Abstract
Because of the lack of sensitivity to small changes in distance by available FRET pairs (a constraint imposed by the dimensions of the enzyme), a DHFR containing two pyrene moieties was prepared to enable the observation of excimer formation. Pyren-1-ylalanine was introduced into DHFR positions 16 and 49 using an in vitro expression system in the presence of pyren-1-ylalanyl-tRNACUA. Excimer formation (λex 342 nm; λem 481 nm) was observed in the modified DHFR, which retained its catalytic competence and was studied under multiple and single turnover conditions. The excimer appeared to follow a protein conformational change after the H transfer involving the relative position and orientation of the pyrene moieties and is likely associated with product dissociation.
Numerous studies have employed proteins containing unnatural amino acids for the study of protein function and structure.1 Of special interest are proteins having reporter groups, particularly fluorescent groups, which can enable the monitoring of properties such as protein dynamics and interactions with other molecules. The site-specific introduction of fluorophores into proteins has been accomplished by derivatization of intrinsically reactive amino acids such as cysteine,2 and also by the suppression of a nonsense codon engineered within the translated region of an mRNA by a misacylated suppressor tRNA. The latter strategy has been used both for the direct introduction of fluorescent amino acid analogues,3 and for the placement of functional groups having unique reactivity, enabling subsequent post-translational modification by chemical means.4 Proteins so modified have, e.g., been employed for Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) experiments to monitor changes in protein conformation5 and connectivity.6
Another application of fluorescent reporter groups in proteins might involve excimer formation, which has been demonstrated between two pyrene moieties introduced into positions 416 and 537 of Dictyostelium discoideum myosin via derivatization of cysteine moieties.2b This phenomenon operates optimally over shorter distances than FRET, providing a potentially important complementary technique for studying protein structure and dynamics. Presently, we describe the synthesis of (S)-pyren-1-ylalanine, its attachment to the 3’-terminus of a suppressor tRNA transcript, and its direct introduction into positions 16 and 49 of dihydrofolate reductase by suppression of UAG codons, affording a catalytically competent DHFR which exhibited excimer formation (Scheme 1). The excimer has been used to monitor the conformational change likely associated with product release from DHFR.
Scheme 1.
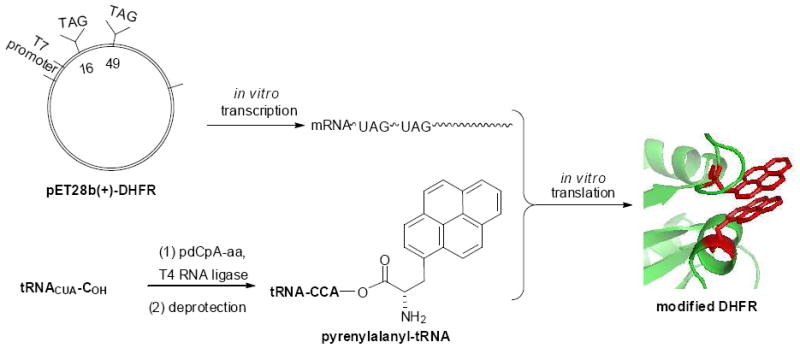
Strategy employed for the incorporation of pyren-1-ylalanine into DHFR at positions 16 and 49.
The preparation of a bis-pyren-1-yl-DHFR began with the alteration of an expression plasmid for DHFR.7 Site-directed mutagenesis employing mutagenic primers8 permitted TAG sequences to be inserted at positions corresponding to 16 and 49 of the expressed DHFR. Coupled in vitro transcription and translation9 in the presence of (S)-pyren-1-ylalanyl-tRNACUA10 then afforded bis-pyrenyl-DHFR containing pyrenylalanine moieties at positions 16 and 49 of the protein. Also prepared from suitably modified expression plasmids were DHFRs containing a pyrene moiety only at position 16, or only at position 49. The DHFRs containing a single pyrene at position 16 or 49 were obtained in suppression yields of 22 and 39%, respectively, while the bis-pyrenyl-DHFR (the formation of which involved the suppression of two UAG codons) was formed in 12% yield relative to unmodified DHFR (Figure 1).16 The crude modified proteins (Figure S1) were purified by successive chromatographies on Ni-NTA and DEAE-Sepharose CL-6B columns, as illustrated for bis-pyrenyl-DHFR in Figure S2.
Figure 1.
