Abstract
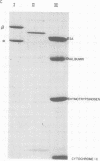
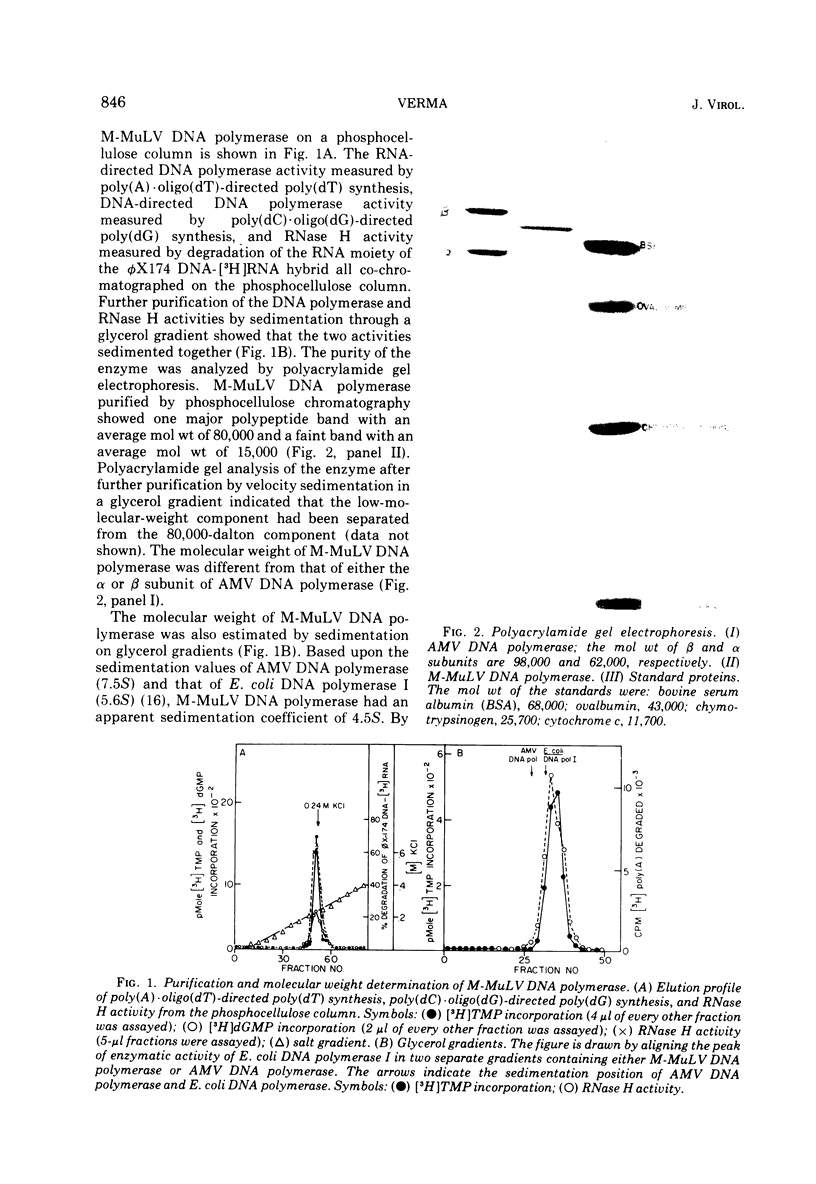
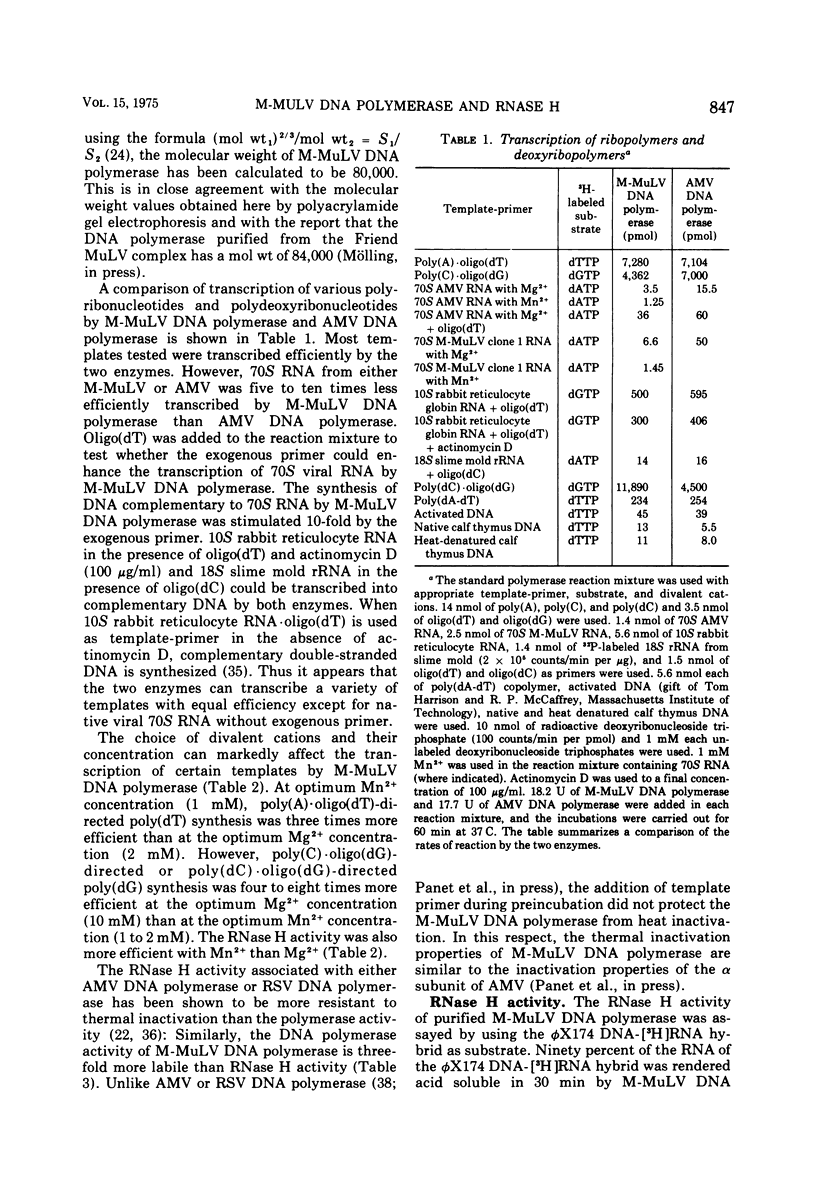
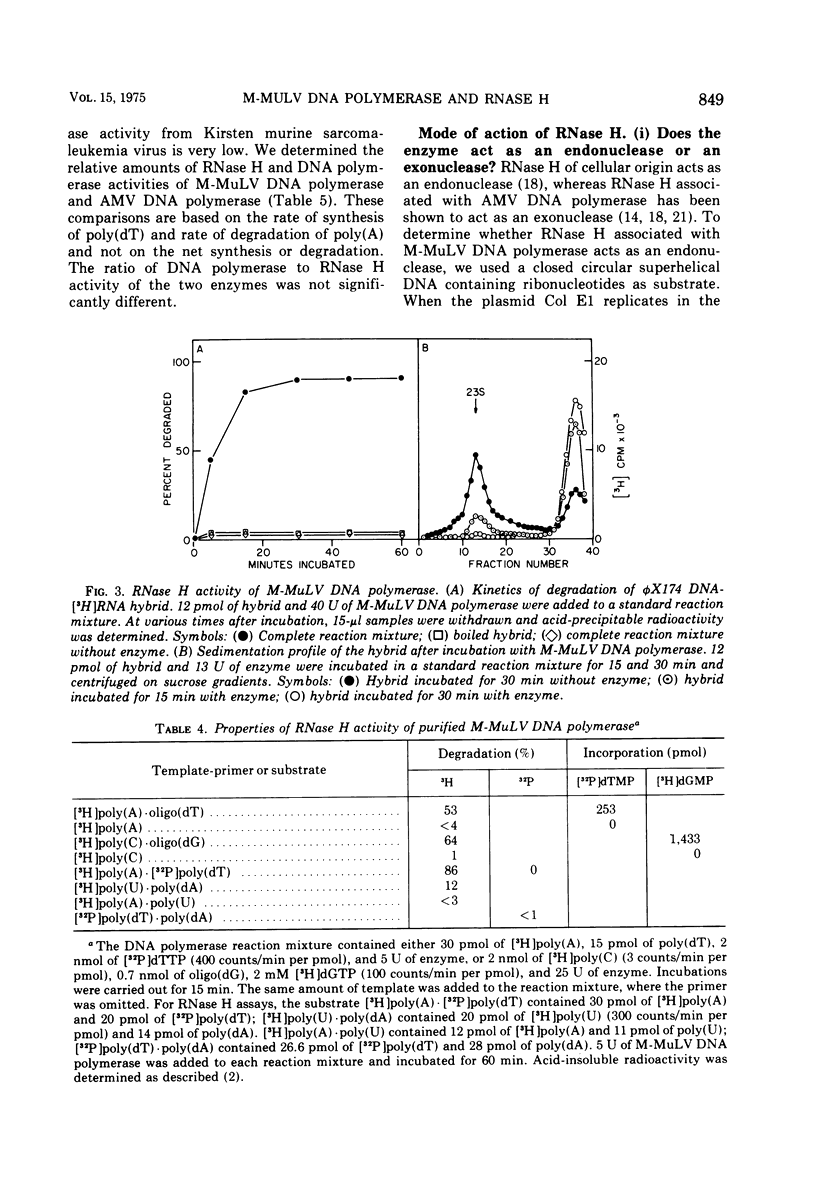
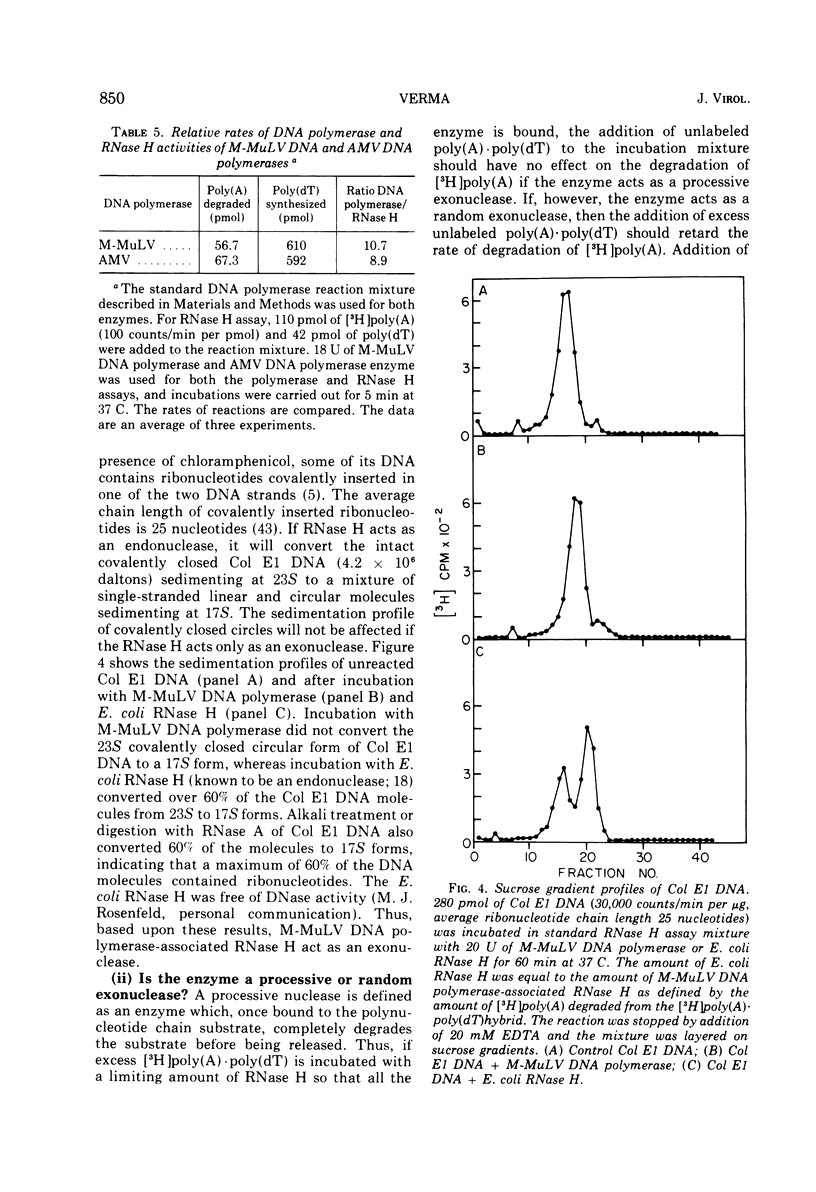
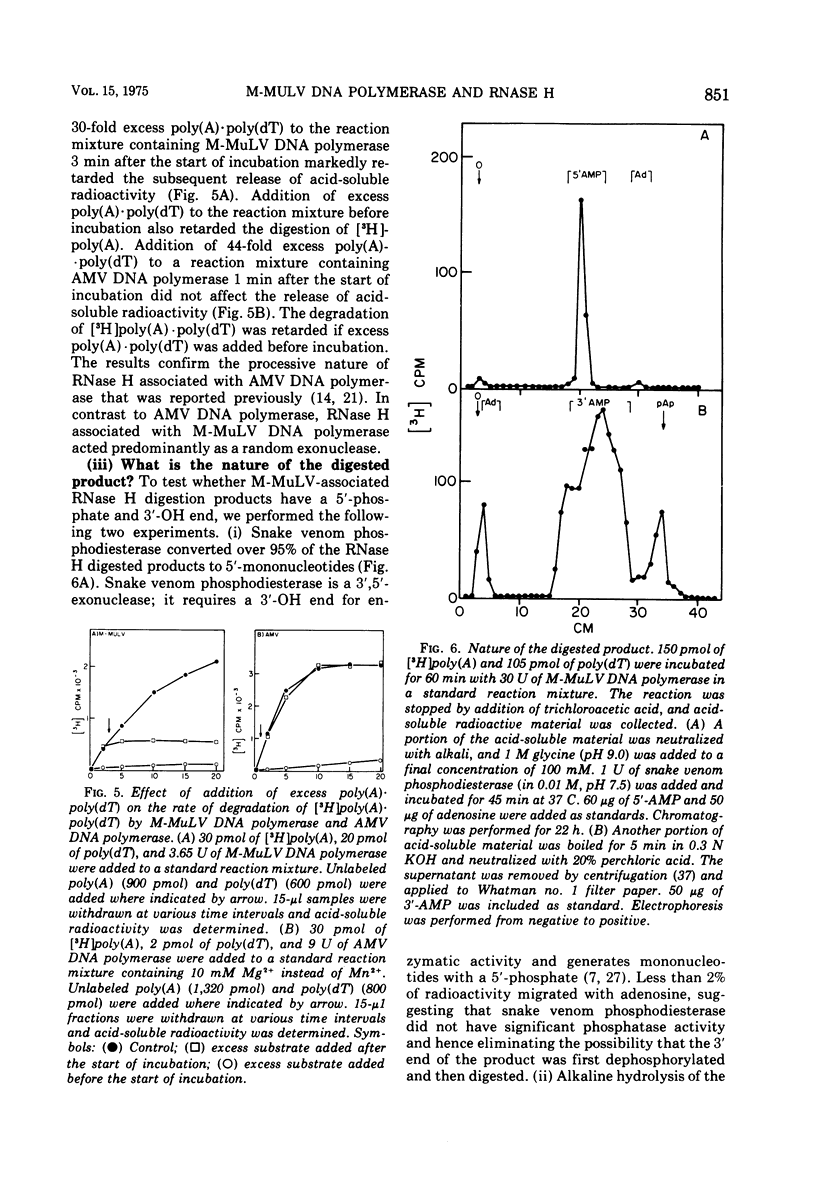
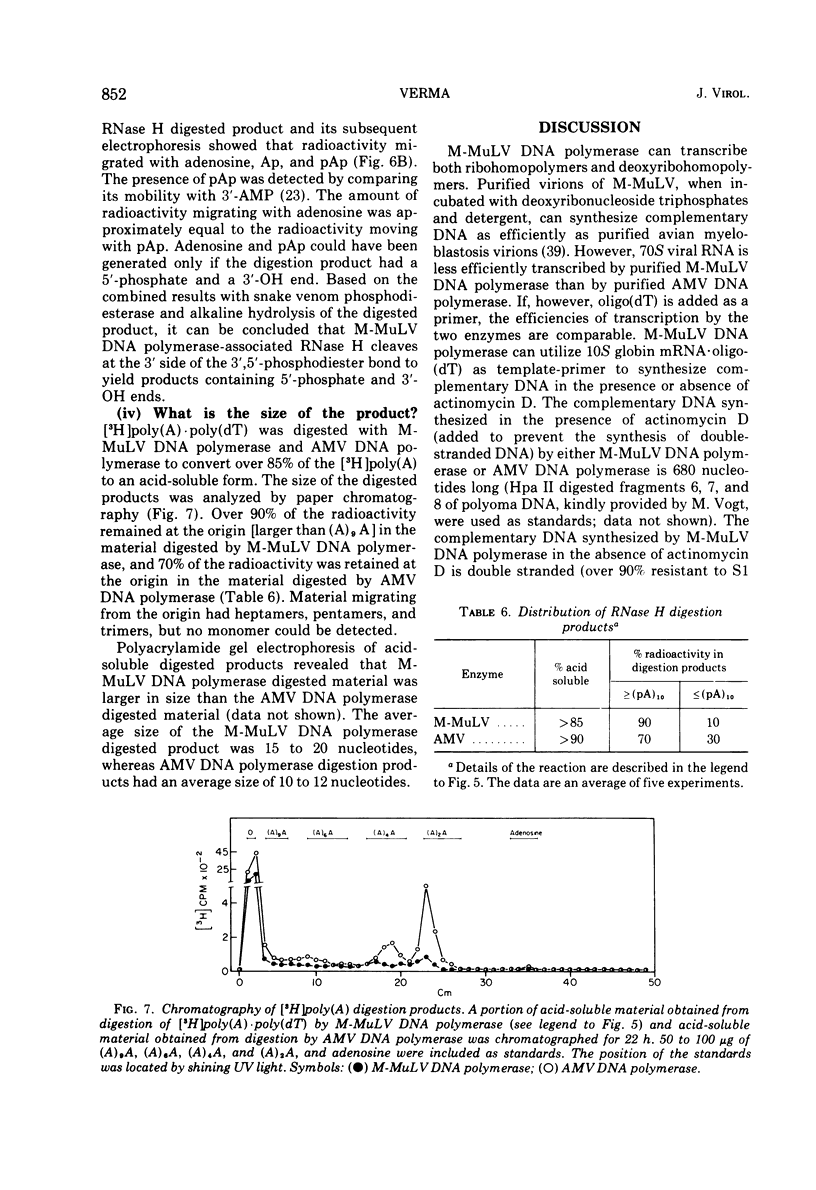
DNA polymerase was purified from a cloned isolate of Moloney murine leukemia virus (M-MuLV). Purified M-MuLV DNA polymerase, upon analysis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, showed one major polypeptide of mol wt 80,000. Estimation of molecular weight from the sedimentation rate of the purifed enzyme in a glycerol gradient was consistent with a structure containing one polypeptide. M-MuLV DNA polymerase could transcribe ribopolymers, deoxyribopolymers, and heteropolymers as efficiently as did purified DNA polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV). M-MuLV DNA polymerase, however, transcribed native 70S viral RNA less efficiently than did AMV DNA polymerase. Addition of oligo(dT) enhanced five to tenfold the transcription of 70S viral RNA by M-MuLV DNA polymerase. Purified enzyme also exhibited nuclease activity (RNase H) that selectively degraded the RNA moiety of the RNA-DNA hybrid. It did not degrade single-stranded RNA, single-stranded DNA, double-stranded RNA, and double-stranded DNA. M-MuLV DNA polymerase-associated RNase H acted as a random exonuclease. When [3-H]poly(A)-poly(dT) was used as a substrate, the size of the M-MuLV DNA polymerase-associated RHase H digested product was larger than the size of the digestion products by AMV DNA polymerase. The oligonucleotide digestion products could be further digested to 5'-AMP by snake venom phosphodiesterase, indicating that the products were terminated by 3'-OH groups. Alkaline hydrolysis of the oligonucleotide digestion products generated pAp, suggesting that M-MuLV DNA