the A-repeat can form a silent chromatin domain. Repressed X-linked gene loci are included in the silent chromatin domain formed by wild-type Xist RNA (left). Silencing-defective Xist RNA lacking the A-repeat can form a silent compartment, characterized by enrichments of macroH2A, SAF-A and Ash2L as well as typical repressive epigenetic modifications, but fails to incorporate the X-linked gene loci into the silent compartment (right).
DNA-FISH using X-linked sequences showed that while repetitive sequences on the X chromosome are included in the domain of Xist RNA lacking the A-repeat, genic regions are often found outside or at the periphery of the domain [58]. These findings raise the idea that one role of Xist RNA is to create a transcriptionally silent domain that represses repetitive sequences by recruiting PRCs and by excluding RNAPII in a manner independent of A-repeat function, and a second role is to incorporate genic regions on the X chromosome from outside or at the periphery of the Xist RNA domain into the interior in a manner dependent on the A-repeat. Therefore, silencing depends on whether or not genes are translocated into the Xist RNA domain (figure 3). It will be important to elucidate how the silent domain is formed by the accumulation of Xist RNA in order to establish how Xist RNA induces silencing.
It has been shown using a conditional allele of Xist that the inactive X chromosome in female MEFs can maintain the inactive state even after Xist RNA has been removed [59]. This was consistent with an earlier finding that a human inactive X chromosome does not require the XIC for maintenance of X-inactivation once the inactive state is established in human cultured cells [60]. That the loss of XistIVS RNA in differentiating TS cells appears to facilitate reactivation of the hitherto inactive X seems to run counter to the idea that Xist is not required to maintain X-inactivation in differentiated cells. A recent study, however, demonstrates that maintenance of X-inactivation is Xist-RNA-dependent in some differentiated cell types [61]. Ohhata et al. [61] showed that induced expression of Tsix by doxycycline could counteract Xist and shut it off in the visceral endoderm, leading to reactivation of the X-linked GFP transgene that had been repressed on the inactive X chromosome. This effect was not seen in the trophoblastic lineages. These observations imply that, contrary to the prevailing view, there is a lineage-specific difference in Xist RNA-dependency for the maintenance of X-inactivation, and that some of the extraembryonic tissues may require Xist RNA to maintain the silent state. In fact, it has been demonstrated that Xist RNA, DNA methylation and histone hypoacetylation synergistically contribute to the maintenance of the inactive X chromosome in female MEFs [62]. Given that DNA methylation seems to be less important for the maintenance of X-inactivation in the extraembryonic lineages than in the embryonic lineage [63], it may be reasonable to assume that the extraembryonic lineages depend more on Xist RNA than the embryonic lineage.
4. Rsx, an Xist-like molecule in marsupials
Mammalian species in which Xist homologues have been identified have provided a useful resource for defining conserved and hence potentially important sequences and features of Xist RNA. In marsupial mammals, X-inactivation resembles that of eutherian mammals in many, albeit not all, aspects (table 1). With this in mind, it was assumed for a considerable time that marsupials have an Xist homologue. This however has been shown not to be the case [78]. Specifically, the Xist gene appears to have evolved from the protein-coding gene Lnx3, which in marsupials retains normal protein coding capacity and is expressed in both sexes. It was further shown that the evolution of Xist RNA involved acquisition of sequences from common repeat elements present in ancestral lineages [79]. It follows that marsupials must have evolved their X-inactivation mechanism independently. A recent study has described a marsupial cis-acting ncRNA, termed Rsx (RNA on the silent X), that appears to be equivalent to Xist RNA in eutherians [64].
Table 1.
Similarities and differences in X-inactivation in marsupials.
| eutherian | marsupial | references | |
|---|---|---|---|
| cis-acting ncRNA | Xist | Rsx | [64] |
| paternal X only or random | both | paternal X only | [65] |
| completeness/stability | high | variablea | [66–68] |
| barr body | yes | yesb | |
| late replication of inactive X | yes | yes | [69,70] |
| H3/H4 hypoacetylation | yes | yes | [71] |
| PRC2 and H3K27me3 | yes | yes | [68,72] |
| PRC1 and H2AK119u1 | yes | nt | |
| RNAPII depletion | yes | yes | [72] |
| H3K4me2 depletion | yes | yes | [72,73] |
| H3K9me2 | yes | yes | [72] |
| H3K9me3 | noc | yes | [72–74] |
| H4K20me1 | yes | no | [72] |
| H4K20me3 | no | yes | [72,73] |
| MacroH2A | yes | nt | |
| CpG island methylation | yes | no | [75,76] |
aInstability observed in tissue culture cells but not in tissues.
bDAPI dense structure observed in various studies.
cHas been observed in some species [77].
