The ErbB2 receptor is a validated cancer target whose internalization and trafficking remain poorly understood. The authors propose that ErbB2 internalization upon geldanamycin (GA) occurs predominantly via clathrin-mediated endocytosis and that GA affects endosomal structure and sorting, forcing recycling cargoes toward mixed endo/lysosomal compartments, irrespective of their HSP90 interaction.
Abstract
The ErbB2 receptor is a clinically validated cancer target whose internalization and trafficking mechanisms remain poorly understood. HSP90 inhibitors, such as geldanamycin (GA), have been developed to target the receptor to degradation or to modulate downstream signaling. Despite intense investigations, the entry route and postendocytic sorting of ErbB2 upon GA stimulation have remained controversial. We report that ErbB2 levels inversely impact cell clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME) capacity. Indeed, the high levels of the receptor are responsible for its own low internalization rate. GA treatment does not directly modulate ErbB2 CME rate but it affects ErbB2 recycling fate, routing the receptor to modified multivesicular endosomes (MVBs) and lysosomal compartments, by perturbing early/recycling endosome structure and sorting capacity. This activity occurs irrespective of the cargo interaction with HSP90, as both ErbB2 and the constitutively recycled, HSP90-independent, transferrin receptor are found within modified endosomes, and within aberrant, elongated recycling tubules, leading to modified MVBs/lysosomes. We propose that GA, as part of its anticancer activity, perturbs early/recycling endosome sorting, routing recycling cargoes toward mixed endosomal compartments.
INTRODUCTION
ErbB-2/HER2/neu is a type 1 transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family, chaperoned by HSP90. At variance with the other members of the ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase (HER) family, ErbB2 is an orphan receptor. When trans-activated, ErbB-2 stimulates several downstream signaling cascades, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway (Citri and Yarden, 2006; Hynes and MacDonald, 2009). Although moderately expressed in normal adult tissues, in which it regulates cell growth, differentiation, and motility (Marone et al., 2004; Liu et al., 2010), it plays an important role in the pathogenesis of breast cancers, as well as other carcinomas. Approximately 20–30% of breast cancers have an amplification of the HER2/neu gene or overexpression of its protein product. High levels of receptor expression are associated with increased disease recurrence and worse prognosis in breast cancers. ErbB2 is therefore a key factor in the carcinogenesis process. Endocytosis of ErbB receptors represents a common event upon stimulation; however, ErbB2 appears to be internalized less efficiently compared with EGFR (Sorkin et al., 1993; Hommelgaard et al., 2004; Longva et al., 2005; Roepstorff et al., 2008), as the ErbB2 surface pool has been reported to either undergo slow cycles of constitutive endocytosis and recycling (Austin et al., 2004) or be retained on the surface and excluded from active endocytosis, thus promoting uncontrolled signaling of the receptor (Wang et al., 1999; Hommelgaard et al., 2004). Furthermore, ErbB2 overexpression interferes with EGFR receptor internalization by sequestering the ErbB2/ErbB1 heterodimers at the cell surface, as well as by inhibiting the EGF-induced formation of clathrin-coated structures (Haslekas et al., 2005; Sorkin and Goh, 2008).
In the past decade, intense investigation into the complex process of endocytosis, using advanced light and electron microscopy (EM) techniques, has led to the discovery of several morphologically and structurally distinct endocytic carriers. Moreover, the concept of derailed endocytosis has recently emerged as a hallmark of cancer cells, placing internalization and recycling routes as crucial targets of the processes driving cancer initiation and progression (Mosesson et al., 2008; Abella and Park 2009). Among the various endocytic portals, the most extensively studied is clathrin-mediated endocytosis (CME). CME supports many vital processes, ranging from nutrient uptake, cellular movement, and proliferation, to complex developmental morphogenetic events (Vaccari and Bilder, 2009). Recent work reports that CME is important for the efficacy of anti-ErbB2 receptor monoclonal antibody–based tumor therapy (Ben-Kasus et al., 2009), suggesting CME is the route taken by ErbB2 under specific conditions. In addition to CME, caveolae and three new endocytic pathways that do not depend on caveolae or clathrin (clathrin-independent endocytosis or CIE) have been defined on the basis of specific regulation by RhoA, Arf6, and cdc42, and tubular morphology (Kirkham and Parton, 2005; Mayor and Pagano, 2007; Sandvig et al., 2008; Howes et al., 2010). More recently, the molecular composition and the ultrastructural morphology of the major tubular CIE route, that is, the clathrin independent carrier/GPI-AP–enriched early endosomal compartment (CLIC/GEEC) have been described. One specific regulator of the CLIC/GEEC pathway, the Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain containing the protein GRAF1 (Lundmark et al., 2008; Doherty and Lundmark, 2009; Doherty et al., 2011; Howes et al., 2010), provides a specific and useful tool to dissect this pathway. Endocytosis can be viewed under different perspectives, for example, as a way to internalize membranes and cargoes or as master organizer of signaling circuits in space and time (Pelkmans et al., 2005; Lanzetti and Di Fiore, 2008; Scita and Di Fiore, 2010). According to the latter view, cargo proteins (e.g., signaling receptors and toxins) are fully integrated with, and modulate, the endocytic network (Romer et al., 2007; Mettlen et al., 2010).
Owing to its role in cancer, HER2/neu has been identified as a therapeutic target leading to the development of several molecule-targeted therapeutic agents, including the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin; Genentech-Roche, South San Francisco, CA). Trastuzumab is currently used as a highly effective frontline therapy in ErbB2-positive breast cancers. However, due to the frequent acquisition of drug resistance, combinatorial anticancer therapies have gained favor over single-molecule inhibition (Zsebik et al., 2006; Raja et al., 2008). In this context, the search for other possible therapeutic molecules targeting ErbB2 has continued. Among them, HSP90 inhibitors, such as geldanamycin (GA) and the less toxic derivatives 17-AAG and 17-DMAG, have rapidly emerged as a class of promising drugs that can target multiple oncogenic pathways simultaneously (Citri et al., 2004; Fukuyo et al., 2010). Preclinical and clinical data with HSP90 inhibitors in various cancer models are promising, and evidence hints at the potential for tumor-selective cytotoxicity and enhanced sensitization to chemo- and radiotherapy (Jones and Buzdar, 2009).
ErbB2 is particularly sensitive to GA and its derivatives and undergoes several changes upon treatment, including receptor polyubiquitylation, extensive endocytic redistribution, and degradation (Tikhomirov and Carpenter, 2000, 2003; Citri et al., 2002). However, no full consensus has been reached on ErbB2’s endocytic route and final fate. Indeed, using the well-characterized breast cancer cell line SK-BR-3, studies have reported both CME (Austin et al., 2004; Pedersen et al., 2008, 2009) and CIE pathways similar to clathrin-independent carriers (CLICs; Barr et al., 2008) to be involved in ErbB2 internalization upon GA treatment.
In this paper, we have used a combination of light microscopy and EM techniques to clarify ErbB2’s endocytic pathway and sorting upon GA treatment, showing that: 1) constitutive ErbB2 internalization is mediated by CME and subject to a negative regulation operated by ErbB2 overexpression on the rate of clathrin-coated pit (CCP) and vesicle (CCV) formation; 2) GA treatment does not potentiate ErbB2 internalization via CME; and 3) the intracellular fate of recycling receptors, namely ErbB2 and Transferrin (Tf) receptor, is dramatically affected by a GA-dependent remodeling of the endosome morphology and routing pathways, highlighting GA as a potential new tool to manipulate endosomal functions.
RESULTS
ErbB2 regulates CME endocytosis in SK-BR-3 cells
ErbB2 is thought to be either retained on the cell surface or constitutively internalized via CME with slow kinetics in SK-BR-3 cells (Sorkin et al., 1993; Austin et al., 2004; Hommelgaard et al., 2004; Longva et al., 2005). GA appears to promote ErbB2 internalization via a CIE pathway similar to CLICs (Barr et al., 2008). These two observations suggest SK-BR-3 cells are inefficient in CME, or alternatively, the low efficiency of ErbB2 internalization is solely restricted to this receptor.
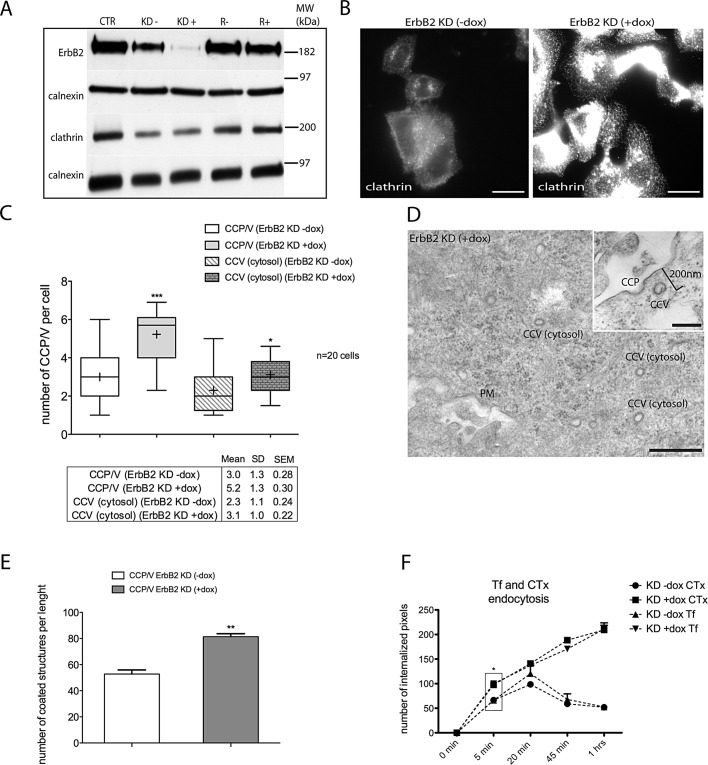
To evaluate the potential role of ErbB2 overexpression in CCP and CCV formation, we took advantage of SK-BR-3 knockdown (KD) cells, a stably transfected SK-BR-3 cell line expressing an ErbB2 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) upon doxycycline treatment (see Materials and Methods). Although both wild-type and silenced cells expressed comparable levels of total clathrin heavy chain (Figure 1A), immunofluorescence displayed a more intense punctate staining within the cytoplasm in ErbB2-silenced cells (Figure 1B) compared with control. To better characterize this phenotype, we performed morphometric EM analysis. We found a significant increase in the number of total CCP/CCV per cell in ErbB2-silenced cells, compared with nonsilenced cells (Figure 1, C and D, box plot). In addition, we quantified CCP/V at, or close to (>200 nm), the plasma membrane (PM) to evaluate the endocytosis capacity of our system. As shown in Figure 1E, the number of CCP/Vs per micrometer length of PM is significantly increased in ErbB2 KD cells compared with nonsilenced cells.
