Abstract
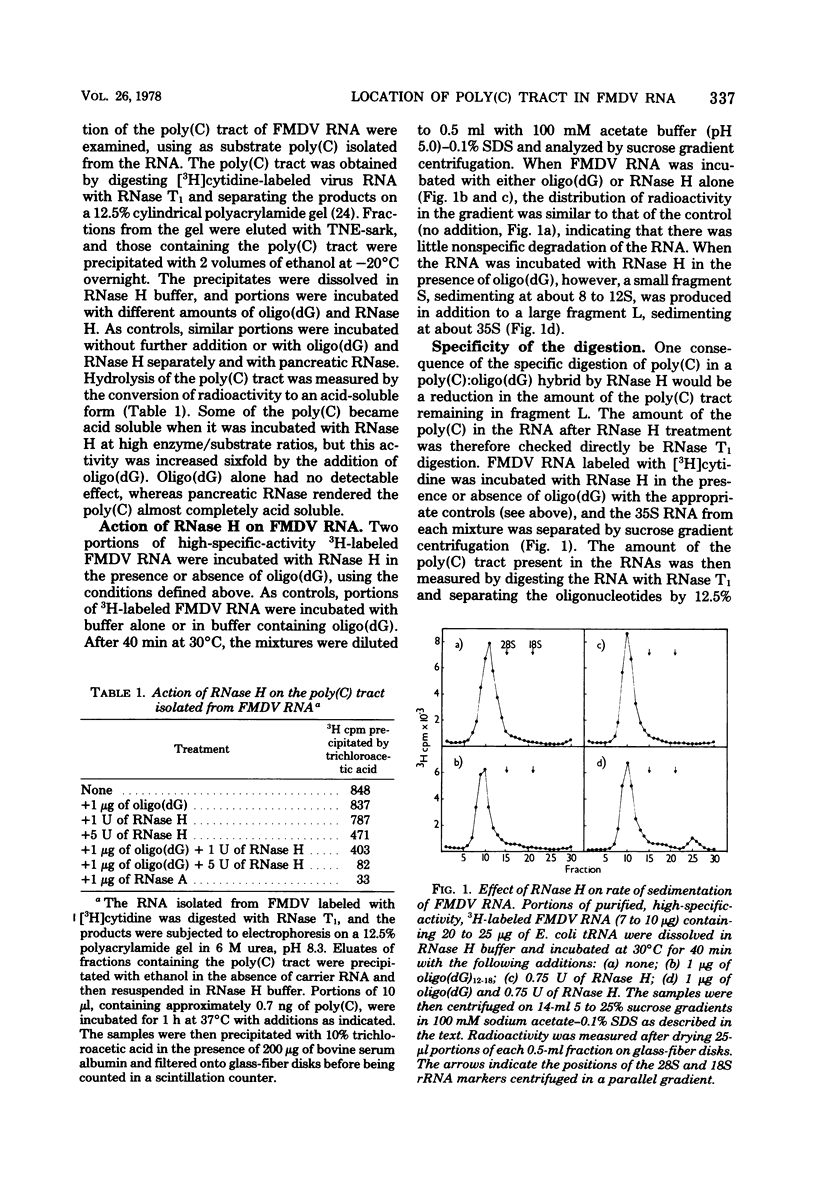
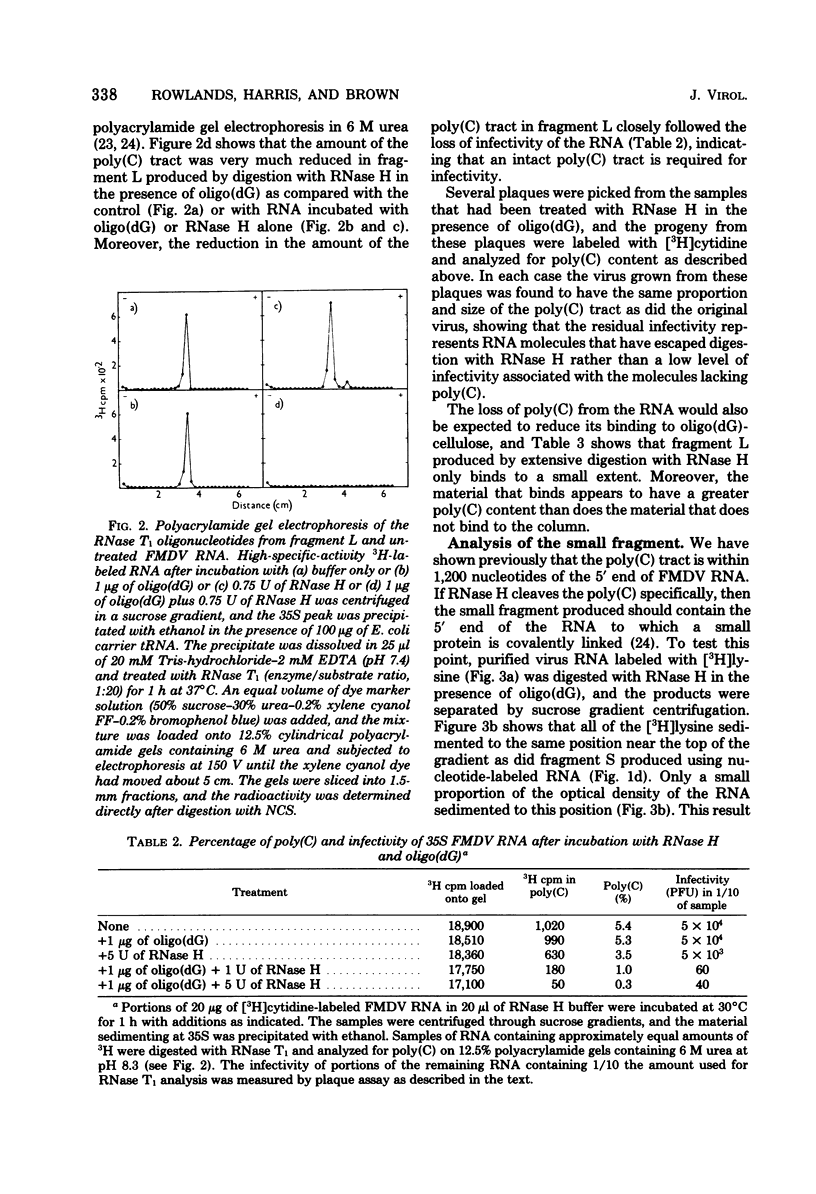
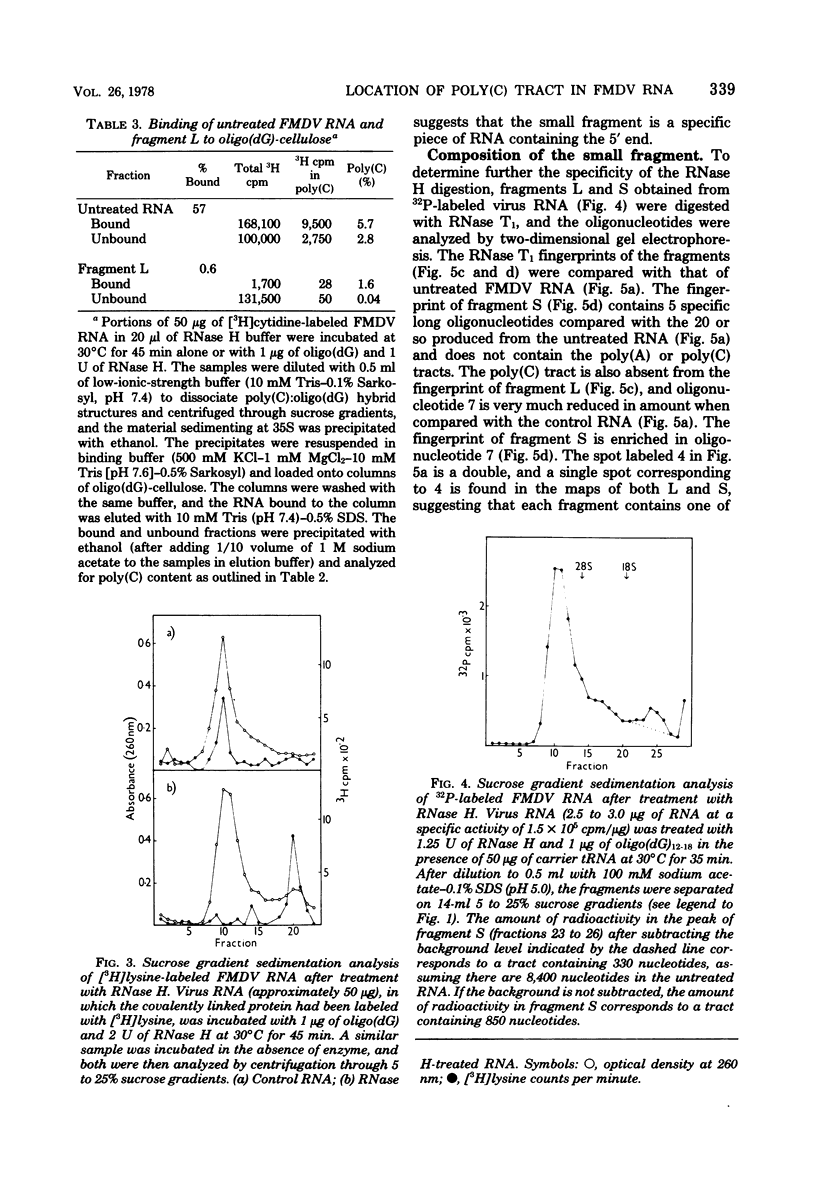
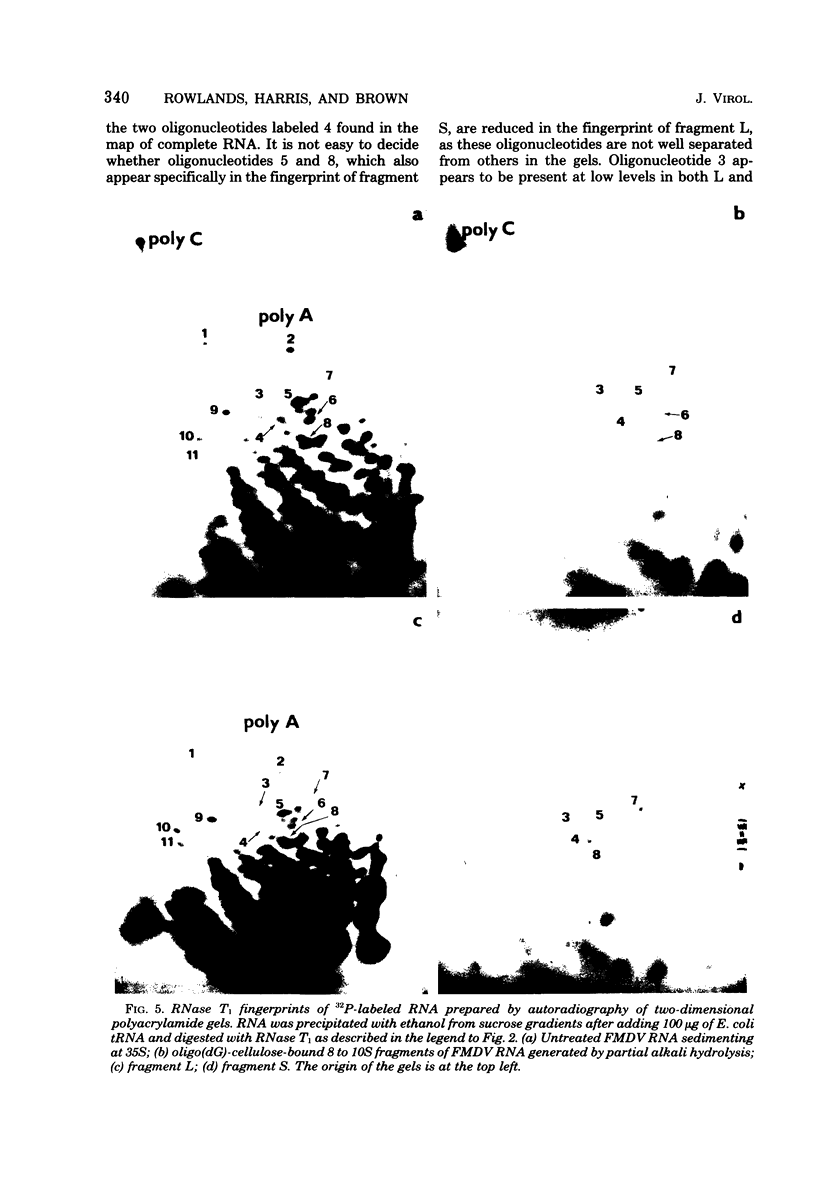
The polycytidylic acid [poly(C)] tract in foot and mouth disease virus RNA has been located about 400 nucleotides from the 5' end of the RNA by analysis of the products from the digestion of the RNA with RNase H in the presence of oligodeoxyguanylic acid [oligo(dG)]. This treatment produces a small fragment (S) containing the small protein covalently linked to the RNA and a large fragment (L) that migrates faster than untreated RNA on low-percentage polyacrylamide gels, lacks the poly(C) tract as shown by RNase T1 digestion and oligo(dG)-cellulose binding, and is no longer infective. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of fragment S suggests that it is about 400 nucleotides long, in agreement with the size estimated from the proportion of radioactivity in the fragment. Analysis of the RNase T1 digestion products of S shows that it contains only those oligonucleotides mapping close to the poly(C) tract that is situated near the 5' end of the virus RNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown F., Newman J., Stott J., Porter A., Frisby D., Newton C., Carey N., Fellner P. Poly(C) in animal viral RNAs. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):342–344. doi: 10.1038/251342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee N. K., Bachrach H. L., Polatnick J. Foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Presence of 3'-terminal polyriboadenylic acid and absence of amino acid binding ability. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D., Eaton M., Fellner P. Absence of 5' terminal capping in encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2771–2787. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Brown F. Biochemical analysis of a virulent and an avirulent strain of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):87–105. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Brown F. The location of the ploy(C) tract in the RNA of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):493–501. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Doel T. R., Brown F. Moleculas aspects of the antigenic variation of swine vesicular disease and Coxsackie B5 viruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 May;35(2):299–315. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Wildy P. The synthesis of polyadenylated messenger RNA in herpes simplex type I virus infected BHK cells. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):299–312. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Rees M. W., Short M. N. Studies on alfalfa mosaic virus. I. The protein and nucleic acid. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):404–415. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Brown F. Absence of poly (A) from the infective RNA of Nodamura virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jan;30(1):137–140. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Bercoff R., Gander M. The genomic RNA of mengovirus. I. Location of the poly(C) tract. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):426–429. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A., Carey N., Fellner P. Presence of a large poly(rC) tract within the RNA of encephalomyocarditis virus. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):675–678. doi: 10.1038/248675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Requirement of 3'-terminal poly(adenylic acid) for the infectivity of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2983–2987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




