Abstract
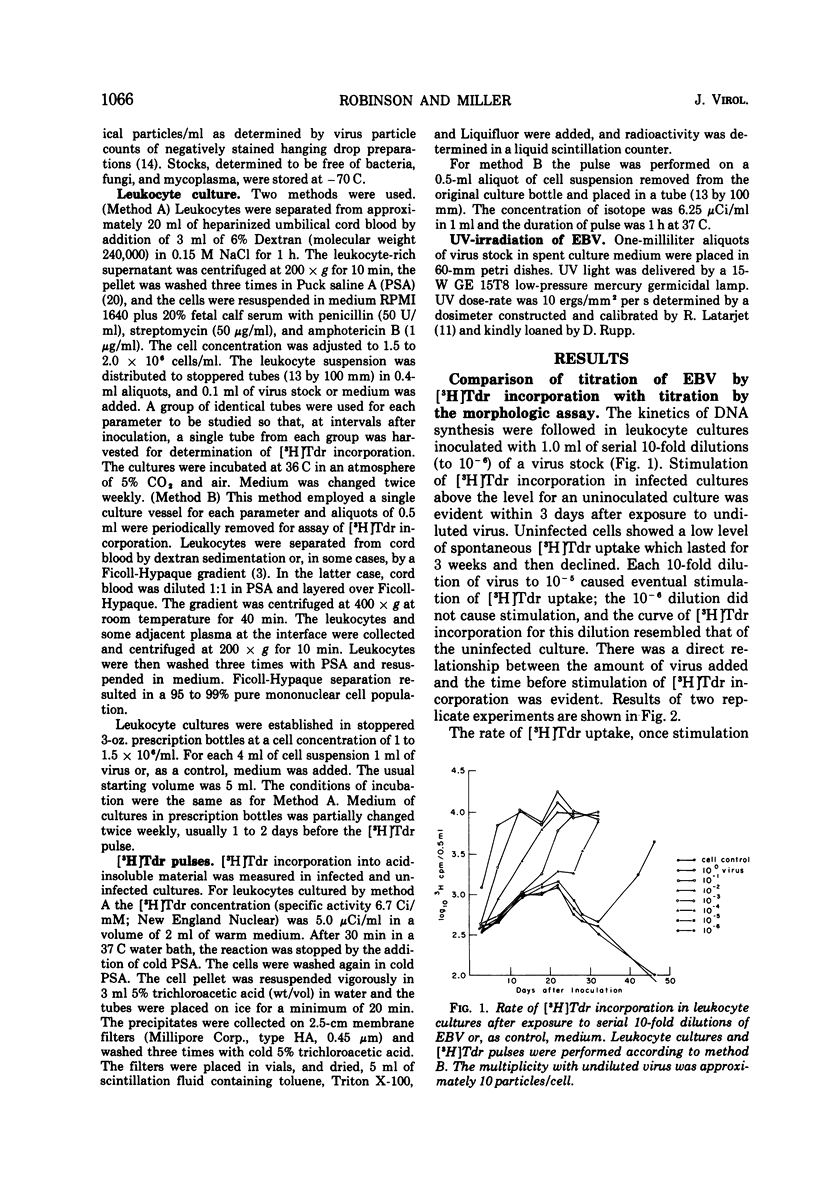
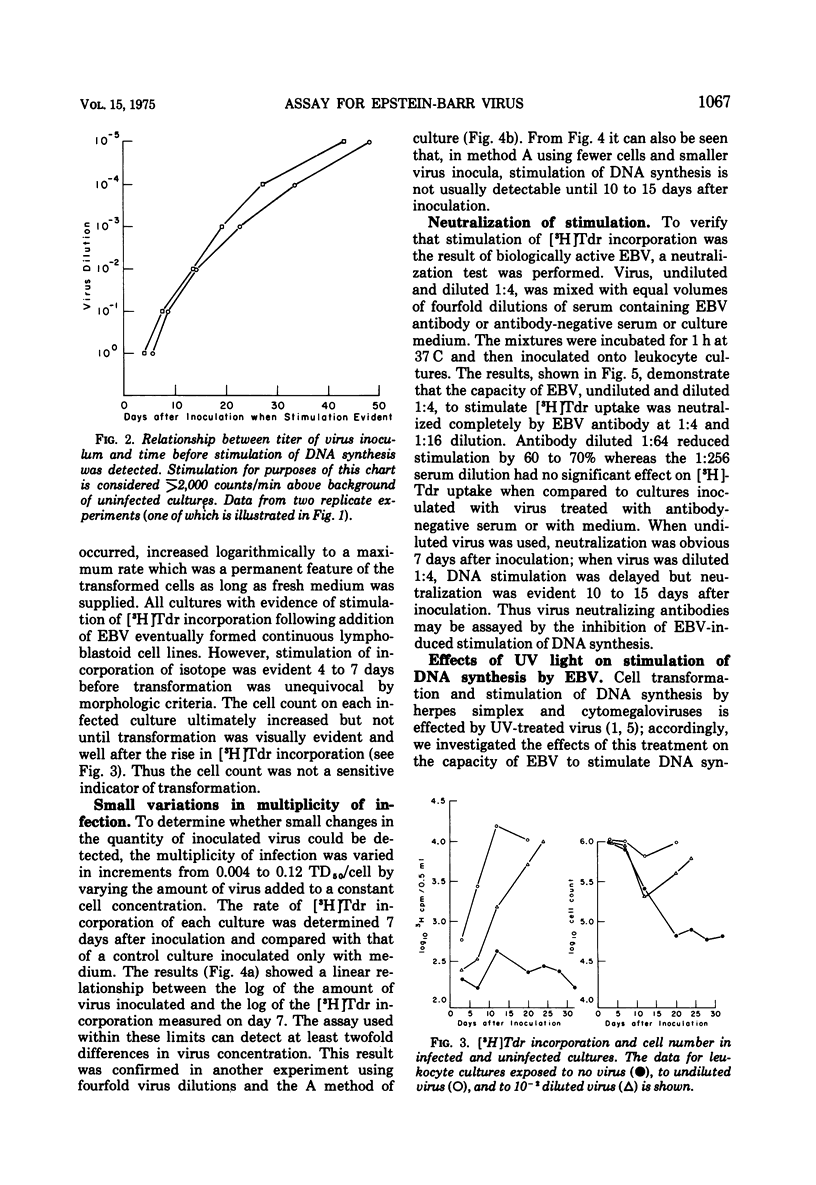
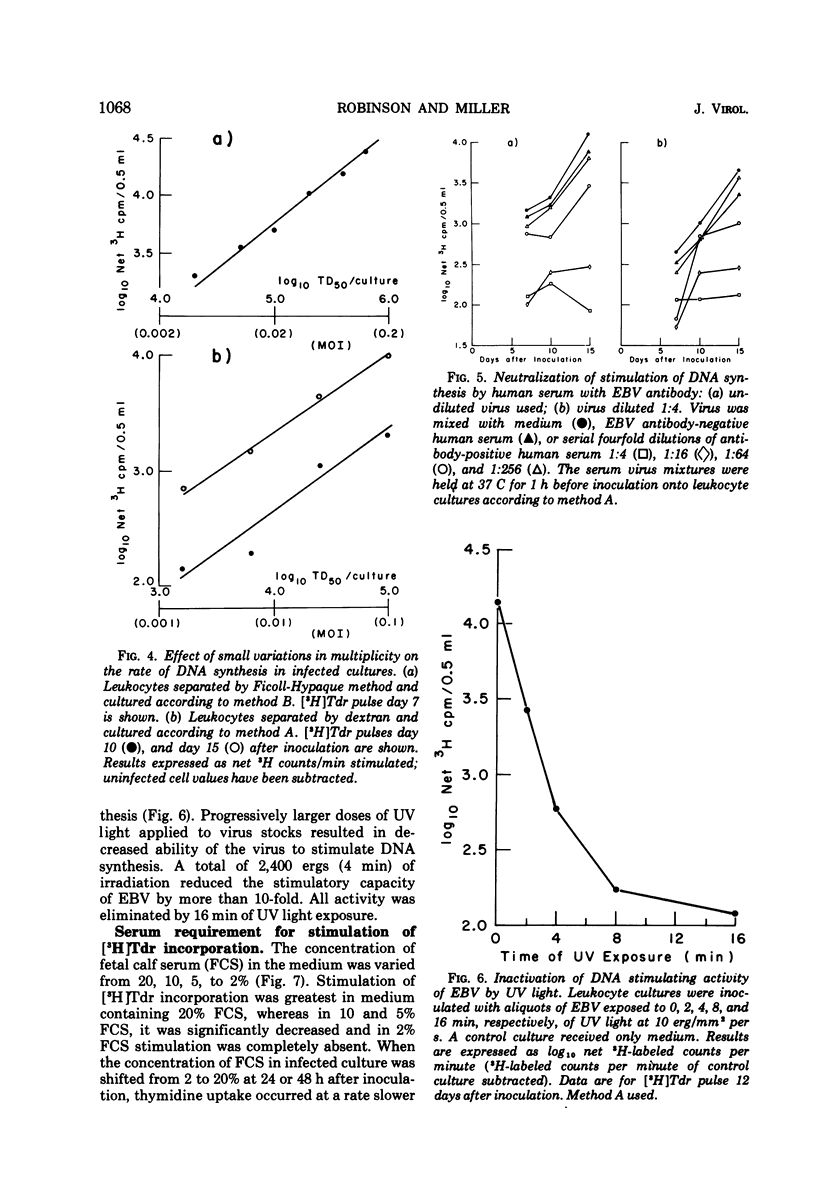
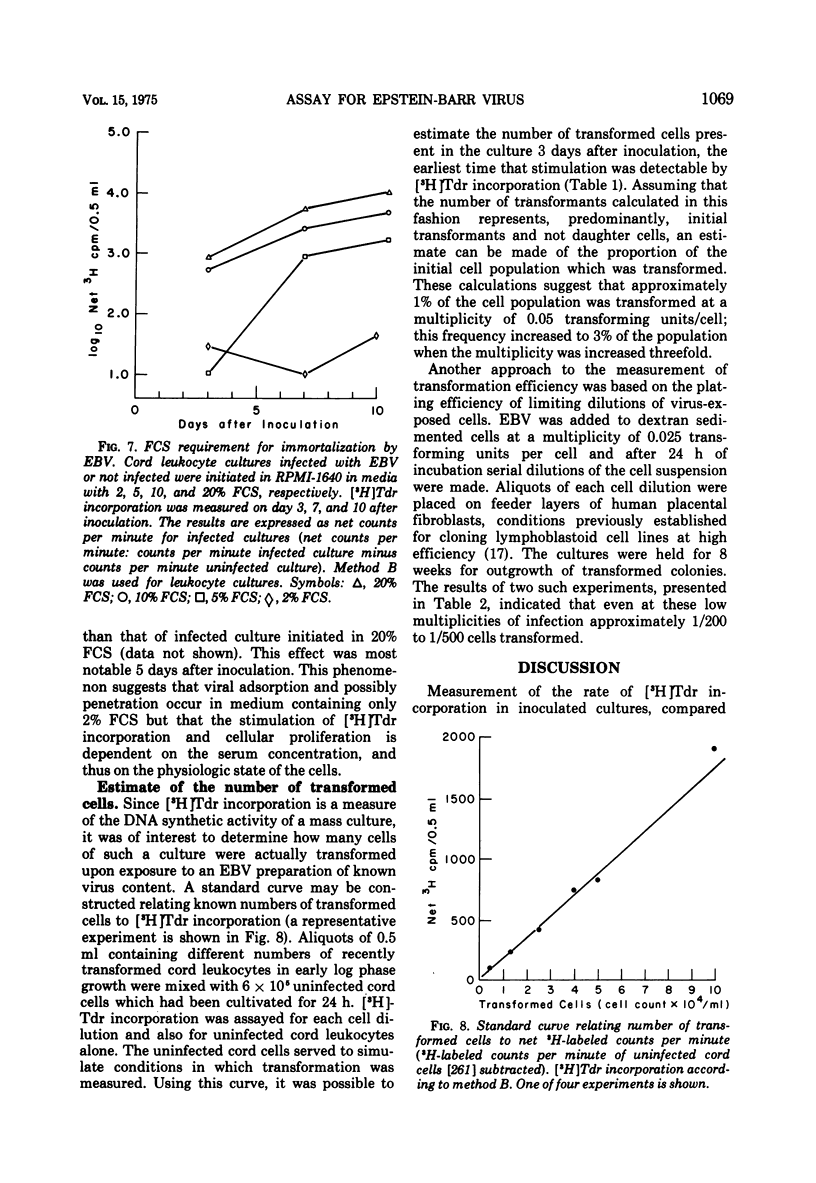
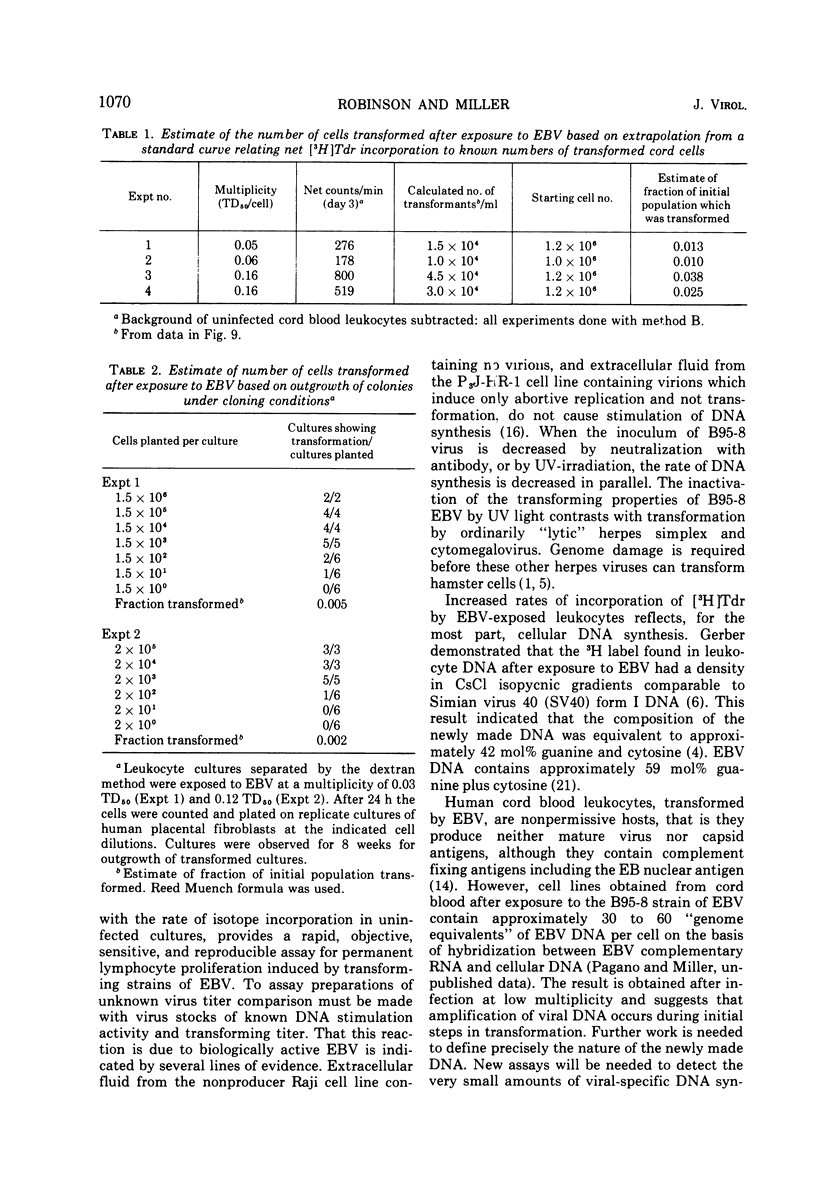
Relationships between the rate of DNA synthesis in cultured human umbilical cord leukocytes and the multiplicity of added Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) were studied. At low multiplicities of approximately 0.1 transforming units/cell (approximately 10 physical particles/cell), inoculated cultures demonstrated increased rates of DNA synthesis, by comparison to uninoculated cultures, 3 days after inoculation. Stimulation of DNA synthesis was evident of progressively longer intervals after inoculations of 10-fold dilutions of virus. The rate of DNA synthesis, determined by short [-3H]thymidine pulses, reflected as small as twofold changes in multiplicity and thus can serve as a quantitative assay for the virus. Changes in the rate of DNA synthesis were evident before increases in cell number or alteration in morphology. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in umbilical cord leukocytes was inhibited by treatment of EBV with antibody and also in graded fashion, by progressive doses of UV irradiation to the virus. Induction of DNA synthesis by EBV was serum dependent. Estimates of the number of cells transformed were obtained by extrapolation from a standard curve relating known numbers of transformed cells to [-3H]thymidine incorporation and also by cloning cells after exposure to virus. At the low multiplicities of infection used in these experiments approximately 0.04 to 0.002 of the total cellular population was transformed. The high efficiency of cell transformation by EBV by comparison to other DNA tumor viruses is emphasized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht T., Rapp F. Malignant transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts following exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basilico C., Marin G., di Mayorca G. Requirement for the integrity of the viral genome for the induction of host DNA synthesis by polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):208–215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V., BLACK P. H. THE NUCLEIC ACID OF SIMIAN VIRUS 40. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:388–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Properties of hamster embryo fibroblasts transformed in vitro after exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):469–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.469-477.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Hoyer B. H. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis in human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1971 May 7;231(5297):46–47. doi: 10.1038/231046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Lucas S. J. In vitro stimulation of human lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Cell Immunol. 1972 Oct;5(2):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerper P., Whang-Peng J., Monroe J. H. Transformation and chromosome changes induced by Epstein-Barr virus in normal human leukocyte cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):740–747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampar B., Derge J. G., Martos L. M., Walker J. L. Persistence of a repressed Epstein-Barr virus genome in Burkitt lymphoma cells made resistant to 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3185–3189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Diehl V., Kohn G., Zur Hausen H., Henle G. Herpes-type virus and chromosome marker in normal leukocytes after growth with irradiated Burkitt cells. Science. 