Abstract
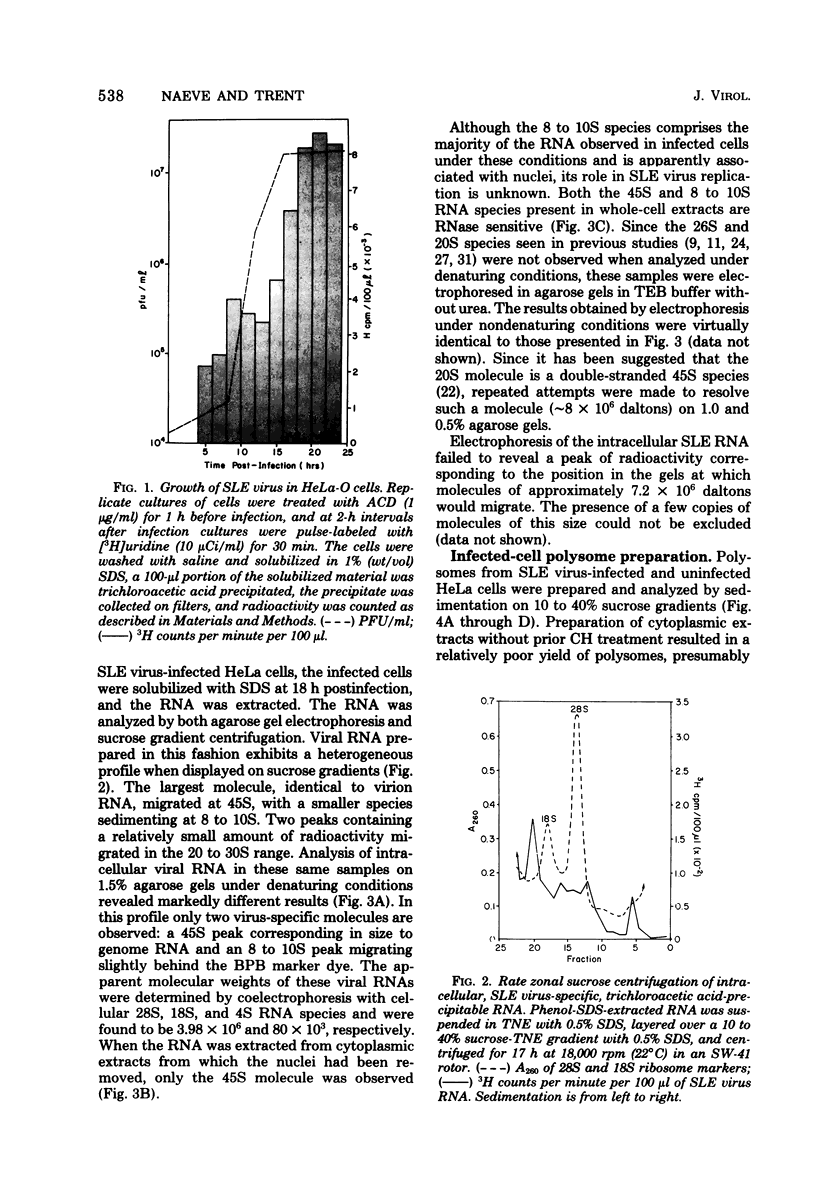
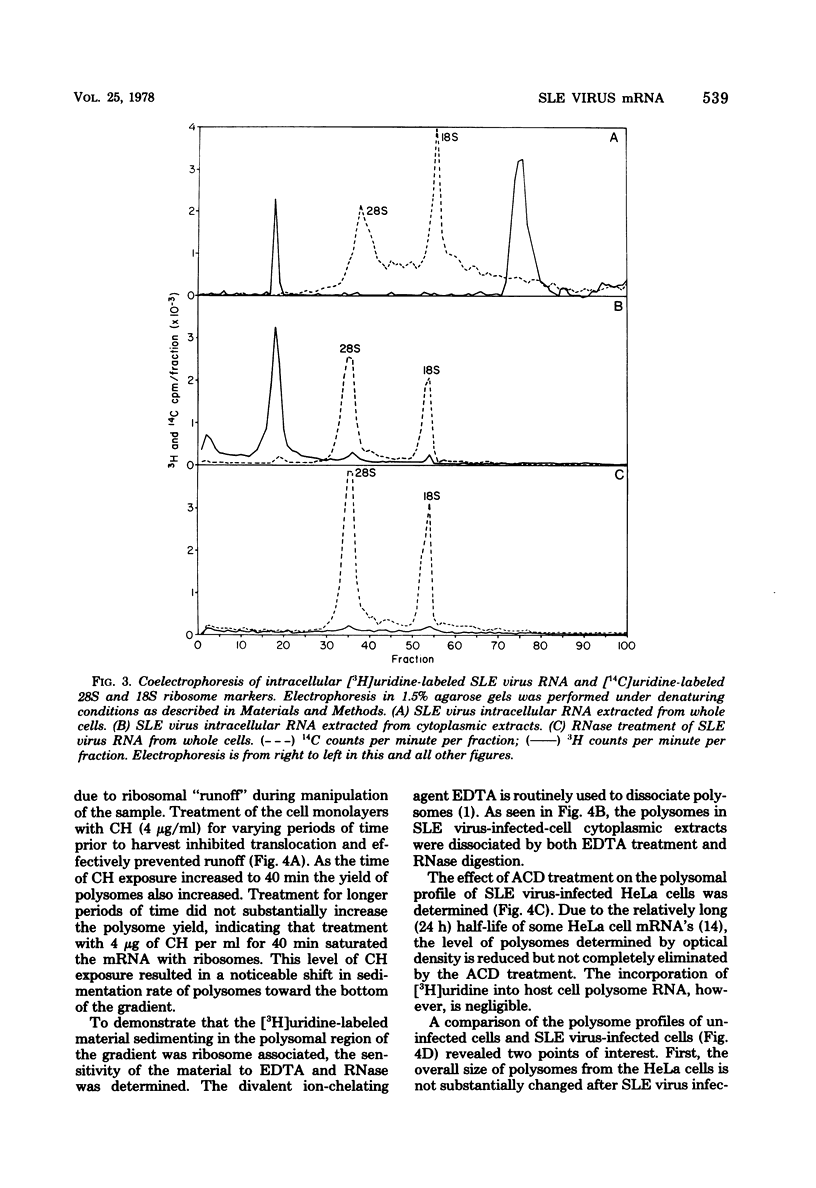
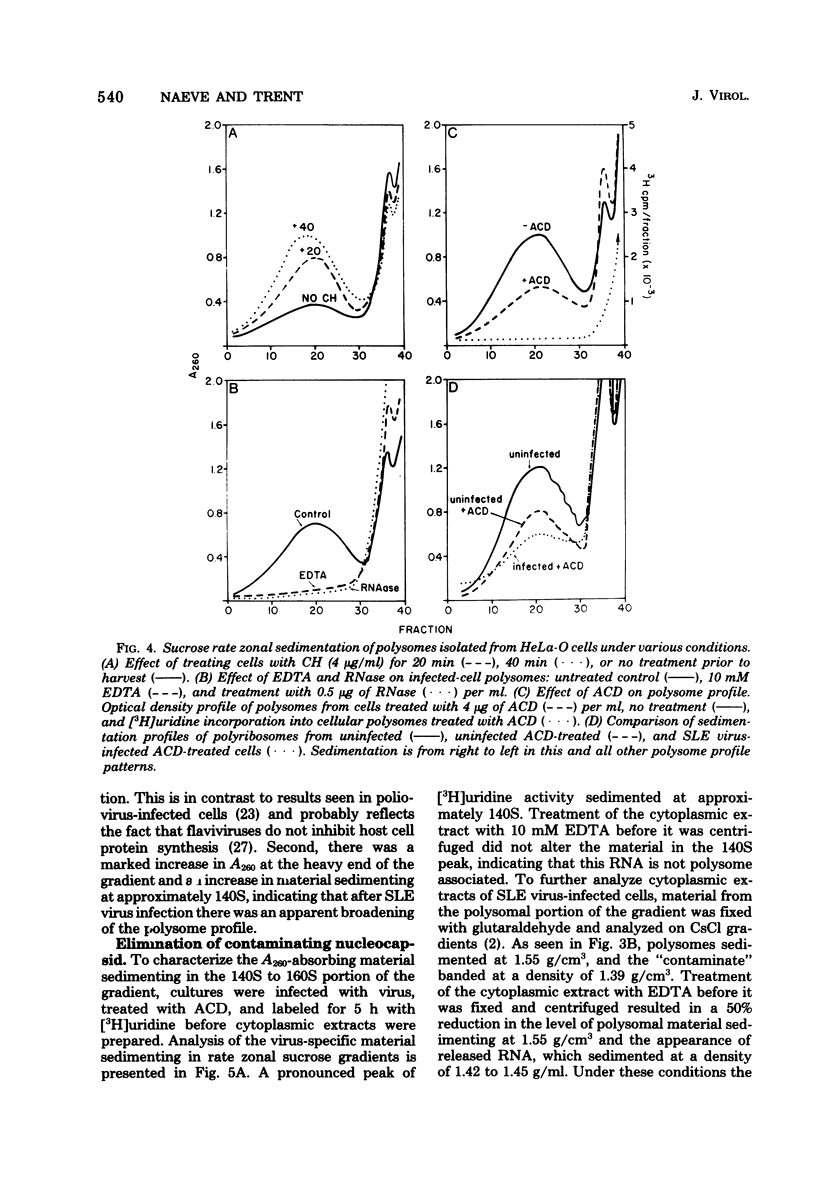
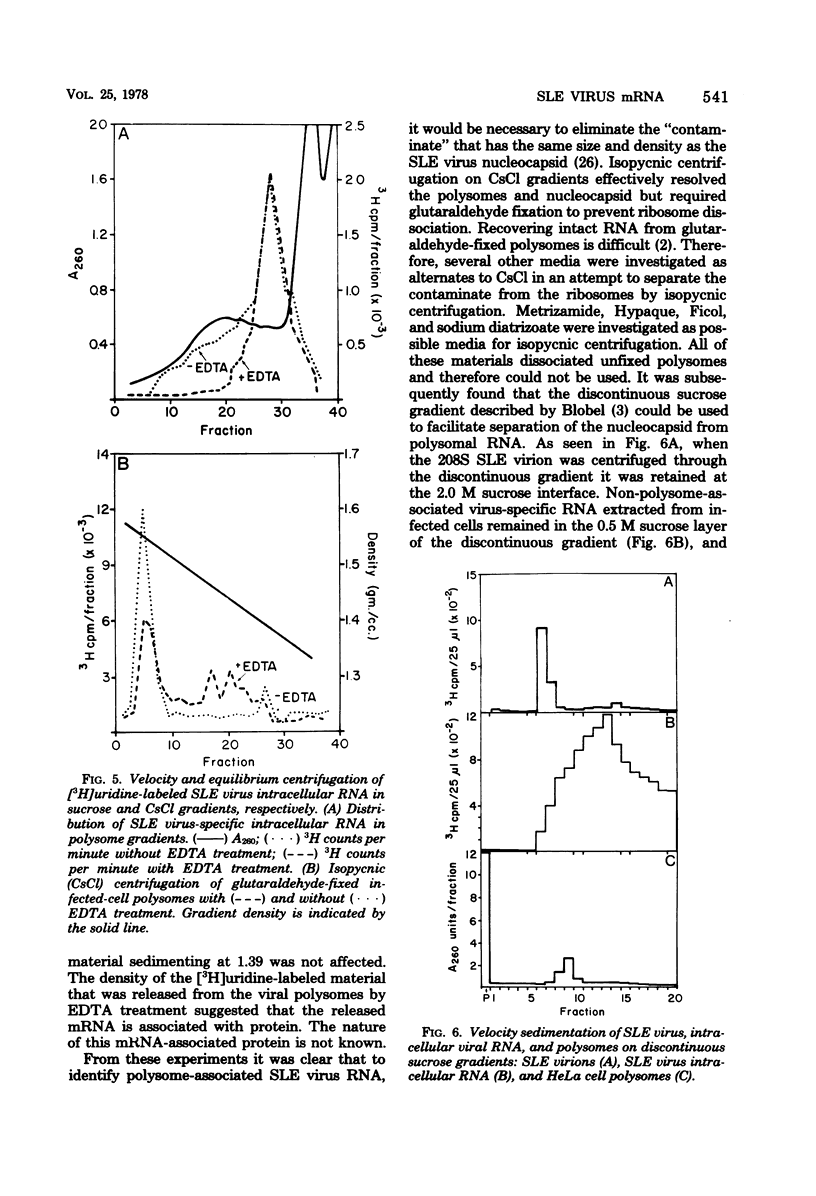
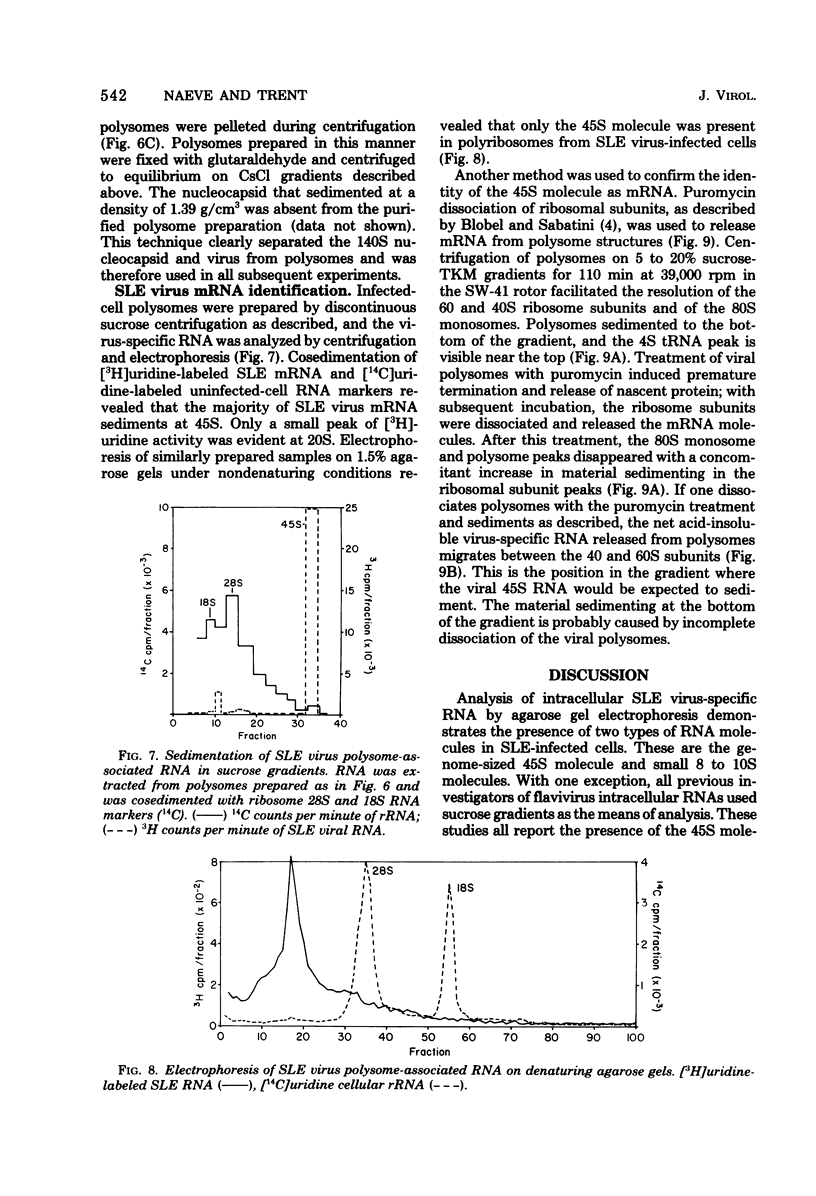
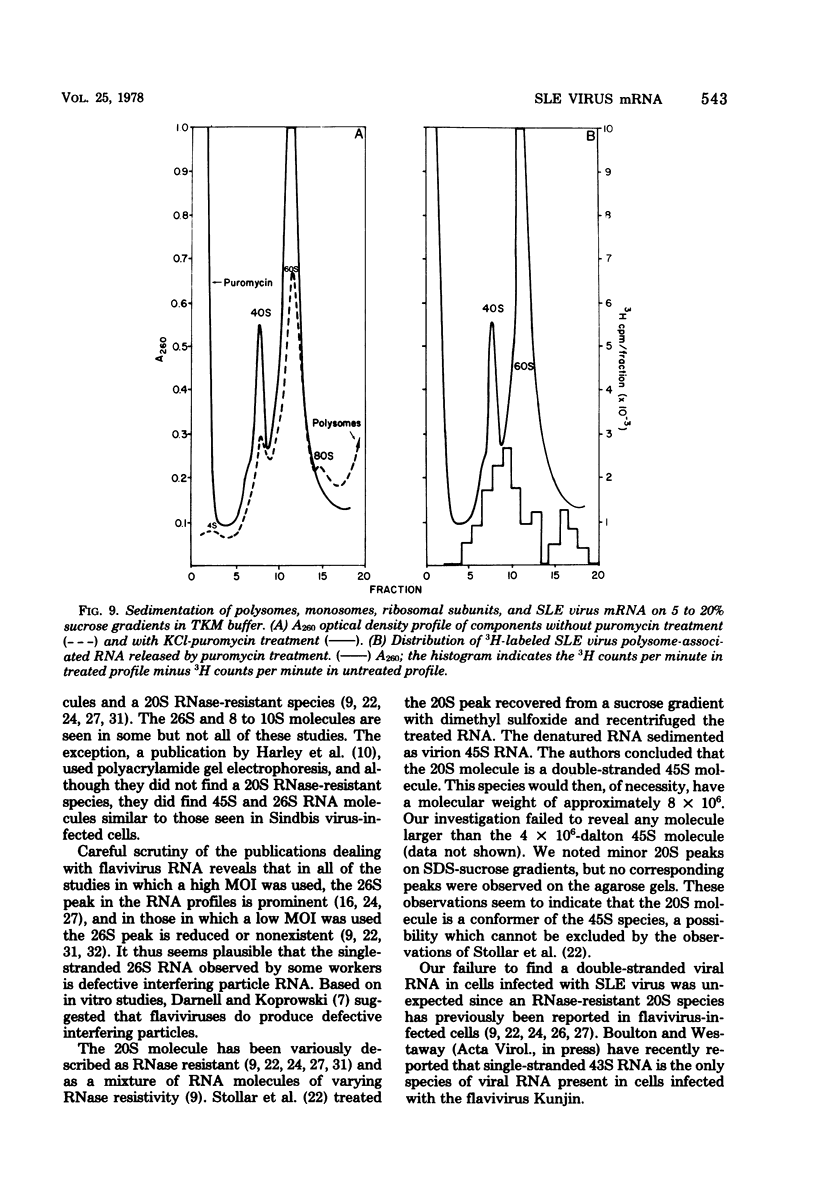
Saint Louis encephalitis (SLE) virus-specific RNA was recovered from infected HeLa cells by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-phenol-chloroform extraction, and the molecular species were resolved by SDS-sucrose gradient centrifugation and agarose gel electrophoresis. Sucrose gradient centrifugation revealed the presence of a 45S species, minor 20 to 30S heterogeneous species, and an 8 to 10 S RNA species in the cytoplasmic extract. Analysis of the same samples by electrophoresis on agarose gels, under both nondenaturing and denaturing conditions, revealed only two virus-specific RNA molecules, the 45S genome-sized RNA and an 8 to 10S species. Varying the gel concentration to facilitate analysis of nucleic acids with molecular weights ranging from 25,000 to 25 X 10(6) failed to reveal additional RNA species, although low levels of a putative double-stranded replicative form could conceivably have escaped detection. From our observations it appears that the heterogeneous RNA species and presumably the 20S RNase-resistant species reported in other investigations of flavivirus RNA are degradation products or conformers of the 45S molecule. Polysomes from SLE virus-infected cells were prepared and separated