polymerase-associated RNase H cleaves at the 3' side of the 3',5'-phosphodiester bond. The ratios of the rates of DNA polymerase activity and RNase H activity were not significantly different in the murine and avian enzymes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S., Stampfer M. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus, II. An RNA polymerase in the virion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):572–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. F. Association of an endoribonuclease with the avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7282–7287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. Primer requirement and template specificity of the DNA polymerase of RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Sherratt D. J., Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Isolation of supercoiled colicinogenic factor E 1 DNA sensitive to ribonuclease and alkali. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELIX F., POTTER J. L., LASKOWSKI M. Action of venom phosphodiesterase on deoxyribooligonucleotides carrying a monoesterified phosphate on carbon 3'. J Biol Chem. 1960 Apr;235:1150–1154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Paskind M. Measurement of the sequence complexity of cloned Moloney murine leukemia virus 60 to 70S RNA: evidence for a haploid genome. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):421–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.421-429.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwin B. I., Milstien J. B. An oligonucleotide affinity column for RNA-dependent DNA polymerase from RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2599–2603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Polyoma virus proteins: a description of the structural proteins of the virion based on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and peptide analysis. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Gerard G. F., Green M. A single subunit from avian myeloblastosis virus with both RNA-directed DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):230–234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Gerard G. F., Green M. Ribonuclease H: a ubiquitous activity in virions of ribonucleic acid tumor viruses. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1136–1142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1136-1142.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Green M. Different mode of action of ribonuclease H in purified alpha and alpha beta ribonucleic acid-directed deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5148–5152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J., Leis J. P. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity of RNA tumor viruses. I. Directing influence of DNA in the reaction. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):116–129. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.116-129.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., Englund P. T., Bertsch L. L. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXVI. Physical and chemical studies of a homogeneous deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):2996–3008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Watson K. F., Burny A., Spiegelman S. Purification of the DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 24;246(3):365–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Crouch R. Degradation of DNA RNA hybrids by ribonuclease H and DNA polymerases of cellular and viral origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P., Berkower I., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of action of ribonuclease H isolated from avian myeloblastosis virus and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohrmann R., Orgel L. E. Urea-inorganic phosphate mixtures as prebiotic phosphorylating agents. Science. 