Abstract
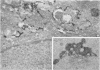
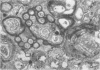
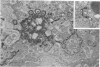
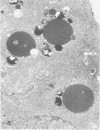
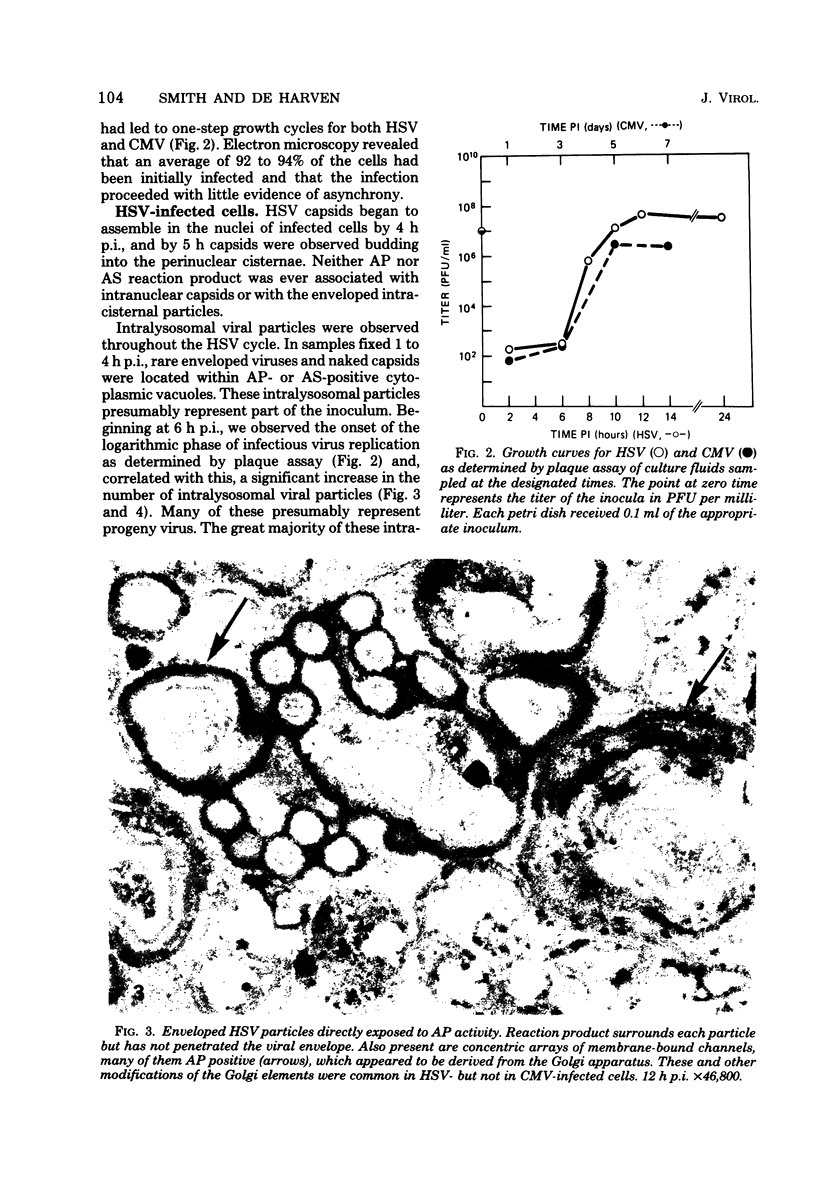
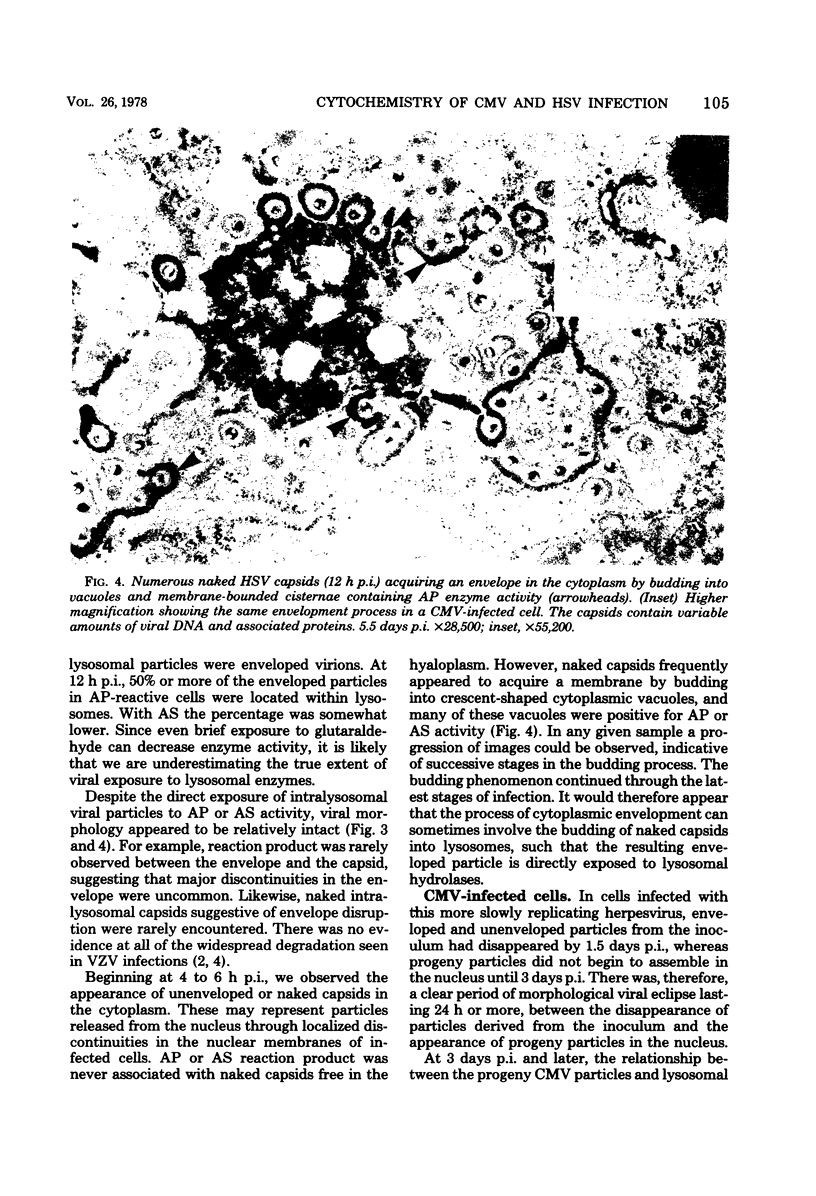
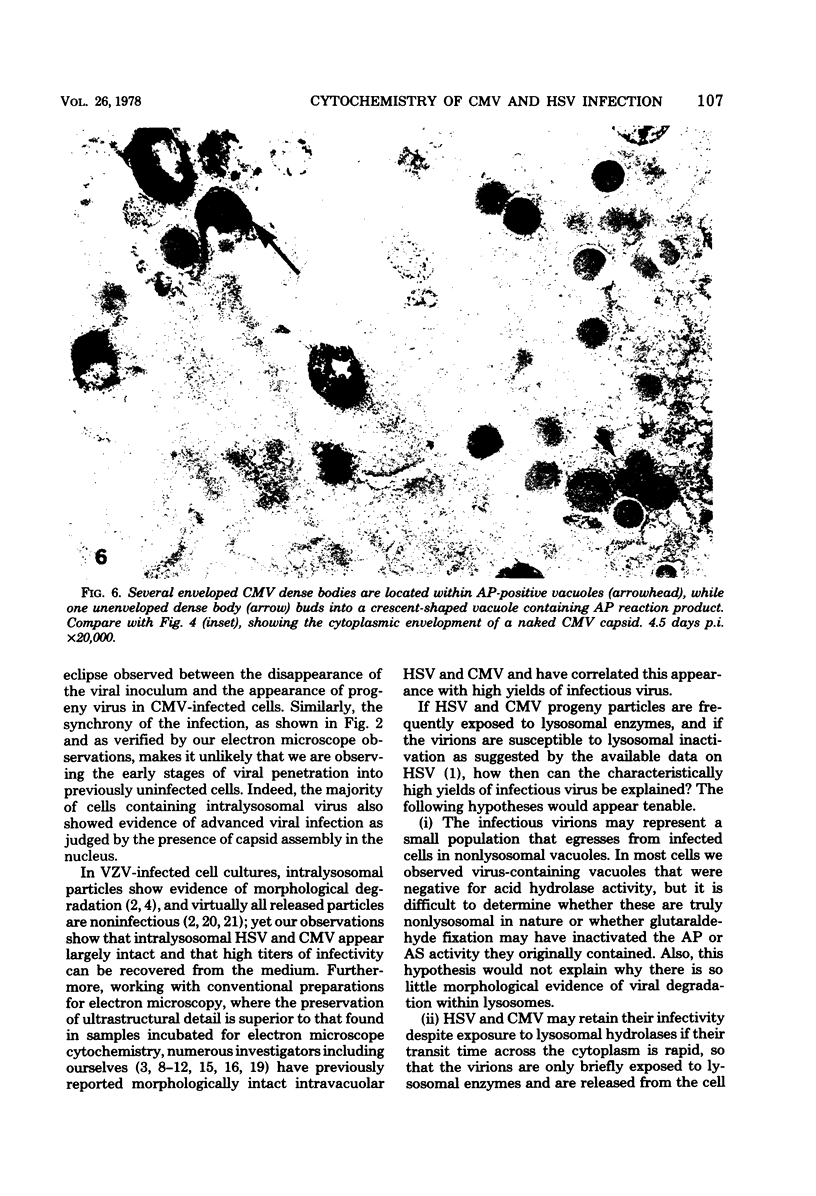
Cytochemical localization of the lysosomal enzymes acid phosphatase and arylsulfatase in cells infected by herpes simplex virus (HSV) or human cytomegalovirus (CMV) showed the following interactions between viruses and host cell lysosomes: (i) many enveloped progeny viruses were located within cytoplasmic vacuoles containing lysosomal enzyme activity; (ii) naked cytoplasmic capsids appeared to acquire an envelope by budding directly into lysosomes; and (iii) many of the cytoplasmic dense bodies that are characteristic of CMV-infected cells and are thought to represent noninfectious aggregates of CMV structural proteins (I. Sarov and I. Abady, Virology 66:464-473, 1975) also acquired a limiting membrane by budding into lysosomes. Autophagy of other cytoplasmic elements was not observed, suggesting that there is some specificity involved in the association of viral particles and CMV dense bodies with lysosomes. Despite the presence of potentially destructive hydrolases, there was little evidence of significant morphological damage to intralysosomal viruses, and high titers of infectious particles were released into the medium. It would therefore appear that significant levels of HSV and CMV infectivity normally persist even though many progeny particles are directly exposed to lysosomal enzymes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMOS H. The inactivation of herpes simplex virus by phosphatase enzymes. J Exp Med. 1953 Oct;98(4):365–372. doi: 10.1084/jem.98.4.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Labile coat: reason for noninfectious cell-free varicella-zoster virus in culture. J Virol. 1968 Dec;2(12):1458–1464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.12.1458-1464.