Rsx shares a number of key properties with Xist. The locus transcribes a large RNA that is spliced and polyadenylated, lacks obvious protein coding potential and is only expressed in females. Rsx expression leads to formation of RNA clouds in the interphase nucleus resembling those produced by Xist RNA. Similar to Xist, Rsx sequence includes multiple copies of simple repeat sequences that may form stem-loop structures resembling those predicted to be formed by Xist A-repeats. Strikingly, expression of Rsx in a mouse ES cell line leads to formation of an RNA cloud and, moreover, following differentiation of the ES cells, genes localized on the same chromosome, in cis with the Rsx transgene, are silenced. This is similar to human XIST transgenes in mouse ES cells that also silence only following in vitro differentiation [80], although differentiation is not required for silencing by mouse Xist RNA in mouse ES cells [81].
Despite the obvious similarity of Rsx and Xist, it is clear that Rsx arose entirely independently in the marsupial lineage, a remarkable example of convergent evolution. That chromatin modifications of the marsupial inactive X closely resemble those seen in eutherians (table 1), together with the fact that Rsx can function in mouse ES cells, suggests that the mechanism by which these ncRNAs silence the chromosome could be related. Marsupial X-inactivation is different in some respects, notably it is always the paternal X that is inactivated, silencing is relatively unstable in marsupial tissue culture cells, and, possibly linked to this, there is apparently no DNA methylation at CpG islands of genes on the marsupial inactive X chromosome [66,75]. It remains to be determined whether these reflect fundamental differences in mechanism or only in detail. If the silencing mechanism is indeed shared, then the discovery of Rsx offers an unprecedented opportunity to further elucidate the mechanism of Xist-mediated silencing in eutherians.
5. Concluding remarks
One of the most important unanswered questions in the X-inactivation field is, how does Xist RNA mediate chromosome silencing? One can predict that Xist RNA recruits specific proteins required for gene silencing and heterochromatinization and, in fact, a number of such proteins have been shown to localize on the inactive X chromosome (table 2). For some of these proteins, X chromosome localization has been found to depend on the presence of Xist RNA, although it should be noted that this does not discriminate between direct and indirect recruitment. Other proteins localizing to the inactive X have not yet been tested for Xist RNA dependency and it will be important in the future to establish this. However, it is likely that key factors required for silencing have yet to be identified. This is suggested both from genetic analysis of the known X-inactivation factors, and also because with the exception of SAF-A/hnRNPU, none of the these factors has a known bona fide RNA binding domain, a feature that would be predicted to occur in critical factors that interact directly with Xist RNA.
Table 2.
Proteins known to localize on the inactive X chromosome.
A further point relating to this is that although Xist RNA lacking the A-repeat is defective in silencing, it can bring about recruitment of PRC1 and PRC2 to the inactive X chromosome, and in addition can establish chromosome wide loss of H4 acetylation and H3K4 methylation. A-repeat deficient RNA is also able to recruit macroH2A, SAF-A and Ash2L [45]. Either these proteins interact with regions of Xist RNA other than the A-repeats or their recruitment is secondary to the establishment of a transcriptionally silent domain that occurs using A-repeat deficient transgenes [58]. As discussed earlier, it has been suggested that the silent domain corresponds to common repeat sequences on the X chromosome and it follows that these could also be the site of recruitment of other factors. Thus, the function of the A-repeats would be to allow the silencing factors to spread from common repeat elements into genes.
Acknowledgements
We thank colleagues in the field for discussions and apologise to those whose results we were unable to cover owing to space constraints. We thank James Turner for providing advanced access to his results. Takashi Sado is funded by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan. Neil Brockdorff is funded by the Wellcome Trust (grant no. 081385).