FIGURE 1:
ErbB2 interferes with CME in SK-BR-3 cells. (A) Western blot analysis of total lysates of SK-BR-3 (CTR); SK-BR-3 ErbB2 KD without doxycycline (KD−); SK-BR-3 ErbB2 KD doxycycline–treated (KD+); SK-BR-3 transfected with Tet repressor only, without doxycycline (R−); and SK-BR-3 Tet repressor treated with doxycycline (R+). (B) Epifluorescence microscopy of SK-BR-3 ErbB2 KD (−doxycycline) compared with ErbB2 KD (+doxycycline). Paraformaldehyde (PFA)-4%-fixed cells were quenched with 30 mM NH4Cl and permeabilized with 0.2% saponin. Clathrin heavy chain was labeled with monoclonal anticlathrin antibody (X22; Abcam) followed by Alexa Fluor 555–conjugated proper secondary antibody. All images were captured at 0.1 s of exposure with a Hamamatsu Orca1 digital camera and IPLab software. The different pattern of clathrin intensity and distribution in ErbB2 expressing (−dox) vs. silenced cells (+dox) is shown. (C and D) TEM analysis of CCP/V in ErbB2 KD SK-BR-3 cells. (C) TEM analysis of CCP/V in ErbB2 KD SK-BR-3 cells was performed in two independent experiments measuring the number of CCP/Vs in 10 cells for each experiment (n = 20) and plotted as a box-and-whisker plot. All values were normalized by cell size (see Materials and Methods). CCP/Vs were separated into two categories, CCP/V and CCP/V cytosol. We included in the category CCP/V all CCPs attached to the PM and putative vesicles located within 200 nm of the PM (inset in D; KD−dox: n = 60; KD+dox: n = 104). In the category CCP/V cytosol, we included all the CCP/Vs found at a distance of > 200 nm from the PM (KD−dox: n = 46; KD+dox: n = 62). The plot shows the median value as a horizontal bar, the mean as (+), the interquartile range as a box; the whiskers are the minimum and maximum values. The table shows the mean, SD, and SEM of the total structures counted per category. An unpaired Student's t test was applied comparing CCP/V±dox (p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.0001) and CCV cytosol±dox (p < 0.05; *, p = 0.017). (D) TEM micrograph of SK-BR-3 KD (+dox) showing several CCP/Vs (category cytosol), PM is indicated (arrow). Scale bar: 500 nm. Inset: TEM image showing a CCP and a putative CCV (category CCP/V) in SK-BR-3 KD (+dox). Scale bar: 200 nm. (E) Bar graph showing the number of CCP/Vs per unit length (μm). We counted all CCP/Vs connected to the PM and putative vesicles within 200 nm from the PM (PM length counted = 1000 μm) in two different experiments. Bars and error bars show mean and SD. An unpaired Student's t test was used (p < 0.05; **, p = 0.0071). (F) CTx and Tf endocytic assays were performed in SK-BR-3, either silenced or not for ErbB2 (+dox and −dox, respectively), and analyzed by confocal microscopy. After 20 min of ligand binding on ice, uptake of Tf-647 (1 mg/ml) and CTx-555 (1 μg/ml) was traced for 5, 20, and 30 min and 1 h at 37°C and the internalized fraction was quantified by pixel intensity. Cells were acid-washed prior to fixation to exclude noninternalized ligand. Confocal images of 30 cells for each of two independent experiments (n = 60) were analyzed with Adobe Photoshop CS2. The line graph shows the percentage of Tf-647 and CTx-555 internalized pixels for the two markers during the time course indicated. Error bars represent SD. Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired Student's t test analysis comparing the 5-min time points (p < 0.05) of Tf and CTx (±dox). We observed a significant increase (*) of both Tf and CTx internalization in KD cells (+dox): Tf-647 (p = 0.0171); CTx-555 (p = 0.0131).
To test whether this phenotype interfered with CME internalization, we compared the endocytosis kinetics of transferrin receptor (TfR), a cargo exclusively internalized via CME, and of cholera toxin B subunit (CTx), a protein internalized through both the CME and CIE pathways (Kirkham et al., 2005; Howes et al., 2010). To this end, we incubated silenced and nonsilenced SK-BR-3 KD cells with the TfR ligand, Tf, conjugated to the fluorophore Alexa Fluor 647 (Tf-647) and CTx conjugated to the fluorophore Alexa Fluor 555 (CTx-555) for 15 min on ice.
After cells were transferred at 37°C for 5, 20, 30, and 60 min, they were acid-washed to remove PM labeling, and intracellular fluorescence was quantified. The line graph in Figure 1F shows the Tf and CTx internalization measured by pixel intensity. We observed an increase in Tf-647 and CTx-555 uptake in silenced cells over the time course considered but not in nonsilenced and wild-type cells (unpublished data). These results showed that ErbB2 expression is inversely related to the efficiency of CCP and CCV formation and that it interferes with CME in SK-BR-3 cells. In addition, the similar kinetics of uptake of Tf-647 and CTx-555 suggested that CME is the major endocytic route regulated by ErbB2.
GA-stimulated internalization of ErbB2 is mediated by the clathrin-dependent pathway
The slow rate of ErbB2 internalization may be due to the negative role of receptor overexpression on CME. Therefore it is possible that GA treatment may induce the ErbB2 internalization via a clathrin/tyrosine kinase/caveolae–independent pathway. Indeed, under these conditions, ErbB2 was shown to colocalize with CTx and glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored proteins and to associate with short tubules or large vesicles, similar to CLICs (Barr et al., 2008).
CLICs are membrane carriers, distinct from caveolae, that stem from the PM in a dynamin-independent manner. They mature into GPI-enriched endocytic compartments (GEECs) within 5 min (Sabharanjak et al., 2002; Kalia et al., 2006), as they acquire Rab5 and EEA-1, and merge with early endosomes (EEs). CLIC/GEECs are associated with the activity of the small G proteins Cdc42, and GRAF1 (GTPase regulator associated with focal adhesion kinase 1), a Rho-GAP domain–containing protein. GRAF1 is a unique marker for the CLIC/GEEC pathway that localizes to PtdIns(4,5)P2-enriched tubular and punctate lipid intracellular compartments via N-terminal BAR and PH domains (Lundmark et al., 2008; Doherty et al., 2011).
At variance with the canonical CLIC/GEEC pathway, GA-induced ErbB2 internalization does not require Rho-family GTPase activity (Barr et al., 2008). This observation led us to further explore and characterize the GA-induced ErbB2 internalization pathway. To this end, we: 1) tested the dynamin dependency of the process, using dynasore (a selective inhibitor of dynamin) and the dominant-negative mutant DynK44A, to sort out the possible involvement of alternative pathways to CLIC/GEEC; and 2) explored the association of the ErbB2 endocytic compartments with the CLIC/GEEC marker GRAF1.
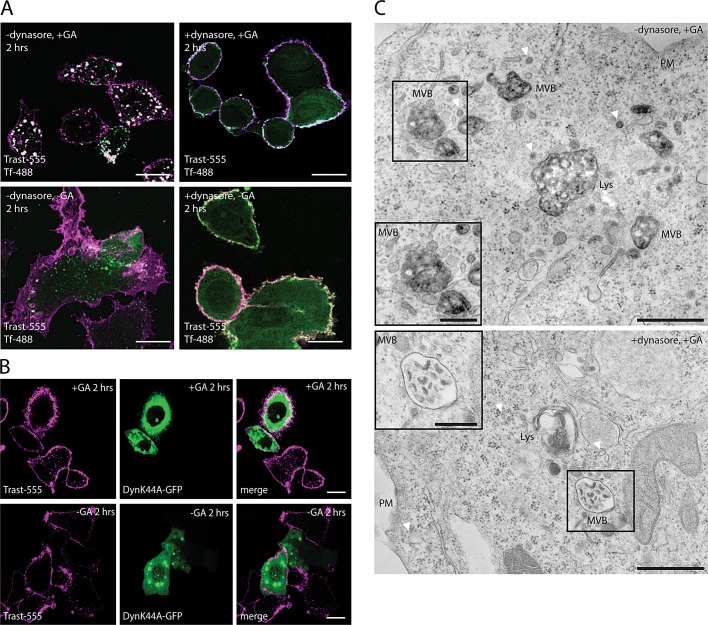
SK-BR-3 cells were incubated at 4°C in the presence or absence of GA and dynasore. ErbB2 was traced by labeling with trastuzumab–Alexa Fluor 555; the endocytosis was promoted by shifting the cells at 37°C. Western blot analysis revealed that GA treatment was sufficient to induce ErbB2 degradation irrespective of the presence of trastuzumab (Supplemental Figure S1A). This result suggests that trastuzumab did not interfere with GA activity. Under these conditions, immunofluorescence studies (Figure 2A) showed that ErbB2 internalization could be detected after 2 h from the temperature shift in GA-treated control cells, whereas dynasore caused a complete block of ErbB2 endocytosis, either in the presence or in the absence of GA treatment. The simultaneous block of the uptake of Tf-488 demonstrated the efficacy of the inhibitor on the CME pathway. The dynamin dependency of the GA-induced ErbB2 endocytic pathway was further studied by transiently transfecting SK-BR-3 cells with the nonfunctional dynamin-K44A mutant, a condition known to result in the blocking of CCV formation. Indeed, dynamin-K44A induced a complete block of ErbB2 internalization (Figure 2B).
FIGURE 2:
ErbB2 internalization is dynamin-dependent. (A) SK-BR-3 cells were either preincubated with 80 μM dynasore in CO2-independent medium and then incubated on ice with trastuzumab-555 and Tf-488 with and without GA (10 μg/ml) for 15 min. Cells were extensively washed with cold medium to remove unbound antibodies and allowed to internalize with or without dynasore for 2 h. Cells were then washed, fixed, and examined by confocal microscopy. As shown, both Tf-488 and Trast-555 internalization were completely abolished upon dynasore treatment. Scale bar: 10 μm. (B) Confocal images of SK-BR-3 cells transiently transfected with GFP-tagged Dynamin-K44A mutant for 18 h. Cells were treated with or without GA (10 μg/ml) for 2 h in the presence of trastuzumab-555 and then processed for confocal immunofluorescence. Scale bar:10 μm. (C) DAB-peroxidase EM visualization of internalized trastuzumab-HRP (+ 2 h GA, +AA) in GA-treated SK-BR-3 cells, in the absence (−dynasore) or presence (+dynasore) of dynasore. Trastuzumab-HRP is found in multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and lysosomes (Lys). The boxed areas (enlarged in the insets) identify MVBs, whereas arrowheads point to vesicles. Scale bars: 500 nm (−dynasore); 1 μm (+dynasore). Only the MVBs and vesicles in cells untreated with dynasore display a dense, specific, DAB precipitate, indicating that trastuzumab-HRP was not internalized in the presence of dynasore. Scale bars: 1 μm (−dynasore), 2 μm (+dynasore).
Similar results were obtained in EM experiments (Figure 2C) using trastuzumab–horseradish peroxidase (HRP) as a probe to trace ErbB2 and a modified immunoperoxidase diaminobenzidine/ascorbic acid (DAB/AA) method (Kirkham et al., 2005; Howes et al., 2010) previously described to visualize CLICs, caveolae, and CCVs carrying surface cargoes. In this procedure, the removal of the surface-associated DAB reaction product with AA leaves only the staining associated with endocytic compartments not connected to cell surface.
To evaluate whether ErbB2 endocytic compartments associate with the CLIC/GEEC marker GRAF1 upon GA treatment, we took advantage of the flat morphology of COS7 cells, which gives an advantage in confocal microscopy analysis compared with SK-BR-3 cells. COS7 cells were transiently cotransfected with ErbB2 and green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged GRAF1, either wild type (GFP-[wt]GRAF1), or mutated in the BAR+PH domain (GFP-[BAR+PH]GRAF1). This mutant has been shown to trap cargo proteins within stabilized CLIC tubules and to completely abolish further trafficking. Thus, if ErbB2 traffics through this compartment, it should be easily detectable (Lundmark et al., 2008).