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E., Kanich R. E., Almeida J. D. Nonviral microbodies with viral antigenicity produced in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):766–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.766-775.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon A., Cosio L., Brunell P. A. Observations on the growth of varicella-zoster virus in human diploid cells. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jan;18(1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S., Gennaro D. E., Weissmann G., Hirsch J., Streuli F., Fox A. C. Cytochemical localization of lysosomal enzyme activity in normal and ischemic dog myocardium. Am J Pathol. 1975 May;79(2):193–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu-Havu V. K., Arstila A. U., Helminen H. J., Kalimo H. O. Improvements in the method for the electron microscopic localization of arylsulphatase activity. Histochemie. 1967;8(1):54–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00279874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Furukawa T., Plotkin S., Koprowski H. Ultrastructural study on the sequence of human cytomegalovirus infection in human diploid cells. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;40(3):311–324. doi: 10.1007/BF01242551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanich R. E., Craighead J. E. Human cytomegalovirus infection of cultured fibroblasts. II. Viral replicative sequence of a wild and an adapted strain. Lab Invest. 1972 Sep;27(3):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGAVRAN M. H., SMITH M. G. ULTRASTRUCTURAL, CYTOCHEMICAL, AND MICROCHEMICAL OBSERVATIONS ON CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS) INFECTION OF HUMAN CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nii S., Morgan C., Rose H. M. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus. II. Sequence of development. J Virol. 