Abstract
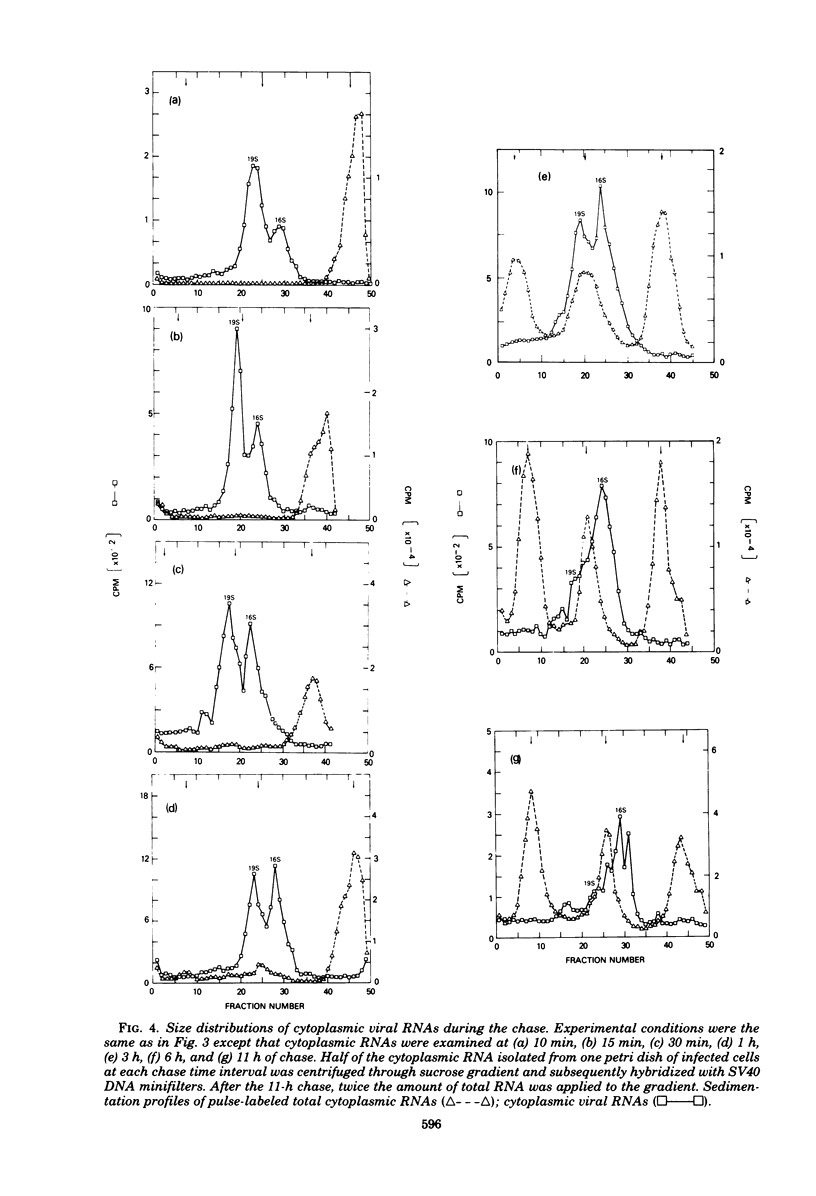
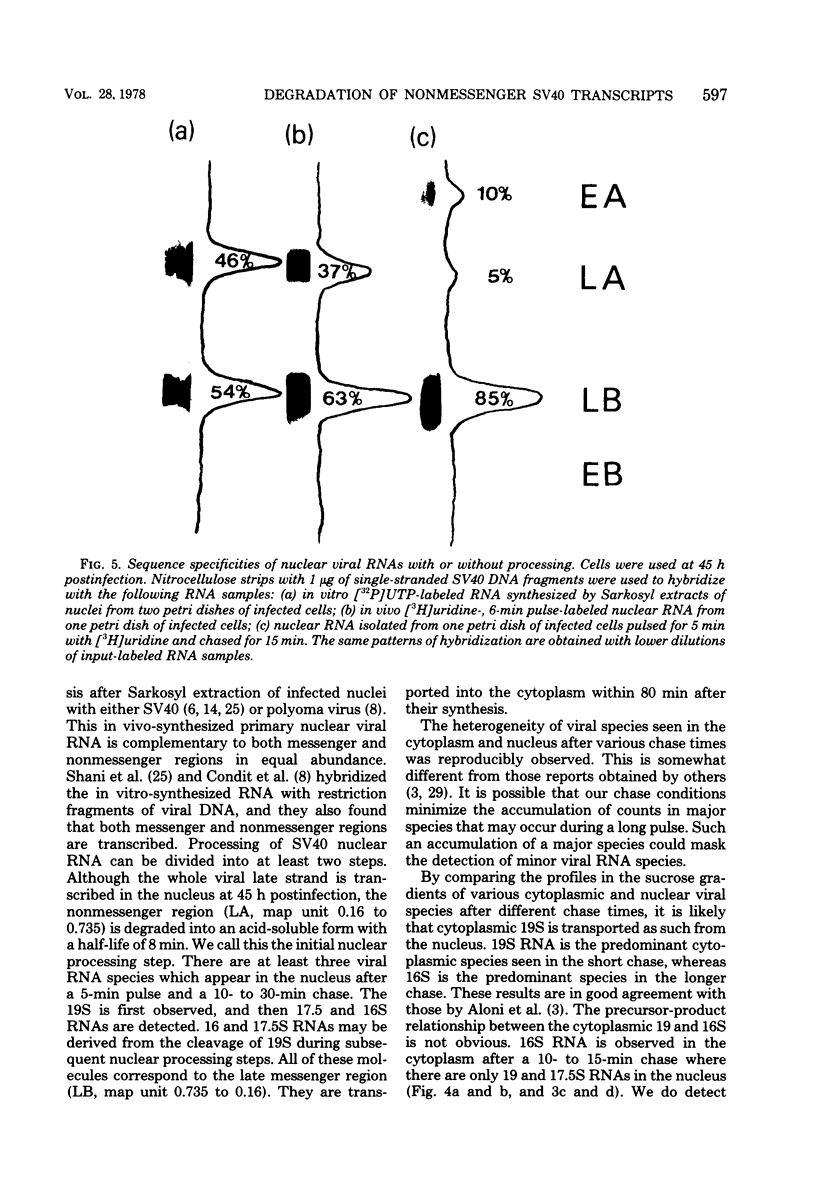
By pretreating simian virus 40-infected BSC-1 cells with glucosamine, [3H]uridine labeling of both cellular and viral RNA can be halted instantaneously by addition of cold uridine. We have studied the fate of pulse-labeled viral RNA from cells at 45 h postinfection under these conditions. During a 5-min period of labeling, both the messenger and nonmessenger regions of the late strand were transcribed. After various chase periods, nuclear viral species which sediment at 19, 17.5, and 16S were observed. Nuclear viral RNA decays in a multiphasic manner. Of the material present at the beginning of the chase period, 50% was degraded rapidly with a half-life of 8 min (initial processing). This rapidly degraded material was that fraction of the late strand which did not give rise to stable late mRNA species. Forty percent was transported to the cytoplasm, and 10% remained in the nucleus as material which sedimented in the 2 to 4S region. These 2 to 4S viral RNAs had a half-life of 3 h, and hybridization studies suggest that they are in part coded for by the late-strand nonmessenger region and are derived from the initial nuclear processing step. Another part is coded for by the late-strand messenger region and may be generated by some subsequent nuclear cleavages of 19S RNA into 17.5 and 16S RNAs. Transport of nuclear viral RNA into the cytoplasm was detected after a 5-min pulse and a 7-min chase. The maximum amount of labeled viral RNA was accumulated in the cytoplasm after a 30-min to 1-h chase. At least two viral cytoplasmic species were observed. Kinetic data suggest that 19S RNA is transported directly from the nucleus. Whether cytoplasmic 16S is formed by cleavage of 19S RNA in the cytoplasm is not clear. The half-lives of cytoplasmic 19 and 16S RNAs can be approximated as 2 and 5 h, respectively.
