Abstract
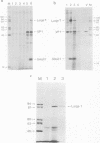
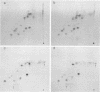
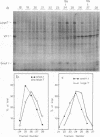
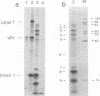
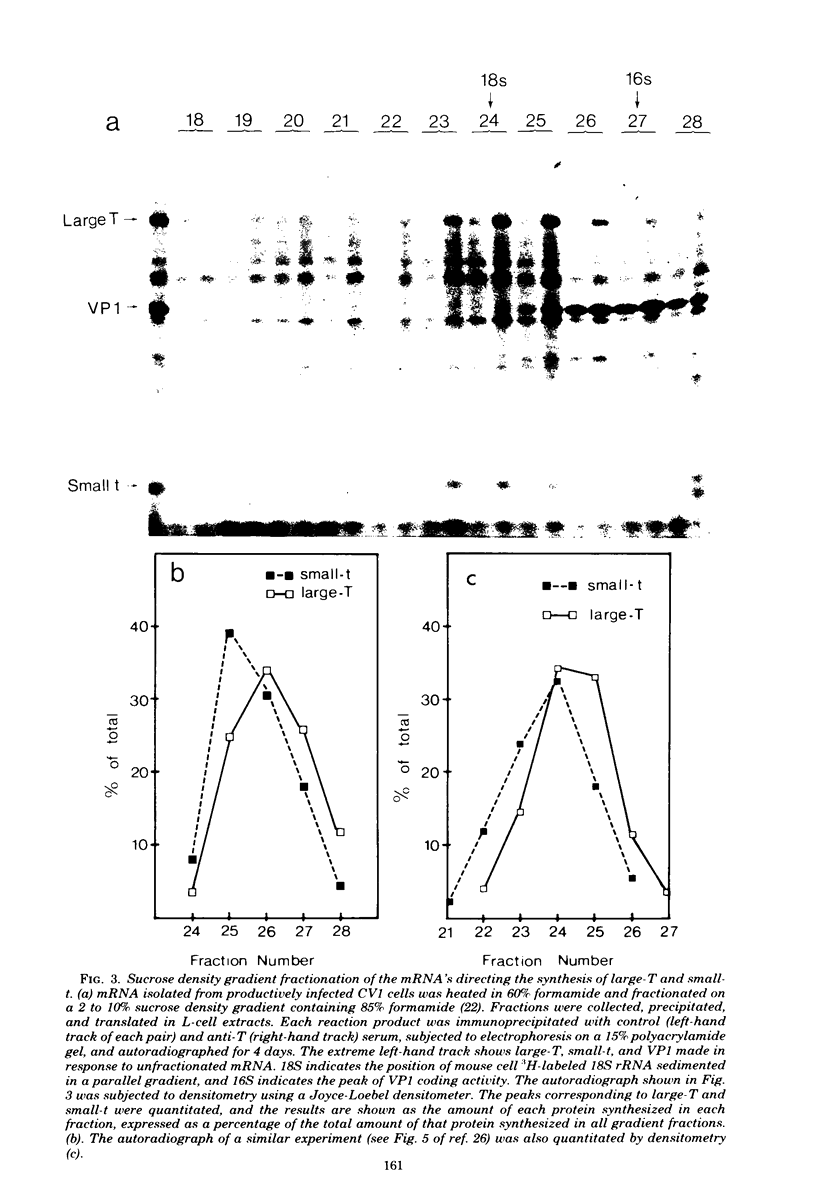
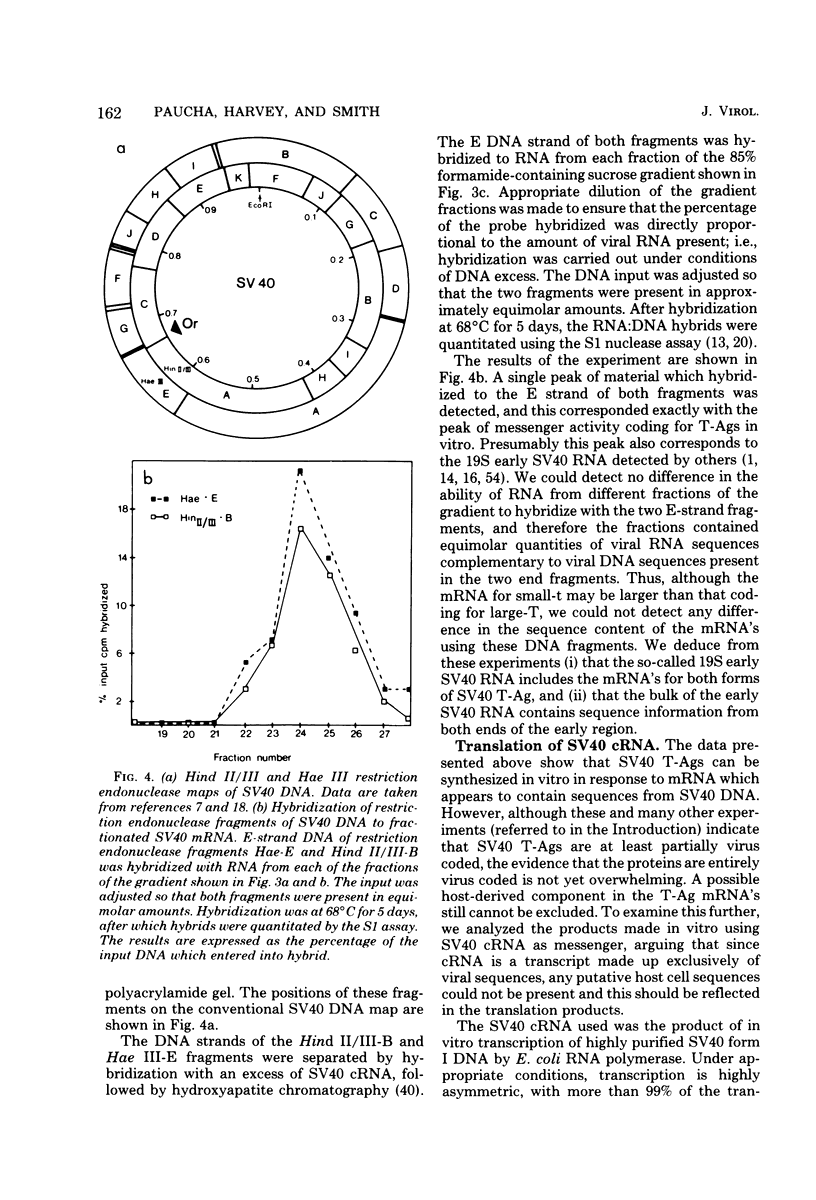
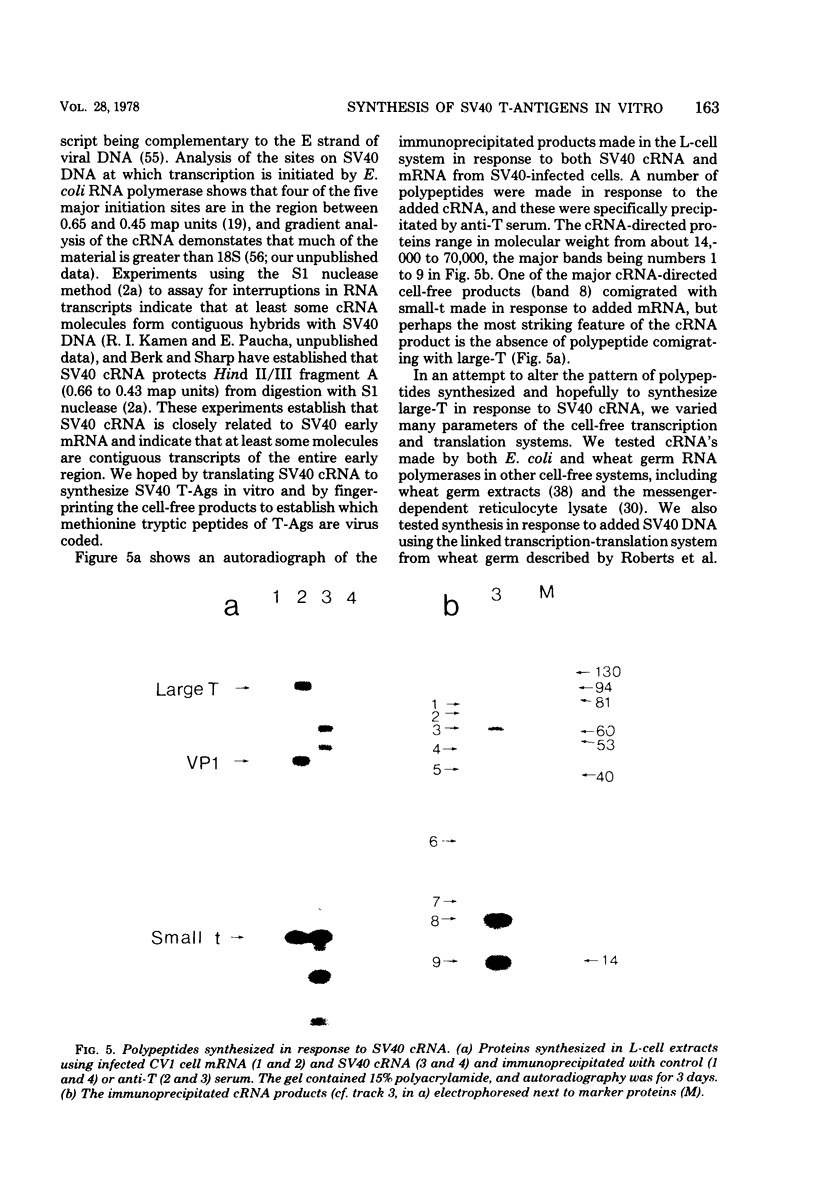
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and tryptic peptide fingerprint analysis of the proteins made in a cell-free system derived from L-cells and immunoprecipitated with simian virus 40 (SV40) anti-T serum demonstrated that both SV40 large-T and small-T antigens are synthesized in vitro in response to mRNA isolated from productively infected CV1 CELLS. Sucrose density centrifugation in gradients containing 85% formamide showed that the mRNA's for both forms of T-antigen sediment at about 17.5S, with the mRNA for small-t sedimenting marginally, but reproducibly, ahead of the mRNA for large-T. Hybridization experiments using restriction endonuclease fragments Hae III-E and Hind II/III-B showed that all fractions active in the cell-free synthesis of both forms of T-antigen hybridized equally to both fragments. This suggests that the mRNA's for SV40 T-antigens are at least partly virus coded and that the bulk of the early SV40 mRNA contains sequence information from both ends of the early region. The data are consistent with the suggestion that the large-T mRNA is spliced. SV40 complementary RNA (the product of transcription of SV40 DNA using Escherichia coli RNA polymerase) was also translated in the L-cell system and gave two families of polypeptides which specifically immunoprecipitate with anti-T serum. One family (the small-t family) includes a polypeptide indistinguishable by gel electrophoresis and tryptic peptide fingerprinting from small-t isolated from cells. The other family (the 60K family) has a major component with molecular weight approximately 60,000 and includes other polypeptides with molecular weights ranging from approximately 14,000 to about 70,000. The 60K family has petides in common with large-T but not with small-T. Together, the peptides of the small-t and 60K families account for virtually all of the methionine peptides of SV40 large-T. We conclude from these results (i) that small-t is probably entirely, and large-T at least predominantly, virus coded; (ii) that the small-t and 60K families represent the translation products of two different portions of the early region of SV40 DNA (approximately 0.65 to 0.55 map units and 0.54 to 0.17 map units); and (iii) that although most, if not all, of the large-T and small-t peptides are present in the cell-free product, some feature of sequence arrangement of SV40 complementary RNA prevents the translation of full-length large-T and results instead in the synthesis of fragments. We suggest that the absence of a splice in the complementary RNA is responsible for this result.