Cells treated with GA (10 μg/ml) for 20 min at 37°C were further incubated for 20 min on ice with 9G6, a monoclonal antibody directed to the ErbB2 extracellular domain (Figure S2), and mixed with CTx-647 as a marker for both CME and CIE pathways. Cells were warmed at 37°C for 5, 20, and 45 min and washed with acid buffer, to remove the surface-bound antibodies, and CTx-647, to highlight the internalized labeling. On fixation and permeabilization, 9G6 was revealed with an Alexa Fluor 546–labeled secondary antibody.
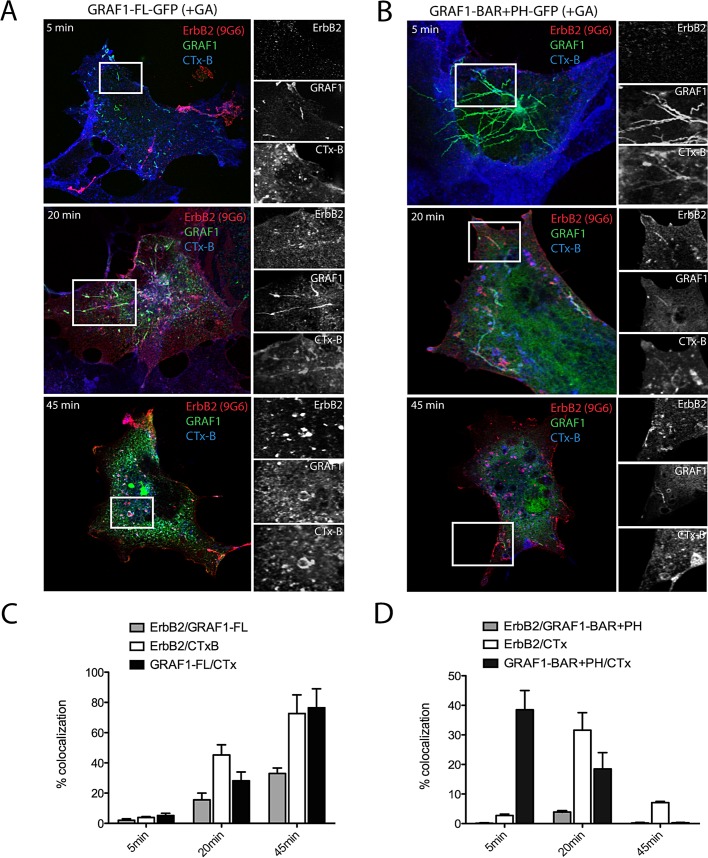
Overall, after GA treatment, the number of intracellular compartments labeled by ErbB2 in cells transfected with either wild-type or mutant GRAF1 conditions was dramatically increased (Figure 3) compared with untreated controls (Figure S1B). After 5 min of chase, CTx-647 labeled both [wt]GRAF1- and [BAR+PH]GRAF1-positive compartments, whereas ErbB2 was poorly internalized and colocalized with neither of them, suggesting that ErbB2 was not internalized through CLICs. At later time points, ErbB2 colocalized with CTx-647 in the context of [wt]GRAF1 compartments, whereas partial colocalization was observed within [BAR+PH]GRAF1-stabilized tubules (Figure 3), supporting the hypothesis that [wt]GRAF1-positive tubules may merge with ErbB2 endocytic carriers other than CLICs. The alternative use of 9G6 anti-ErbB2 antibody to track the receptor in these experiments did not influence the internalization pathway and sorting of ErbB2 and TfR compared with trastuzumab (Figure S2). After 5 min of internalization (with or without GA), only a few ErbB2-positive vesicles colocalizing with Tf-555 were observed, suggesting that the onset of internalization was slow. After 2 h, we observed extensive colocalization between internalized ErbB2 and Tf-555. Because Tf is internalized exclusively via CCVs (see Figure 7D later in this article), these data suggested that ErbB2 is primarily internalized via CME and sorted to recycling compartments.
FIGURE 3:
GA-induced ErbB2 endocytosis is not mediated by GRAF1. (A and B) COS7 cells were cotransfected with wild-type ErbB2 (red), and either GFP-tagged, full-length GRAF1 (left; green), or GRAF1 BAR+PH (right; green). Anti-ErbB2 antibodies (9G6, red) and CTxB-647 (blue) were bound to cells for 15 min on ice prior to induction of internalization at 37°C for the indicated times. Surface labeling was removed by acid wash, and cells were fixed, permeabilized, and labeled with anti-Alexa Fluor 546 antibodies to detect internalized ErbB2. Insets on the right side of each image show an enlargement of the corresponding boxed areas. Internalized ErbB2 (top), GRAF1 tubules (middle), internalized CTx-647 (bottom). (C and D) Bar graphs show the percentage of internalized ErbB2 pixels that colocalized with GRAF1 (gray bars) and CTxB (white bars) over the time course calculated using Adobe Photoshop CS2. Black bars represent the percentage of GRAF1 pixels that colocalize with CTx over the time course. Note that the percentage of internalized ErbB2 pixels is very low after 5 min of internalization. Bars show the mean, and error bars indicate the standard errors of the mean (SEMs) of pixels calculated on 10 images across two independent experiments.
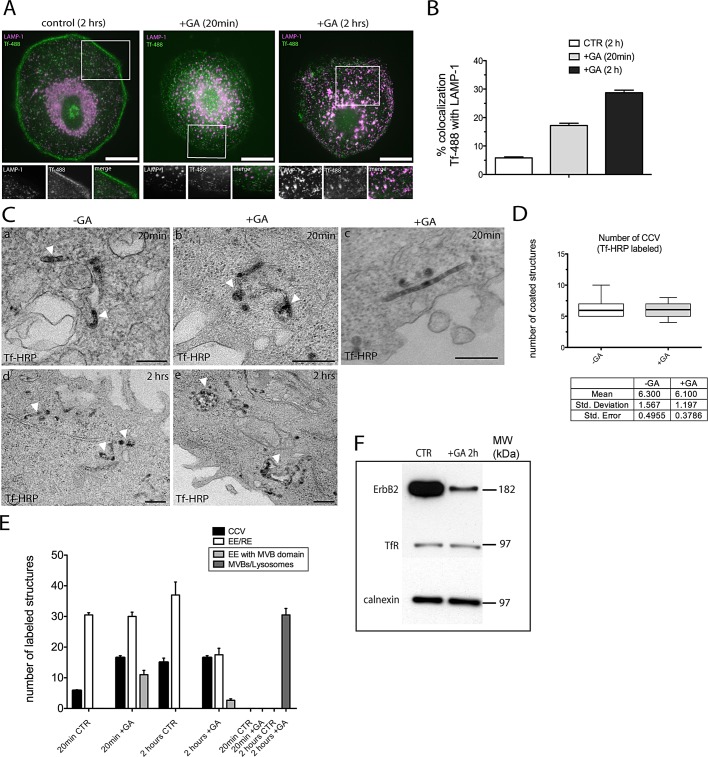
FIGURE 7:
GA impinges upon Tf recycling. (A) Immunofluorescence of Tf-488 uptake in control and GA-treated SK-BR-3 cells. Tf-488 was bound to the cell surface on ice for 15 min, either in the presence or in the absence of GA. Cells were washed and warmed at 37°C for different times, as indicated, and processed for immunofluorescence. Anti-LAMP1 antibody was used to label the lysosomal compartment (magenta). In contrast with untreated cells, Tf-488 localizes in LAMP-1 lysosomal compartments in GA-treated cells. Scale bars: 10 μm. (B) Colocalization between Tf-488 and LAMP-1 was quantified by pixel intensity in 10 cells over two independent experiments. The percentage of overlap was plotted as a bar graph. Bar and error bars show mean ± SEM. (C) TEM analysis of Tf-HRP uptake. Control and GA-treated SK-BR-3 were incubated with 1 mg/ml Tf-HRP for 15 min on ice, washed out in cold medium, and allowed to internalize at 37°C for the indicated time points. Cells were treated with DAB (+AA) to visualize the reaction product. Note that Tf-HRP is found in the MVB domain of EEs and in elongated tubules upon 20 min of GA treatment (b, arrowheads, and c). Sorting into MVB domain of EEs was not observed in untreated cells, in which Tf-HRP localized within EE/REs (a, arrowheads). After 2 h, Tf-HRP is found in EE/REs in untreated cells (d, arrowheads), whereas it is missorted to MVBs/lysosomes in cells treated with GA (e, arrowheads). Scale bars: 200 nm (a); 500 nm (b–e). (D) Box-and-whisker plot showing the quantification of Tf-HRP (+AA)-labeled clathrin-coated structures (±GA) upon 5 min of internalization in 10 cells across two independent experiments. Note that there is no difference in the number of internalized coated structures with/without treatment. (E) Quantification of Tf-HRP endocytic structures (±GA) performed in 10 cells across two independent experiments. Bars and error bars show mean ± SEM. CCVs were defined as coated vesicles, EE/REs as in Figure 7C (a and d, arrowheads), EEs with MVB domain as in Figure 7C (b, arrowheads), MVBs/lysosomes as in Figure 7C (e, arrowheads). Categories boxed are present only in GA-treated cells. (F) Western blot analysis of ErbB2 and TfR degradation upon GA treatment. TfR is not degraded compared with ErbB2 upon GA treatment (see Discussion).
To definitively identify the GA-induced ErbB2 entry route, we ruled out the involvement of other two CIE pathways, that is, those requiring caveolin1 and flotillin1 pathways. By comparing ErbB2-transfected mouse embryonic fibroblast wild-type (MEFwt) and caveolin-1 knockout (KO) MEF (MEFcav−) cells (Kirkham et al., 2005; Figure S3A), we found that ErbB2 is internalized in the absence of caveolae (MEFcav− cells) Similarly, ErbB2 and flotillin1-GFP cotransfected COS7 cells (Glebov et al., 2006; Frick et al., 2007; Otto and Nichols, 2011) showed no ErbB2/flotillin1 colocalization at 5 min, whereas colocalization appeared at 20 min of GA treatment (Figure S3B). These results excluded the involvement of both caveolin1 and flotillin1 pathways for the internalization of ErbB2. As expected, after 20 min of treatment, ErbB2 also colocalized with Tf-647–labeled compartments, further supporting the merge of the ErbB2 entry vesicles with endosomal compartments.
Altogether these data demonstrate that upon GA treatment, ErbB2 is mainly internalized via a CME pathway and routed to recycling compartments.
