Abstract
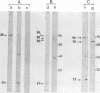
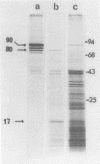
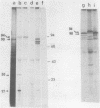
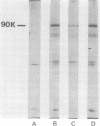
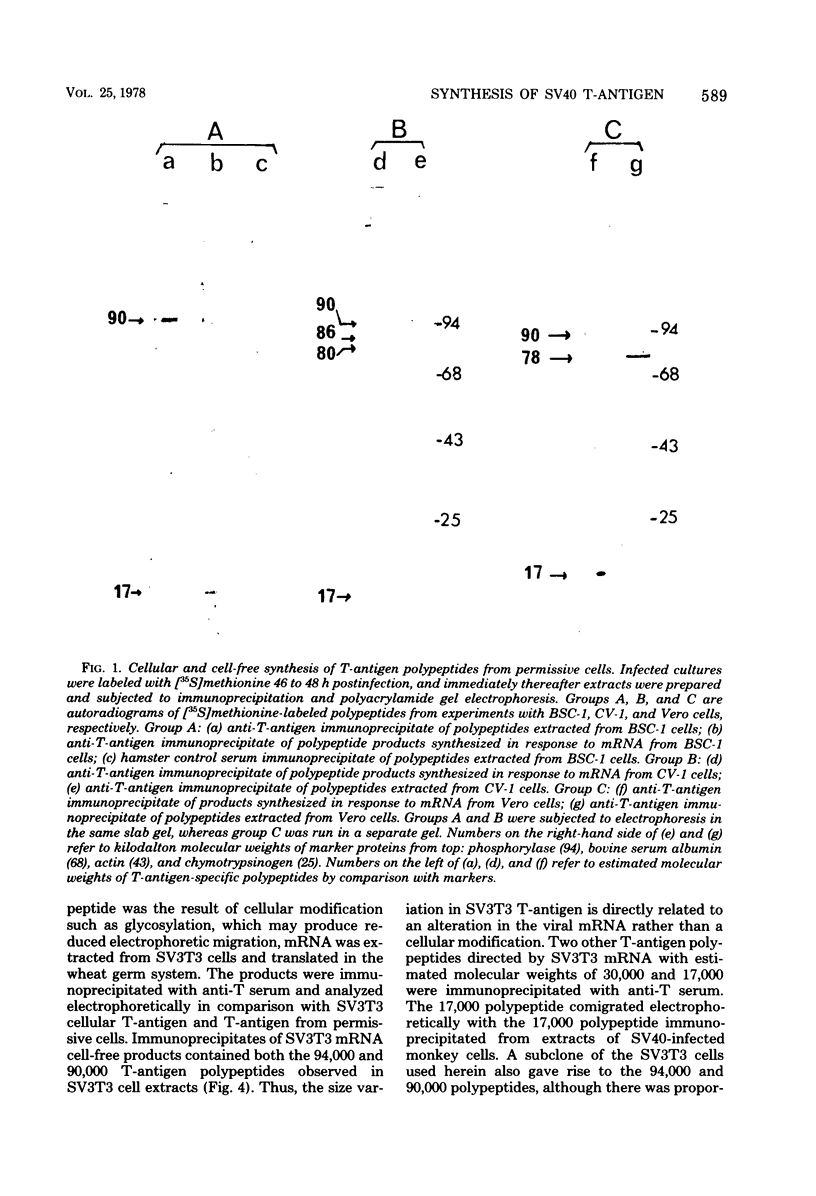
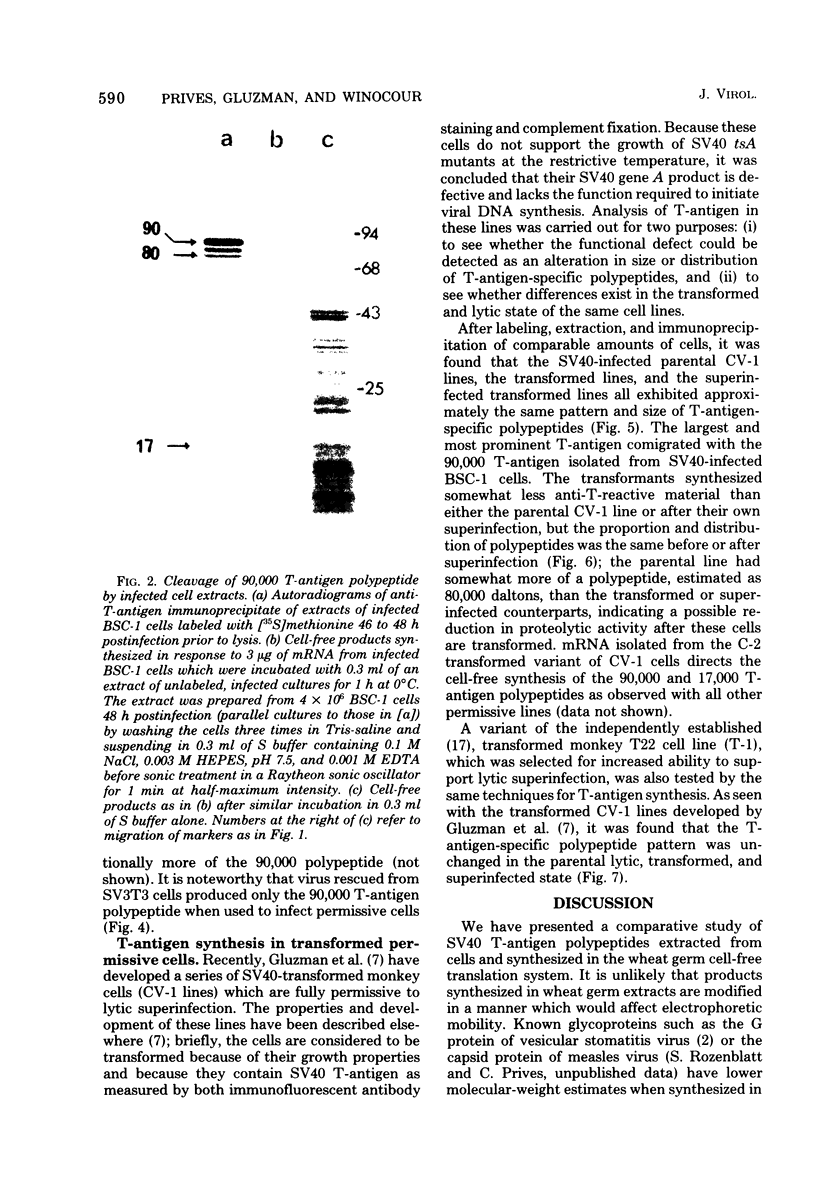
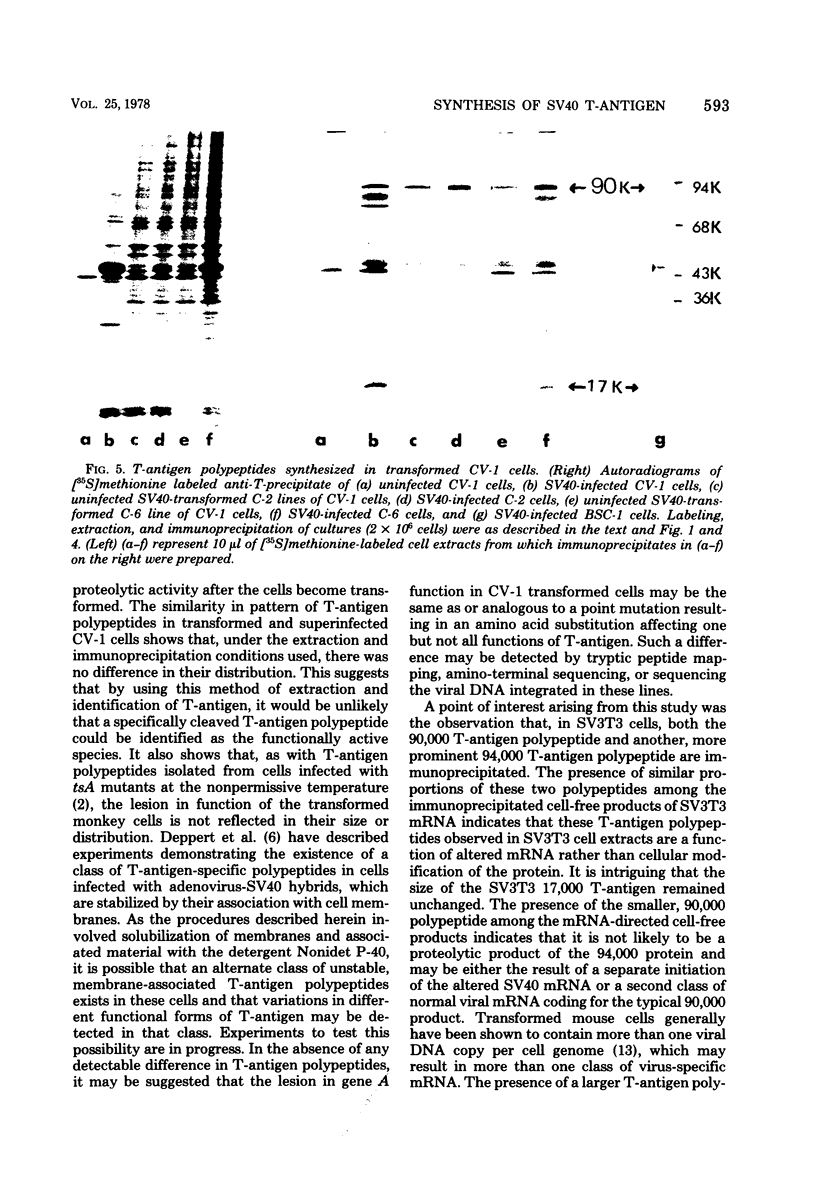
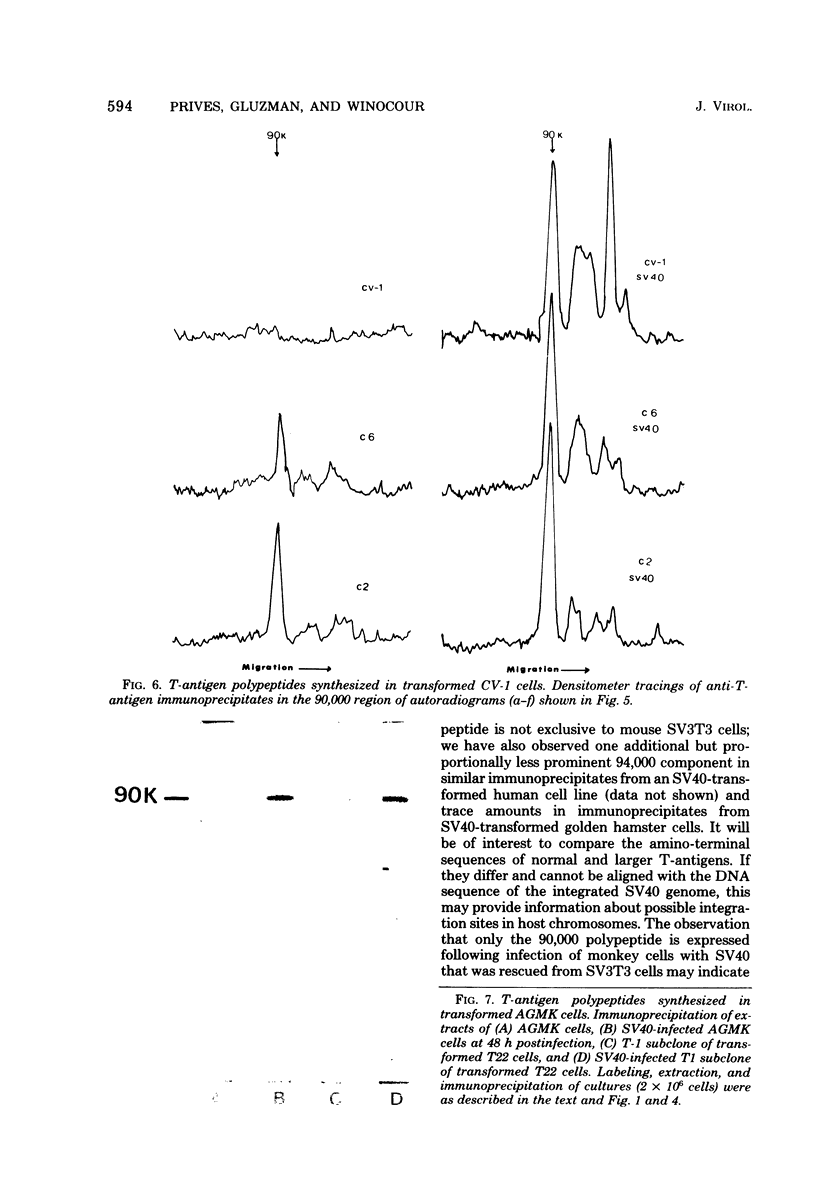
mRNA extracted from a variety of simian virus 40 (SV40)-infected monkey cell lines directs the cell-free synthesis of viral T-antigen polypeptides with molecular weights estimated as 90,000 and 17,000. However, the size, abundance, and distribution of these T-antigens synthesized in vivo vary greatly over a range of permissive and transformed cell lines. To establish whether differences in the size of T-antigen polypeptides can be correlated with the transformed or lytic state, recently developed lines of SV40-transformed monkey cells that are permissive to lytic superinfection were analyzed for T-antigen. In these cells, regardless of the state of viral infection, the size and pattern of T-antigen are the same. However, species differences in the largest size of T-antigen are the same. However, species