Abstract
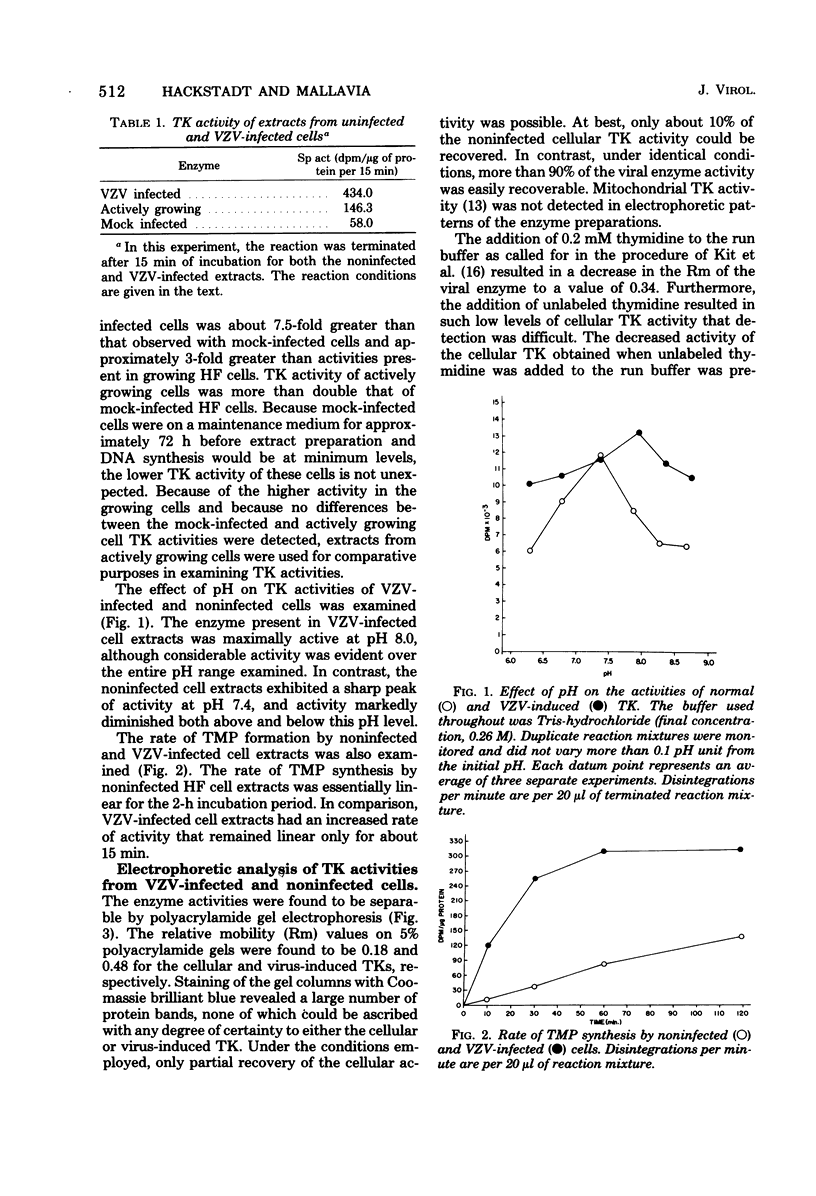
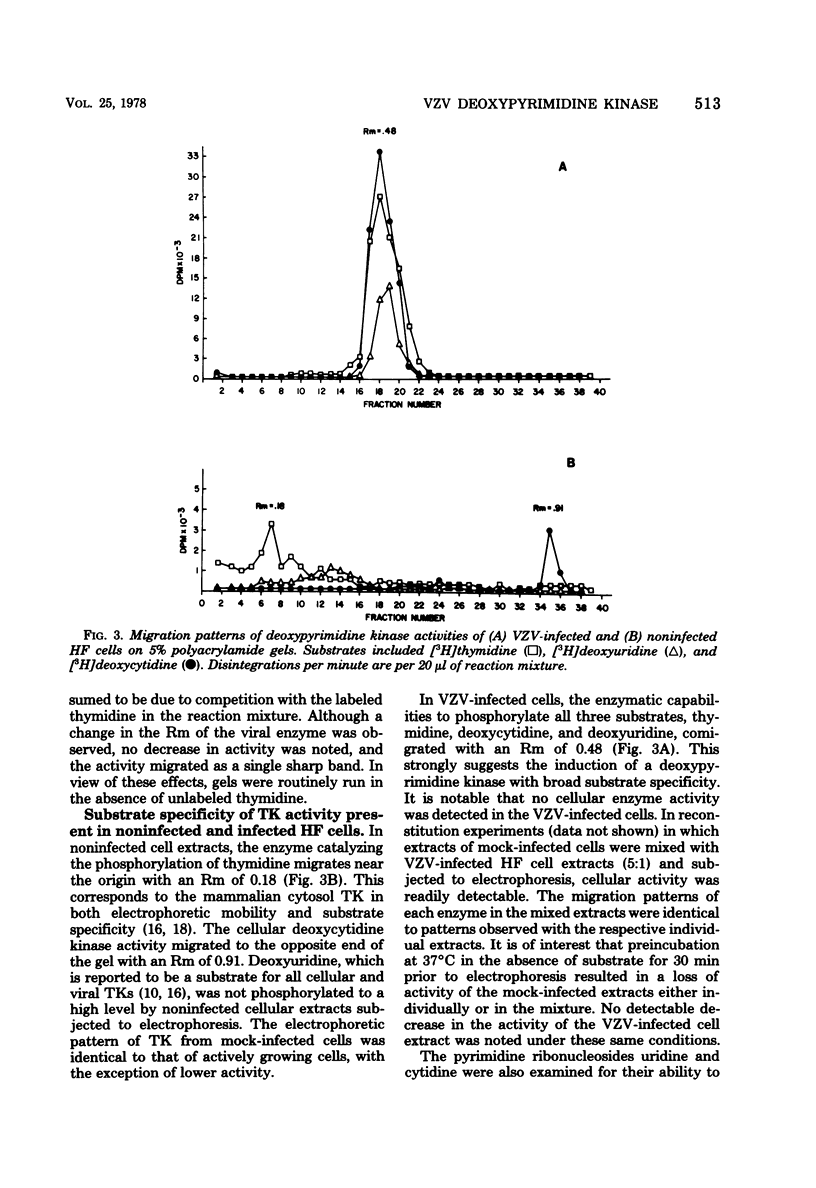
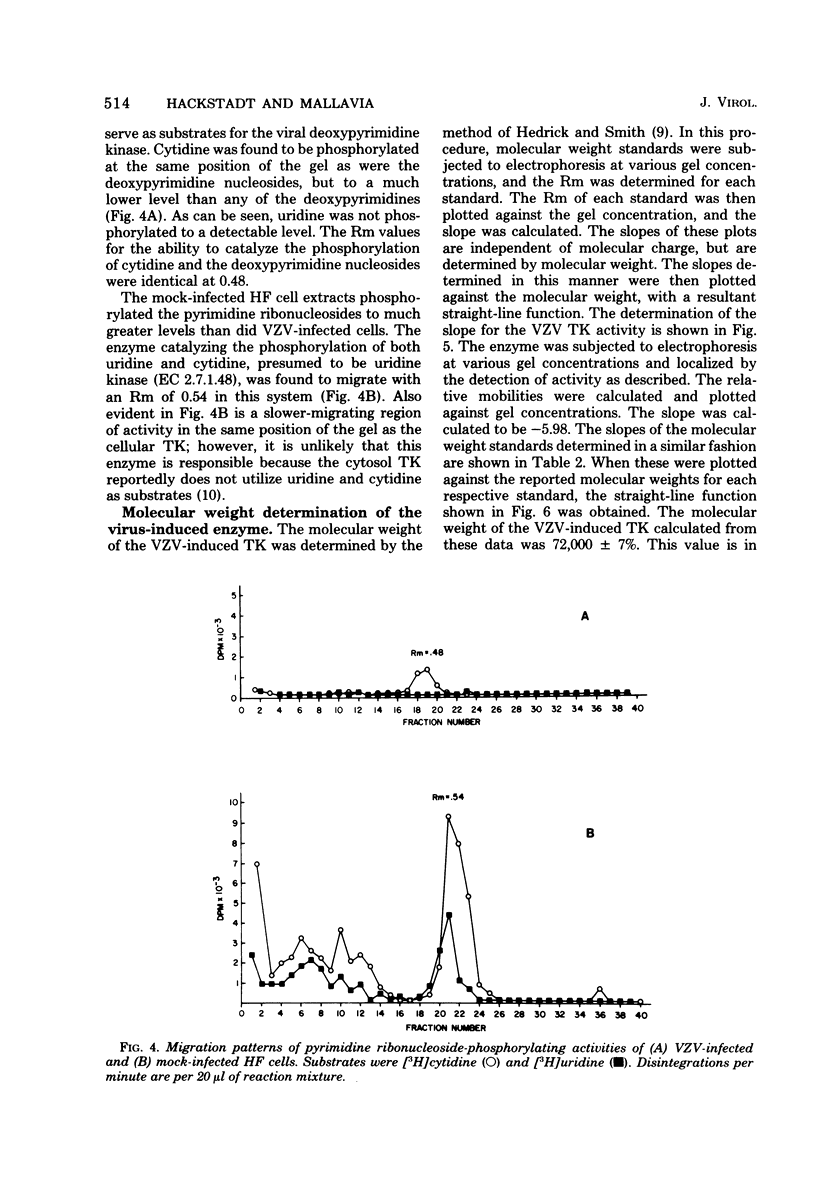
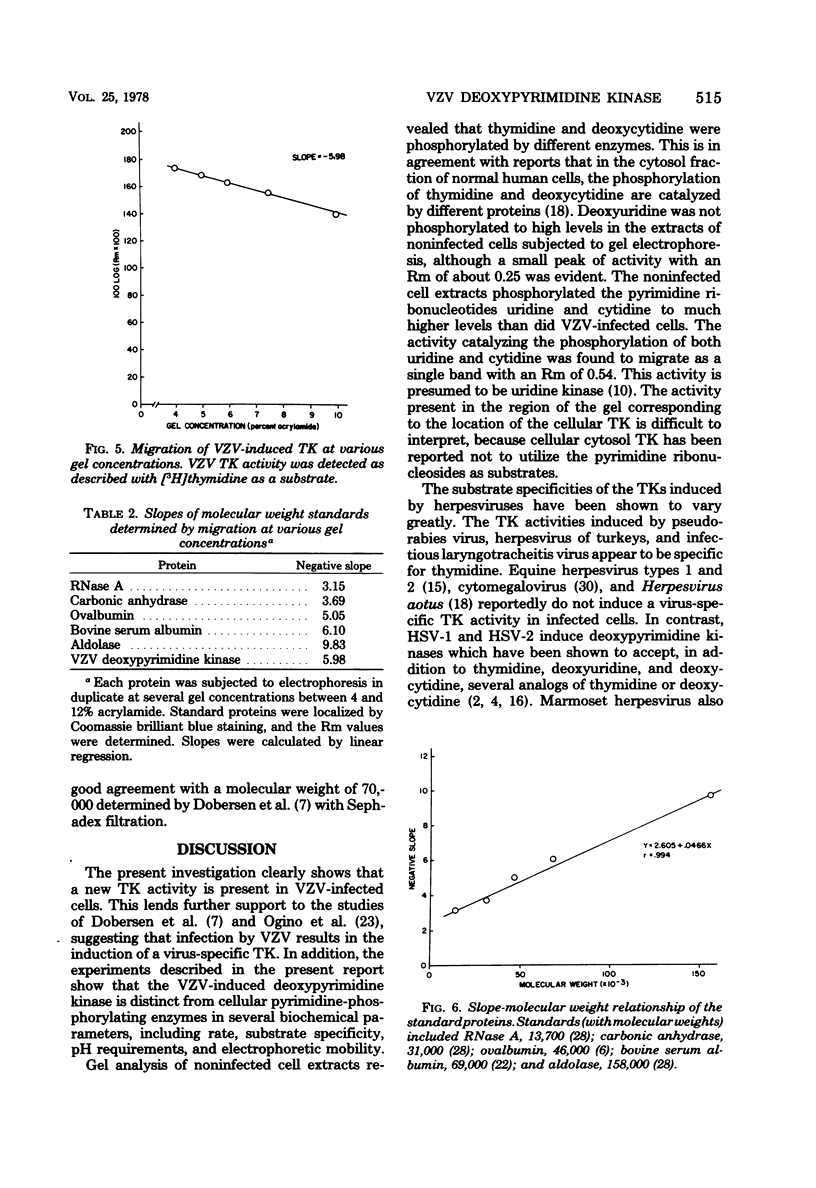
Noninfected and varicella-zoster virus (VZV)-infected human foreskin fibroblasts were examined for thymidine kinase activity. The specific activity of VZV-infected cell extracts was approximately 7.5-fold greater than that of mock-infected cells and 3-fold greater than that of actively growing cells. The pH optimum of VZV-infected cell thymidine kinase activity was found to be 8.0, whereas thymidine kinase activity in noninfected cells exhibited a sharp pH optimum at 7.4. Electrophoretic analysis of cellular enzymes involved in pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylation revealed at least three enzymes distinguishable by electrophoretic mobility and substrates used. These enzymes were presumed to be thymidine kinase, deoxycytidine kinase, and uridine kinase. The relative mobilities of these enzymes on 5% polyacrylamide gels were 0.18, 0.91, and 0.54, respectively. In VZV-infected cells, a single band of activity catalyzing the phosphorylation of thymidine, deoxyuridine, deoxycytidine, and cytidine was observed with a relative mobility of 0.48. Cellular pyrimidine-phosphorylating enzymes were not detected in VZV-infected cells. The molecular weight of the VZV-induced enzyme was determined to be 72,000 +/- 7%.