Abstract
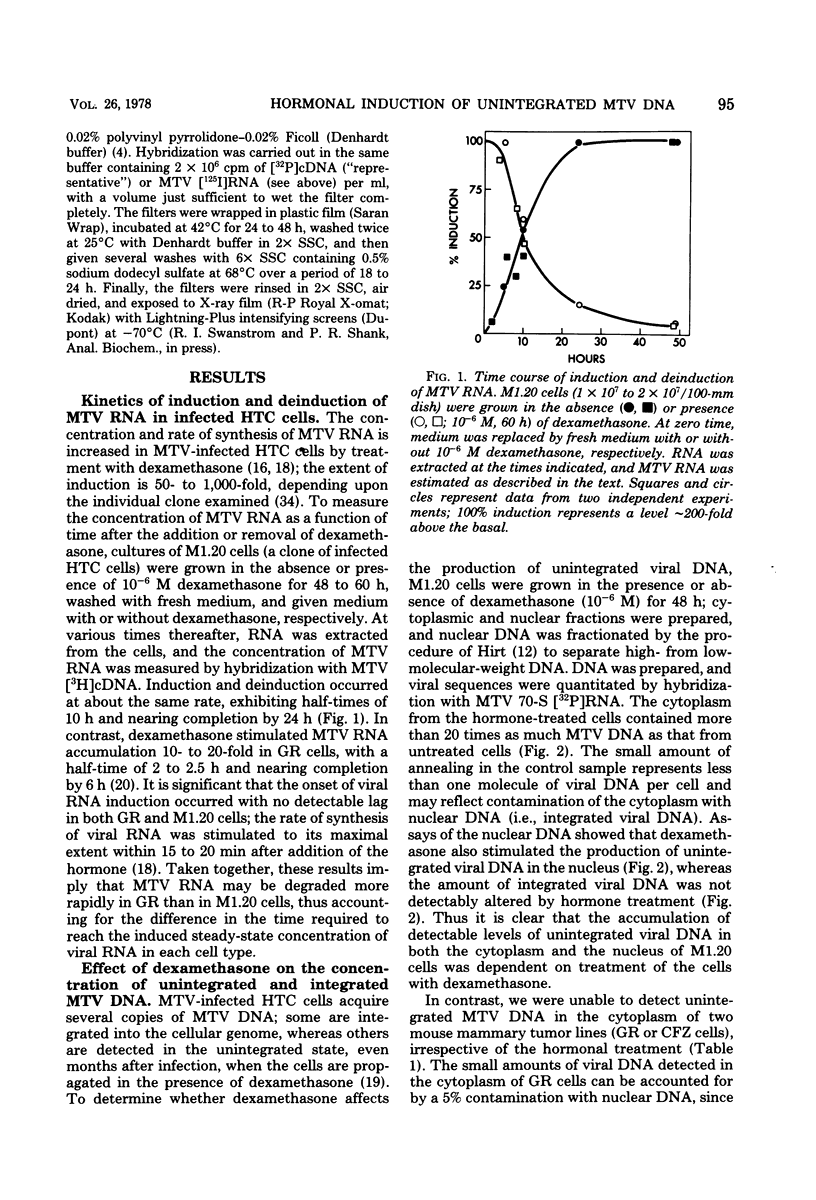
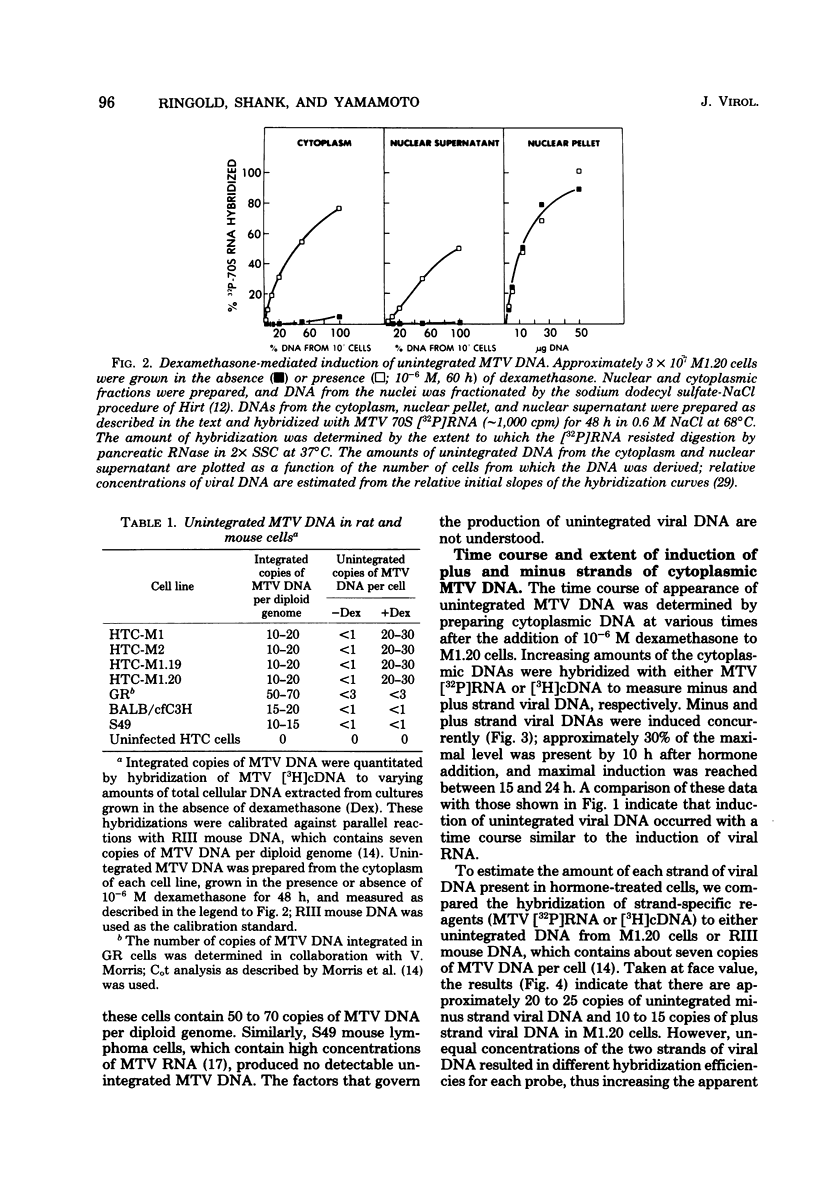
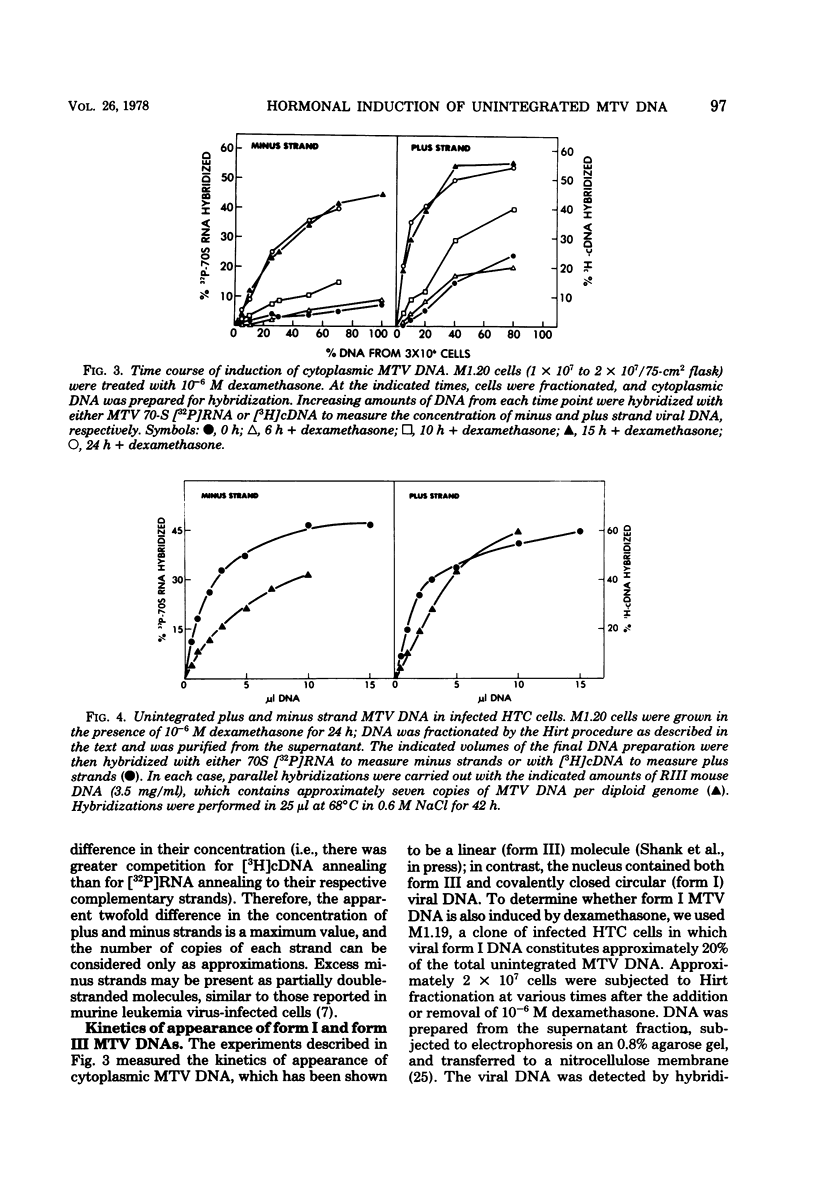
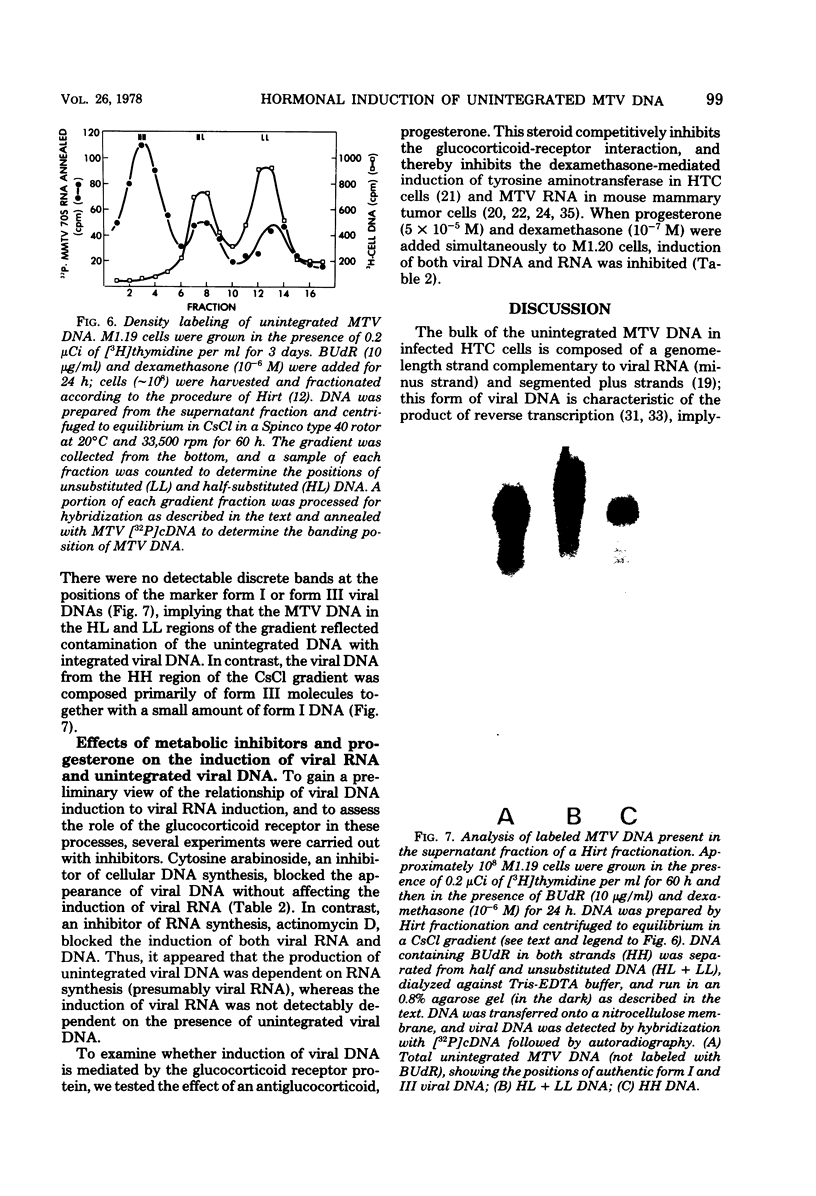
Dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid, selectively increased the rate of synthesis of mouse mammary tumor virus (MTV) RNA in clonal isolates of chronically infected rat hepatoma tissue culture cells. This hormonal effect occurred extremely rapidly and appeared to be mediated directly by the glucocorticoid-specific receptor protein. In addition to the viral RNA, unintegrated MTV DNA was also detected in these cells. Several lines of evidence are consistent with the idea that the unintegrated viral DNA is synthesized by reverse transcription of MTV RNA. (i) Unintegrated viral DNA accumulated only in the presence of dexamethasone and was produced with a time course that closely paralleled the increased accumulation of viral RNA. (ii) Density labeling of the viral DNA revealed that both strands were newly synthesized, implying a non-semiconservative mode of replication. (iii) Inhibitors of viral RNA synthesis prevented the appearance of unintegrated viral DNA. These data suggest that the production of unintegrated MTV DNA after dexamethasone treatment occurs as a secondary consequence of the hormonal induction of synthesis of viral RNA. In contrast to infected rat hepatoma cells, no