from contaminating nucleocapsid by centrifugation on discontinuous sucrose gradients. RNA extracted from these polysome preparations was analyzed by sucrose gradient centrifugation and agarose gel electrophoresis. The 45S SLE virus genome-size molecule was found to be the only RNA species associated with the polysomes. This molecule was sensitive to RNase digestion and was released from polysomes by EDTA and puromycin treatment. These findings provide direct evidence that the 45 S SLE virus RNA serves as the messenger during virus replication, in contrast to the 26S RNA species which functions as the predominant messenger during alphavirus replication.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman M. R., Sabatini D. D., Blobel G. Ribosome-membrane interaction. Nondestructive disassembly of rat liver rough microsomes into ribosomal and membranous components. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):206–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Isopycnic separation of subcellular components from poliovirus-infected and normal HeLa cells. Science. 1968 Nov 1;162(3853):572–574. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3853.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Release, identification, and isolation of messenger RNA from mammalian ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):832–835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Sabatini D. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton R. W., Westaway E. G. Replication of the flavivirus Kunjin: proteins, glycoproteins, and maturation associated with cell membranes. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):416–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90473-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski H., Kennedy S. I. Synthesis of Sindbis virus nonstructural polypeptides in chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):420–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.420-429.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell M. B., Koprowski H. Genetically determined resistance to infection with group B arboviruses. II. Increased production of interfering particles in cell cultures from resistant mice. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):248–256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar O. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Thermal inactivation of type 1 Dengue virus strains. Acta Virol. 1975 Apr;19(2):167–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K. Characteristics of Japanese encephalitis virus-specific RNA synthesized in BHK-21 cells. Kobe J Med Sci. 1973 Mar;19(1):23–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano T., Suzuki K., Yamaguchi T. Morphological, chemical, and biological characterization of Japanese encephalitis virus virion and its hemagglutinin. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):631–639. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.631-639.