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Transcription during productive infection with polyoma virus and Simian virus 40. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Reed S. I., Stark G. R. Characterization of the autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):22–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.22-27.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. A SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN PRESENT IN SV40 TUMOR AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1148–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Avila J., Martin R. G. Viral DNA synthesis in cells infected by temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.116-124.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Cole C. N., Smith A. E., Paucha E., Tegtmeyer P., Rundell K., Berg P. Organization and expression of early genes of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):117–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Sack G. H., Jr, Nathans D. Studies of simian virus 40 DNA. VII. A cleavage map of the SV40 genome. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Haegemann G., Rogiers R., Van de Voorde A., Van Heuverswyn H., Van Herreweghe J., Volckaert G., Ysebaert M. Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):113–120. doi: 10.1038/273113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graessmann M., Graessman A. "Early" simian-virus-40-specific RNA contains information for tumor antigen formation and chromatin replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):366–370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Brocklehurst J. R., Dulbecco R. Virus-specific proteins in the plasma membrane of cells lytically infected or transformed by pol-oma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4666–4670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Shure H. Topography of polyoma virus messenger RNA molecules. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):361–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Nathans D. The genome of simian virus 40. Adv Virus Res. 1977;21:85–173. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60762-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Carter B. J., Ferdinand F. J., Howley P. M., Brown M., Martin M. A. Genome localization of simian virus 40 RNA species. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):832–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.832-840.