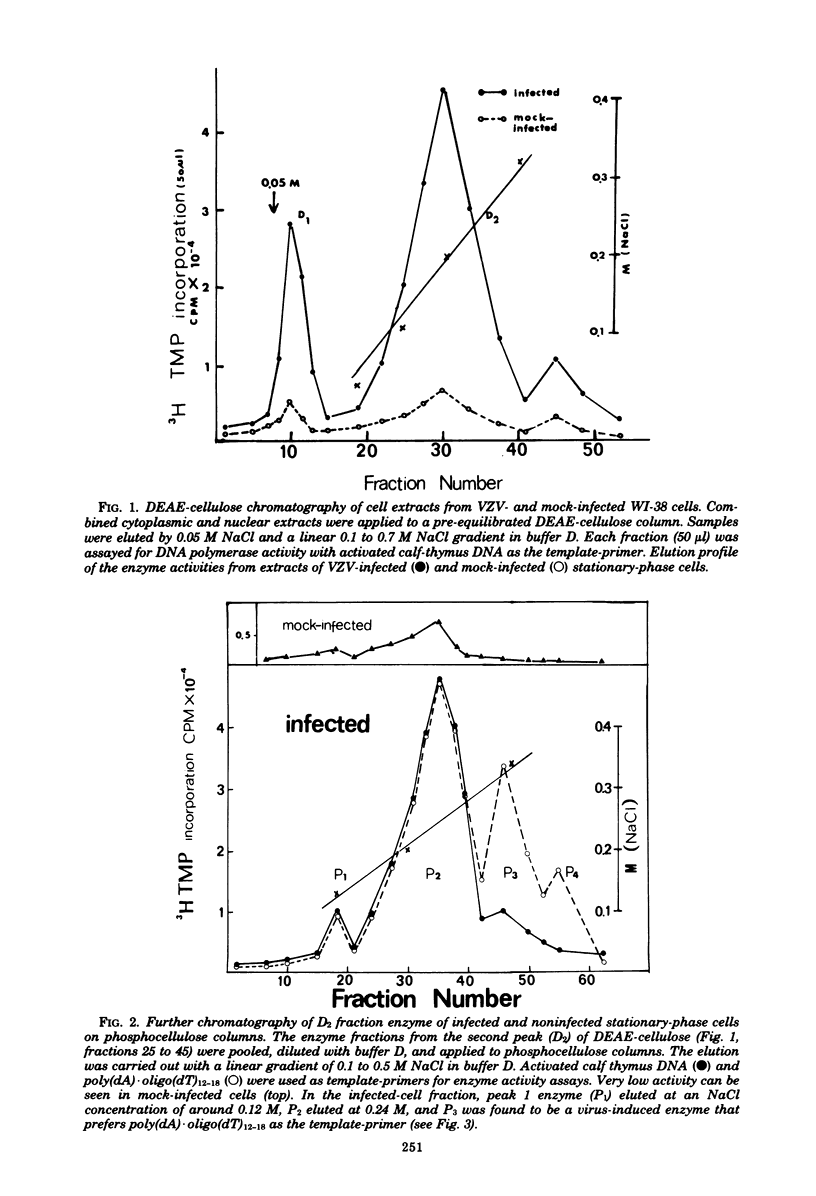
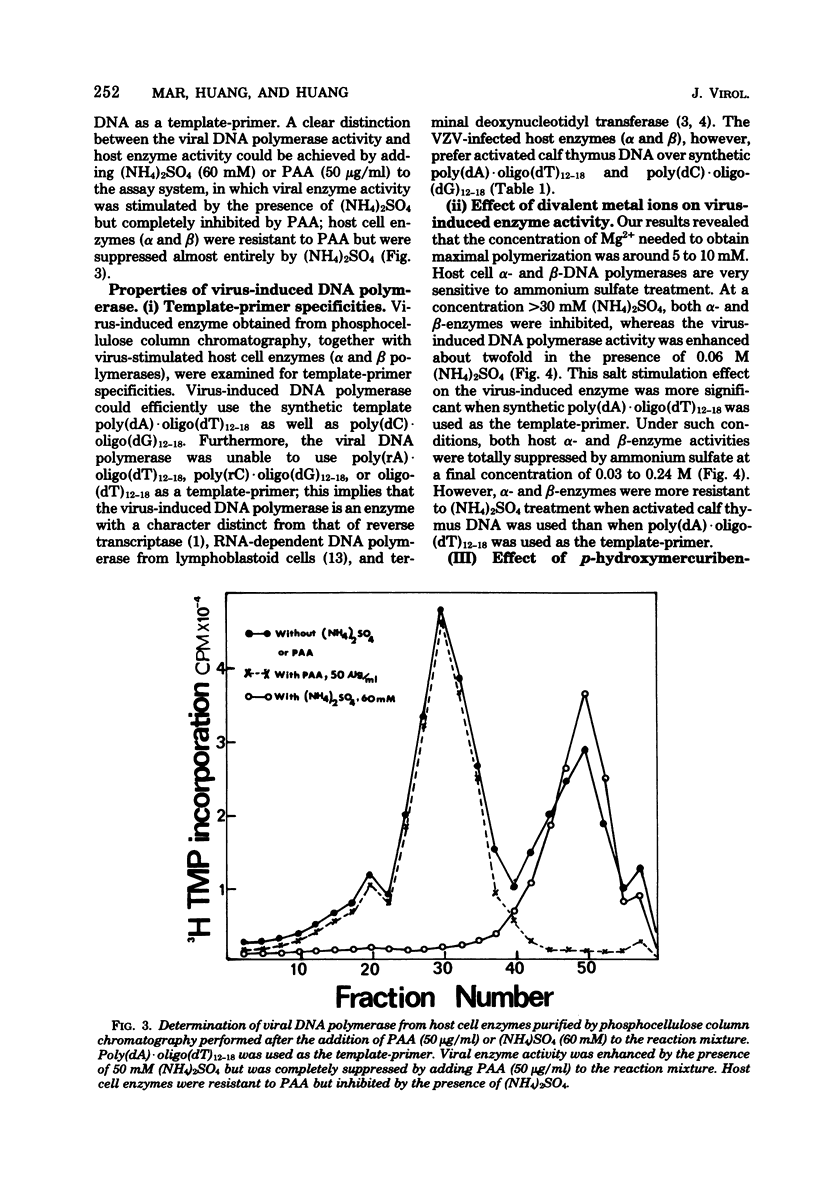
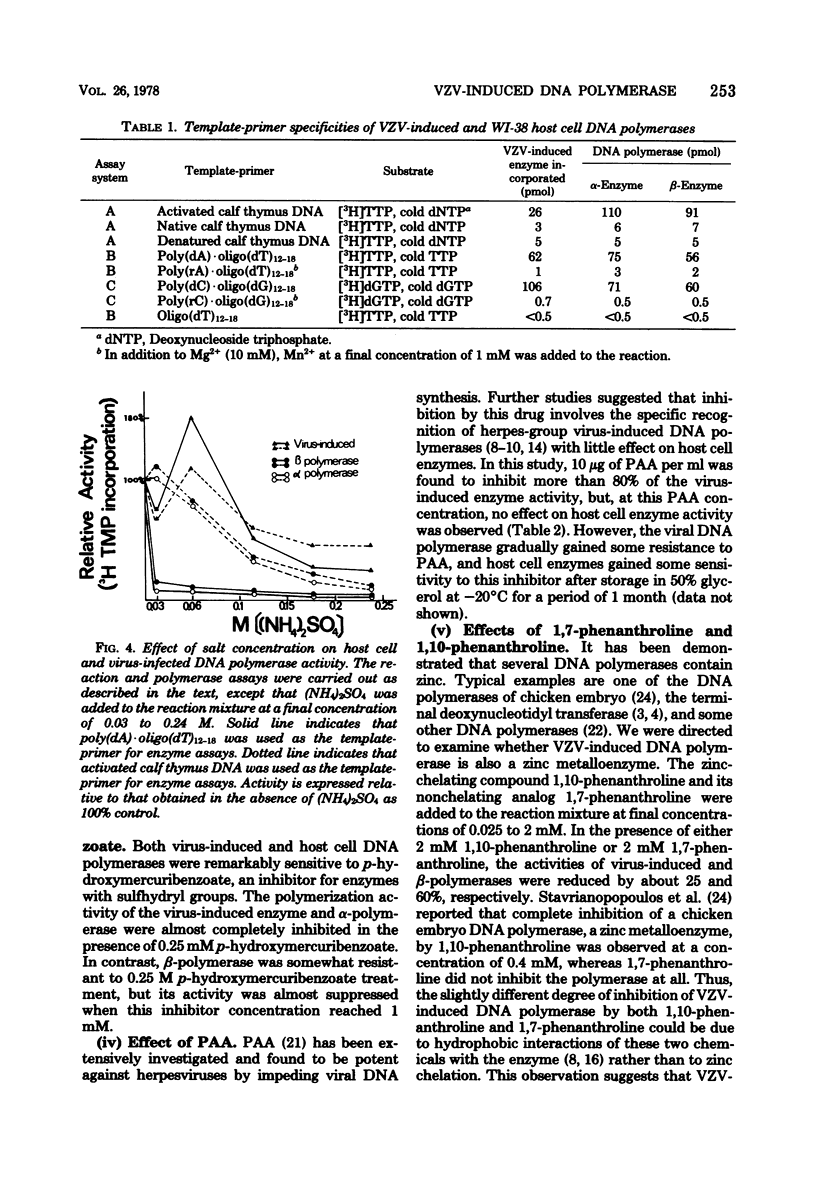
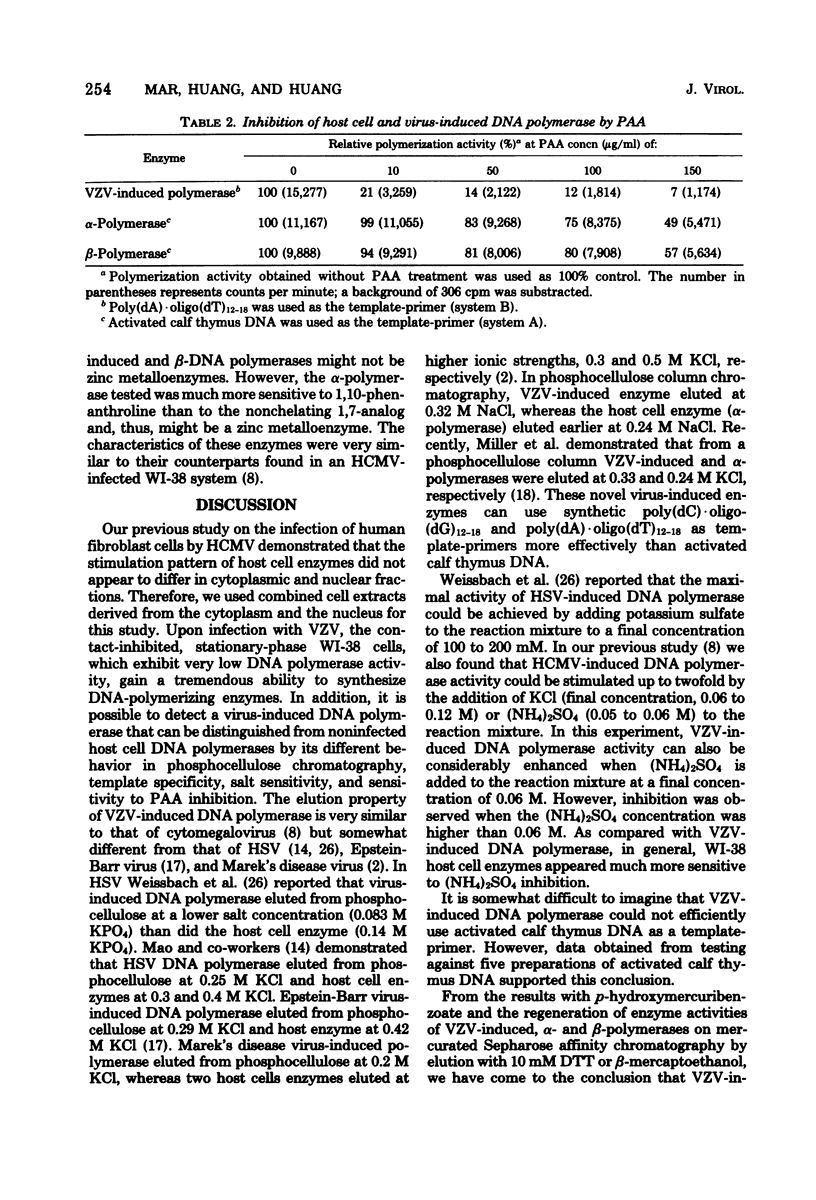
Abstract
Infection of WI-38 human fibroblasts with varicella-zoster virus led to the stimulation of host cell DNA polymerase synthesis and induction of a new virus-specific DNA polymerase. This virus-induced DNA polymerase was partially purified and separated from host cell enzymes by DEAE-cellulose and phosphocellulose column chromatographies. This virus-induced enzyme could be distinguished from host cell enzyme by its chromatographic behavior, template specificity, and its requirement of salt for maximal activity. The enzyme could efficiently use poly(dC).oligo(dG)12-18 as well as poly(dA).oligo(dT)12-18 as template-primers. It required Mg2+ for maximal polymerization activity and was sensitive to phosphonoacetic acid, to which host alpha- and beta-DNA polymerase were relatively resistant. In addition, this induced DNA polymerase activity was enhanced by adding 60 mM (NH4)2SO4 to the reaction mixture.