References
- 1.Lyon MF. 1961. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature 190, 372–373 10.1038/190372a0 (doi:10.1038/190372a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Grompe M, Tonlorenzi R, Willard HJ. 1991. A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 349, 38–44 10.1038/349038a0 (doi:10.1038/349038a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brockdorff N, et al. 1991. Conservation of position and exclusive expression of mouse Xist from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 351, 329–331 10.1038/351329a0 (doi:10.1038/351329a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Borsani G, et al. 1991. Characterization of a murine gene expressed from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 351, 325–329 10.1038/351325a0 (doi:10.1038/351325a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brown CJ, Hendrich BD, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Xing Y, Lawrence J, Willard HF. 1992. The human XIST gene: analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell 71, 527–542 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90520-M (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90520-M) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brockdorff N, Ashworth A, Kay GF, McCabe VM, Norris DP, Cooper PJ, Swift S, Rastan S. 1992. The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell 71, 515–526 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90519-I (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90519-I) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Marahrens Y, Panning B, Dausman J, Strauss W, Jaenisch R. 1997. Xist-deficient mice are defective in dosage compensation but not spermatogenesis. Genes Dev. 11, 156–166 10.1101/gad.11.2.156 (doi:10.1101/gad.11.2.156) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Penny GD, Kay GF, Sheardown SA, Rastan S, Brockdorff N. 1996. Requirement for Xist in X chromosome inactivation. Nature 379, 131–137 10.1038/379131a0 (doi:10.1038/379131a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sheardown SA, et al. 1997. Stabilization of Xist RNA mediates initiation of X chromosome inactivation. Cell 91, 99–107 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)80012-X (doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)80012-X) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Panning B, Jaenisch R. 1996. DNA hypomethylation can activate Xist expression and silence X-linked genes. Genes Dev. 10, 1991–2002 10.1101/gad.10.16.1991 (doi:10.1101/gad.10.16.1991) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Herzing LBK, Romer JT, Horn JM, Ashworth A. 1997. Xist has properties of the X-chromosome inactivation centre. Nature 386, 272–275 10.1038/386272a0 (doi:10.1038/386272a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee J, Strauss WM, Dausman JA, Jaenisch R. 1996. A 450 kb transgene displays properties of the mammalian X-inactivation center. Cell 86, 83–94 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80079-3 (doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80079-3) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee J, Davidow LS, Warshawsky D. 1999. Tsix, a gene antisense to Xist at the X-inactivation centre. Nat Genet. 21, 400–404 10.1038/7734 (doi:10.1038/7734) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee JT. 2000. Disruption of imprinted X inactivation by parent-of-origin effects at Tsix. Cell 103, 17–27 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00101-X (doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00101-X) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sado T, Wang Z, Sasaki H, Li E. 2001. Regulation of imprinted X-chromosome inactivation in mice by Tsix. Development 128, 1275–1286 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sado T, Hoki Y, Sasaki H. 2005. Tsix silences Xist through modification of chromatin structure. Dev Cell. 9, 159–165 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.05.015 (doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2005.05.015) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Navarro P, Pichard S, Ciaudo C, Avner P, Rougeulle C. 2005. Tsix transcription across the Xist gene alters chromatin conformation without affecting Xist transcription: implications for X-chromosome inactivation. Genes Dev. 19, 1474–1484 10.1101/gad.341105 (doi:10.1101/gad.341105) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sun BK, Deaton AM, Lee JT. 2006. A transient heterochromatic state in Xist preempts X inactivation choice without RNA stabilization. Mol. Cell. 21, 617–628 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.028 (doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.028) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bacher CP, Guggiari M, Brors B, Augui S, Clerc P, Avner P, Elis R, Heard E. 2006. Transient colocalization of X-inactivation centres accompanies the initiation of X inactivation. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 293–299 10.1038/ncb1365 (doi:10.1038/ncb1365) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xu N, Tsai CL, Lee JT. 2006. Transient homologous chromosome pairing marks the onset of X inactivation. Science 311, 1149–1152 10.1126/science.1122984 (doi:10.1126/science.1122984) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Navarro P, Chambers I, Karwacki-Neisius V, Chureau C, Morey C, Rougeulle C, Avner P. 2008. Molecular coupling of Xist regulation and pluripotency. Science 321, 1693–1695 10.1126/science.1160952 (doi:10.1126/science.1160952) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Navarro P, et al. 2010. Molecular coupling of Tsix regulation and pluripotency. Nature 468, 457–460 10.1038/nature09496 (doi:10.1038/nature09496) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Donohoe ME, Silva SS, Pinter SF, Xu N, Lee JT. 2009. The pluripotency factor Oct4 interacts with Ctcf and also controls X-chromosome pairing and counting. Nature 460, 128–132 10.1038/nature08098 (doi:10.1038/nature08098) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jonkers I, Barakat TS, Achame EM, Monkhorst K, Kenter A, Rentmeester E, Grosveld F, Grootegoed JA, Gribnau J. 2009. RNF12 is an X-encoded dose-dependent activator of X chromosome inactivation. Cell 139, 999–1011 10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.034 (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.034) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tian D, Sun S, Lee JT. 2010. The long noncoding RNA, Jpx, is a molecular switch for X chromosome inactivation. Cell 143, 390–403 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.049 (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.049) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wutz A, Rasmussen TP, Jaenisch R. 2002. Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA. Nat. Genet. 30, 167–174 10.1038/ng820 (doi:10.1038/ng820) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Barakat TS, Jonkers I, Monkhorst K, Gribnau J. 2010. X-changing information on X inactivation. Exp. Cell Res. 316, 679–687 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.01.015 (doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.01.015) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jeon Y, Sarma K, Lee JT. 2012. New and Xisting regulatory mechanisms of X chromosome inactivation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 22, 62–71 10.1016/j.gde.2012.02.007 (doi:10.1016/j.gde.2012.02.007) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brockdorff N. 2011. Chromosome silencing mechanisms in X-chromosome inactivation: unknown unknowns. Development 138, 5057–5065 10.1242/dev.065276 (doi:10.1242/dev.065276) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ma M, Strauss WM. 2005. Analysis of the Xist RNA isoforms suggests two distinctly different forms of regulation. Mamm. Genome 16, 391–404 10.1007/s00335-004-2464-3 (doi:10.1007/s00335-004-2464-3) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Beletskii A, Hong YK, Pehrson J, Egholm M, Strauss WM. 2001. PNA interference mapping demonstrates functional domains in the noncoding RNA Xist. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9215–9220 10.1073/pnas.161173098 (doi:10.1073/pnas.161173098) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sarma K, Levasseur P, Aristarkhov A, Lee JT. 2010. Locked nucleic acids (LNAs) reveal sequence requirements and kinetics of Xist RNA localization to the X chromosome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 22 196–22 201 10.1073/pnas.1009785107 (doi:10.1073/pnas.1009785107) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jeon Y, Lee JT. 2011. YY1 tethers Xist RNA to the inactive X nucleation center. Cell 146, 119–133 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.026 (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.026) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Duszczyk MM, Wutz A, Rybin V, Sattler M. 2011. The Xist RNA A-repeat comprises a novel AUCG tetraloop fold and a platform for multimerization. RNA 17, 1973–1982 10.1261/rna.2747411 (doi:10.1261/rna.2747411) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Maenner S, et al. 2010. 2-D structure of the A region of Xist RNA and its implication for PRC2 association. PLoS Biol. 8, e1000276. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000276 (doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000276) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Royce-Tolland ME, Andersen AA, Koyfman HR, Talbot DJ, Wutz A, Tonks ID, Kay GF, Panning B. 2010. The A-repeat links ASF/SF2-dependent Xist RNA processing with random choice during X inactivation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 948–954 10.1038/nsmb.1877 (doi:10.1038/nsmb.1877) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hoki Y, Kimura N, Kanbayashi M, Amakawa Y, Ohhata T, Sasaki H, Sado T. 2009. A proximal conserved repeat in the Xist gene is essential as a genomic element for X-inactivation in mouse. Development 136, 139–146 10.1242/dev.026427 (doi:10.1242/dev.026427) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Caparros ML, Alexiou M, Webster Z, Brockdorff N. 2002. Functional analysis of the highly conserved exon IV of Xist RNA. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 99, 99–105 10.1159/000071580 (doi:10.1159/000071580) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Senner CE, Nesterova TB, Norton S, Dewchand H, Godwin J, Mak W, Brockdorff N. 2011. Disruption of a conserved region of Xist exon 1 impairs Xist RNA localisation and X-linked gene silencing during random and imprinted X chromosome inactivation. Development 138, 1541–1550 10.1242/dev.056812 (doi:10.1242/dev.056812) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hoki Y, Ikeda R, Mise N, Sakata Y, Ohhata T, Sasaki H, Sado T. 2011. Incomplete X-inactivation initiated by a hypomorphic Xist allele in the mouse. Development 138, 2649–2659 10.1242/dev.061226 (doi:10.1242/dev.061226) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ohhata T, Hoki Y, Sasaki H, Sado T. 2008. Crucial role of antisense transcription across the Xist promoter in Tsix-mediated Xist chromatin modification. Development 135, 227–235 10.1242/dev.008490 (doi:10.1242/dev.008490) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kim JD, Hinz AK, Bergmann A, Huang JM, Ovcharenko I, Stubbs L, Kim J. 2006. Identification of clustered YY1 binding sites in imprinting control regions. Genome Res. 16, 901–911 10.1101/gr.5091406 (doi:10.1101/gr.5091406) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Clemson CM, McNeil JA, Willard HF, Lawrence JB. 1996. XIST RNA paints the inactive X chromosome at interphase: evidence for a novel RNA involved in nuclear/chromosome structure. J. Cell Biol. 132, 259–275 10.1083/jcb.132.3.259 (doi:10.1083/jcb.132.3.259) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Helbig R, Fackelmayer FO. 2003. Scaffold attachment factor A (SAF-A) is concentrated in inactive X chromosome territories through its RGG domain. Chromosoma 112, 173–182 10.1007/s00412-003-0258-0 (doi:10.1007/s00412-003-0258-0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pullirsch D, Hartel R, Kishimoto H, Leeb M, Steiner G, Wutz A. 2010. The Trithorax group protein Ash2l and Saf-A are recruited to the inactive X chromosome at the onset of stable X inactivation. Development 137, 935–943 10.1242/dev.035956 (doi:10.1242/dev.035956) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kipp M, Gohring F, Ostendorp T, van Drunen CM, van Driel R, Przybylski M, Fackelmayer FO. 2000. SAF-Box, a conserved protein domain that specifically recognizes scaffold attachment region DNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 7480–7489 10.1128/MCB.20.20.7480-7489.2000 (doi:10.1128/MCB.20.20.7480-7489.2000) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hasegawa Y, Brockdorff N, Kawano S, Tsutui K, Nakagawa S. 2010. The matrix protein hnRNP U is required for chromosomal localization of Xist RNA. Dev. Cell 19, 469–476 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.08.006 (doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.08.006) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Plath K, et al. 2003. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in X inactivation. Science 300, 131–135 10.1126/science.1084274 (doi:10.1126/science.1084274) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Silva J, et al. 2003. Establishment of histone h3 methylation on the inactive X chromosome requires transient recruitment of Eed-Enx1 polycomb group complexes. Dev. Cell 4, 481–495 10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00068-6 (doi:10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00068-6) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fang J, Chen T, Chadwick B, Li E, Zhang Y. 2004. Ring1b-mediated H2A ubiquitination associates with inactive X chromosomes and is involved in initiation of X inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 52 812–52 815 10.1074/jbc.C400493200 (doi:10.1074/jbc.C400493200) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.de Napoles M, et al. 2004. Polycomb group proteins ring1A/B link ubiquitylation of histone H2A to heritable gene silencing and X inactivation. Dev. Cell 7, 663–676 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.005 (doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2004.10.005) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhao J, Sun BK, Erwin JA, Song JJ, Lee JT. 2008. Polycomb proteins targeted by a short repeat RNA to the mouse X chromosome. Science 322, 750–756 10.1126/science.1163045 (doi:10.1126/science.1163045) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kaneko S, Li G, Son J, Xu CF, Margueron R, Neubert TA, Reinberg D. 2010. Phosphorylation of the PRC2 component Ezh2 is cell cycle-regulated and up-regulates its binding to ncRNA. Genes Dev. 24, 2615–2620 10.1101/gad.1983810 (doi:10.1101/gad.1983810) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kanhere A, et al. 2010. Short RNAs are transcribed from repressed polycomb target genes and interact with polycomb repressive complex-2. Mol. Cell 38, 675–688 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.019 (doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.03.019) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Leeb