Abstract
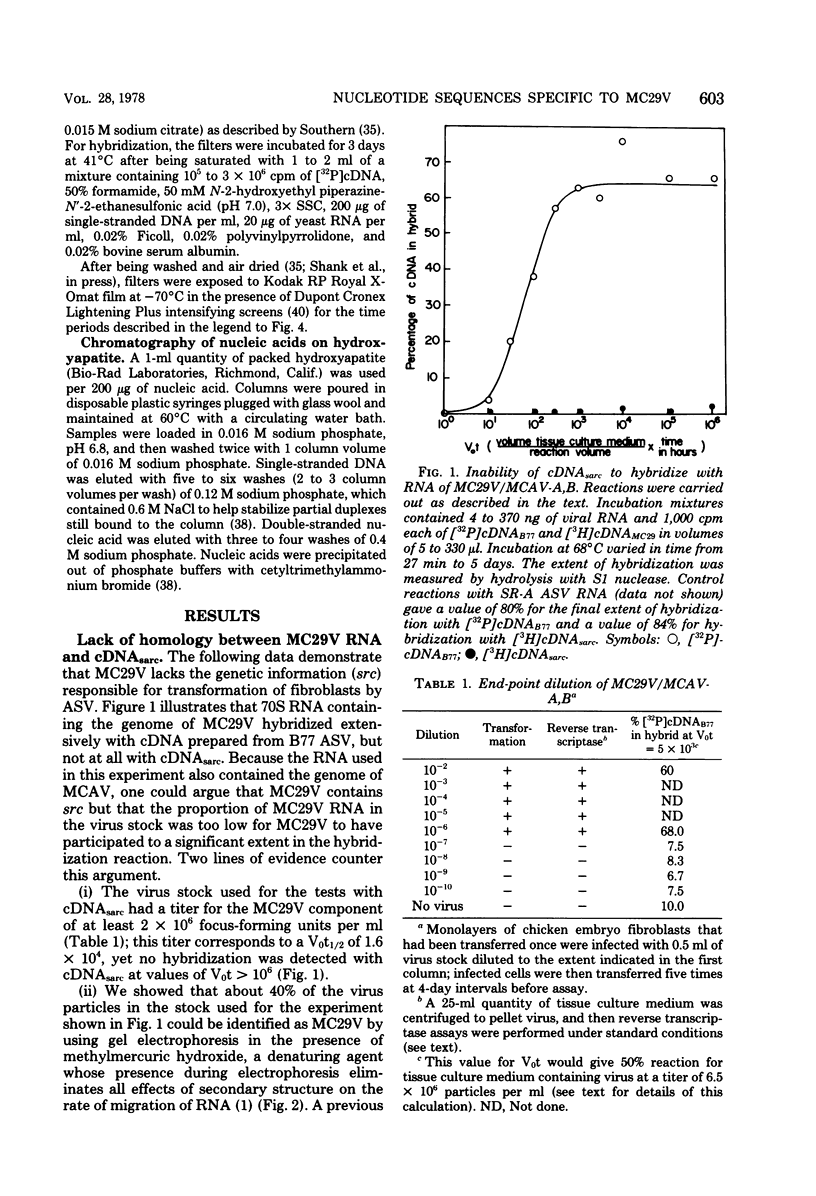
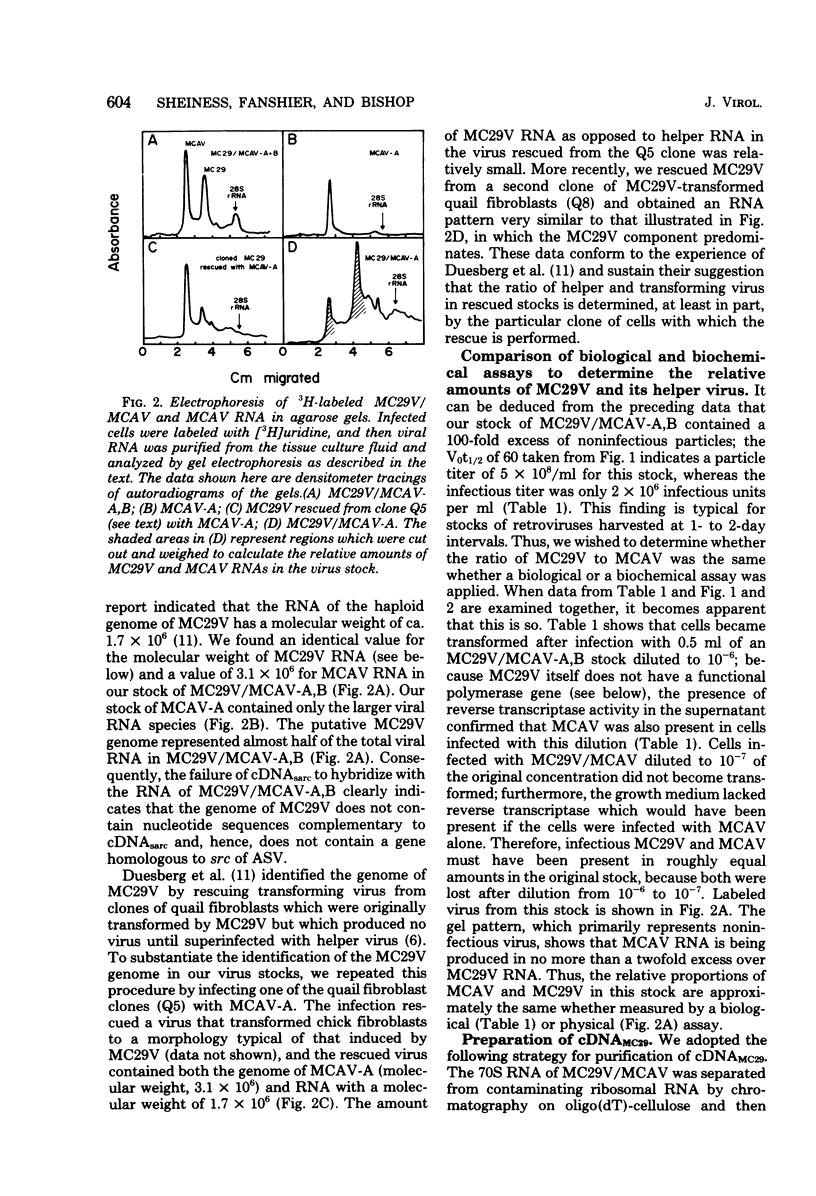
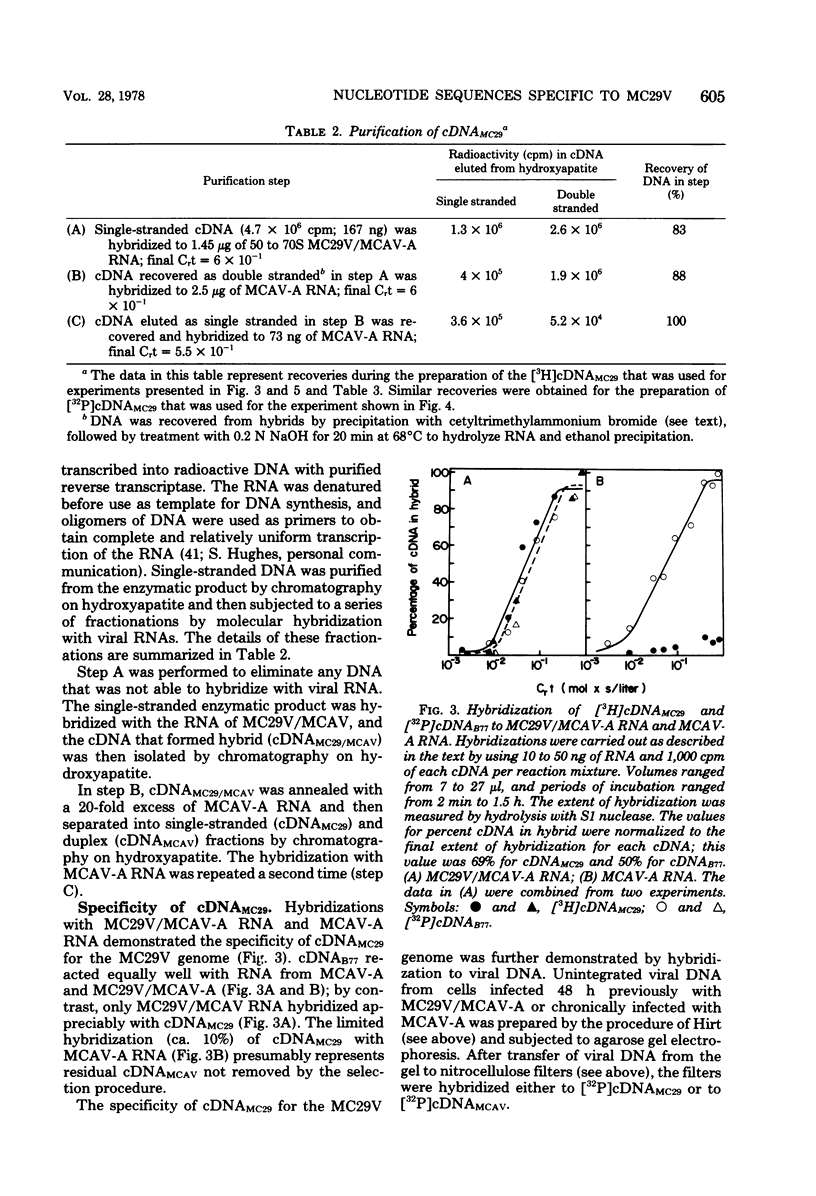
The retrovirus strain MC29 induces a variety of tumors in chickens, including myelocytomatosis and carcinomas of the kidney and liver. In addition, the virus can transform cultures of embryonic avian macrophages and fibroblasts. We have characterized the genome of MC29 virus and have identified nucleotide sequences that may encode the oncogenic potential ofthe virus. MC29 virus can replicate only with the assistance of a related helper virus. The defect in replication is apparently a consequence of a deletion in one or more viral genes: the haploid genome of the MC29 virus has a molecular weight of ca. 1.7 X 10(6), whereas the genome of the helper virus MCAV has a molecular weight of ca. 3.1 X 10(6). Although MC29 virus transforms fibroblasts in culture, its genome has no detectable homology with the gene src that is responsible for transformation of fibroblasts by avian sarcoma viruses. We prepared radioactive single-stranded DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences present in the genome of MC29 virus but not in the genome of MCAV (cDNA(MC29)). If they are contiguous, these sequences (ca. 1,500 nucleotides) are sufficiently complex to encode at least one protein. Homologous sequences were not detectable in several strains of avian sarcoma viruses or in an endogenous virus of chickens. Our findings confirm and extend recent reports from other laboratories and lead to the conclusion that MC29 virus may contain a previously unidentified gene(s) that is capable of transforming several distinct target cells. The evolutionary origins of this putative gene and its location on the viral genome can be explored with cDNA(MC29).
Full text
PDF


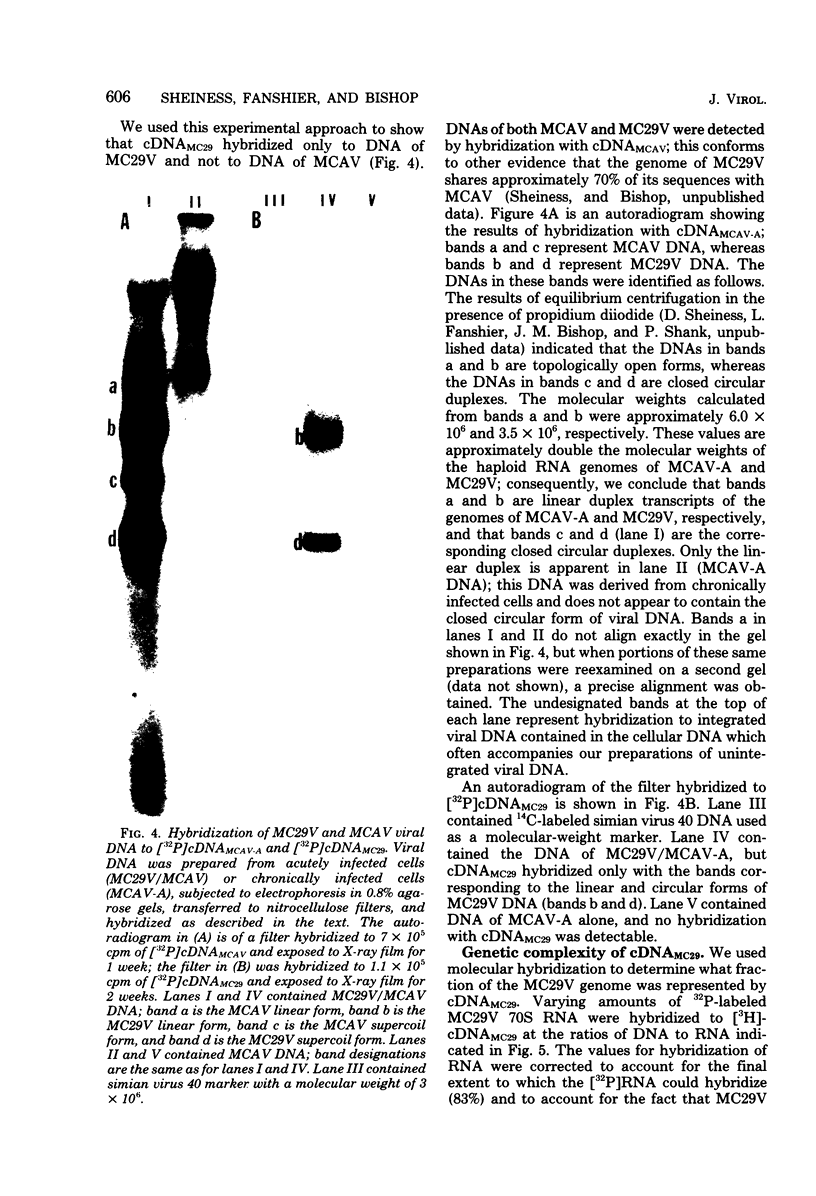
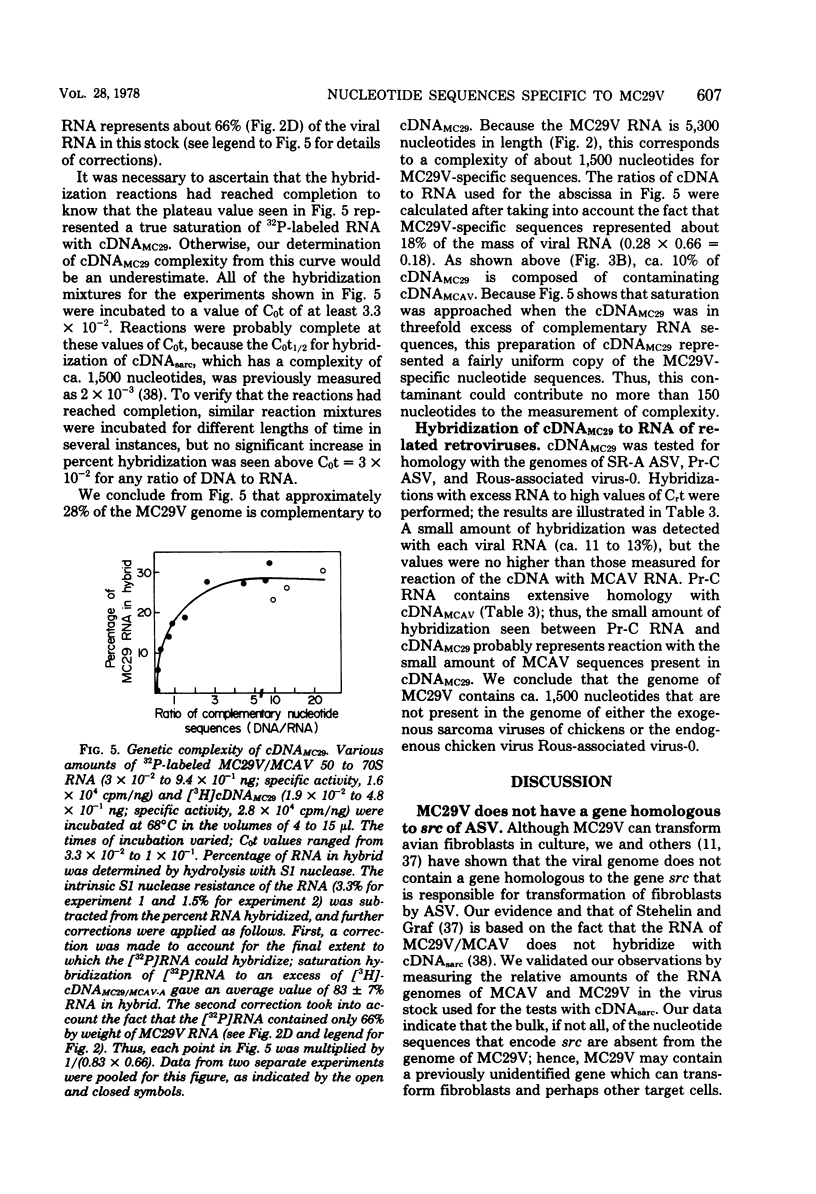



