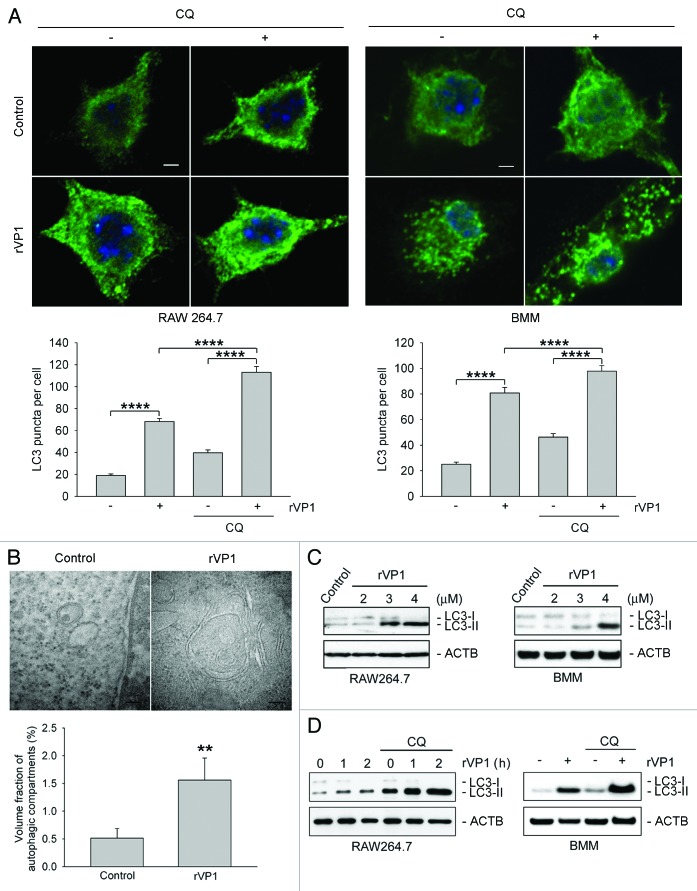
Figure 1. rVP1 induced autophagy in macrophages. RAW 264.7 or bone marrow-derived macrophage (BMM) cells were incubated with or without 2 μM chloroquine (CQ) and then 4 μM rVP1 for 4 h as indicated. (A) rVP1 induced LC3 puncta formation. After treatment, cells were fixed, stained with DAPI (blue), and immunolabeled with LC3 antibody followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (green). Fluorescent images were acquired by confocal microscopy. Scale bar: 2 μm. Data represent means ± SEM of quantitative analyses of LC3 puncta per cell in at least 50 cells/experiment in three independent experiments; ****p < 0.0001. (B) rVP1 induced formation of double-membrane autophagosomes. After treatment, cells were observed with transmission electron microscopy. Data represent means ± SEM of volume fraction of autophagic compartments; **p < 0.01. (C) rVP1 increased LC3 lipidation. Cells were treated with serial concentrations of rVP1 as indicated and their lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies against LC3. (D) Lysosomal degradation inhibitor CQ enhanced rVP1-mediated LC3 lipidation. Cells were incubated with 2 μM CQ for 30 min and then 4 μM rVP1 for another 4 h, unless specified otherwise. Cell lysates were collected and analyzed by immunoblot using anti-LC3 antibodies. ACTB was used as a loading control. Blots are representative of three independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.