M, Wutz A. 2007. Ring1B is crucial for the regulation of developmental control genes and PRC1 proteins but not X inactivation in embryonic cells. J. Cell Biol. 178, 219–229 10.1083/jcb.200612127 (doi:10.1083/jcb.200612127) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tavares L, et al. 2012. RYBP-PRC1 complexes mediate H2A ubiquitylation at polycomb target sites independently of PRC2 and H3K27me3. Cell 148, 664–678 10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.029 (doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.029) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kohlmaier A, Savarese F, Lachner M, Martens J, Jenuwein T, Wutz A. 2004. A chromosomal memory triggered by Xist regulates histone methylation in X inactivation. PLoS Biol. 2, E171. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020171 (doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020171) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chaumeil J, Le Baccon P, Wutz A, Heard E. 2006. A novel role for Xist RNA in the formation of a repressive nuclear compartment into which genes are recruited when silenced. Genes Dev. 20, 2223–2237 10.1101/gad.380906 (doi:10.1101/gad.380906) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Csankovszki G, Panning B, Bates B, Pehrson JR, Jaenisch R. 1999. Conditional deletion of Xist disrupts histone macroH2A localization but not maintenance of X inactivation. Nat. Genet. 22, 323–324 10.1038/11887 (doi:10.1038/11887) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Brown CJ, Willard HF. 1994. The human X-inactivation centre is not required for maintenance of X-chromosome inactivation. Nature 368, 154–156 10.1038/368154a0 (doi:10.1038/368154a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ohhata T, Senner CE, Hemberger M, Wutz A. 2011. Lineage-specific function of the noncoding Tsix RNA for Xist repression and Xi reactivation in mice. Genes Dev. 25, 1702–1715 10.1101/gad.16997911 (doi:10.1101/gad.16997911) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Csankovszki G, Nagy A, Jaenisch R. 2001. Synergism of Xist RNA, DNA methylation, and histone hypoacetylation in maintaining X chromosome inactivation. J. Cell Biol. 153, 773–784 10.1083/jcb.153.4.773 (doi:10.1083/jcb.153.4.773) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sado T, Fenner MH, Tan SS, Tam P, Shioda T, Li E. 2000. X inactivation in the mouse embryo deficient for Dnmt1: distinct effect of hypomethylation on imprinted and random X inactivation. Dev. Biol. 225, 294–303 10.1006/dbio.2000.9823 (doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9823) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Grant J, et al. 2012. Rsx, an RNA that exhibits properties consistent with a role in X-chromosome inactivation in metatherian mammals. Nature 487, 254–258 10.1038/nature11171 (doi:10.1038/nature11171) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cooper DW, VandeBerg JL, Sharman GB, Poole WE. 1971. Phosphoglycerate kinase polymorphism in kangaroos provides further evidence for paternal X inactivation. Nat. New Biol. 230, 155–157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kaslow DC, Migeon BR. 1987. DNA methylation stabilizes X chromosome inactivation in eutherians but not in marsupials: evidence for multistep maintenance of mammalian X dosage compensation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 84, 6210–6214 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6210 (doi:10.1073/pnas.84.17.6210) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Al Nadaf S, Waters PD, Koina E, Deakin JE, Jordan KS, Graves JA. 2010. Activity map of the tammar X chromosome shows that marsupial X inactivation is incomplete and escape is stochastic. Genome Biol. 11, R122. 10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r122 (doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r122) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Mahadevaiah SK, Royo H, VandeBerg JL, McCarrey JR, Mackay S, Turner JM. 2009. Key features of the X inactivation process are conserved between marsupials and eutherians. Curr. Biol. 19, 1478–1484 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.041 (doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.041) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Graves JA. 1967. DNA synthesis in chromosomes of cultured leucocytes from two marsupial species. Exp. Cell Res. 46, 37–57 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90407-7 (doi:10.1016/0014-4827(67)90407-7) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sharman GB. 1971. Late DNA replication in the paternally derived X chromosome of female kangaroos. Nature 230, 231–232 10.1038/230231a0 (doi:10.1038/230231a0) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wakefield MJ, Keohane AM, Turner BM, Graves JA. 1997. Histone underacetylation is an ancient component of mammalian X chromosome inactivation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9665–9668 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9665 (doi:10.1073/pnas.94.18.9665) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chaumeil J, Waters PD, Koina E, Gilbert C, Robinson TJ, Graves JA. 2011. Evolution from XIST-independent to XIST-controlled X-chromosome inactivation: epigenetic modifications in distantly related mammals. PLoS ONE 6, e19040. 