Full text
PDF

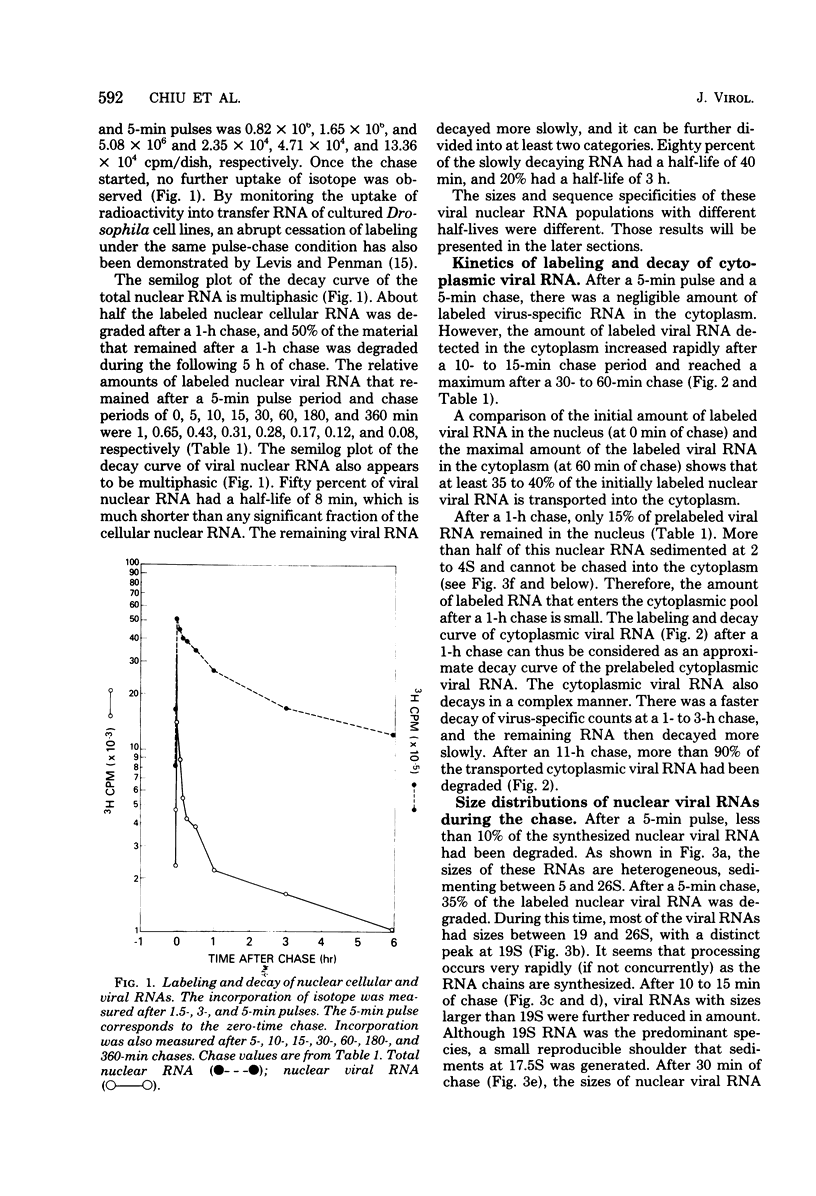
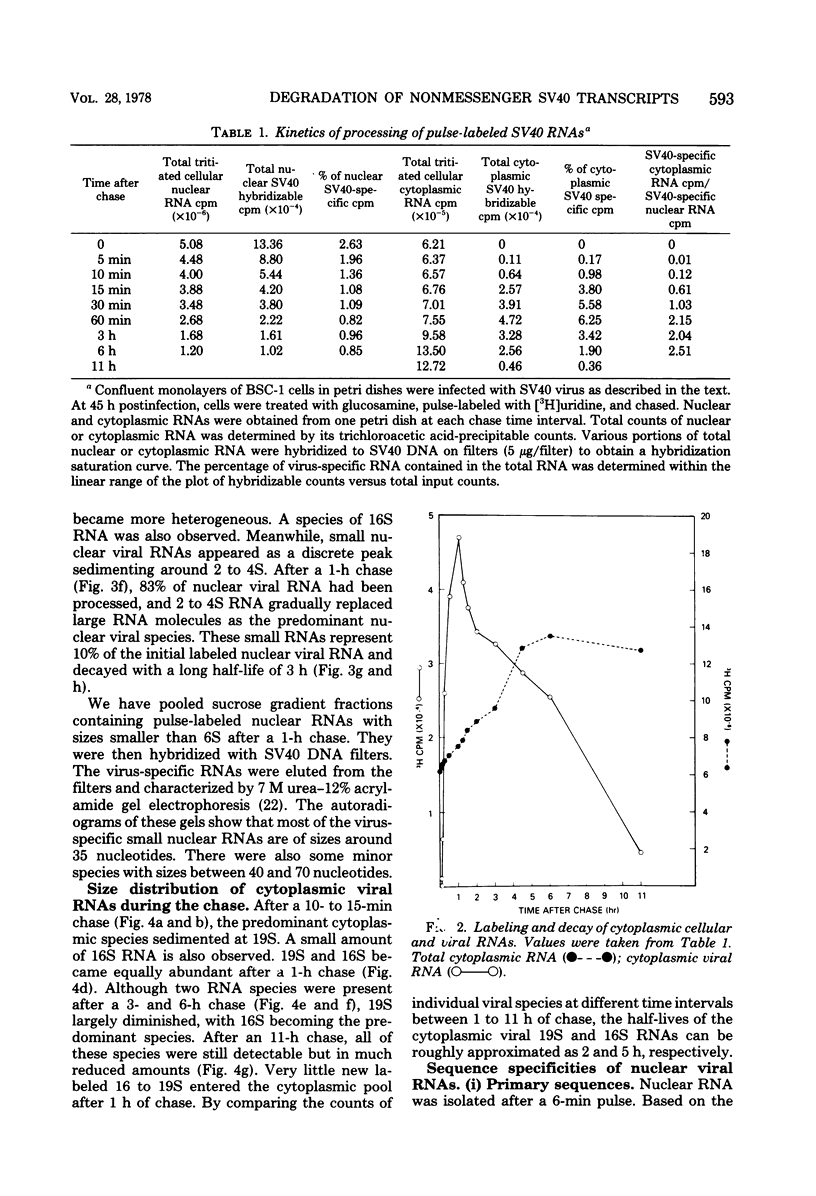
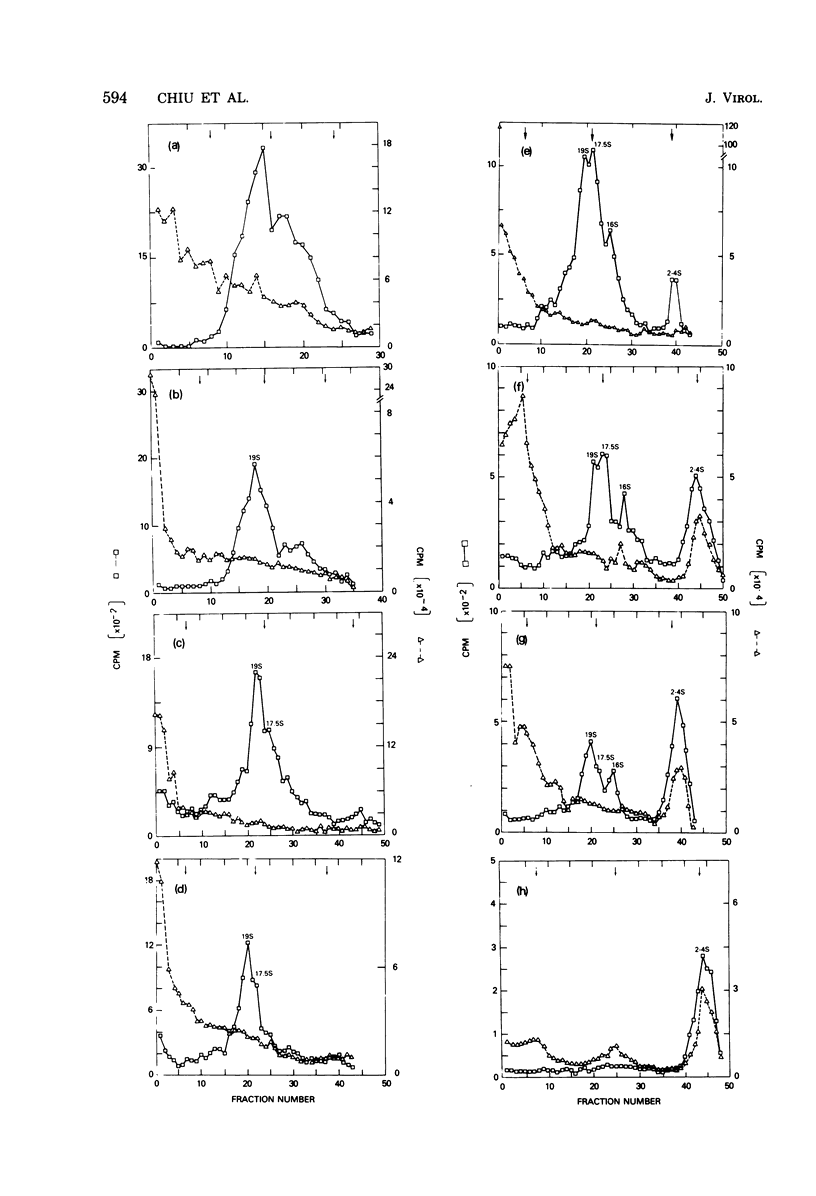



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Transcription during productive infection with polyoma virus and Simian virus 40. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y., Dhar R., Laub O., Horowitz M., Khoury G. Novel mechanism for RNA maturation: the leader sequences of simian virus 40 mRNA are not transcribed adjacent to the coding sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloni Y., Shani M., Reuveni Y. RNAs of simian virus 40 in productively infected monkey cells: kinetics of formation and decay in enucleate cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2587–2591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Moore C., Sharp P. A. Spliced segments at the 5' terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., May E., Salzman N. P. Characterization of simian virus 40 tsA58 transcriptional intermediates at restrictive temperatures: relationship between DNA replication and transcription. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):702–710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.702-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Gelinas R. E., Broker T. R., Roberts R. J. An amazing sequence arrangement at the 5' ends of adenovirus 2 messenger RNA. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Cowie A., Kamen R., Birg F. Polyoma virus transcription in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 15;115(2):215–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jelinek W. R., Molloy G. R. Biogenesis of mRNA: genetic regulation in mammalian cells. Science. 