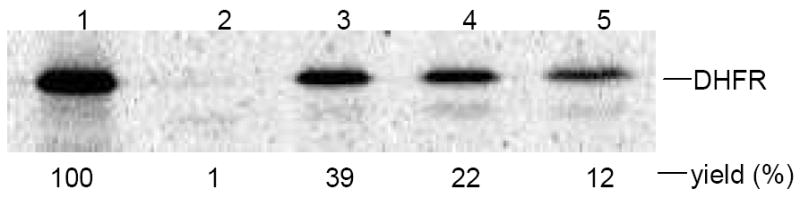
In vitro incorporation of pyren-1-ylalanine into DHFR at positions 16 and 49. The protein synthesis reaction was analyzed by 15% SDS-PAGE at 100 V for 2 h. Phosphorimager analysis was performed using an Amersham Biosciences Storm 820 equipped with ImageQuant version 5.2 software from Molecular Dynamics. Lane 1, wild-type DHFR; lane 2, suppression of an mRNA UAG codon at DHFR position 49 with unacylated tRNACUA-COH; lane 3, suppression of a mRNA UAG codon at DHFR position 49 with pyren-1-ylalanyl-tRNACUA; lane 4, suppression of a mRNA UAG codon at DHFR position 16 with pyren-1-ylalanyl-tRNACUA; lane 5, suppression of mRNA UAG codons at DHFR positions 16 and 49 with pyren-1-ylalanyl-tRNACUA.
The fluorescence emission spectra of the three modified DHFRs were measured, following irradiation at 310 nm. As shown in Figure 2, the modified DHFRs containing a single pyrene moiety, either at position 16 or 49, gave emission spectra having a single maximum at 389 nm. In comparison, bis-pyrenyl-DHFR also had a second, stronger emission with a maximum at 481 nm corresponding to excimer formation. The concentration dependence of the emission spectra for the bis-pyrenyl-DHFR was determined at 10 different concentrations from 0.1 – 1.0 μM (Figure S3).
Figure 2.
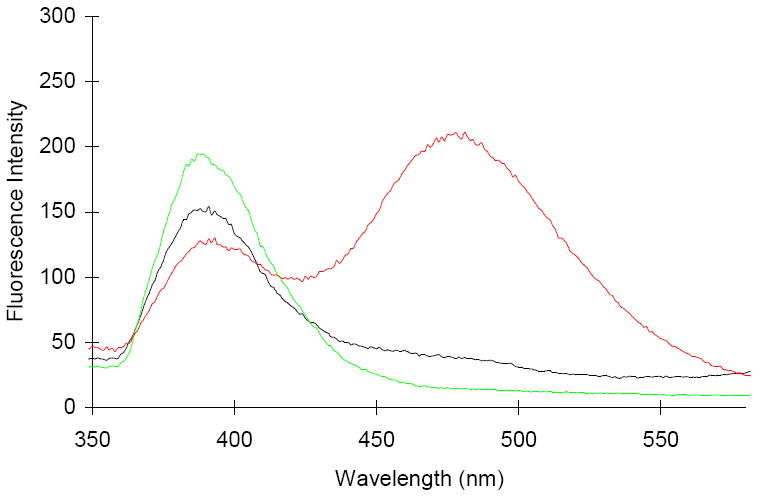
Fluorescence emission spectra of modifed DHFRs containing pyren-1-ylalanine at position 16 (black curve), position 49 (green curve) or positions 16 and 49 (red curve). The fluorescence emission was monitored from 350–580 nm following irradiation at 310 nm.
Initially, bis-(pyren-1-yl)-DHFR was used to measure the steady-state turnover number by monitoring the conversion of NADPH to NADP+; kcat was found to be 3.1±0.4/s, which is approximately four-fold lower than wild-type DHFR (12±2/s), typical of modified DHFRs bearing amino acid substitutions around these two positions.17a Further kinetic experiments were performed under both multiple and single turnover conditions by using a stop flow instrument.
By following the loss of NADPH absorbance at 340 nm, the H transfer rate (kH) in the single turnover experiment was found to be 57±8/s, i.e. approximately one-fourth the rate of the wild-type enzyme.17,18 Repeating the same experiment by exciting the excimer complex at 360 nm, and monitoring emission through a 450 nm filter, the fluorescence traces collected were fitted to a single-exponential equation. The fitted rate was 63±5/s (Figure 3). However, as observed in Figure S4, because of the overlap between the stronger fluorescence decay of NADPH versus that of the excimer, the fluorescence signal follows predominantly the disappearance of the NADPH signal. Consequently, the measured rate of 63±5/s agreed with the rate of hydride transfer measured above.
Figure 3.
