Abstract
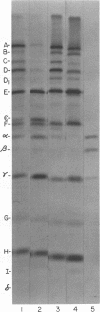
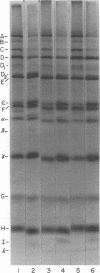
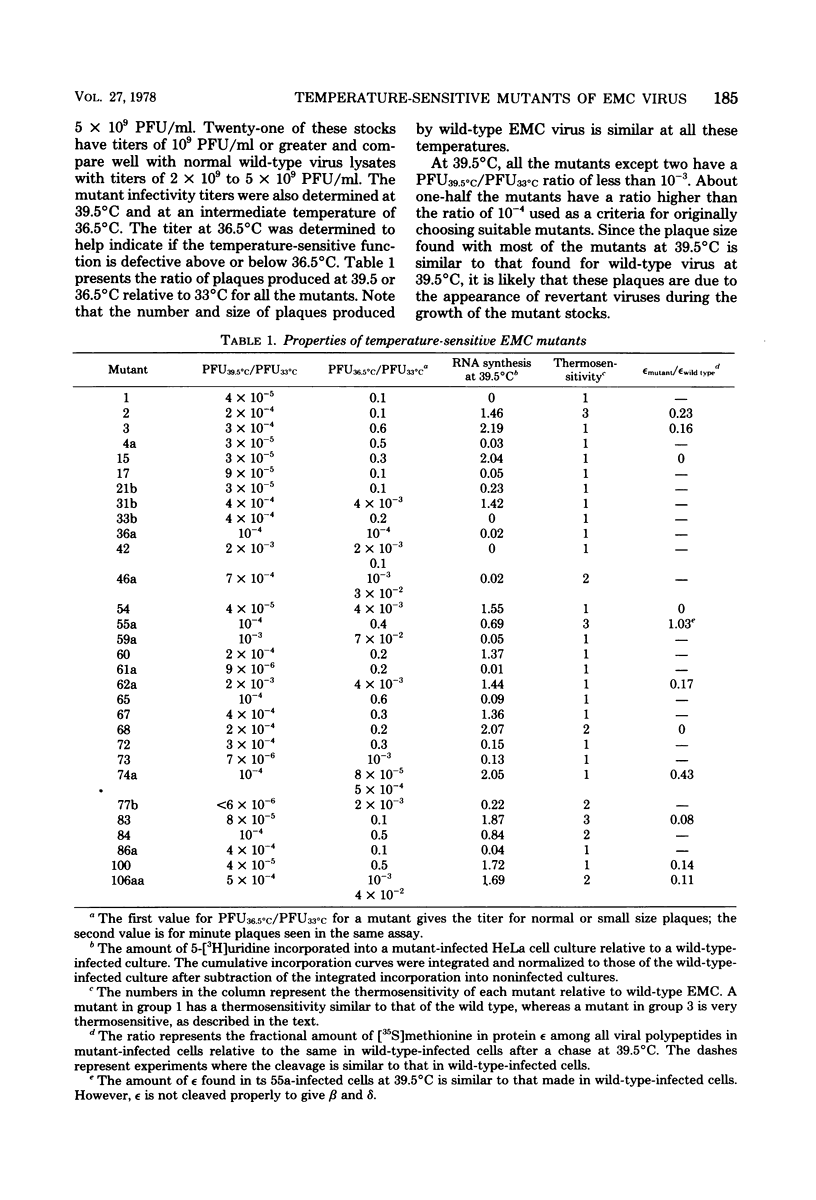
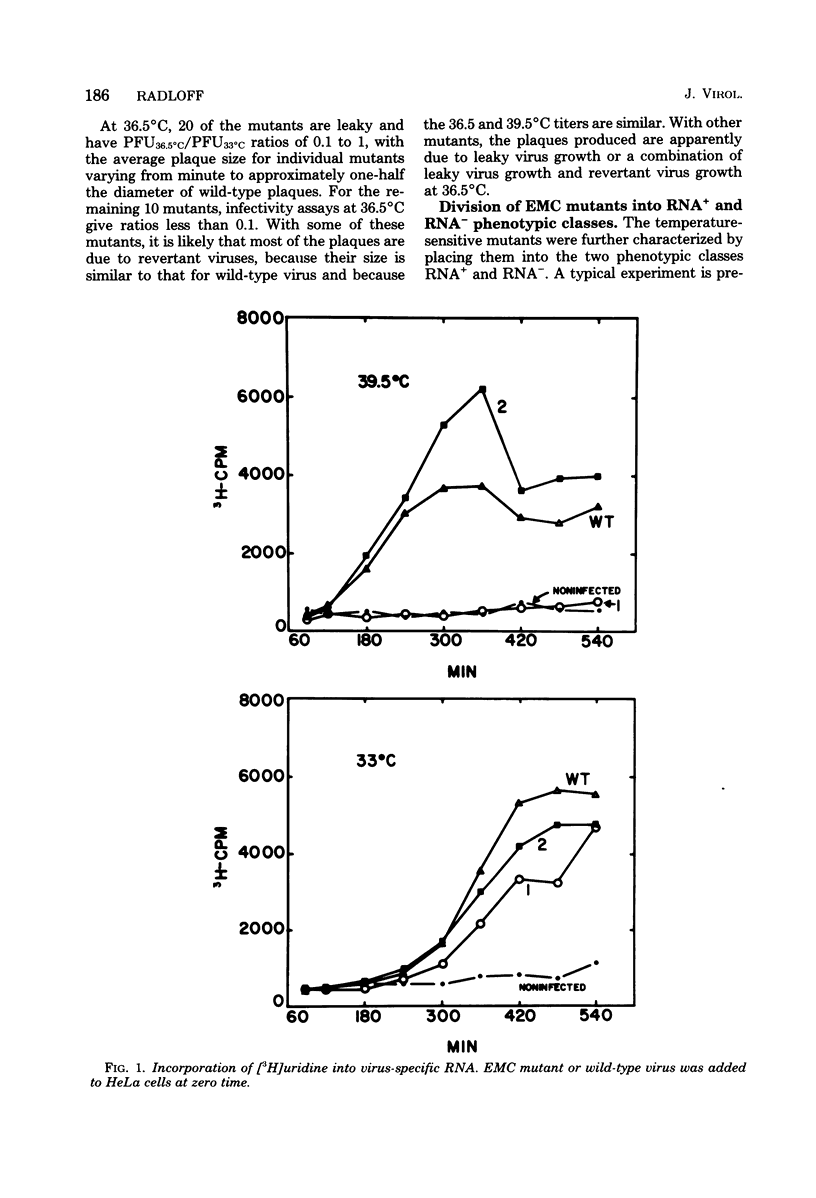
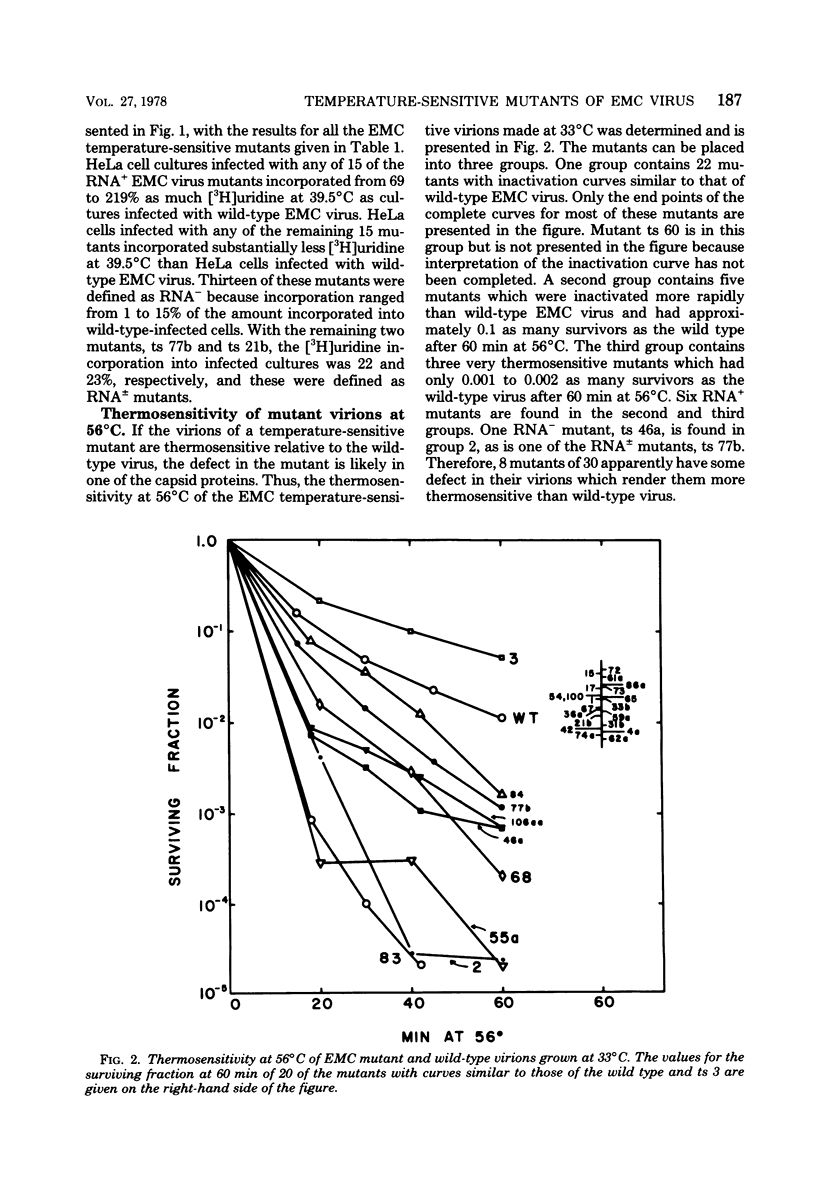
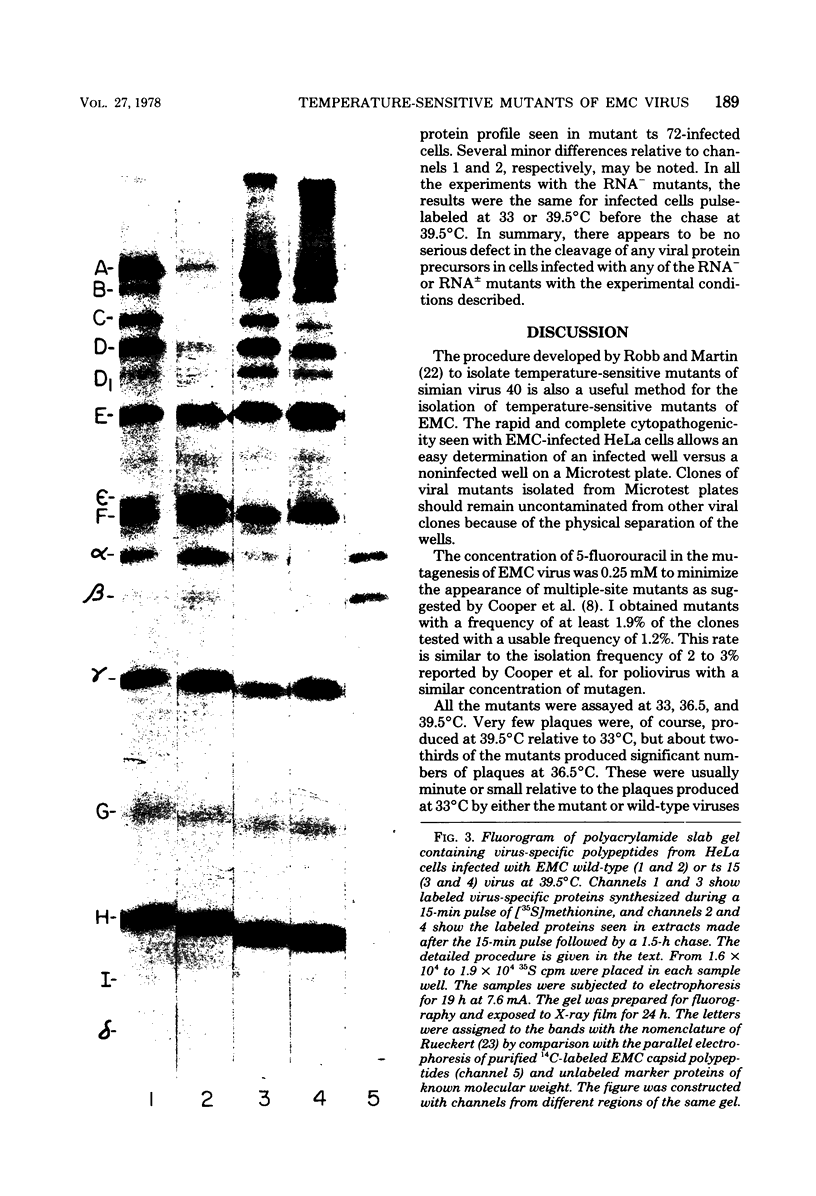
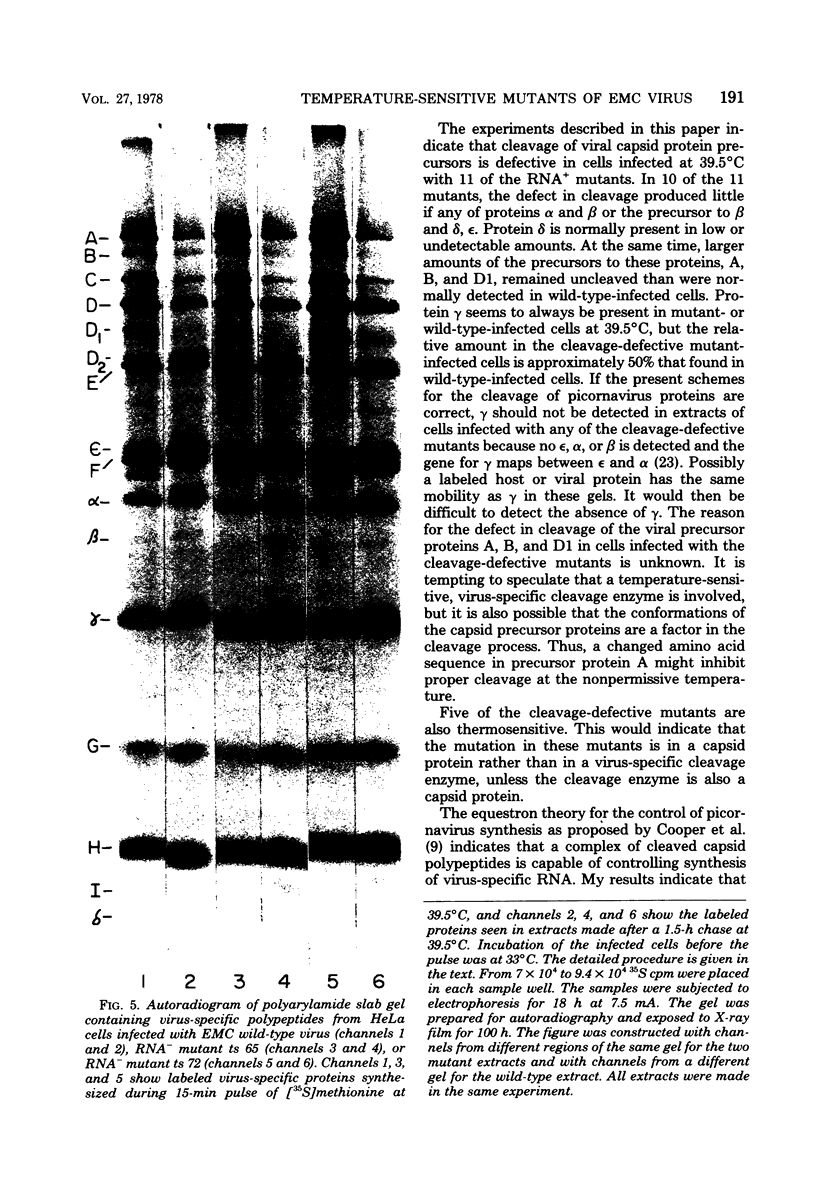
Thirty temperature-sensitive mutants of encephalomyocarditis virus have been isolated and partially characterized. Fifteen of these mutants are phenotypically RNA+ thirteen are RNA-, and two are RNA +/-. Six RNA + mutants, one RNA- mutants, and one RNA +/- mutant have virions which are more thermosensitive at 56 degree C than the wild-type virions. Hela cells infected at the nonpermissive temperature with any of the RNA+ mutants produced neither infective nor noninfective viral particles. The cleavage of the precursor polypeptides in cells infected with 11 of the RNA+ mutants was defective at the nonpermissive temperature. This defect in cleavage occurred only in those precursor polypeptides leading to capsid proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Cooper P. D. Poliovirus polypeptides examined in more detail. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):199–213. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond C. W., Swim H. E. Physiological characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of mengovirus. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):288–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.288-296.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Rueckert R. R. Gene order of encephalomyocarditis virus as determined by studies with pactamycin. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):823–828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.823-828.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Rueckert R. R. Kinetics of synthesis and cleavage of encephalomyocarditis virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90405-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. THE MUTATION OF POLIOVIRUS BY 5-FLUOROURACIL. Virology. 1964 Feb;22:186–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Johnson R. T., Garwes D. J. Physiological characterization of heat-defective (temperature-sensitive) poliovirus mutants: preliminary classification. Virology. 1966 Dec;30(4):638–649. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Steiner-Pryor A., Wright P. J. A proposed regulator for poliovirus: the equestron. Intervirology. 1973;1(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000148826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer D. N., Sunderland S., Colter J. S. Isolation and partial characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Mengo virus. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L., Rueckert R. R. Infection of mouse fibroblasts by cardioviruses: premature uncoating and its prevention by elevated pH and magnesium chloride. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):152–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN E. M., MALEC J., SVED S., WORK T. S. Studies on protein and nucleic acid metabolism in virus-infected mammalian cells. 1. Encephalomyocarditis virus in Krebs II mouse-ascites-tumour cells. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:585–597. doi: 10.1042/bj0800585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie J. S., Slade W. R., Lake J., Priston R. A., Bisby J., Laing S., Newman J. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus: the isolation of mutants and observations on their properties and genetic recombination. J Gen Virol. 1975 Apr;27(1):61–70. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer H. R., Allen R. C. Useful buffer and gel systems for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1972 May;10(5):220–225. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1972.10.5.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medappa K. C., McLean C., Rueckert R. R. On the structure of rhinovirus 1A. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90258-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overby L. R., Barlow G. H., Doi R. H., Jacob M., Spiegelman S. Comparison of two serologically distinct ribonucleic acid bacteriophages. I. Properties of the viral particles. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):442–448. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.442-448.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Recombination between conditional lethal mutants within a strain of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):199–202. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-1-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond J. Y. Production, isolation, and partial characterization of three foot-and-mouth disease virus temperature-sensitive mutants. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1291–1295. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1291-1295.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A., Martin R. G. Genetic analysis of simian virus 40. I. Description of microtitration and replica-plating techniques for virus. Virology. 1970 Aug;41(4):751–760. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90439-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]