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan T. S. Induction of deoxycytidine deaminase activity in mammalian cell lines by infection with herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1734–1738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C. A rational approach to the development of antiviral chemotherapy: alternative substrates of herpes simplex virus Type 1 (HSV-1) and Type 2 (HSV-2) thymidine kinase (TK). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:594–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Chadha K. C., Hughes R. G., Jr Biochemical and immunological characterization of deoxythymidine kinase of thymidine kinaseless HeLa cells biochemically transformed by herpes simplex virus type. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):486–492. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.486-492.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. M. Phosphorylation of 5-bromodeoxycytidine in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3788–3792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobersen M. J., Jerkofsky M., Greer S. Enzymatic basis for the selective inhibition of varicella-zoster virus by 5-halogenated analogues of deoxycytidine. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.478-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Gentry G. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Induction of both thymidine and deoxycytidine kinase activity by herpes viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):465–480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Biochemical studies on the herpes simplex virus-specified deoxypyrimidine kinase activity. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):481–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C. Genetic control of mitochondrial thymidine kinase in human-mouse and monkey-mouse somatic cell hybrids. J Cell Biol. 1974 Apr;61(1):35–44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C., Jorgensen G. N., Trkula D., Dubbs D. R. Thymidine kinase isozymes of normal and virus-infected cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):703–715. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C., Jorgensen G. N., Trkula D., Dubbs D. R. Viral-induced thymidine kinase isozymes. Prog Med Virol. 1975;21:13–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C., Trkula D., Jorgensen G. Gel electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing of mitochondrial and viral-induced thymidine kinases. Int J Cancer. 1974 Feb 15;13(2):203–218. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemperer H. G., Haynes G. R., Shedden W. I., Watson D. H. A virus-specific thymidine kinase in BHK-21 cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. C., Dubbs D. R., Trkula D., Kit S. Mitochondrial and herpesvirus-specific deoxypyrimidine kinases. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):486–497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.486-497.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Buchsbaum R., Paoletti E., Mann J., Kraiselburd E., Davis D. Electrophoresis of thymidine kinase activity synthesized by cells transformed by herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogino T., Otsuka T., Takahashi M. Induction of deoxypyrimidine kinase activity in human embryonic lung cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1232–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1232-1235.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F. INHIBITION BY METABOLIC ANALOGUES OF PLAQUE FORMATION BY HERPES ZOSTER AND HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUSES. J Immunol. 1964 Oct;93:643–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAWLS W. E., COHEN R. A., HERRMANN E. C., Jr INHIBITION OF VARICELLA VIRUS BY 5-IODO-2'-DEOXYURIDINE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:123–127. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaky D. A., Betts R. F., Douglas R. G., Jr, Bengali K., Neil G. L. Varicella-zoster virus and subcutaneous cytarabine: correlation of in vitro sensitivities to blood levels. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):229–232. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Závada V., Erban V., Rezácová D., Vonka V. Thymidine-kinase in cytomegalovirus infected cells. Arch Virol. 1976;52(4):333–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01315622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