differences in the largest size of T-antigen do exist. In addition to the 90,000 T-antigen, mouse SV3T3 cells contain a 94,000 T-antigen polypeptide as well. Unlike the size variations in monkey cells, which are due to modification of T-antigen polypeptides, the 94,000 SV3T3 T-antigen results from an altered mRNA, since the cell-free products of SV3T3 mRNA also contains the 94,000 T-antigen polypeptide.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Moyer S. A., Banerjee A. K. Translation and identification of the viral mRNA species isolated from subcellular fractions of vesicular stomatitis virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):1012–1019. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.1012-1019.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R. B., Smith A. E. Monomer molecular weight of T antigen from simian virus 40-infected and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2254–2258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Villano B. C., Defendi V. Characterization of the SV40 T antigen. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):34–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Walter G., Linke H. Simian virus 40 tumor-specific proteins: subcellular distribution and metabolic stability in HeLa cells infected with nondefective adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1170–1186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1170-1186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Davison J., Oren M., Winocour E. Properties of permissive monkey cells transformed by UV-irradiated simian virus 40. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):256–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.256-266.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Itagaki A. Initiation and maintenance of cell transformation by simian virus 40: a viral genetic property. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):673–677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Jensen F. C., Steplewski Z. Activation of production of infectious tumor virus SV40 in heterokaryon cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):127–133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Winocour E. Acquisition of sequences homologous to host deoxyribonucleic acid by closed circular simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):309–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.309-316.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Transcription of simian virus 40. II. Hybridization of RNA extracted from different lines of transformed cells to the separated strands of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.90-98.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. L., Aviv H., Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Rozenblatt S., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA of simian virus 40: synthesis of the major capsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Shimojo H. Transformation of green monkey kidney cells by SV40 genome: the establishment of transformed cell lines and the replication of human adenoviruses and SV40 in transformed cells. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Collins J. K. Modification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):647–657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.647-657.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]