GA induces dramatic remodeling of endocytic pathways
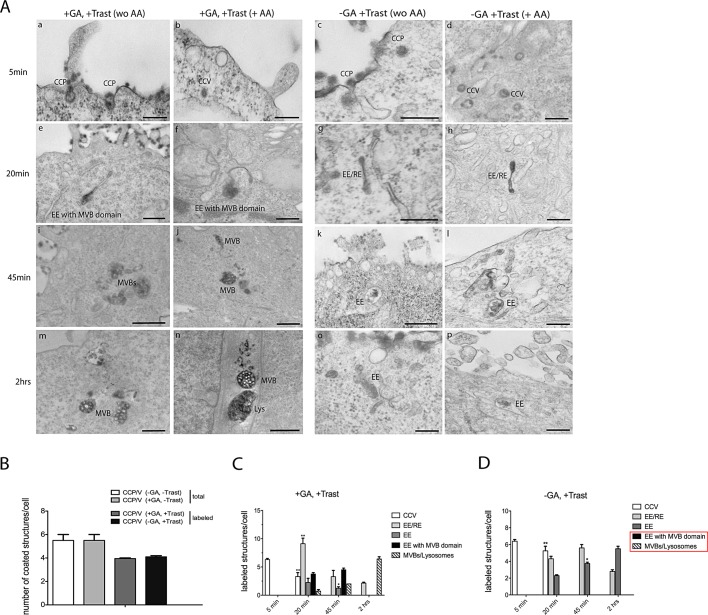
A detailed analysis of the morphology of [wt]GRAF1- and [BAR+PH]GRAF1-expressing COS7 cells showed that the morphology of CTx-647–labeled [wt]GRAF1 tubules was dramatically modified by GA treatment and assumed an elongated configuration (Figures 3 and S4). This observation prompted us to verify whether GA induced a modification of endocytic compartments in SK-BR-3 cells as well. Therefore we used trastuzumab-HRP to trace ErbB2 and combined the modified immunoperoxidase DAB/AA method (Kirkham et al., 2005; Howes et al., 2010) with two- and three-dimensional EM analysis. SK-BR-3 cells were pretreated with 10 μg/ml GA for 20 min at 37°C, transferred on ice, and labeled with trastuzumab-HRP. After the excess of trastuzumab-HRP was washed off, cells were transferred at 37°C in the presence of GA and processed after 0, 5, 20, 45, and 120 min of chase. Control cells were processed in the same way but in the absence of GA treatment. We used morphological criteria to define early, recycling, and multivesicular endosome (MVB) structures. Briefly, because inner vesicles accumulate progressively upon endosome maturation, their number is considered indicative of the maturation stage (Klumperman et al., 1993; Mari et al., 2007). On average, in our model system, correlating the morphology of the endosomes to the known time-dependent appearance of internalized bovine serum albumin (BSA)-gold in the different endocytic compartments (see Materials and Methods), we found that EEs contained from 1 to 10 intraluminal vesicles, whereas MVBs contained more than 10 intraluminal vesicles. Tubular endosomes devoid of BSA-gold were instead defined as recycling endosomes (EE/REs). Of note, the dense DAB reaction within endosomes did not impair the visualization of inner vesicles, allowing their identification (see Figure 6 later in this article).
FIGURE 6:
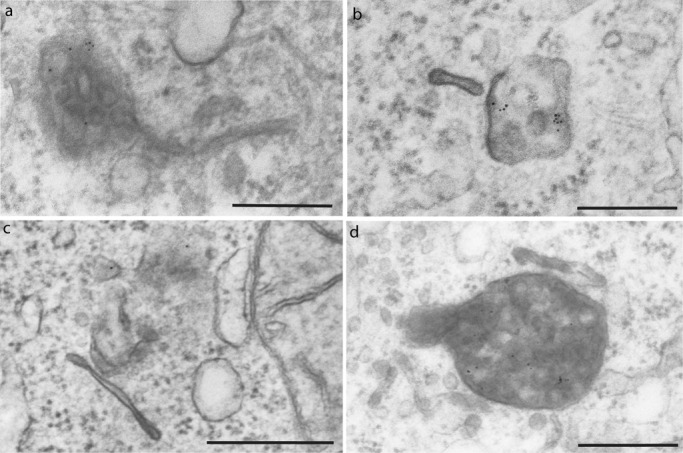
BSA-gold (5 nm) uptake. (a–c) Accumulation of BSA-gold at 20-min internalization time in HRP-labeled MVB, either isolated or as part of the MVB domain of the GA-modified compartments, whereas it never localized in the tubular domains. (d) BSA-gold accumulation in MVB upon 2 h of GA treatment. Scale bars: 300 nm (a, b); 500 nm (c, d).
After 5 min, trastuzumab-HRP localized within CCPs and CCVs in GA-treated cells (Figure 4A, a and b). A morphometric analysis of EM experiments showed that the total number of CCP/Vs per cell, and the number of trastuzumab-HRP–labeled CCP/Vs (with or without GA), were comparable in GA-treated and GA-untreated cells (Figure 4B), suggesting that GA does not interfere with CCP/V formation and internalization, but it is likely hampering postendocytic trafficking. After 20 min, the labeling filled the lumen of tubular endosomes either isolated (EE/RE) or terminating with an enlarged MVB domain (defined as EE with MVB domain; Figure 4A, e and f) and within vacuolar EEs (see Figure S5). In addition, some of these structures were abnormally elongated (≤1 micron in length), similarly to the GA-induced tubules in [wt]GRAF1 cells (Figure 3A). At later time points (Figure 4A, i, j, m, and n), ErbB2/trastuzumab-HRP was found in MVBs containing several intralumenal vesicles and displaying connections with the tubular compartments and in lysosomes. Morphometric analysis of endocytic compartments labeled with trastuzumab-HRP (with or without GA) is shown in Figure 4, C and D. A more detailed morphology of the elongated compartments was obtained by performing dual-axis tomograms (−60°, +60°) on 300-nm-thick sections of trastuzumab-HRP–labeled (DAB+AA) SK-BR-3 cells after 20 min of GA treatment (Figure 5A and Movies S1 and S2). Under these conditions, the endosomes were characterized by isolated large flat cisterns or an enlarged terminal MVB domain at one end. This morphology might in part recall CLICs ultrastructure as viewed by EM and three-dimensional tomography (Howes et al., 2010; Figure 5B and Movies S3 and S4).
FIGURE 4:
GA alters the morphology of endosomal compartments. (A) SK-BR-3 cells were incubated with trastuzumab-HRP at 4°C for 30 min in the presence of GA. They were then washed with CO2-independent cold medium and warmed for 5, 20, 45 and 120 min at 37°C with or without GA and DAB-treated in the presence or absence of AA to remove surface labeling. All samples were fixed and processed for EM without permeabilization. Trastuzumab-HRP reaction product is evident over the entire cell surface and within vesicular clathrin-coated profiles (CCP and CCV) after 5 min at 37°C either in cells treated with GA or trastuzumab-HRP alone (a–d). CCP/Vs were defined as coated carriers identified on the PM or within 200 nm of the PM. On 20 min of internalization in the presence of GA, trastuzumab-HRP was found within the lumen of GA-modified elongated EE/RE (≥500-nm length, 50-nm diameter), either isolated or with an MVB domain at one end (e and f). In the absence of GA, instead, (f) DAB reaction was detectable only within the lumen of tubular domains of EE/REs (g and h; ≤500-nm length, 40- to 50-nm diameter). At later stages of incubation with GA (45 and 120 min), trastuzumab-HRP labeling was found within the MVB domain of the modified EE/RE, which assumed a more enlarged morphology, and within lysosomes (Lys) (i, j, m, and n). Scale bars: 200 nm (a–d, g, h, l, o, and p); 500 nm (e, f, i, j, m, and n); 1000 nm (k). In the absence of GA, after 45 min and 2 h (k, l, o, p), trastuzumab-HRP labeled the lumen of EE/REs. (B) Quantitation of CCP/V structures in SK-BR-3 cells untreated (−GA, −Trast) and in the presence of GA (+GA, −Trast), of trastuzumab (−GA, +Trast), and of trastuzumab and GA (+GA, +Trast). CCP/V included CCP at the PM, and putative vesicles located 200 nm from the PM (10 cells for each of two independent experiments). (C and D) Quantitation of trastuzumab-HRP internalized structures in SK-BR-3 cells in the presence of trastuzumab and GA (+GA, +Trast) or in the absence of GA (−GA, +Trast) after AA washing. Endocytic structures were defined as reported in (A) and were counted in 10 cells for each of two independent experiments (n = 20). The bar graph and error bars show the mean ± SEM. An unpaired Student's t test (p < 0.05) was applied comparing the same categories for each time point of (+GA, +Trast) and (−GA, +Trast). Mean differences were highly significant for EE/REs at 20 min (+GA, +Trast; **, p = 0.0021), CCV at 20 min (−GA, +Trast; **, p = 0.016), and significant for EE at 45 min (−GA, +Trast; *, p = 0.011). Categories boxed in red are present only in GA-treated cells.
FIGURE 5:
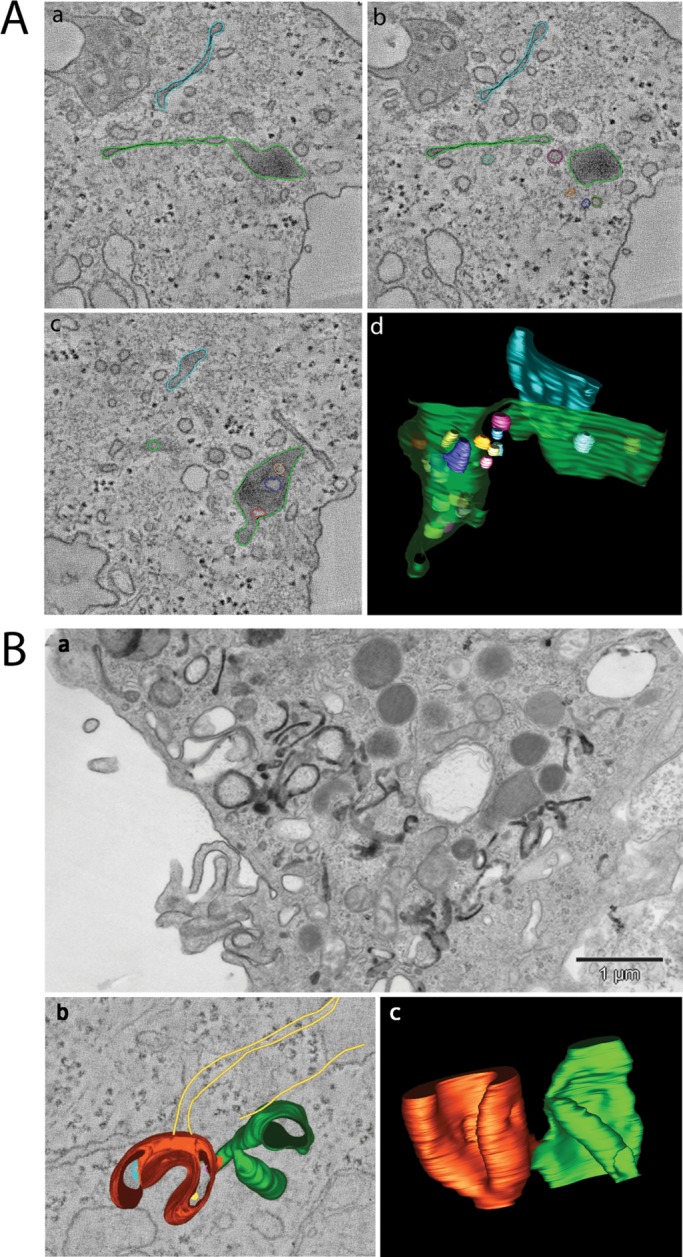
(A) three-dimensional tomography of GA-modified endosomes. GA-treated SK-BR-3 cells were incubated with trastuzumab-HRP for 30 min on ice, prior to internalization at 37°C for 20 min in the presence of GA. The DAB reaction was performed on ice, and cells were processed for plastic embedding and electron tomography as described in Materials and Methods. Three tomographic slices at different z-axes of the original tomogram (a–c; see also Movies S1 and S2) and a three-dimensional view of the model obtained (d) are shown. Trastuzumab-HRP reaction product was found within the globular domain of the endosome, typical feature of receptors committed to degradation, as well as within the elongated tubular domain. (B) CLICs in Epon-embedded MEFs caveolin1 KO cells after 15 s of CTx-HRP internalization (+AA). (b) Dual-axis tomogram of internalized CLIC (CTx-HRP) in 300-nm-thick sections of conventionally fixed MEFs caveolin1 KO. Note the semi-ring structure with membrane invaginations and few internal vesicles (red) and the cistern domain (green; see Movie S3). Actin cytoskeleton elements (yellow) in close proximity to CLIC are depicted. (c) Three-dimensional model (Movie S4).