1971 Feb 5;171(3970):490–494. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3970.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mölling K., Bolognesi D. P., Bauer H., Büsen W., Plassmann H. W., Hausen P. Association of viral reverse transcriptase with an enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of RNA-DNA hybrids. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 22;234(51):240–243. doi: 10.1038/newbio234240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson B., Hamelin R., Tchen P., Tavitian A. Présence d'une activité RNase H non associée à activité transcriptase inverse dans les virions du sarcome murine de Moloney. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 May 27;278(22):2851–2854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZZELL W. E., KHORANA H. G. Studies on polynucleotides. IV. Enzymic degradation; the stepwise action of venom phosphodiesterase on deoxyribo-oligonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):2114–2117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Burny A., Das M. R., Keydar J., Schlom J., Trávnícek M., Watson K. Synthetic DNA-RNA hybrids and RNA-RNA duplexes as templates for the polymerases of the oncogenic RNA viruses. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):430–432. doi: 10.1038/228430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. Mechanism of DNA replication by highly purified DNA polymerase of chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2609–2613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Baltimore D. RNA-directed DNA synthesis and RNA tumor viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1972;17:129–186. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60749-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Mizutani S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1211–1213. doi: 10.1038/2261211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P. Reversible inactivation of the deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase of Rauscher leukemia virus. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):885–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.885-888.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Vogt P. K., Bishop J. M. Integration of deoxyribonucleic acid specific for Rous sarcoma virus after infection of permissive and nonpermissive hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3067–3071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Baltimore D. Purification of the RNA-directed DNA polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus and its assay with polynucleotide templates. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:125–130. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Mason W. S., Drost S. D., Baltimore D. DNA polymerase activity from two temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus is thermolabile. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):27–31. doi: 10.1038/251027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Meuth N. L., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage between ribonucleic Acid primer and deoxyribonucleic Acid product of the avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic Acid polymerase. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):622–627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.622-627.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Meuth N. L., Bromfeld E., Manly K. F., Baltimore D. Covalently linked RNA-DNA molecule as initial product of RNA tumour virus DNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):131–134. doi: 10.1038/newbio233131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Meuth N. L., Fan H., Baltimore D. Hamster leukemia virus: lack of endogenous DNA synthesis and unique structure of its DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1075–1082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1075-1082.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. Studies on reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses. I. Localization of thermolabile DNA polymerase and RNase H activities on one polypeptide. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.121-126.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Temple G. F., Fan H., Baltimore D. In vitro synthesis of DNA complementary to rabbit reticulocyte 10S RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):163–167. doi: 10.1038/newbio235163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P. H. DNA polymerase of murine sarcoma-leukemia virus: lack of detectable RNase H and low activity with viral RNA and natural DNA templates. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1512–1521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1512-1521.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimann B. J., Schmidt J., Wolfrum D. I. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H from Friend virions. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 1;43(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams H., Boyer H. W., Helsinki D. R. Size and base composition of RNA in supercoiled plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3744–3748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Separation of ribonuclease H and RNA directed DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase) of murine type-C RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1871–1876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]