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Harrison A. K., Gary G. W., Jr, Whitfield S. G., Forrester F. T. St. Louis encephalitis virus infection in mice. Electron microscopic studies of central nervous system. Lab Invest. 1968 Dec;19(6):652–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi A. A., Trent D. W. Group B arbovirus structural and nonstructural antigens. 3. Serological specificity of solubilized intracellular viral proteins. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):993–999. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.993-999.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi A. A., Trent D. W. Saint Louis encephalitis viral ribonucleic acid replication complex. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):565–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.565-573.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Woo S. L., Holder J. W., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Preparation and preliminary characterization of purified ovalbumin messenger RNA from the hen oviduct. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):69–78. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Schlesinger S. Large-molecular-weight precursors of sindbis virus proteins. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):1013–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.1013-1016.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D., Trent D., Brandt W. E., Russell P. K. Comparison of the virion polypeptides of group B arboviruses. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):206–209. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.206-209.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soria M., Little S. P., Huang A. S. Characterization of vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsids. I. Complementary 40 S RNA molecules in nucleocapsids. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):270–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr The decrease in size and synthetic activity of poliovirus polysomes late in the infectious cycle. Virology. 1967 Mar;31(3):427–435. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda H., Oya A., Hashimoto K., Yamada M. Intracellular distribution of virus-specific RNA in chick embryo cells infected with Japanese encephalitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):201–205. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent D. W. Antigenic characterization of flavivirus structural proteins separated by isoelectric focusing. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):608–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.608-618.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent D. W., Qureshi A. A. Structural and nonstructural proteins of Saint Louis encephalitis virus. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):379–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.379-388.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent D. W., Swensen C. C., Qureshi A. A. Synthesis of Saint Louis encephalitis virus ribonucleic acid in BHK-21-13 cells. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):385–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.385-394.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Hampel A. Preparative agarose gel electrophoresis of ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4361–4367. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Proteins specified by group B togaviruses in mammalian cells during productive infections. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):454–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Strategy of the flavivirus genome: evidence for multiple internal initiation of translation of proteins specified by Kunjin virus in mammalian cells. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):320–335. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebovitz E., Leong J. K., Doughty S. C. Involvement of the host cell nuclear envelope membranes in the replication of Japanese encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.204-211.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zebovitz E., Leong J. K., Doughty S. C. Japanese encephalitis virus replication: a procedure for the selective isolation and characterization of viral RNA species. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;38(4):319–327. doi: 10.1007/BF01262822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