unintegrated MTV DNA was detected in mouse mammary tumor cells or mouse lymphoma cells, despite the presence of high levels of viral RNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianni A. M., Smotkin D., Weinberg R. A. Murine leukemia virus: detection of unintegrated double-stranded DNA forms of the provirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulian M. Incorporation of oligodeoxynucleotides into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):284–291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntaka R. V., Mahy B. W., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Ethidium bromide inhibits appearance of closed circular viral DNA and integration of virus-specific DNA in duck cells infected by avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):507–511. doi: 10.1038/253507a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntaka R. V., Richards O. C., Shank P. R., Kung H. J., Davidson N. Covalently closed circular DNA of avian sarcoma virus: purification from nuclei of infected quail tumor cells and measurement by electron microscopy and gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):337–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Ransom J. C., Young H. A., Scolnick E. M. Mammary tumor virus induction by glucocorticoids. Characterization of specific transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3330–3336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Cardiff R. D., Varmus H. E., Yamamoto K. R. Infection of cultured rat hepatoma cells by mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Glucocorticoid-stimulated accumulation of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: increased rate of synthesis of viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2879–2883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Shank P. R., Varmus H. E. Mouse mammary tumor virus DNA in infected rat cells: characterization of unintegrated forms. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G., Lasfargues E. Y., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Production of mouse mammary tumor virus by cultured cells in the absence and presence of hormones: assay by molecular hybridization. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):135–147. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Young H. A., Parks W. P. Biochemical and physiological mechanisms in glucocorticoid hormone induction of mouse mammary tumor virus. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):148–156. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala G., Dickson C. Relationship between receptor and mammary tumour virus production after stimulation by glucocorticoid. Nature. 1976 Jul 8;262(5564):107–112. doi: 10.1038/262107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Baltimore D. RNA-directed DNA synthesis and RNA tumor viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1972;17:129–186. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60749-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Guntaka R. V., Deng C. T., Bishop J. M. Synthesis, structure and function of avian sarcoma virus-specific DNA in permissive and nonpermissive cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):987–996. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Medeiros E., Bishop J. M., Nowinski R. C., Sarkar N. H. Transcription of mouse mammary tumor virus genes in tissues from high and low tumor incidence mouse strains. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 5;79(4):663–679. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Structure of the intermediates leading to the integrated provirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 21;473(1):39–55. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P. Glucocorticoid-receptor interaction and induction of murine mammary tumor virus. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3337–3343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P. Steroid induction of mouse mammary tumor virus: effect upon synthesis and degradation of viral RNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.139-146.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]