In the absence of GA, we found that trastuzumab-HRP localized within CCP/V after 5 min of treatment (Figure 4, c and d) and within tubular EE/REs after 20 min (Figure 4, g and h). At later stages, trastuzumab-HRP labeled vacuolar (EEs) and short tubules (EE/RE; Figure 4, k, l, o, and p). Trastuzumab-488–labeled short, dynamic tubules were also observed by in vivo fluorescence microscopy detaching from larger compartments and traveling in the cytoplasm, often leading to the PM (Movie S5 and Figure S7). These data indicate that ErbB2 enters the cells via CME independently of GA treatment and is likely sorted to EEs and REs. As expected, we did not observe elongated EEs with MVB domain and elongated EE/REs at any stage of the time course (up to 2 h), showing that GA is altering the ultrastructure of the endosomal system. Double immunofluorescence studies, performed at late times of chase (2 h, 37°C), identified the localization of the internalized trastuzumab-488 with respect to early (EEA-1), recycling (TfR), and late (CD63) endosomal markers. Confocal microscopy analysis showed colocalization with early endocytic markers and a partial overlap with CD63 (Figure S6A). In addition, endocytosis of trastuzumab-488 was checked by immunogold labeling of Tokuyasu cryosections. As shown in Figure S6B, trastuzumab-488 was found within CCPs and early endosomal compartments. These data indicate that, in the absence of GA, trastuzumab induces ErbB2 internalization via CME and is mainly routed to EE/REs, rather than to degradation (Figure S1A). In addition, trastuzumab appears to have no role in the degradative sorting of ErbB2 upon GA, as ErbB2 is degraded irrespective of the presence of trastuzumab (see Figure S1A). These observations suggested that GA drives ErbB2 trafficking to late/lysosomal compartments, modifying the ultrastructure of EEs and RE, such that elongated tubules may represent modified recycling compartments entering the MVB domain under the effect of GA. To demonstrate this hypothesis, we performed trastuzumab-HRP internalization assays using the modified immunoperoxidase DAB/AA method in the presence of BSA-gold (5 nm), with or without GA treatment. BSA-gold has been shown to be internalized as a fluid-phase marker and to be sorted to the EE compartments, and eventually to MVBs and lysosomes, without being recycled to the PM (Kleijmeer et al., 1997). In the presence of GA, we observed that BSA-gold progressively accumulated in time in trastuzumab-HRP–labeled lysosomes and MVBs, either isolated or as part of the MVB domain of the modified compartments, whereas it never localized in the tubular domains (Figure 6). These data support the hypothesis that the elongated tubules may be GA-induced dysfunctional recycling compartments directed to the MVB, suggesting mixing of endosomal domains.
GA alters sorting compartments irrespective of HSP90 dependency of cargoes
HSP90 has been recently implicated in important cellular processes regulating membrane trafficking, such as GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI)-dependent Rab recycling (Chen and Balch, 2006), Rab11a-dependent recycling of α-synuclein (Liu et al., 2009), and regulation of actin dynamics (Taiyab and Rao, 2011), suggesting an important role for HSP90 in postendocytic membrane trafficking. On GA, ErbB2 and trastuzumab-488 colocalize persistently with Tf at long internalization times (Austin et al., 2004). In view of our previous results showing GA-induced modification of EEs and RE, we reasoned that, upon treatment, proteins that are normally directed to recycling compartments might be missorted to MVBs/lysosomes, irrespective of their possible interaction with HSP90. To test this hypothesis, we evaluated the GA effect on endosomal trafficking of Tf, a constitutively recycling cargo not chaperoned by HSP90. To this end, we performed time-course endocytic assays of Tf-488 and used LAMP-1 as lysosomal marker. As shown in Figure 7A, GA dramatically interfered with Tf-488 trafficking, leading to its aberrant delivery to lysosomes. Tf-488 colocalization with LAMP-1 was further evaluated by determining the percentage of overlap by pixel intensity (Figure 7B). The bar graph shows that ∼30% of Tf-488 is found within LAMP-1 compartments upon 2 h of GA treatment, compared with 6% of colocalization found in untreated cells. We next used EM to evaluate and quantify Tf trafficking after GA treatment (Figure 7, C and D). We incubated SK-BR-3 cells with Tf-HRP for 5 and 20 min and 2 h at 37°C and found that GA did not modify the initial uptake of Tf-HRP by CCVs (Figure 7D, box plot), but affected its subsequent fate. In particular, we found Tf-HRP localized within GA-modified tubular endosomes (EE/REs) after 20 min of internalization and within the MVB domain of EEs, suggesting missorting to modified MVBs/lysosomal compartments (Figure 7, C, b and c, and E). Indeed, after 2 h in the presence of GA, Tf-HRP was found in MVBs and lysosomes (Figure 7, C, e, and E).
To assess whether accumulation of TfR within LAMP-1–positive compartments upon GA treatment enhanced TfR's degradation, we performed Western blot analyses at early (2 h, Figure 7F) and late (8 and 24 h, unpublished data) GA treatment times. We found that while ErbB2 is efficiently degraded, TfR is not, suggesting a mechanism involving an altered recycling and accumulation within MVBs/lysosomes, rather than induction of degradation.
Taken together, these data suggest that the HSP90-dependent GA effect on endosomal sorting is cargo independent.
DISCUSSION
The interest in ErbB2 endocytosis has increased with the development of novel therapeutics that modulate or exploit the ErbB2 internalization process. Notwithstanding this, there is still little understanding of this aspect of ErbB2 biology (Sorkin and Goh, 2008; Roepstorff et al., 2008). Indeed, it has been shown that ErbB2 dimers are constitutively internalized with slow kinetics and largely recycled back to the PM for reactivation (Austin et al., 2004; Citri et al., 2004). This is in contrast to EGFR, which is efficiently internalized and routed to the lysosomal pathway for subsequent degradation. ErbB2 can transfer its endocytosis properties to the heterodimer partners (Citri et al., 2002, 2004). The slow internalization kinetics can be efficiently bypassed by HSP90 inhibitors, such as GA and derivatives, that lead to rapid ErbB2 ubiquitylation and degradation (Xu et al., 2002, Zhou et al., 2003). In addition, Haslekas et al. (2005) reported that ErbB2 overexpression in PAE.B2 cells specifically inhibited EGF-induced CCP formation, a process determined by EGFR-ErbB2 oligomerization. GA-stimulated ErbB2 internalization has been reported to occur either via a clathrin-dependent (Austin et al., 2004; Lerdrup et al., 2006, 2007; Pedersen et al., 2008) or a clathrin-independent process (Barr et al., 2008), in EGFR-positive, ErbB2-overexpressing SK-BR-3 cells. Irrespective of the endocytic route empowered for ErbB2 internalization, our data show that ErbB2 silencing in SK-BR-3 cells results in the increase of the internalization rate of Tf and CTx-B, two CME-internalized cargoes, and in the number of CCP/Vs per cell, suggesting that the ErbB2 overexpression itself interferes with the overall CME capacity involved in both constitutively and regulated receptor internalization, extending the observation by Haslekas et al. (2005) beyond the context of ErbB1/ErbB2 dimers. Other studies support the ability of signaling receptors to globally regulate the number and/or the activity of CCPs present in the PM by downstream signaling events, such as activation of various kinases (Pelkmans et al., 2005). Indeed, the presence of compositionally distinct CCP subsets that facilitate saturable but noncompetitive endocytosis of cargoes has been proposed, suggesting cargo-specific regulation (Puri et al., 2005; Tosoni et al., 2005).
Although these conclusions, in view of the impaired CME in these cells, apparently support the hypothesis that GA treatment may potentiate a CIE internalization of ErbB2 (Barr et al., 2008), our results seem to go in a different direction. In our study, ErbB2 is not detected in endocytic vesicles before 5 min of GA stimulation of SK-BR-3, COS-7, MEF wild-type, and MEF caveolin-1 KO cells, suggesting that the canonical CLICs/GEEC pathway may not be involved. Furthermore, the GA-dependent ErbB2 internalization process is dynamin dependent, as defined by the use of the specific inhibitor dynasore and the dynamin mutant K44A, and uses carriers that colocalize with markers of the CME pathway, and not with GRAF1. Because dynamin independence and association with the BAR domain containing the protein GRAF1 are defining characteristics of the CLICs/GEEC pathway, it is likely that CME represents the major route of ErbB2 internalization upon GA treatment. GA does not appear to bypass the ErbB2-induced CME impairment, as the total number of CCP/Vs and the number of ErbB2-containing CCP/Vs is similar in GA-treated and GA-untreated cells. Our data also exclude that in our studies trastuzumab itself influences the rate of ErbB2 internalization, as the receptor is internalized at a comparable rate in the absence of GA.
Thus GA is likely playing a more complex role on the endocytic pathway to cause increased ErbB2 degradation. Indeed, GA modifies the morphology of GRAF1 tubules, causing their aberrant elongation. These compartments correspond to altered EE/REs, as shown by ultrastructural and immunofluorescence analysis of ErbB2 sorting. On treatment, EE/REs, identified by the presence of Tf, become tubular, with some of them becoming very elongated (1 µm), and can be visualized by light microscopy. Therefore we would suggest extreme caution in interpreting the nature of endosomal compartments in GA-treated cells by light microscopy. We observed two types of elongated endosomal structures. One appears as an isolated tubule and the second as a long tubule extending out from, or leading to, the connected MVB terminal domains. The use of specific markers of early, recycling, and late endosomes and lysosomes (e.g., EEA-1, TfR, CD63) shows that both Tf and ErbB2 are predominantly sorted to the same recycling compartments in the absence of GA and to late endosomes and lysosomes upon treatment. Therefore GA impacts ErbB2 and Tf sorting, likely rerouting them from EE/REs to late endosomes and lysosomes, confirming the observation by Austin et al. (2004) for ErbB2. Morphologically, the endosomal network is formed by interconnected vacuolar and tubular elements, and it is generally considered that cargo recycling is achieved through these tubular structures (Murk et al., 2003; van Weering et al., 2012). Indeed, specialized recycling tubules emanating from EEs mediating distinct types of recycling for specific cargoes has been reported (Puthenveedu et al., 2010). The ultrastructure of the GA-induced compartments appears to be intermediate between the tubular network of recycling endosomes, and the multivesicular endosomes, likely corresponding to the early-to-late transition intermediates (Rink et al., 2005; van Weering et al., 2012). Within the latter compartments (Gruenberg and Stenmark 2004; Falguieres et al., 2009, 2012), down-regulated receptors are collected exclusively within multivesicular regions, which then detach (or mature) and become transport intermediates (endosomal carrier vesicles/multivesicular bodies) to late endosomes. The persistent colocalization of ErbB2 with the constitutively recycled cargo Tf, within both the elongated tubules and the multivesicular domains of EEs, and their common fate allow us to speculate that the elongated, single, tubular cisterns might be dysfunctional membrane domains in which recycling/sorting functions are compromised. However, because we also observed abnormal elongated recycling tubules lacking the multivesicular domain, it may also be that these tubules are missorted to MVBs, suggesting a mixing of endosomal compartments. In support of this hypothesis are the observations that BSA-gold (a fluid-phase marker sorted to lysosomes; Kleijmeer et al., 1997) labels the MVBs but not the tubular domains. In addition, GA appears to missort recycling cargoes, independently of whether they directly interact (ErbB2) or not (Tf) with HSP90.