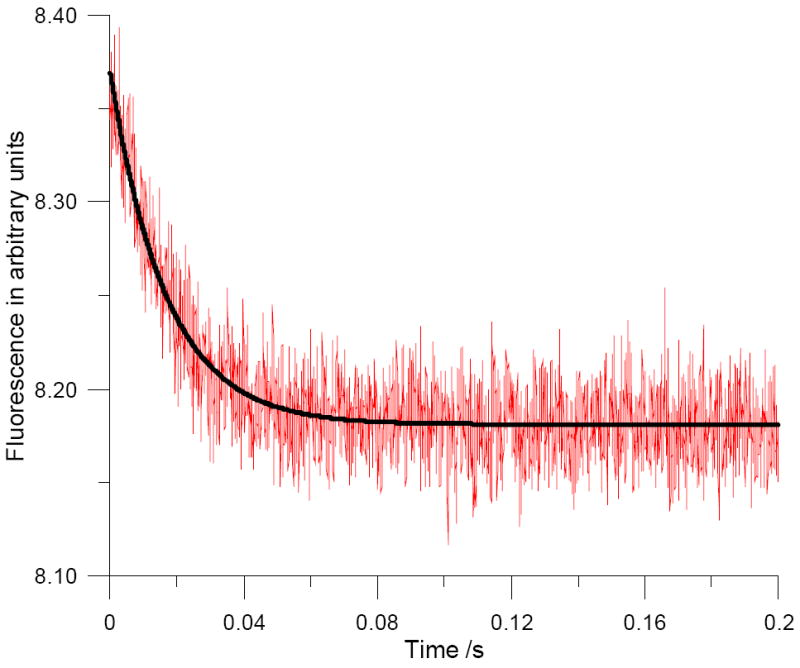
Stopped-flow time course for the reaction of (~8 μM) bis-(pyren-1-yl)-DHFR with 1.25 μM NADPH and 100 μM dihydrofolate at pH 7.0. The reaction was initiated by rapid mixing with 0.2 mM dihydrofolate. Excitation was at 360 nm with a 450 nm cutoff filter for emission. The data (red trace) were fitted to a single-exponential curve (black curve).
In multiple turnover experiments, where we anticipated accumulation of the DHFR•NADP+•H4F complex, ~2 μM bis-(pyren-1-yl)-DHFR was preincubated with 100 μM NADPH in MTEN buffer, pH 7.0, and the reaction was initiated by rapid mixing with 200 μM dihydrofolate. The excimer complex was excited at 370 nm and monitored through a 450 nm cutoff filter. Noting the remarkable disparity in time scales in Figure 4 versus Figure 3, the rapid phase in the latter was not defined. However, the exponential decay of fluorescence due to the NADPH oxidation subsided so that the fluorescence change from the excimer was observed. The fluorescence traces collected were fitted to the equation shown in Figure 4, where kf represents the conformational change for the conversion of EP* to EP** (see Scheme S2 in the Supporting Information). EP* and EP** designate different conformations of the above complex; the fitted rate was 2.6±0.5/s (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
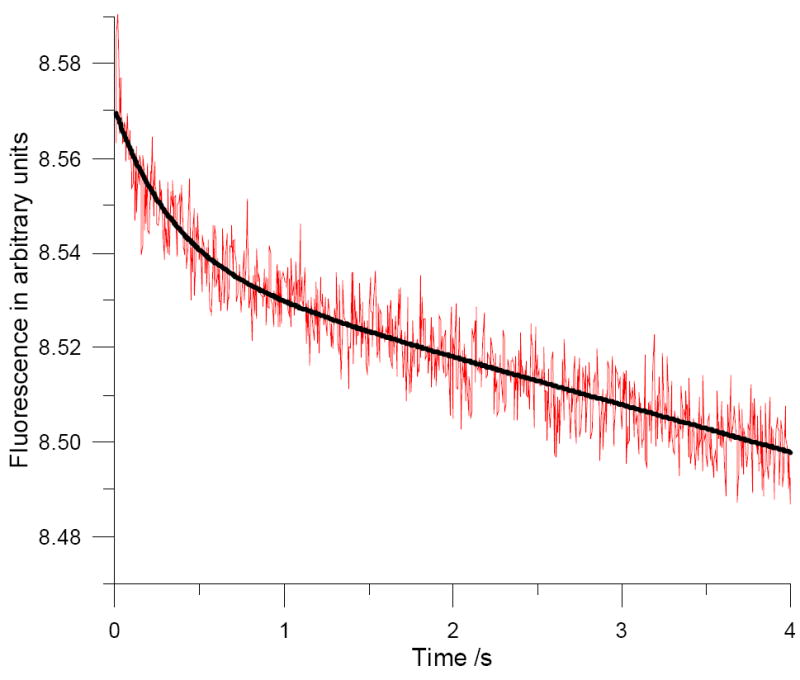
Stopped-flow time course for the reaction of (~2 μM) bis-(pyren-1-yl)-DHFR with 100 μM NADPH and 100 μM dihydrofolate at pH 7.0. Excitation was at 370 nm with a 450 nm cutoff filter for emission. As the rapid phase in Figure 3 was not defined, the data (red trace) were fitted to the function f(t) = a · e−kf·t + b · t + c, where a, b, c, kf are constants (black curve).