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard J. W., Chabot J. F., Beard D., Heine U., Houts G. E. Renal neoplastic response to leukosis virus strains BAI A (avian myeloblastosis virus) and MC29. Cancer Res. 1976 Feb;36(2 Pt 1):339–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard J. W., Hillman E. A., Beard D., Lapis K., Heine U. Neoplastic response of the avian liver to host infection with strain Mc29 leukosis verus. Cancer Res. 1975 Jul;35(7):1603–1627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggs P. M., Milne B. S., Graf T., Bauer H. Oncogenicity of non-transforming mutants of avian sarcoma viruses. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):399–403. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Levinson W. E., Quintrell N., Sullivan D., Fanshier L., Jackson J. The low molecular weight RNAs of Rous sarcoma virus. I. The 4 S RNA. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):182–195. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P., Langlois A. J., Sverak L., Bonar R. A., Beard J. W. In vitro chick embryo cell response to strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):576–586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.576-586.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Purchase H. G., Bockman D. E., Gathings W. E. Studies on the nature of the abnormality of B cell differentiation in avian lymphoid leukosis: production of heterogeneous IgM by tumor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1210–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Bister K., Vogt P. K. The RNA of avian acute leukemia virus MC29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4320–4324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. Differences between the ribonucleic acids of transforming and nontransforming avian tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1673–1680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Vogt P. K. RNA species obtained from clonal lines of avian sarcoma and from avian leukosis virus. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Neubauer R. L., Fischinger P. J. Fractionation of DNA nucleotide transcripts from Moloney sarcoma virus and isolation of sarcoma virus-specific complementary DNA. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):481–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.481-490.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich R., Kung H. J., Baker B., Varmus H. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Characterization of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences at the 5'-terminus of the avian sarcoma virus genome. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):198–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90345-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garapin A. C., Varmus H. E., Faras A. J., Levinson W. E., Bishop J. M. RNA-directed DNA synthesis by virions of Rous sarcoma virus: further characterization of the templates and the extent of their transcription. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):264–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T. A plaque assay for avian RNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Analysis of endonuclease R-EcoRI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1235-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki R., Langlois A. J., Chabot J., Beard J. W. Component of strain MC29 avian leukosis virus with the property of defectiveness. J Virol. 1971 Dec;8(6):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.6.821-827.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Duesberg P. H., Horst J., Vogt P. K. Avian tumor virus RNA: a comparison of three sarcoma viruses and their transformation-defective derivatives by oligonucleotide fingerprinting and DNA-RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2266–2270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois A. J., Fritz R. B., Heine U., Beard D., Bolognesi D. P., Beard J. W. Response of bone marrow to MC29 avian leukosis virus in vitro. Cancer Res. 1969 Nov;29(11):2056–2074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois A. J., Sankaran S., Hsiung P. H., Beard J. W. Massive direct conversion of chick embryo cells by strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):1082–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.1082-1084.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois A. J., Veprek L., Beard D., Fritz R. B., Beard J. W. Isolation of a non-focus-forming agent from strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. Cancer Res. 1971 Jul;31(7):1010–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. A., Garapin A. C., Jackson N., Fanshier L., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in cells producing rous sarcoma virus: detection and characterization. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):891–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.891-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. S. Rous sarcoma virus: a function required for the maintenance of the transformed state. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1021–1023. doi: 10.1038/2271021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mladenov Z., Heine U., Beard D., Beard J. W. Strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. Myelocytoma, endothelioma, and renal growths: pathomorphological and ultrastructural aspects. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1967 Mar;38(3):251–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G., Lasfargues E. Y., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Production of mouse mammary tumor virus by cultured cells in the absence and presence of hormones: assay by molecular hybridization. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):135–147. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Maryak J. M., Parks W. P. Levels of rat cellular RNA homologous to either Kirsten sarcoma virus or rat type-C virus in cell lines derived from Osborne-Mendel rats. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1435–1444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1435-1444.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Fujita D. J., Padgett T., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Detection and enumeration of transformation-defective strains of avian sarcoma virus with molecular hybridization. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Guntaka R. V., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Purification of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences required for neoplastic transformation of fibroblasts by avian sarcoma viruses. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):349–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Vogt P. K. DNA related to the transforming gene(s) of avian sarcoma viruses is present in normal avian DNA. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):170–173. doi: 10.1038/260170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stéhelin D., Graf T. Avian myelocytomatosis and erythroblastosis viruses lack the transforming gene src of avian sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):745–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Shank P. R. X-Ray Intensifying Screens Greatly Enhance the Detection by Autoradiography of the Radioactive Isotopes 32P and 125I. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiapalis C. M., Houts G. E., Beard J. W. Influence of phosphate on activity and stability of reverse transcriptase from avian myeloblastosis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2267–2275. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K. Spontaneous segregation of nontransforming viruses from cloned sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]