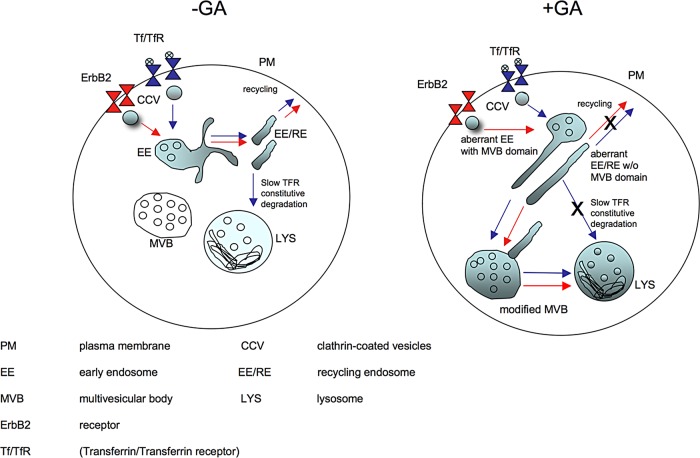
Of note, at variance with ErbB2, TfR is not degraded upon GA treatment. TfR is a nonsignaling, nonubiquitylated, mostly recycling receptor that undergoes a very slow constitutive degradation (Matsui et al., 2011). This process appears to be regulated by the small GTPase Rab12. Rab12 does not impinge upon either the conventional endocytic pathway involved in ubiquitylated EGFR degradation or the TfR recycling pathway (Matsui et al., 2011). Rab12 has been found uniquely localized at EE/REs and lysosomes and not at EEs or late endosomes/MVBs, and has been proposed to act as a molecular determinant governing the degradative fate of nonubiquitylated TfR, promoting its sorting from recycling endosomes to lysosomes by fusion of compartments. Therefore a possible interfering role of GA on the Rab12-mediated fusion between RE and lysosomes may explain the TfR missorting to MVBs. In support of this model, a role for HSP90 in GDI-dependent Rab recycling has been reported (Chen et al., 2005; Chen and Balch, 2006). In particular, GA interferes with the activity of Rab11a, a Rab involved in TfR recycling (Liu J et al., 2009). Therefore we can speculate that GA, by interfering with Rab12, may lead to missorting of aberrant EE/REs to MVBs. Within MVBs, at variance with the ubiquitylated ErbB2 receptor, the nonubiquitylated TfR may accumulate without being efficiently degraded (Saftig and Klumperman, 2009; see Figure 8, model).
FIGURE 8:
Model for ErbB2 and TfR endocytic traffic upon GA. In SK-BR-3 cells, ErbB2 and Tf are internalized via CME and transported to EEs and EE/REs for recycling to the cell surface and are not delivered to MVBs and lysosomes (LYS). According to Matsui et al. (2011), TfR undergoes Rab12-dependent constitutive degradation by fusion of REs with lysosomes. In the presence of GA, ErbB2 and Tf/TfR are internalized by CME and sorted to the MVB domain of aberrant EEs (EEs with MVB domain) and to dysfunctional elongated EE/RE compartments, eventually leading to MVBs and lysosomes (LYS). Within MVBs, at variance with the ubiquitylated ErbB2 receptor, the nonubiquitylated TfR may accumulate without being efficiently degraded.
An alternative model may instead involve a role for the cytoskeleton, since HSP90 has been implicated in regulating actin dynamics, suggesting that alterations in endosomal morphology observed upon GA treatment might be a consequence of disregulation of the actin cytoskeleton (Taiyab and Rao, 2011; Gomez et al., 2012). We are currently investigating both hypotheses.
In summary, we show that GA treatment perturbs endosomal sorting, forcing recycling cargoes to modified MVBs/lysosomal compartments as part of its activity as an anticancer agent.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
Human breast cancer (SK-BR-3) cells; COS-7 cells (African Green Monkey kidney cells, derived from immortalized CV-1); and wild-type and caveolin1 KO MEF cells (Kirkham et al., 2005) were grown in DMEM (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum and 2 mM glutamine (Life Technologies) and maintained in 5% CO2. Confluent cells were split with trypsin-EDTA (Life Technologies) and passaged at an appropriate density. COS7 and MEF cells were transiently transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and examined 18 h posttransfection according to the manufacturer's instructions. SK-BR-3 cells stably transfected with inducible shRNA for ErbB2 silencing were treated with 1 μg/ml doxycycline (Fluka; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) for 48 h before processing.
Antibodies and reagents
ShRNAs for ErbB2 (targeted sequence 5′-TCACAGGGGCCTCCCCAGG-3′) were first cloned into the pSUPER TetO vector downstream of the H1 promoter. Then the entire cassette was subcloned in the lentiviral vector pCCLsin.PPT.hPGK.GFP.Wpre. Lentivirus for the TetR and shErbB2 was produced as described in Vigna and Naldini (2000) and used to transduce SK-BR-3 cells. All the vectors used are described in detail in Corso et al. (2008).
Expression plasmids: pEGFPC3-GRAF1 full length and pEGFC3-GRAF1 BAR+PH, a kind gift from R. Lundmark (Umea University, Umea, Sweden); pcDNA3-ErbB2 wild type, a kind gift from D. A. Brown (Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York); and pEGFC3-DynK44A, a kind gift from Simona Polo (FIRC Institute for Molecular Oncology [IFOM], Milan, Italy). Antibodies: rabbit anti-ErbB2 (C18 sc-284; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) was used for Western blot analysis, and mouse anti-ErbB2 9G6 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used for EM studies and fluorescence microscopy. Anti–Alexa Fluor 488 antibody (A-11094; Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA) was used for EM cryoimmunolabeling of trastuzumab-488. Trastuzumab (Herceptin; Genentech-Roche) was from the weekly residues of the pharmacy of the Istituto Nazionale Tumori (Genoa, Italy, kindly donated to C.T. for research purposes), at a concentration of 21 mg/ml. Mouse anti-clathrin heavy chain (X22) was from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Mouse monoclonal anti-EEA1 was from Transduction Laboratories (Franklin Lakes, NJ), mouse monoclonal anti-LAMP1 (H4A4) and mouse monoclonal anti-CD63 (H5C6) were from the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA). Mouse anti–human Tf receptor (clone H68.4) was from Zymed Laboratories (Carlton Court, South San Francisco, CA). Trastuzumab and Tf conjugations with HRP were made using Lightning-Link TM technology (Innova Bioscience, Cambridge, UK) according to manufacturer's instructions. Trastuzumab conjugation with Alexa Fluor 488 and Alexa Fluor 555 dye was made with the Alexa Fluor conjugation kit (A10235; Invitrogen). Geldanamycin, dynasore, ascorbic acid, and DAB (3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride) tablets (D5905) were from Sigma-Aldrich. Cholera toxin B subunit and Tf conjugates with Alexa Fluor 488/555/647 were from Molecular Probes. Colloidal gold–protein A (5- and 10-nm size) and BSA-gold (5 nm) were from Utrecht University (Utrecht, Netherlands).
Electron microscopy
Uptake of 5-nm BSA-gold.
After being washed with CO2-independent medium, SK-BR-3 cells were incubated with BSA-gold (OD520 = 5) for different times in combination with the modified immunoperoxidase protocol and processed as described below.
Trastuzumab-HRP internalization assay.
SK-BR-3 cells, cultured on 3-cm dishes, were washed in CO2-independent medium (cat. number 18045070; Life Technologies) and incubated in CO2-independent medium containing 10 μg/ml trastuzumab-HRP on ice for 30 min in the presence or in the absence of 10 μg/ml GA. After extensive washing with cold CO2-independent medium to remove unbound trastuzumab-HRP, cells were shifted at 37°C in CO2-independent medium for desired times in the presence/absence of the drug. Internalization was ended as follows: cells were placed on ice in prechilled CO2-independent medium, incubated for 20 min at 4°C in freshly prepared DAB buffer (1 mg/ml DAB and 0.012% H2O2) with or without 50 mM AA in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde (Electron Microscopy Science, Hatfield, PA) for 1 h. The cells were subsequently processed for standard EM. Cells were embedded in Epon epoxy resin (Poly/Bed 812; Polyscience, Valley Road Warrington, PA) and cut parallel to the culture substratum. Electron micrographs were taken using a JEOL 1011 transmission electron microscope (TEM; JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) and a Tecnai Bio-TWIN G12 (FEI company; Eindhoven, The Netherlands) and were analyzed with iTEM software (Olympus-SYS, Münster, Germany).
Trastuzumab-488 internalization assay.
SK-BR-3 cells, cultured on 6-cm dishes, were washed in CO2-independent medium and incubated on ice in CO2-independent medium containing 10 μg/ml trastuzumab-488 for 30 min. Cells were then washed to remove unbound trastuzumab-488 and warmed at 37°C for 5, 20, 45, and 120 min. Cells were then prepared for cryo-immunoEM according to the Tokuyasu method. Briefly, cells were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde plus 0.2% glutaraldehyde in PBS for 2 h at room temperature. Next cells were gently scraped and embedded in 12% gelatin. After an overnight sucrose (2.3 M) infusion, small squared blocks were mounted on aluminum pins and frozen in liquid nitrogen. Ultrathin cryosections of 60 nm were cut with Leica UltraCut UCT microtome (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) and double-immunolabeled with anti–Alexa Fluor 488 (Molecular Probes) and ErbB2 (9G6; Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Protein A–gold (10 nm and 15 nm) was used to reveal trastuzumab-488 and ErbB2, respectively.
Tf-HRP internalization assay.
SK-BR-3 cells, cultured on 3-cm dishes, were incubated on ice in CO2-independent medium (cat. number 18045070; Life Technologies) containing 1 mg/ml Tf-HRP for 15 min in the presence or in the absence of 10 μg/ml GA. After extensive washing, cells were shifted at 37°C in CO2-independent medium for desired times in the presence/absence of the drug. Internalization was ended as follows: cells were placed on ice in prechilled CO2-independent medium, incubated for 20 min at 4°C in freshly prepared DAB buffer (1 mg/ml DAB and 0.012% H2O2) with or without 50 mM ascorbic acid (AA) in PBS, and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde (Electron Microscopy Science) for 1 h. The cells were subsequently processed for standard EM. Cells were embedded in Epon epoxy resin (Poly/Bed 812; Polyscience) and cut parallel to the culture substratum. Electron micrographs were taken at Tecnai F20 (200 kV) and Tecnai Bio-TWIN G12 (120 kV; FEI Company) and analyzed with Macnification 2.0 software (Orbicule, Leuven, Belgium).
