Abstract
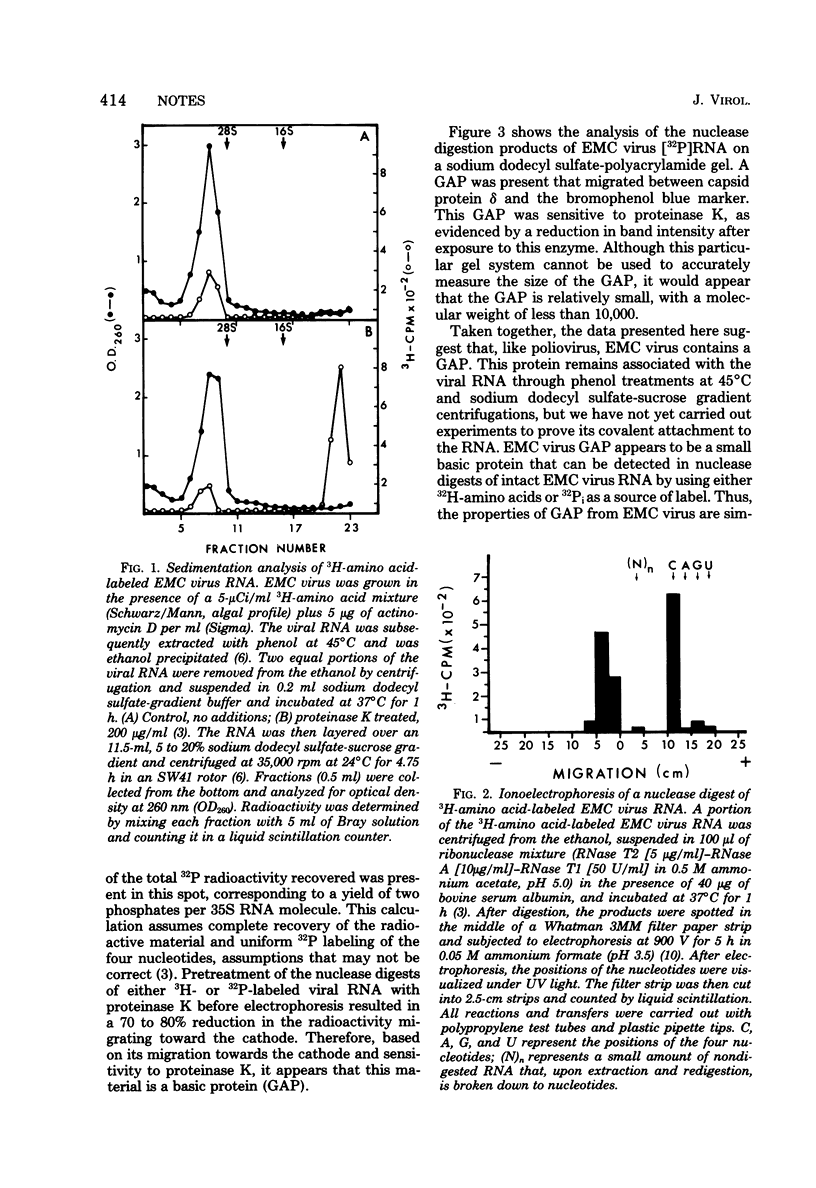
A low-molecular-weight protein was found to be associated with intact 35S RNA isolated from purified encephalomyocarditis virus. This protein was positively charged at pH 3.5, sensitive to proteinase K treatment, and labeled with either 3H-amino acids or 32Pi.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Emtage J. S., Carey N. H., Stebbing N. Structural features of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA from analysis of reverse transcription products. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):69–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Muñoz R., Lavi U. 5' termini of poliovirus RNA: difference between virion and nonencapsidated 35S RNA. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):820–824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.820-824.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D., Eaton M., Fellner P. Absence of 5' terminal capping in encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2771–2787. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Brown F. The location of the ploy(C) tract in the RNA of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):493–501. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. II. Polyadenylic acid requirement for efficient translation. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):338–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.338-344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. The genome of poliovirus is an exceptional eukaryotic mRNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;19:89–96. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K. Studies on RNA synthesis in Ehrlich ascites cells extraction and properties of labeled RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 8;108(3):474–488. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