1968 May;2(5):517–536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.5.517-536.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff P. M., Novikoff A. B., Quintana N., Hauw J. J. Golgi apparatus, GERL, and lysosomes of neurons in rat dorsal root ganglia, studied by thick section and thin section cytochemistry. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):859–886. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUEBNER B. H., HIRANO T., SLUSSER R. J., MEDEARIS D. N., Jr HUMAN CYTOMEGALOVIRUS INFECTION. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC AND HISTOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN CULTURES OF HUMAN FIBROBLASTS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Mar;46:477–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruebner B. H., Hirano T., Slusser R., Osborn J., Medearis D. N., Jr Cytomegalovirus infection. Viral ultrastructure with particular reference to the relationship of lysosomes to cytoplasmic inclusions. Am J Pathol. 1966 Jun;48(6):971–989. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Abady I. The morphogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. Isolation and polypeptide characterization of cytomegalovirions and dense bodies. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):464–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., De Harven E. Concentration of herpesviruses. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):325–328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.325-328.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., WITTON H. M., BELL E. J. The etiologic agents of varicella and herpes zoster; isolation, propagation, and cultural characteristics in vitro. J Exp Med. 1958 Dec 1;108(6):843–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.6.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of Herpesvirus hominis on human embryonic fibroblasts. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):588–592. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]