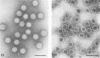
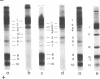
Abstract
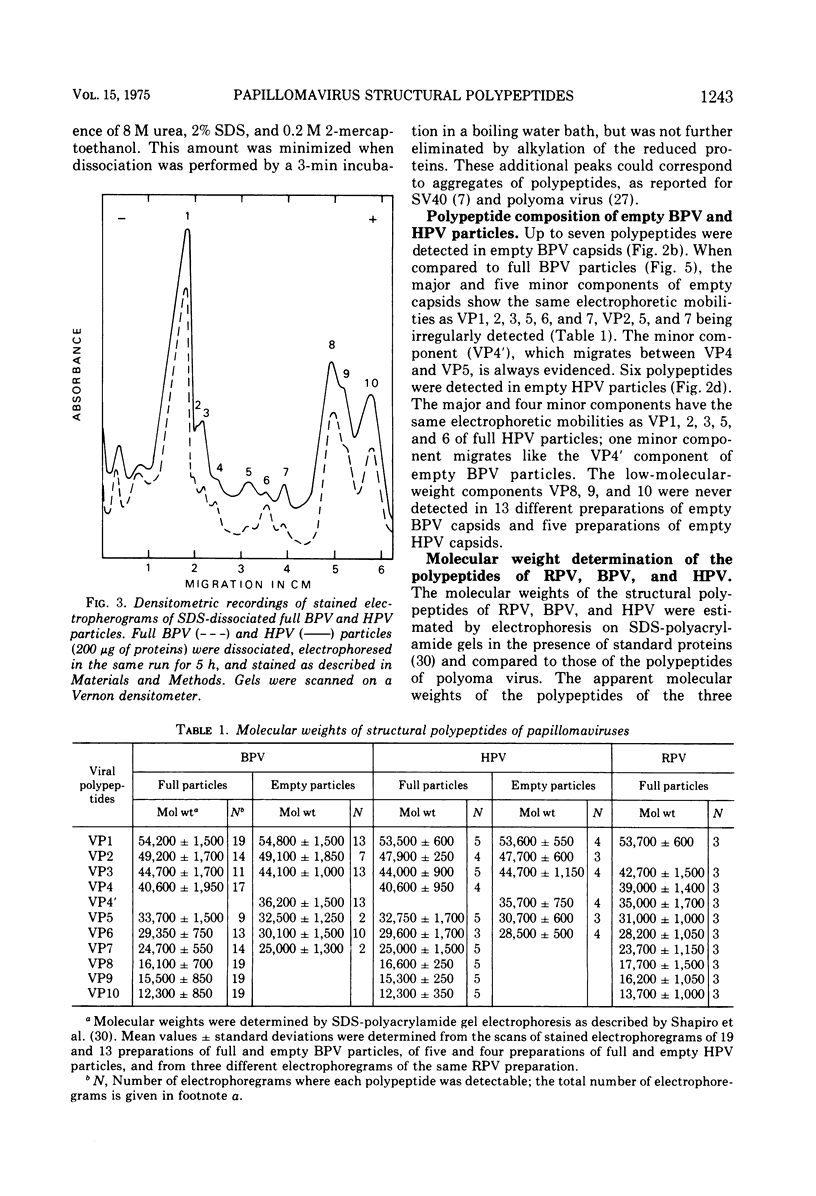
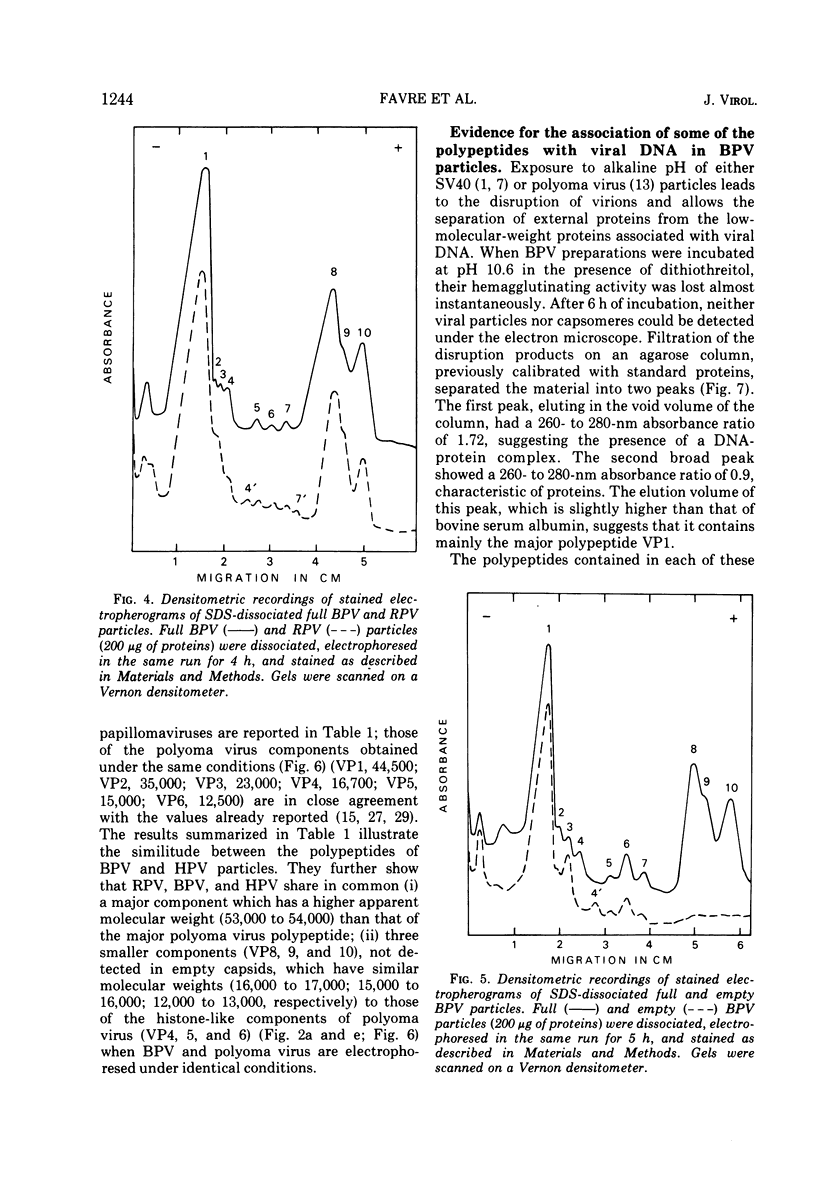
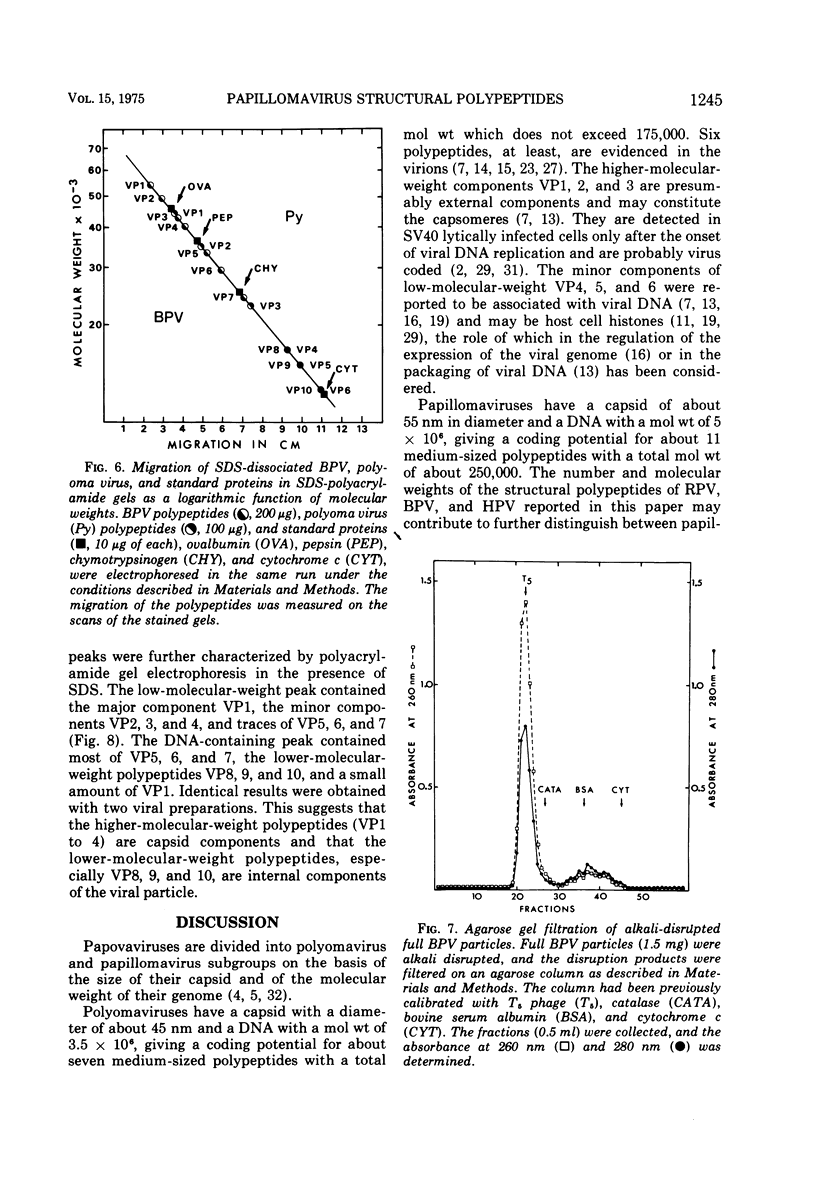
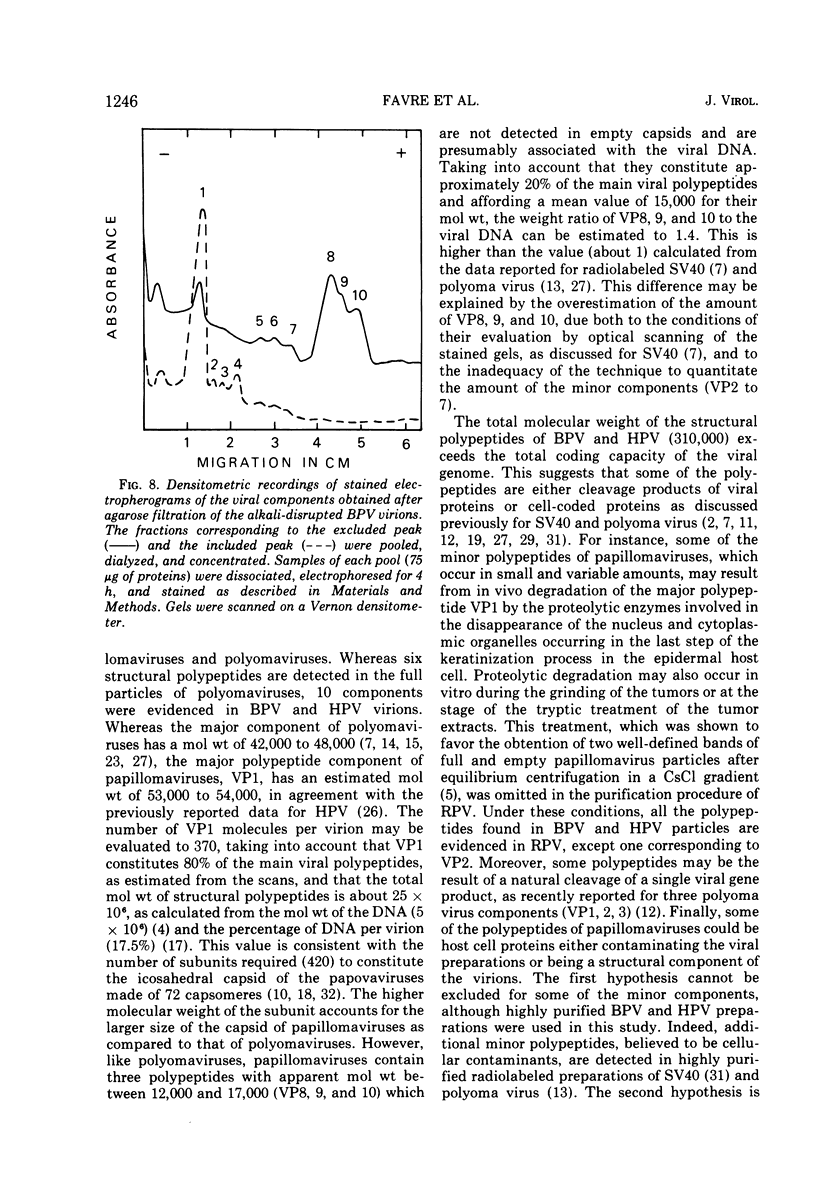
The number and apparent molecular weight of the structural polypeptides of Shope rabbit papilloma virus (RPV), bovine papilloma virus (BPV), and human papilloma virus (HPV) were estimated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Up to 10 polypeptides were detected in highly purified BPV and HPV full particles; a close homology was found between the polypeptide composition of both viruses. Purified RPV virions gave a similar polypeptide pattern. The main components of the three papillomaviruses are the major polypeptide (VP1) with a mol wt of approximately 54,000 and the three smaller polypeptides (VP8, 9, 10) with mol wt of about 16,500, 15,500 and 12,500, respectively. VP8, VP9, and VP10 are never detected in empty capsids. When BPV virions were disrupted with alkaline buffer, the six lower-molecular-weight polypeptides (VP5 to 10) remained associated with viral DNA. This suggests