Three-dimensional tomography.
Semi-thin (300-nm) sections were cut from plastic-embedded SK-BR-3s with a Leica UltraCut UCT microtome (Leica Microsystems) and collected onto Formvar-coated copper slot grids (2 mm × 1 mm slot). Colloidal gold particles (10 nm; Utrecht University) were placed on both surfaces of the sections for use as fiducial markers during the image alignment. Thick sections were also lightly coated with carbon to minimize charging in the EM during “tilt series” image acquisition. Thick sections were imaged using a Tecnai F30 intermediate voltage EM (FEI Company) operated at 300 kV and motorized with tilt–rotate specimen holders (models 650 and CT3500TR; Gatan, Pittsburgh, PA). Tilt series images (each 2048 × 2048 pixels) digitally acquired by an UltraScan 4000 (USC4000, model 895; Gatan) using semiautomated methods for charge-coupled device imaging, microscope tilt control, data acquisition, and image alignment were performed with the microscope control program SERIALEM versions 2.5.1–2.7.7. Prior to data acquisition, the sections were preirradiated in the electron beam at low magnification/low beam current at 0° and 60° for 10 min. Dual-axis tilt series were collected over a total angular tilt range from –60° to +60° at 1° increments. Tilt series were first aligned with one another by cross-correlation and subsequently by tracking the positions of gold fiducials using the IMOD version 3.11.1 software package version. A single reconstructed tomogram was obtained from each tilt series. Tomograms calculated using the IMOD (Kremer et al., 1996) software package (which incorporates the eTomo and 3dmod graphical user interfaces) from each set of aligned tilts collected around two orthogonal axes were then aligned with each other and combined to produce a single, high-resolution dual-axis volume. Intracellular membranes and vesicles within each volume were manually segmented at high fidelity and meshed for three-dimensional visualization. To compensate for the collapse of plastic sections that occurs immediately on exposure to the electron beam, we stretched tomograms in the direction of the electron beam (which was defined as the z-axis) by a factor of 1.6 for Epon-embedded samples.
EM morphometry.
Box-and-whisker plots were used to show the position and spread of a single variable. In the box-and-whisker plot of Figure 1C, the variable (e.g., number of CCP/V structures per cell in SK-Br-3 KD cells with or without doxycycline) is represented by a box, the top and bottom of which represent the upper and lower quartiles (i.e., the box covers the interquartile range). The box is divided at the median value. A plus symbol (+) indicates the mean value, and a line (the whisker) represents the full range. We included in the category CCP/V all CCPs attached to the PM and putative vesicles located within 200 nm from the PM. In the category CCV cytosol, we included all the CCVs found at a distance > 200 nm from the PM. Because the cell profile area observed in SK-BR-3 ErbB2 KD+dox cells, was on average 1.3 times larger, compared with SK-BR-3 ErbB2 KD−dox cells, data were normalized by this factor. The cell surface data were obtained by a flat embedding approach, comparing 15 cell profiles for each condition using ImageJ software.
The number of CCP/Vs per cell-surface length (Figure 1E) was normalized to a 1000-μm length for each condition. To determine the statistical significance of the results, we applied an unpaired Student's t test (p < 0.05).
Quantification of trastuzumab-HRP+AA (corresponding to cell compartments not in continuity with the PM; Figure 4, B and C) is represented as a bar chart in which the means ± SEM of labeled structures counted in 10 cells, across two independent experiments, are plotted. We defined the following categories: CCV, coated vesicles not connected to the cell surface; GA-modified elongated EEs with MVB domain, >500-nm-width and 50-nm-length endosomes; EE/RE, <500-nm (−GA) or >500-nm (+GA)-width and 40- to 50-nm-length tubular endosomes; vacuolar EEs, endosomes containing <10 internal vesicles; MVBs and lysosomes, multivesicular endosomes containing >10 internal vesicles and large dense vacuoles, respectively. An unpaired Student's t test (p < 0.05) was applied to determine statistical significance (see Figure 4 legend).
The criteria for distinguishing between vacuolar EEs (<10 internal vesicles) and MVBs (>10 internal vesicles) were assessed in a time-course, BSA-gold, fluid-phase endocytic assay correlating the number of inner vesicles in the decorated compartments to the known time-dependent appearance of BSA-gold, according to Klumperman et al. (1993) and Mari et al. (2007).
Immunofluorescence
Dynamin inhibition.
Cells were serum-starved for 1 h in serum-free DMEM before preincubation for 20 min at 37°C with 80 μM dynasore (Sigma-Aldrich). Cells were then incubated with Tf-488 and trastuzumab-555 as markers of interest in the presence of dynasore for indicated periods at 37°C. Untreated cells were processed in parallel with dynasore-treated cells.
ErbB2 internalization assays.
For ErbB2 internalization assays in SK-BR-3, COS7 (transfected with ErbB2/GRAF1wt, ErbB2/GRAF1-BAR+PH, or flotillin1-GFP), and MEFs (wild-type and caveolin1 KO) cells, anti-ErbB2 9G6 antibodies were bound to cells at 4°C for 20 min before internalization was started at indicated time points by addition of prewarmed media. Residual surface-bound antibodies were stripped with acid wash (100 mM Gly, 50 mM KCl, 20 mM magnesium acetate, pH 2.3), using three washes of 3 min each. Cells were than processed for immunofluorescence.
Internalization assay in stably silenced SKBR3 cells.
SK-BR-3 cells (with or without ErbB2) grown on 12-mm coverslips were placed on 40-μl drops of Tf-647 (1 mg/ml) and CTx-555 (1 μg/ml) diluted in CO2-independent media on ice for 20 min. The coverslips were washed with prewarmed growth media and shifted in 5% CO2 incubators for desired times. After internalization, the coverslips were removed and extensively washed on ice-cold CO2-independent media. After 3% paraformaldehyde fixation, cells were quenched with 30 mM NH4Cl for 10 min, mounted with Mowiol medium on coverslips, and imaged using an Axiovert 200 m SP LSM 500 META confocal laser-scanning microscope (Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Images were captured under oil with a 63× Plan-Apochromat objective. Images were processed and analyzed with Adobe Photoshop CS2-CS5 (San Jose, CA).
Western blotting
SK-BR-3 and SK-BR-3 stably silenced for ErbB2 whole-cell lysates were prepared using EB lysis buffer (HEPES, pH 7.4, 20 mM, NaCl 150 mM, glycerol 10%, Triton X-100 1%) with protease inhibitors cocktail (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) and sodium orthovanadate. The Petri dishes were scraped to collect the whole lysates, and lysates were incubated on ice for 20 min. Lysates were finally centrifuged for 60 s at 13,200 rpm at 4°C to remove cellular debris. Western blot analysis was performed with standard methods, and proteins were detected with ECL Detection Reagent (Amersham, Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, UK).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Australian Research Council (to R.G.P.) and the Italian Cancer Research Foundation, Italian Minister of Research and University (Programmi di ricerca di Rilevante Interesse Nazionale), Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro, and Fondazione San Paolo (to C.T.). We thank Silvia Bruno, Alessia Castagnino, Andrea Rabellino, Laura Mattioli, and Grazia Bellese (MicroSCoBiO, DIMES, University of Genova, Italy) for helpful discussion and support in some of the immunofluorescence data, Manuel Alejandro Fernandez-Rojo (IMB, University of Queensland) for support, and Silvia Giordano (IRCC, Torino, Italy) and Deborah A. Brown (Stony Brook University) for the kind gift of reagents.
Abbreviations used:
- BAR
Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs
- BSA
bovine serum albumin
- CIE
clathrin-independent endocytosis
- CLIC
clathrin-independent carrier
- CLIC/GEEC
clathrin-independent carrier/GPI-AP enriched early endosomal compartment
- CME
clathrin-mediated endocytosis
- CTx
cholera toxin B subunit
- CTx-555
CTx conjugated to Alexa Fluor 555
- DAB/AA
diaminobenzidine/ascorbic acid
- EE
early endosome
- EE/RE
recycling endosome
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- GA
geldanamycin
- GDI
GDP dissociation inhibitor
- GEEC
GPI-enriched endocytic compartments
- GFP
green fluorescent protein
- HER
receptor tyrosine kinase family
- HRP
horseradish peroxidase
- KO
knockout
- MEF
mouse embryonic fibroblasts
- MVB
multivesicular endosome
- PBS
phosphate-buffered saline
- PM
plasma membrane
- shRNA
short hairpin RNA
- TEM
transmission electron microscopy
- Tf
transferrin
- Tf-647
Tf conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647
- TfR
transferrin receptor
Footnotes
This article was published online ahead of print in MBoC in Press (http://www.molbiolcell.org/cgi/doi/10.1091/mbc.E12-04-0282) on November 14, 2012.