1973 Sep 28;181(4106):1215–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4106.1215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Darnell J. E. Relationship of chain transcription to poly(A) addition and processing of hnRNA in HeLa cells. Cell. 1974 Nov;3(3):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Choudary P. V., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. The 5'-terminal leader sequence of late 16 S mRNA from cells infected with simian virus 40. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3643–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. T., Jelinek W. R. Mapping of inverted repeated DNA sequences within the genome of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1631–1634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub O., Aloni Y. Transcription of simian virus 40. VI. SV 40 DNA-RNA polymerase complex isolated from productively infected cells transcribed in vitro. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Penman S. The metabolism of poly (A)+ and poly(A)-hnRNA in cultured Drosophila cells studied with a rapid uridine pulse-chase. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Units of transcription and translation: sequence components of heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):77–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Units of transcription and translation: the relationship between heterogeneous nuclear RNA and messenger RNA. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Kopecka H., May P. Mapping the transcription site of the SV40-specific late 16 S mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1995–2005. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner H. C., Meyer J., Maizel J. V., Jr, Westphal H. Visualization and mapping of late nuclear adenovirus RNA. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Zachau G. Partial degradation of transfer RNAs and transfer RNA fragments by spleen phosphodiesterase as studied by disc electrophoretic methods. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):523–538. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Detection of an unstable RNA in chick fibroblasts after reduction of the UTP pool by glucosamine. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec;24(2):358–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Birkenmeier E., May E., Salzman N. P. Properties of simian virus 40 transcriptional intermediates isolated from nuclei of permissive cells. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):20–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.20-28.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Hearst J. E. Mapping of sequences with 2-fold symmetry on the simian virus 40 genome: a photochemical crosslinking approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1363–1367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Dhar R., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of a fragment of SV40 DNA that contains the origin of DNA replication and specifies the 5' ends of "early" and "late" viral RNA. III. Construction of the total sequence of EcoRII-G fragment of SV40 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):355–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Warnaar S. O., Winocour E. Isolation and characterization of simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.193-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W. Method of examining viral RNA metabolism in cells in culture: metabolism of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1340–1344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1340-1344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. B., Sandeen D. The ribonuclease activity of crystallized pancreatic deoxyribonuclease. Anal Biochem. 1966 Feb;14(2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]