that they are internal components of the virions and that the four higher-molecular-weight polypeptides (VP1 to 4) may represent external components. The polypeptide compositions of BPV and polyoma virus, another papovavirus, have been compared. The number of BPV and polyoma virus components (10 and 6, respectively) and the molecular weight of their major polypeptide (54,000 and 44,500, respectively) are different; however, the three main DNA-associated polypeptides of BPV (VP8, 9, 10) and the three histone-like components of polyoma virus (VP4, 5, 6) were shown to have identical apparent molecular weights. The possibility that some of the minor components of papillomaviruses may be proteolytic degradation products or cell protein contaiminants is discussed.
Full text
PDF

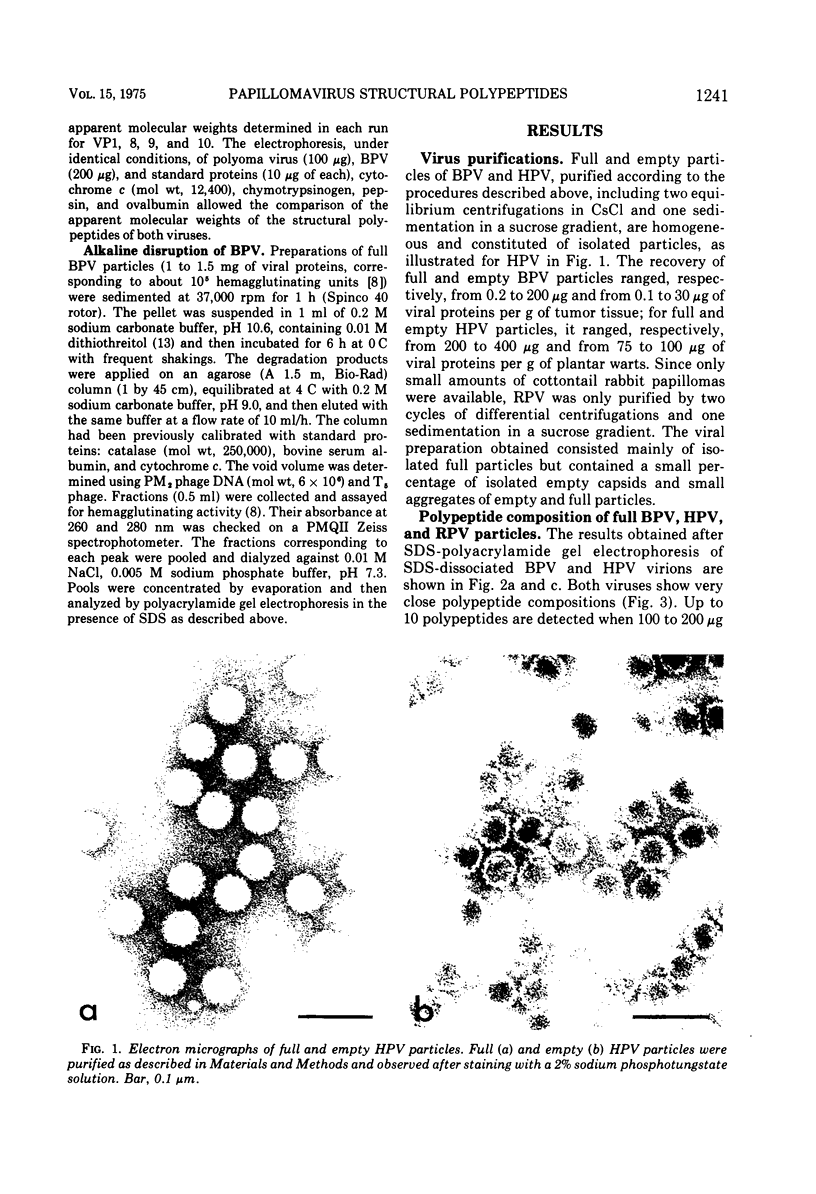
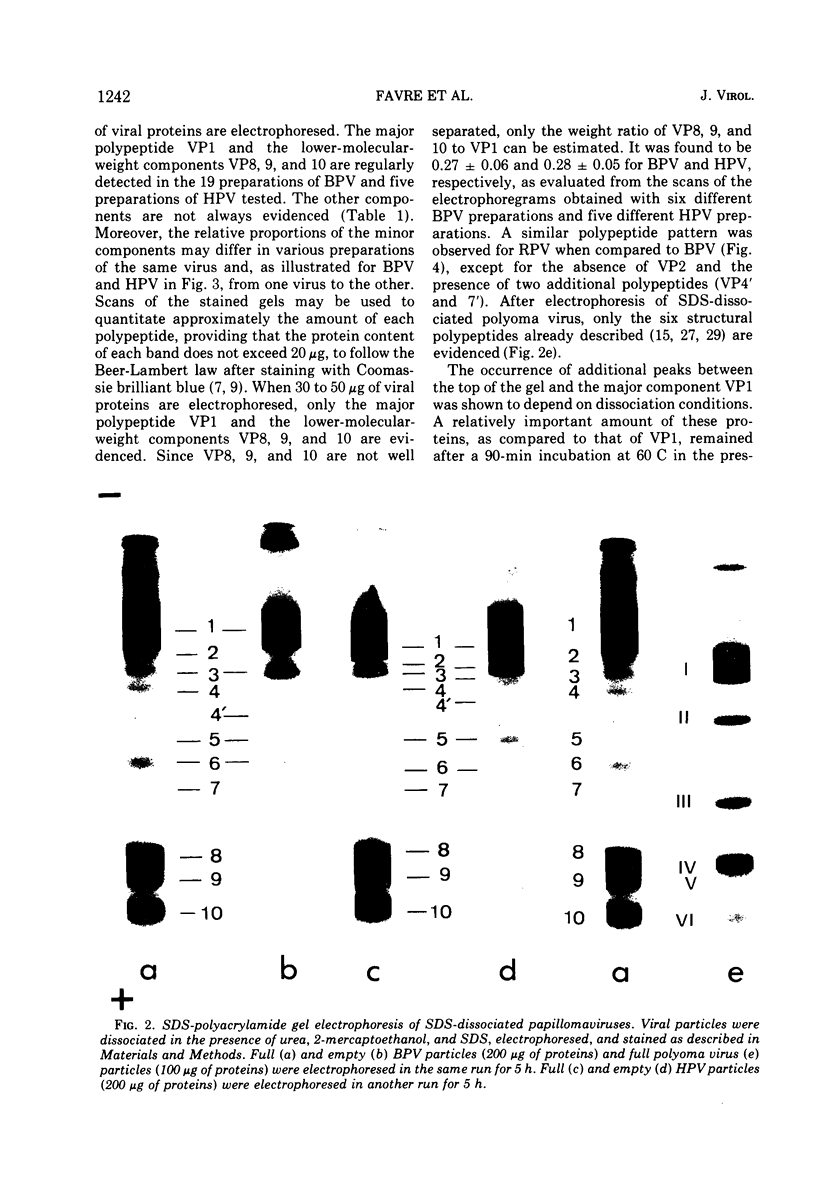

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderer F. A., Koch M. A., Schlumberger H. D. Structure of simian virus 40. 3. Alkaline degradation of the virus particle. Virology. 