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Bollum F. J. Doxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes of calf thymus gland. IV. Inhibition of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase by metal ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1041–1048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M. Development of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity in embryonic calf thymus gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80167-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobersen M. J., Jerkofsky M., Greer S. Enzymatic basis for the selective inhibition of varicella-zoster virus by 5-halogenated analogues of deoxycytidine. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.478-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes J. E., Huang E. S. Stimulation of cellular thymidine kinases by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):13–21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.13-21.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPE-SIMPSON R. E. THE NATURE OF HERPES ZOSTER: A LONG-TERM STUDY AND A NEW HYPOTHESIS. Proc R Soc Med. 1965 Jan;58:9–20. doi: 10.1177/003591576505800106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. III. Virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):298–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.298-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Replication of cytomegalovirus DNA in human lymphoblastoid cells. IARC Sci Publ. 1975;(11 Pt 1):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F., Boezi J. A., Blakesley R. W., Koenig M., Towle H. C. Marek's disease herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1209–1219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1209-1219.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Isbell A. F., Boezi J. A. Mechanism of phosphonoacetate inhibition of herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):426–430. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson P. R., Yost F. J., Jr, Harrison J. H. The absence of zinc in the mitochondrial and supernatant forms of malate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 10;321(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Glaser R., Rapp F. Studies of an Epstein-Barr virus-induced DNA polymerase. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):494–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90232-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Rapp F. Varicella-zoster virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):515–524. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S., Serpick A., Stoler B., Rumack B., Mellin H., Joseph J. M., Block J. Varicella-Zoster infection in patients with cancer. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Feb;76(2):241–254. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-2-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipkowitz N. L., Bower R. R., Appell R. N., Nordeen C. W., Overby L. R., Roderick W. R., Schleicher J. B., Von Esch A. M. Suppression of herpes simplex virus infection by phosphonoacetic acid. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):264–267. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.264-267.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. P., Mildvan A. S., Loeb L. A. Zinc in DNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava B. I. Deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes in normal and malignant human cells. Cancer Res. 1974 May;34(5):1015–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. DNA polymerase of chicken embryo: purification and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Hong S. C., Aucker J., Muller R. Characterization of herpes simplex virus-induced deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6270–6277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