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Siegel W., Sklar J. Hemophilus aegyptius restriction edonuclease cleavage map of the simian virus 40 genome and its colinear relation with the hemophilus influenzae cleavage map of SV40. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):105–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Stern R., Ghosh P. K., Weissman S. M. Specificity of initiation of transcription of simian virus 40 DNA I by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: identification and localization of five sites for initiation with [gamma-32P]ATP. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):430–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.430-445.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. N., Nathans D. A transcriptional map of the SV40 genome in transformed cell lines. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. A., Garapin A. C., Jackson N., Fanshier L., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in cells producing rous sarcoma virus: detection and characterization. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):891–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.891-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luborsky S. W., Chang C., Pancake S. J., Mora P. T. Detergent solubilized and molecular weight estimation of tumor specific surface antigen from SV40 virus transformed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):990–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90752-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Transcription of simian virus 40. II. Hybridization of RNA extracted from different lines of transformed cells to the separated strands of simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):90–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.90-98.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paucha E., Mellor A., Harvey R., Smith A. E., Hewick R. M., Waterfield M. D. Large and small tumor antigens from simian virus 40 have identical amino termini mapping at 0.65 map units. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2165–2169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Martin G. S., Smith A. E. Cell-free translation of virion RNA from nondefective and transformation-defective Rous sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):950–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.950-967.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., KITAHARA T., BUTEL J. S., MELNICK J. L. SYNTHESIS OF SV40 TUMOR ANTIGEN DURING REPLICATION OF SIMIAN PAPOVAVIRUS (SV40). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Gorecki M., Mulligan R. C., Danna K. J., Rozenblatt S., Rich A. Simian virus 40 DNA directs synthesis of authentic viral polypeptides in a linked transcription-translation cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1922–1926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Collins J. K., Tegtmeyer P., Ozer H. L., Lai C. J., Nathans D. Identification of simian virus 40 protein A. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):636–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.636-646.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sharp P. A., Keller W. Transcription of Simian virus 40. I. Separation of the strands of SV40 DNA and hybridization of the separated strands to RNA extracted from lytically infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 14;70(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Sugden B., Keller W., Sharp P. A. Transcription of simian virus 40. 3. Mapping of "early" and "late" species of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3711–3715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Thompson W. S., Lin P. S., Wallach D. F. Simian virus 40-specific proteins in the membranes of simian virus 40-transformed hamster and mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5069–5072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Carbon J., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.664-671.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Kamen R., Mangel W. F., Shure H., Wheeler T. Location of the sequences coding for capsid proteins VP1 and VP2 on polyoma virus DNA. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weissman S. M. The early region of SV40 DNA may have more than one gene. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):837–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90295-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert G., Van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the simian virus 40 small-t gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Ben-Ishai Z., Newbold J. E. Simian virus 40 transcription in productively infected and transformed cells. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1263–1273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1263-1273.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Warnaar S. O., Winocour E. Isolation and characterization of simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.193-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westphal H. SV40 DNA strand selection by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90201-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T., Bayley S. T., Harvey R., Crawford L. V., Smith A. E. Cell-free synthesis of polyoma virus capsid proteins VP1 and VP2. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):215–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.215-224.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]