1968 Mar;34(3):452–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90065-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Gesteland R. F. Pattern of protein synthesis in monkey cells infected by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):758–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.758-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOIRON M., LEVY J. P., THOMAS M., FRIEDMANN J. C., BERNARD J. SOME PROPERTIES OF BOVINE PAPILLOMA VIRUS. Nature. 1964 Jan 25;201:423–424. doi: 10.1038/201423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V., CRAWFORD E. M. A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF POLYOMA AND PAPILLOMA VIRUSES. Virology. 1963 Oct;21:258–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V. Nucleic acids of tumor viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1969;14:89–152. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60558-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Structural polypeptides of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):635–641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.635-641.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favre M., Breitburd F., Croissant O., Orth G. Hemagglutinating activity of bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):572–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90351-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Klug A. The structure of viruses of the papilloma-polyoma type 3. Structure of rabbit papilloma virus, with an appendix on the topography of contrast in negative-staining for electron-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson P. M., Crawford L. V. Polyoma virus basic proteins. J Gen Virol. 1972 Feb;14(2):141–155. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-2-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., David D. Structural roles of polyoma virus proteins. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):776–782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.776-782.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T. Genetic economy of polyoma virus: capsid proteins are cleavage products of same viral gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):257–259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M., Marty L., Suarez F. Capsid proteins of Simian virus 40. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Structure and function of the polypeptides in simian virus 40. II. Transcription of subviral deoxynucleoprotein complexes in vitro. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):930–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.930-937.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLUG A., FINCH J. T. STRUCTURE OF VIRUSES OF THE PAPILLOMA-POLYOMA TYPE. I. HUMAN WART VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:403–423. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass S. J. Chemical studies on polyoma and Shope papilloma viruses. J Virol. 1970 Mar;5(3):381–387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.3.381-387.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. S., Barban S., Salzman N. P. Resolutions and identification of the core deoxynucleoproteins of the simian virus 40. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):640–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullarkey M. F., Hruska J. F., Takemoto K. K. Comparison of two human papovaviruses with simian virus 40 by structural protein and antigenic analysis. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1014–1019. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1014-1019.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOYES W. F. STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN WART VIRUS. Virology. 1964 May;23:65–72. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(64)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON C. CUTANEOUS PAPILLOMATOSIS IN CATTLE AND OTHER ANIMALS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Nov 4;108:1042–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roblin R., Härle E., Dulbecco R. Polyoma virus proteins. 1. Multiple virion components. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowson K. E., Mahy B. W. Human papova (wart) virus. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):110–131. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.110-131.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seehafer J. G., Weil R. Synthesis of polyoma virus structural polypeptides in mouse kidney cells. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Roblin R., Dulbecco R. Protein synthesis in Simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):921–924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]