10.1371/journal.pone.0019040 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019040) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Rens W, Wallduck MS, Lovell FL, Ferguson-Smith MA, Ferguson-Smith AC. 2010. Epigenetic modifications on X chromosomes in marsupial and monotreme mammals and implications for evolution of dosage compensation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 17 657–17 662 10.1073/pnas.0910322107 (doi:10.1073/pnas.0910322107) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Zakharova IS, Shevchenko AI, Shilov AG, Nesterova TB, Vandeberg JL, Zakian SM. 2011. Histone H3 trimethylation at lysine 9 marks the inactive metaphase X chromosome in the marsupial Monodelphis domestica. Chromosoma 120, 177–183 10.1007/s00412-010-0300-y (doi:10.1007/s00412-010-0300-y) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Loebel DA, Johnston PG. 1996. Methylation analysis of a marsupial X-linked CpG island by bisulfite genomic sequencing. Genome Res. 6, 114–123 10.1101/gr.6.2.114 (doi:10.1101/gr.6.2.114) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Piper AA, Bennett AM, Noyce L, Swanton MK, Cooper DW. 1993. Isolation of a clone partially encoding hill kangaroo X-linked hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase: sex differences in methylation in the body of the gene. Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 19, 141–159 10.1007/BF01233530 (doi:10.1007/BF01233530) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Elisaphenko EA, Kolesnikov NN, Shevchenko AI, Rogozin IB, Nesterova TB, Brockdorff N, Zakian SM. 2008. A dual origin of the Xist gene from a protein-coding gene and a set of transposable elements. PLoS ONE 3, e2521. 10.1371/journal.pone.0002521 (doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002521) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Duret L, Chureau C, Samain S, Weissenbach J, Avner P. 2006. The Xist RNA gene evolved in eutherians by pseudogenization of a protein-coding gene. Science 312, 1653–1655 10.1126/science.1126316 (doi:10.1126/science.1126316) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Orishchenko KE, Elisafenko EA, Kel AE, Zakian SM. 2009. Molecular genetic characterization of the regulatory region of the Xist gene in the common vole Microtus rossiaemeridionalis. Genetika 45, 1341–1352 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Heard E, Mongelard F, Arnaud D, Chureau C, Vourc'h C, Avner P. 1999. Human XIST yeast artificial chromosome transgenes show partial X inactivation center function in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 6841–6846 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6841 (doi:10.1073/pnas.96.12.6841) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wutz A, Jaenisch R. 2000. A shift from reversible to irreversible X inactivation is triggered during ES cell differentiation. Mol. Cell. 5, 695–705 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80248-8 (doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80248-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Plath K, Talbot D, Hamer KM, Otte AP, Yang TP, Jaenisch R, Panning B. 2004. Developmentally regulated alterations in Polycomb repressive complex 1 proteins on the inactive X chromosome. J. Cell Biol. 167, 1025–1035 10.1083/jcb.200409026 (doi:10.1083/jcb.200409026) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Arrigoni R, Alam SL, Wamstad JA, Bardwell VJ, Sundquist WI, Schreiber-Agus N. 2006. The Polycomb-associated protein Rybp is a ubiquitin binding protein. FEBS Lett. 580, 6233–6241 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.10.027 (doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.10.027) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Mak W, Baxter J, Silva J, Newall AE, Otte AP, Brockdorff N. 2002. Mitotically stable association of polycomb group proteins eed and enx1 with the inactive X chromosome in trophoblast stem cells. Curr. Biol. 12, 1016–1020 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00892-8 (doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00892-8) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Costanzi C, Pehrson JR. 1998. Histone macroH2A1 is concentrated in the inactive X chromosome of female mammals. Nature 393, 599–601 10.1038/31275 (doi:10.1038/31275) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Baumann C, De La Fuente R. 2009. ATRX marks the inactive X chromosome (Xi) in somatic cells and during imprinted X chromosome inactivation in trophoblast stem cells. Chromosoma 118, 209–222 10.1007/s00412-008-0189-x (doi:10.1007/s00412-008-0189-x) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Blewitt ME, et al. 2008. SmcHD1, containing a structural-maintenance-of-chromosomes hinge domain, has a critical role in X inactivation. Nat. Genet. 40, 663–669 10.1038/ng.142 (doi:10.1038/ng.142) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]