Abstract
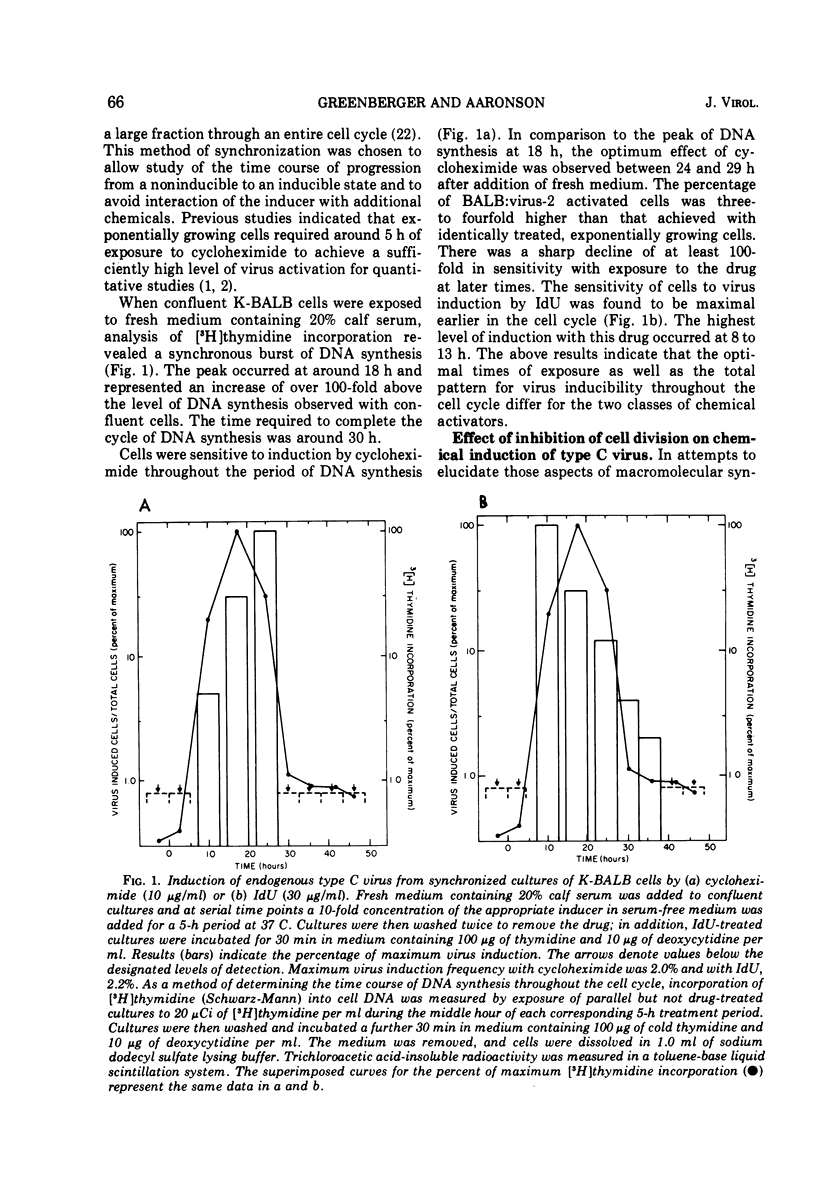
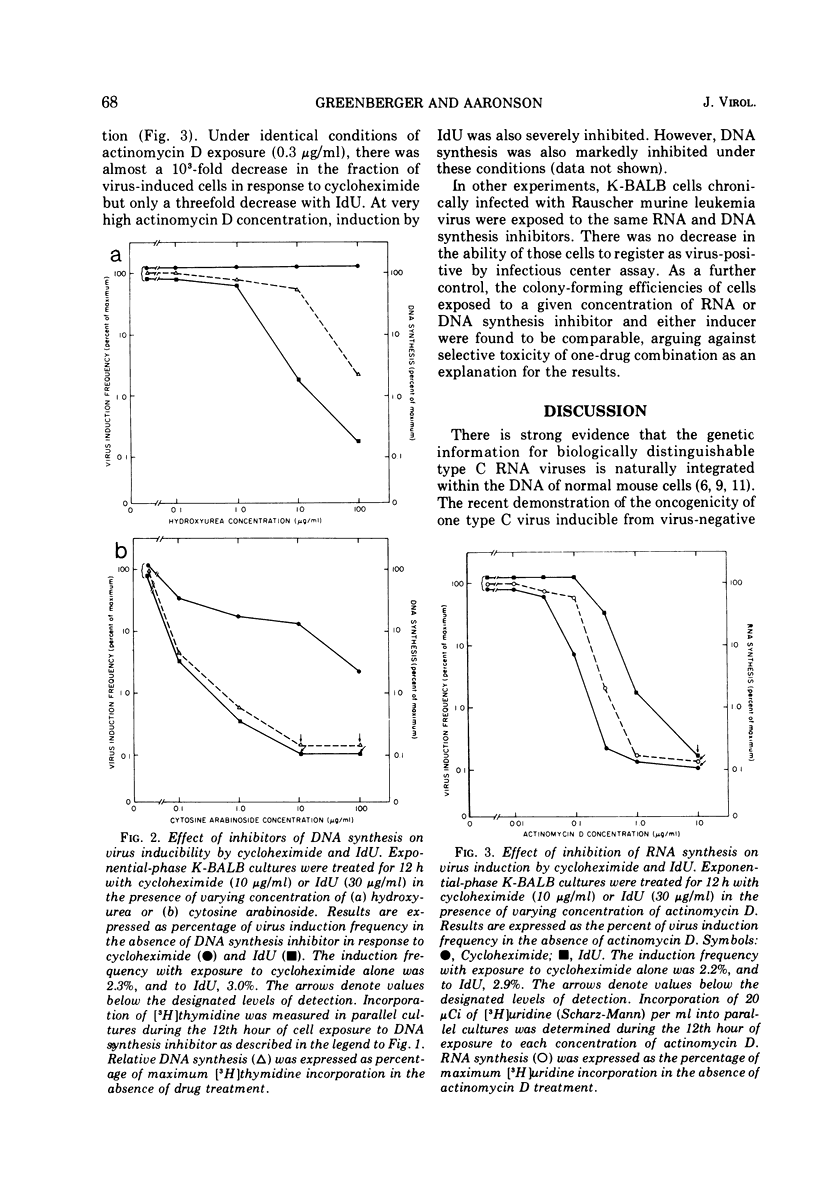
The information for type C RNA viruses is genetically transmitted within the cellular DNA of the normal mouse cell. These viruses can be induced after exposure of cells to two classes of chemicals, inhibitors of protein synthesis and halogenated pyrimidines. The metabolic requirements for activation of one endogenous virus of BALB/c mouse cells by representatives of each class of drugs were studies. Cycloheximide and iododeoxyuridine each induce virus efficiently from cultures in exponential growth but are inactive on cells in stationary phase. However, cells are maximally sensitive to the actions of each drug at different times within the cell cycle. Further, virus induction in response to each is differentially inhibited under conditions of simultaneous cell exposure to inhibitors of DNA or RNA synthesis. The results provide support for the concept that inhibitors of protein synthesis and halogenated pyrimidines act by different mechanisms to induce type C virus release.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Anderson G. R., Dunn C. Y., Robbins K. C. Induction of type-C RNA virus by cycloheximide: increased expression of virus-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3941–3945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Dunn C. Y. Endogenous C-type viruses of BALB-c cells: frequencies of spontaneous and chemical induction. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):181–185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.181-185.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Dunn C. Y. High-frequency C-type virus induction by inhibitors of protein synthesis. Science. 1974 Feb 1;183(4123):422–424. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4123.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Hartley J. W., Todaro G. J. Mouse leukemia virus: "spontaneous" release by mouse embryo cells after long-term in vitro cultivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):87–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Rowe S. P. Nonproducer clones of murine sarcoma virus transformed BALB-3T3 cells. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Stephenson J. R. Independent segregation of loci for activation of biologically distinguishable RNA C-type viruses in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2055–2058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Scolnick E. M. Induction of murine C-type viruses from clonal lines of virus-free BALB-3T3 cells. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):157–159. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaronson S. A., Weaver C. A. Characterization of murine sarcoma virus (Kirsten) transformation of mouse and human cells. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):245–252. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Teich N. M., Levine A. S., Rowe W. P. Evidence that the AKR murine-leukemia-virus genome is complete in DNA of the high-virus AKR mouse and incomplete in the DNA of the "virus-negative" NIH mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Milstien J. B., Martin M. A., Aaronson S. A. Characterization of murine leukaemia virus-specific DNA present in normal mouse cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 18;244(133):76–79. doi: 10.1038/newbio244076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P. Activation of Epstein-Barr virus by 5-bromodeoxyuridine in "virus-free" human cells (complement-fixing antigen-immunofluorescence-leukocytes). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):83–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Derge J. G., Martos L. M., Tagamets M. A., Burroughs M. A. Sequence of spontaneous Epstein-Barr virus activation and selective DNA synthesis in activated cells in the presence of hydroxyurea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2589–2593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Tanaka A., Nonoyama M., Derge J. G. Replication of the resident repressed Epstein-Barr virus genome during the early S phase (S-1 period) of nonproducer Raji cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):631–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huu Duc-Nguyen, Rosenblum E. N., Zeigel R. F. Persistent infection of a rat kidney cell line with Rauscher murine leukemia virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1133-1140.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Xenotropic viruses: murine leukemia viruses associated with NIH Swiss, NZB, and other mouse strains. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rowe W. P., Teich N., Hartley J. W. Murine leukemia virus: high-frequency activation in vitro by 5-iododeoxyuridine and 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):155–156. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Separation of Epstein-Barr virus DNA from large chromosomal DNA in non-virus-producing cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 9;238(84):169–171. doi: 10.1038/newbio238169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. Genetic factors influencing C-type RNA virus induction. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):175–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Crow J. D., Aaronson S. A. Differential activation of biologically distinguishable endogenous mouse type C RNA viruses: interaction with host cell regulatory factors. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Greenberger J. S., Aaronson S. A. Oncogenicity of an endogenous C-type virus chemically activated from mouse cells in culture. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):237–240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.237-240.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teich N., Lowy D. R., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Studies of the mechanism of induction of infectious murine leukemia virus from AKR mouse embryo cell lines by 5-iododeoxyuridine and 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90376-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G., Matsuya Y., Bloom S., Robbins A., Green H. Stimulation of RNA synthesis and cell division in resting cells by a factor present in serum. Wistar Inst Symp Monogr. 1967;7:87–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima K., Vogt P. K. Enhancement and inhibition of avian sarcoma viruses by polycations and polyanions. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):414–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