1967 Sep 1;157(3792):1064–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3792.1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATARJET R., MORENNE P., BERGER R. Un appareil simple pour le dosage des rayonnements ultraviolets émis par les lampes germicides. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Aug;85(2):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., MONTAGNIER L. AGAR SUSPENSION CULTURE FOR THE SELECTIVE ASSAY OF CELLS TRANSFORMED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Jun;23:291–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90301-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Comparison of the yield of infectious virus from clones of human and simian lymphoblastoid lines transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1398–1412. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lisco H., Kohn H. I., Stitt D., Enders J. F. Establishment of cell lines from normal adult human blood leukocytes by exposure to Epstein-Barr virus and neutralization by human sera with Epstein-Barr virus antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1459–1465. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Stitt D., Miller G. Epstein-Barr viral antigen in single cell clones of two human leukocytic lines. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):699–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.699-701.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H., Horne M. K., Scott W. Identification of the filtrable leukocyte-transforming factor of QIMR-WIL cells as herpes-like virus. Int J Cancer. 1969 May 15;4(3):255–260. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Holthausen H., zur Hausen H. Partial purification of the Epstein-Barr virus and some properties of its DNA. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):776–779. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Green H. High frequency of SV40 transformation of mouse cell line 3T3. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):756–759. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Green H., Swift M. R. Susceptibility of human diploid fibroblast strains to transformation by SV40 virus. Science. 1966 Sep 9;153(3741):1252–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3741.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