REFERENCES
- Abella JV, Park M. Breakdown of endocytosis in the oncogenic activation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;296:E973–E984. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90857.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin CD, De Maziere AM, Pisacane PI, van Dijk SM, Eigenbrot C, Sliwkowski MX, Klumperman J, Scheller RH. Endocytosis and sorting of ErbB2 and the site of action of cancer therapeutics trastuzumab and geldanamycin. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:5268–5282. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-07-0591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr DJ, Ostermeyer-Fay AG, Matundan RA, Brown DA. Clathrin-independent endocytosis of ErbB2 in geldanamycin-treated human breast cancer cells. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:3155–3166. doi: 10.1242/jcs.020404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Kasus T, Schechter B, Lavi S, Yarden Y, Sela M. Persistent elimination of ErbB-2/HER2-overexpressing tumors using combinations of monoclonal antibodies: relevance of receptor endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:3294–3299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812059106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen CY, Balch WE. The Hsp90 chaperone complex regulates GDI-dependent Rab recycling. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:3494–3507. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-12-1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen CY, Sakisaka T, Balch WE. Use of Hsp90 inhibitors to disrupt GDI-dependent Rab recycling. Methods Enzymol. 2005;403:339–347. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)03029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri A, Alroy I, Lavi S, Rubin C, Xu W, Grammatikakis N, Patterson C, Neckers L, Fry DW, Yarden Y. Drug-induced ubiquitylation and degradation of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases: implications for cancer therapy. EMBO J. 2002;21:2407–2417. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.10.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri A, Gan J, Mosesson Y, Vereb G, Szollosi J, Yarden Y. Hsp90 restrains ErbB-2/HER2 signalling by limiting heterodimer formation. EMBO Rep. 2004;5:1165–1170. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:505–516. doi: 10.1038/nrm1962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corso S, Migliore C, Ghiso E, De Rosa G, Comoglio PM, Giordano S. Silencing the MET oncogene leads to regression of experimental tumors and metastases. Oncogene. 2008;27:684–693. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty GJ, Ahlund MK, Howes MT, Moren B, Parton RG, McMahon HT, Lundmark R. The endocytic protein GRAF1 is directed to cell-matrix adhesion sites and regulates cell spreading. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22:4380–4389. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-12-0936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty GJ, Lundmark R. GRAF1-dependent endocytosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37:1061–1065. doi: 10.1042/BST0371061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falguieres T, Castle D, Gruenberg J. Regulation of the MVB pathway by SCAMP3. Traffic. 2012;13:131–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falguieres T, Luyet PP, Gruenberg J. Molecular assemblies and membrane domains in multivesicular endosome dynamics. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:1567–1573. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick M, Bright NA, Riento K, Bray A, Merrified C, Nichols BJ. Coassembly of flotillins induces formation of membrane microdomains, membrane curvature, and vesicle budding. Curr Biol. 2007;17:1151–1156. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.05.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyo Y, Hunt CR, Horikoshi N. Geldanamycin and its anti-cancer activities. Cancer Lett. 2010;290:24–35. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glebov OO, Bright NA, Nichols BJ. Flotillin-1 defines a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway in mammalian cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:46–54. doi: 10.1038/ncb1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez TS, Gorman JA, Artal-Martinez de Narvajas A, Koenig AO, Billadeau DD. Trafficking defects in WASH knockout fibroblasts originate from collapsed endosomal and lysosomal networks. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;16:3215–3228. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-02-0101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J, Stenmark H. The biogenesis of multivesicular endosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:317–323. doi: 10.1038/nrm1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslekas C, Breen K, Pedersen KW, Johannessen LE, Stang E, Madshus IH. The inhibitory effect of ErbB2 on epidermal growth factor-induced formation of clathrin-coated pits correlates with retention of epidermal growth factor receptor-ErbB2 oligomeric complexes at the plasma membrane. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:5832–5842. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-05-0456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommelgaard AM, Lerdrup M, van Deurs B. Association with membrane protrusions makes ErbB2 an internalization-resistant receptor. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:1557–1567. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes MT, et al. Clathrin-independent carriers form a high capacity endocytic sorting system at the leading edge of migrating cells. J Cell Biol. 2010;190:675–691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201002119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes NE, MacDonald G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:177–184. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones KL, Buzdar AU. Evolving novel anti-HER2 strategies. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:1179–1187. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M, Kumari S, Chadda R, Hill MM, Parton RG, Mayor S. Arf6-independent GPI-anchored protein-enriched early endosomal compartments fuse with sorting endosomes via a Rab5/phosphatidylinositol-3′-kinase-dependent machinery. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:3689–3704. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-10-0980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkham M, Fujita A, Chadda R, Nixon SJ, Kurzchalia TV, Sharma DK, Pagano RE, Hancock JF, Mayor S, Parton RG. Ultrastructural identification of uncoated caveolin-independent early endocytic vehicles. J Cell Biol. 2005;168:465–476. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200407078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkham M, Parton RG. Clathrin-independent endocytosis: new insights into caveolae and non-caveolar lipid raft carriers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1746:349–363. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleijmeer MJ, Morkowski S, Griffith JM, Rudensky AY, Geuze HJ. Major histocompatibility complex class II compartments in human and mouse B lymphoblasts represent conventional endocytic compartments. J Cell Biol. 1997;139:639–649. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.3.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klumperman J, Hille A, Veenendaal T, Oorschot V, Stoorvogel W, von Figura K, Geuze HJ. Differences in the endosomal distributions of the two mannose 6-phosphate receptors. J Cell Biol. 1993;5:997–1010. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer JR, Mastronarde DN, McIntosh JR. Computer visualization of three-dimensional image data using IMOD. J Struct Biol. 1996;116:71–76. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1996.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetti L, Di Fiore PP. Endocytosis and cancer: an “insider” network with dangerous liaisons. Traffic. 2008;9:2011–2021. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerdrup M, Bruun S, Grandal MV, Roepstorff K, Kristensen MM, Hommelgaard AM, van Deurs B. Endocytic down-regulation of ErbB2 is stimulated by cleavage of its C-terminus. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:3656–3666. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-01-0025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerdrup M, Hommelgaard AM, Grandal M, van Deurs B. Geldanamycin stimulates internalization of ErbB2 in a proteasome-dependent way. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:85–95. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J, Bressan M, Hassel D, Huisken J, Staudt D, Kikuchi K, Poss KD, Mikawa T, Stainier DY. A dual role for ErbB2 signaling in cardiac trabeculation. Development. 2010;137:3867–3875. doi: 10.1242/dev.053736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J, Zhang JP, Shi M, Quinn T, Bradner J, Beyer R, Chen S, Zhang J. Rab11a and HSP90 regulate recycling of extracellular α-synuclein. J Neurosci. 2009;29:1480–1485. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6202-08.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longva KE, Pedersen NM, Haslekas C, Stang E, Madshus IH. Herceptin-induced inhibition of ErbB2 signaling involves reduced phosphorylation of Akt but not endocytic down-regulation of ErbB2. Int J Cancer. 2005;116:359–367. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundmark R, Doherty GJ, Howes MT, Cortese K, Vallis Y, Parton RG, McMahon HT. The GTPase-activating protein GRAF1 regulates the CLIC/GEEC endocytic pathway. Curr Biol. 2008;18:1802–1808. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mari M, Bujny MV, Zeuschner D, Geerts WJ, Griffith J, Petersen CM, Cullen PJ, Klumperman J, Geuze HJ. SNX1 defines an early endosomal recycling exit for sortilin and mannose 6-phosphate receptors. Traffic. 2007;3:380–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marone R, Hess D, Dankort D, Muller WJ, Hynes NE, Badache A. Memo mediates ErbB2-driven cell motility. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:515–522. doi: 10.1038/ncb1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T, Itoh T, Fukuda M. Small GTPase Rab12 regulates constitutive degradation of transferrin receptor. Traffic. 2011;10:1432–1443. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S, Pagano RE. Pathways of clathrin-independent endocytosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:603–612. doi: 10.1038/nrm2216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettlen M, Loerke D, Yarar D, Danuser G, Schmid SL. Cargo- and adaptor-specific mechanisms regulate clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 2010;188:919–933. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200908078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson Y, Mills GB, Yarden Y. Derailed endocytosis: an emerging feature of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:835–850. doi: 10.1038/nrc2521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murk JL, Posthuma G, Koster AJ, Geuze HJ, Verkleij AJ, Kleijmeer MJ, Humbel BM. Influence of aldehyde fixation on the morphology of endosomes and lysosomes: quantitative analysis and electron tomography. J Microsc. 2003;212:81–90. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2818.2003.01238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto GP, Nichols BJ. The roles of flotillin microdomains—endocytosis and beyond. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:3933–3940. doi: 10.1242/jcs.092015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen NM, Breen K, Rodland MS, Haslekas C, Stang E, Madshus IH. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor or ErbB3 facilitates geldanamycin-induced down-regulation of ErbB2. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:275–284. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen NM, Madshus IH, Haslekas C, Stang E. Geldanamycin-induced down-regulation of ErbB2 from the plasma membrane is clathrin dependent but proteasomal activity independent. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6:491–500. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelkmans L, Fava E, Grabner H, Hannus M, Habermann B, Krausz E, Zerial M. Genome-wide analysis of human kinases in clathrin- and caveolae/raft-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 2005;436:78–86. doi: 10.1038/nature03571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri C, Tosoni D, Comai R, Rabellino A, Segat D, Caneva F, Luzzi P, Di Fiore PP, Tacchetti C. Relationships between EGFR signaling-competent and endocytosis-competent membrane microdomains. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:2704–2718. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-07-0596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puthenveedu MA, Lauffer B, Temkin P, Vistein R, Carlton P, Thorn K, Taunton J, Weiner OD, Parton RG, von Zastrow M. Sequence-dependent sorting of recycling proteins by actin-stabilized endosomal microdomains. Cell. 2010;143:761–773. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raja SM, et al. A combination of trastuzumab and 17-AAG induces enhanced ubiquitinylation and lysosomal pathway-dependent ErbB2 degradation and cytotoxicity in ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7:1630–1640. doi: 10.4161/cbt.7.10.6585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink J, Ghigo E, Kalaidzidis Y, Zerial M. Rab conversion as a mechanism of progression from early to late endosomes. Cell. 2005;122:735–749. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff K, Grovdal L, Grandal M, Lerdrup M, van Deurs B. Endocytic downregulation of ErbB receptors: mechanisms and relevance in cancer. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;129:563–578. doi: 10.1007/s00418-008-0401-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romer W, et al. Shiga toxin induces tubular membrane invaginations for its uptake into cells. Nature. 2007;450:670–675. doi: 10.1038/nature05996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabharanjak S, Sharma P, Parton RG, Mayor S. GPI-anchored proteins are delivered to recycling endosomes via a distinct cdc42-regulated, clathrin-independent pinocytic pathway. Dev Cell. 2002;2:411–423. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saftig P, Klumperman J. Lysosome biogenesis and lysosomal membrane proteins: trafficking meets function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:623–635. doi: 10.1038/nrm2745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K, Torgersen ML, Raa HA, van Deurs B. Clathrin-independent endocytosis: from nonexisting to an extreme degree of complexity. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;129:267–276. doi: 10.1007/s00418-007-0376-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scita G, Di Fiore PP. The endocytic matrix. Nature. 2010;463:464–473. doi: 10.1038/nature08910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A, Di Fiore PP, Carpenter G. The carboxyl terminus of epidermal growth factor receptor/erbB-2 chimerae is internalization impaired. Oncogene. 1993;8:3021–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A, Goh LK. Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314:3093–3106. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.07.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taiyab A, Rao ChM. HSP90 modulates actin dynamics: inhibition of HSP90 leads to decreased cell motility and impairs invasion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:213–221. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikhomirov O, Carpenter G. Geldanamycin induces ErbB-2 degradation by proteolytic fragmentation. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:26625–26631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003114200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tikhomirov O, Carpenter G. Identification of ErbB-2 kinase domain motifs required for geldanamycin-induced degradation. Cancer Res. 2003;63:39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosoni D, Puri C, Confalonieri S, Salcini AE, De Camilli P, Tacchetti C, Di Fiore PP. TTP specifically regulates the internalization of the transferrin receptor. Cell. 2005;123:875–888. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z, Zhang L, Yeung TK, Chen X. Endocytosis deficiency of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-ErbB2 heterodimers in response to EGF stimulation. Mol Biol Cell. 1999;10:1621–1636. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.5.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaccari T, Bilder D. At the crossroads of polarity, proliferation and apoptosis: the use of Drosophila to unravel the multifaceted role of endocytosis in tumor suppression. Mol Oncol. 2009;3:354–365. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2009.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Weering JRT, Verkade P, Cullen PJ. SNX-BAR-mediated endosome tubulation is co-ordinated with endosome maturation. Traffic. 2012;13:94–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigna E, Naldini L. Lentiviral vectors: excellent tools for experimental gene transfer and promising candidates for gene therapy. J Gene Med. 2000;2:308–316. doi: 10.1002/1521-2254(200009/10)2:5<308::AID-JGM131>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu W, Marcu M, Yuan X, Mimnaugh E, Patterson C, Neckers L. Chaperone-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase CHIP mediates a degradative pathway for c-ErbB2/Neu. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:12847–12852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202365899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou P, Fernandes N, Dodge IL, Reddi AL, Rao N, Safran H, DiPetrillo TA, Wazer DE, Band V, Band H. ErbB2 degradation mediated by the co-chaperone protein CHIP. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13829–13837. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209640200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebik B, Citri A, Isola J, Yarden Y, Szollosi J, Vereb G. Hsp90 inhibitor 17-AAG reduces ErbB2 levels and inhibits proliferation of the trastuzumab resistant breast tumor cell line JIMT-1. Immunol Lett. 2006;104:146–155. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2005.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.