Based on the foregoing data, we suggest that the attenuation of the excimer signal may be associated with a change in the positions of the pyrene moieties accompanying a change in the conformation of the product–enzyme complex. Distance changes sensed by changes in excimer intensity are subject not only to the separation of the two pyrene moieties but also their relative orientations. The loss of excimer absorbance revealed an increased separation of the two moieties consistent with an opening of an active site pocket sensed by residues at positions 16 and 49. Shown in Figure S5 is a superposition of the backbone structures of the E:NADPH:ddTHF (5,10-dideazatetrahydrofolate; PDB 1rx6, green) and E:NADPH:methotrexate (PDB1rx3, blue) complexes of E. coli DHFR that represent the product and cofactor ternary compexes and illustrate how the distance between the two residues might change.
In summary, we have introduced two pyrene moieties into two positions in DHFR known on the basis of X-ray crystallographic studies to be separated by a distance that would be predicted2b to enable the observation of excimer formation. Excimer formation actually was observed; loss of the signal was found to be associated with the conformation of the enzyme–product complex, permitting the measurement of distances involved in a conformational change. This is the first example of the use of an excimer for that purpose. Further, unlike FRET pairs,19 excimers report on interactions between probes in a protein that are nearly contiguous, thus providing a sensitive tool for measuring small distance changes. Successful conformational analyses of polypeptides containing pyrene moieties within structured domains makes it clear that the conformations and dynamics of such probes contained within proteins should be amenable to analysis.20
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Research Grant GM 092946 from the National Institutes of Health.
Footnotes
Supporting Information
Methods employed for the synthesis of pyren-1-ylalanine and its attachment to tRNACUA, for the preparation and purification of DHFR containing this amino acid, and for biochemical and biophysical assessment of the modified DHFR. This information is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.(a) Noren CJ, Anthony-Cahill SJ, Griffith MC, Schultz PG. Science. 1989;244:182. doi: 10.1126/science.2649980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Hecht SM. Acc Chem Res. 1992;25:545. [Google Scholar]; (c) England PM. Biochemistry. 2004;43:11623. doi: 10.1021/bi048862q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Hendrickson TL, de Crécy-Lagard V, Schimmel P. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.012803.092429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.(a) Rajagopalan PTR, Zhang Z, McCourt L, Dwyer M, Benkovic SJ, Hammes GG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:13481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172501499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Conibear PB, Bagshaw CR, Fajer PG, Kovács M, Málnási-Csizmadia A. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10:831. doi: 10.1038/nsb986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hohsaka T, Kajihara D, Ashizuka Y, Murakami H, Sisido M. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:34. [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) Cornish VW, Hahn KM, Schultz PG. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:8150. [Google Scholar]; (b) Datta D, Wang P, Carrico IS, Mayo SL, Tirrell DA. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:5652. doi: 10.1021/ja0177096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Ryu Y, Schultz PG. Nat Methods. 2006;3:263. doi: 10.1038/nmeth864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Chen S, Fahmi NE, Nangreave RC, Mehellou Y, Hecht SM. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012;20:2679. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.02.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kajihara D, Abe R, Iijima I, Komiyama C, Sisido M, Hohsaka T. Nat Methods. 2006;3:923. doi: 10.1038/nmeth945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anderson RD, Zhou J, Hecht SM. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:9674. doi: 10.1021/ja0205939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Karginov VA, Mamaev SV, An H, Van Cleve MD, Hecht SM, Komatsoulis GA, Abelson JN. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:8166. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sawano A, Miyawaki A. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000;28:E78. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.16.e78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gao R, Zhang Y, Choudhury AK, Dedkova LM, Hecht SM. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:3321. doi: 10.1021/ja044182z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Preparation of the misacylated suppressor tRNA was carried out as described in Schemes 1 and S1. The key transformation involved the alkylation of a chiral Ni(II)-glycine complex with 1-chloromethylpyrene, using a published method for the stereoselective formation of the desired alkylated product.11 Following treatment of the isolated complex with methanolic HCl, the derived pyren-1-ylalanine was protected as the corresponding N-pentenoyl derivative,12 and then activated as the cyanomethyl ester.13 Condensation with pdCpA14 then afforded N-pentenoylpyren-1-ylalanine pdCpA ester, the latter of which was attached covalently to an abbreviated suppressor tRNA transcript (tRNA-COH) via the agency of T4 RNA ligase, as described previously.15
- 11.(a) Belokon’ YN, