Abstract
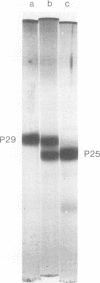
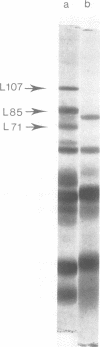
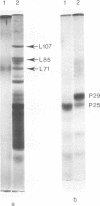
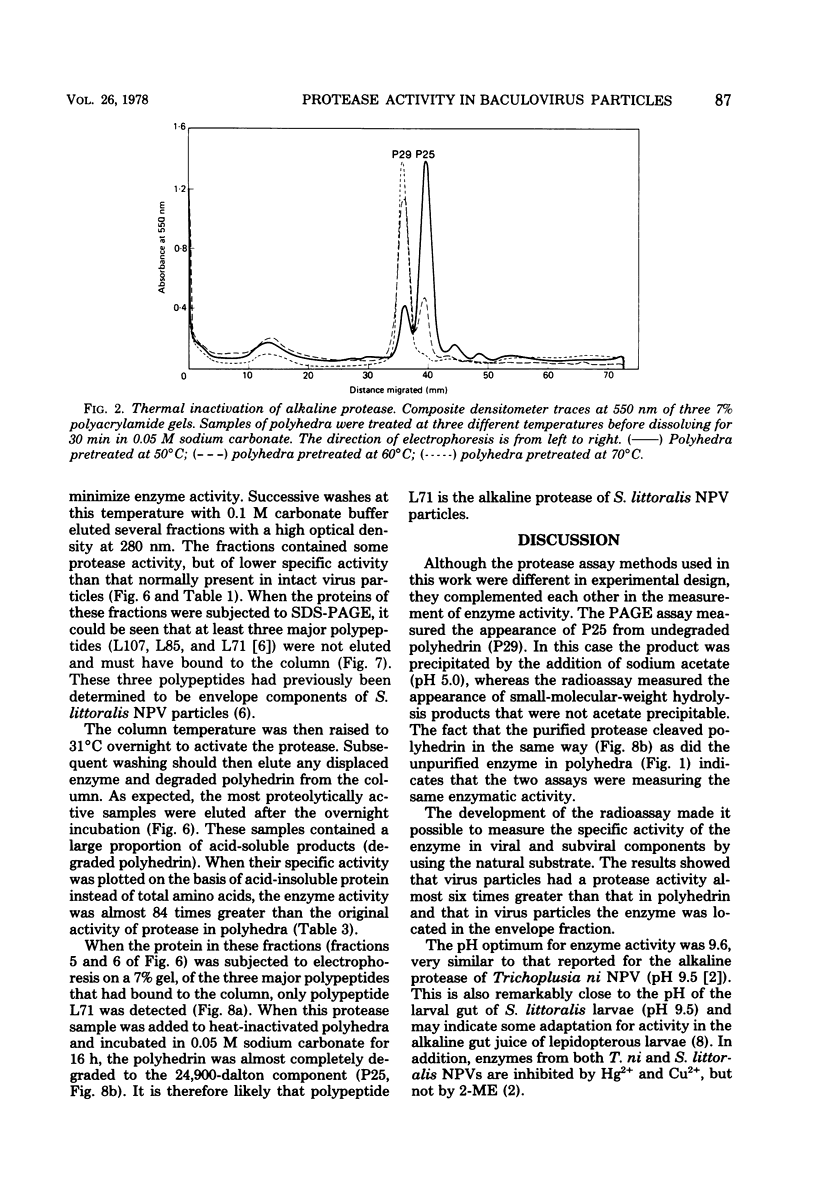
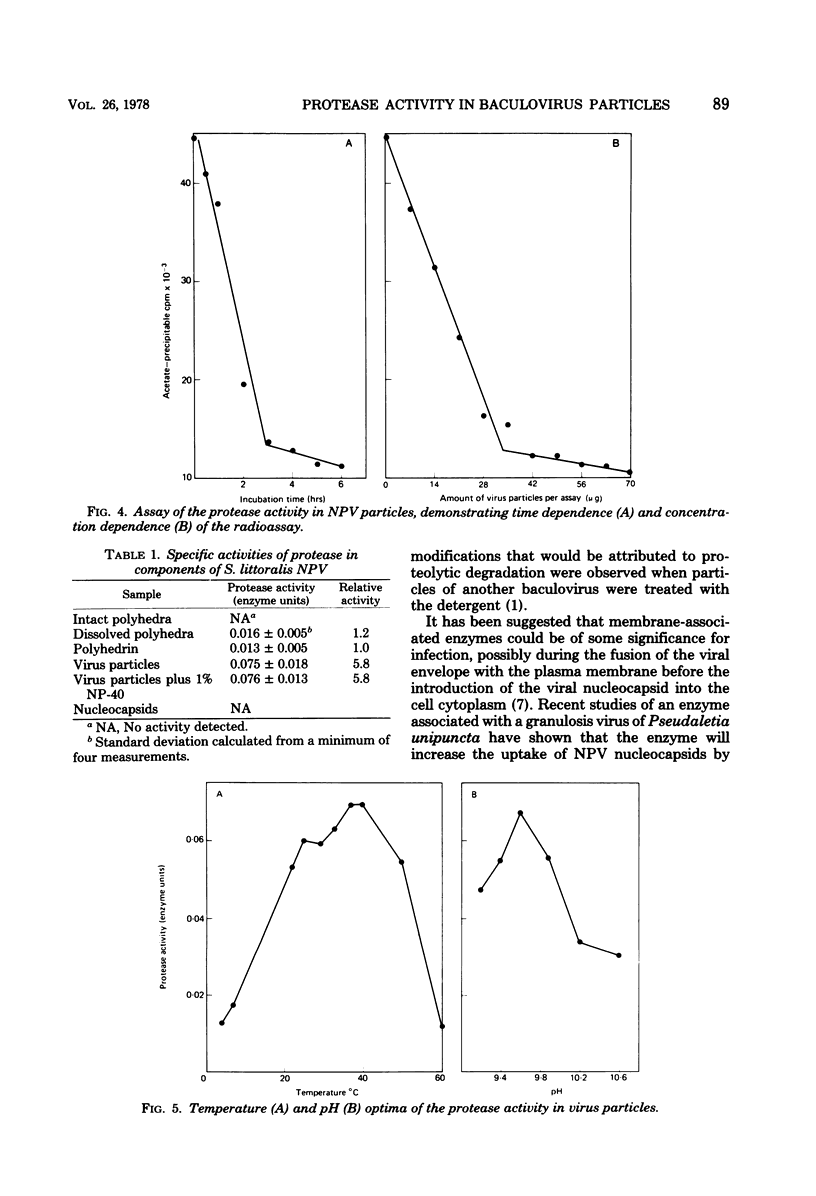
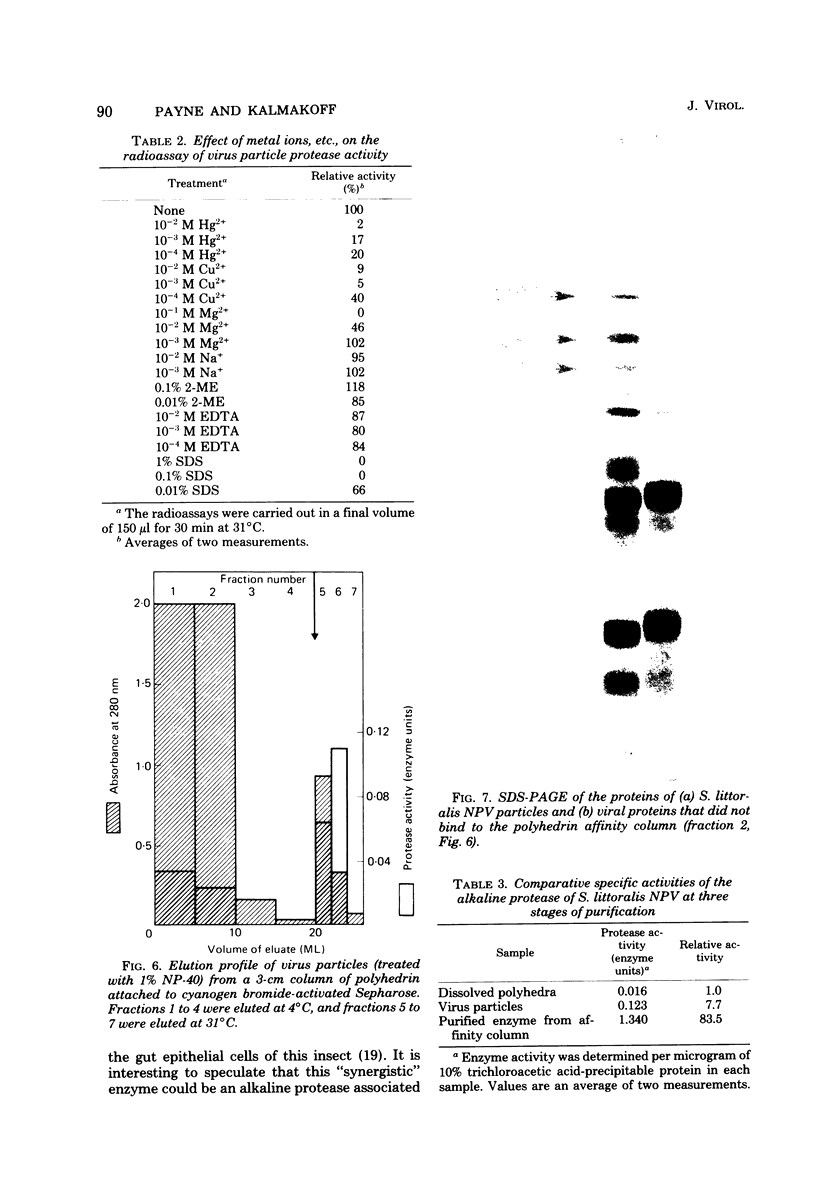
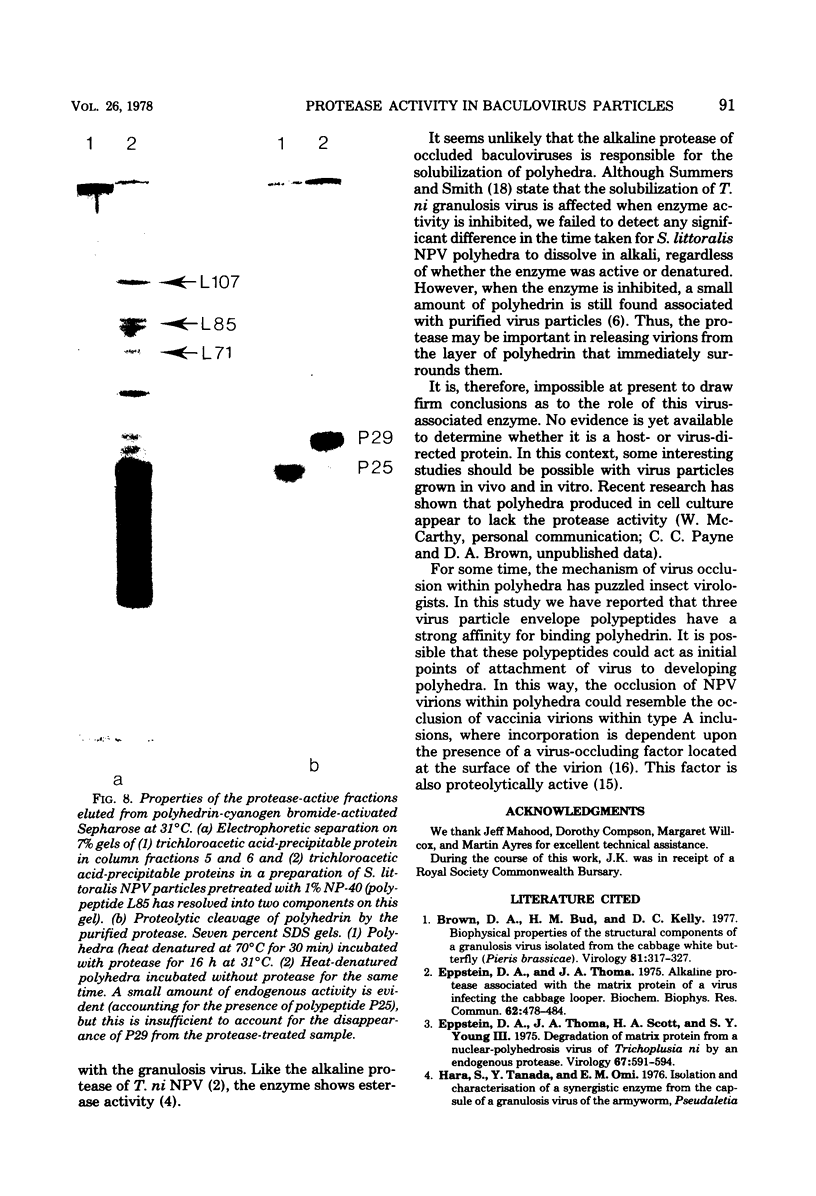
Proteolytic activity was detected within polyhedra of the nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Spodoptera littoralis. The enzyme activity was detected by its ability to degrade the major structural polypeptide of polyhedra (polyhedrin). A quantitative assessment of activity was made by a radioassay technique using 3H-labeled polyhedrin as the substrate. Of the structural components of polyhedra, virus particles showed the greatest specific proteolytic activity. Preparations of purified nucleocapsids were inactive. The virus particle enzyme displayed a temperature optimum for proteolysis of 30 to 40°C and a pH optimum of 9.6. Its activity was inhibited by H2+ and Cu2+, but not by 2-mercaptoethanol. The enzyme was purified from detergent-treated virus particles by affinity column chromatography, using polyhedrin linked to cyanogen bromide-activated Sepharose. Three major envelope polypeptides (L107, L85, and L71) bound to the column at 4°C, but after incubation at 31°C, polypeptide L71 alone was eluted. The fractions containing this protein exhibited a specific enzyme activity more than 80-fold greater than that present in polyhedra. The possible significance of the alkaline protease, and other proteins with affinity for polyhedrin, is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown D. A., Bud H. M., Kelly D. C. Biophysical properties of the structural components of a granulosis virus isolated from the cabbage white butterfly (Pieris brassicae). Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Thoma J. A. Alkaline protease associated with the matrix protein of a virus infecting the cabbage looper. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 20;62(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Thoma J. A., Scott H. A., Young S. Y., 3rd Degradation of matrix protein from a nuclear-polyhedrosis virus of Trichoplusia ni by an endogenous protease. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):591–594. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90459-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Doyle M., Perrault J., Kingsbury D. T., Etchison J. Proteinase activity in purified animal viruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):634–639. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov E. A., Sidorova N. M., Serebryani S. B. Proteolytic cleavage of polyhedral protein during dissolution of inclusion bodies of the nuclear polyhedrosis viruses of Bombyx mori and Galleria mellonella under alkaline conditions. J Invertebr Pathol. 1975 Jan;25(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(75)90288-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne C. C., Compson D., de looze S. M. Properties of the nucleocapsids of a virus isolated from Oryctes rhinoceros. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. D., Egawa K. Physical and chemical properties of Trichoplusia ni granulosis virus granulin. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1092–1103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1092-1103.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. D., Smith G. E. Trichoplusia ni granulosis virus granulin: a phenol-soluble, phosphorylated protein. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1108–1116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1108-1116.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAFUJI K., MUKAI J., YOSHIHARA F. Desoxyribonuclease and protease in polyhedral viral particles. Enzymologia. 1960 Jun 1;22:1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]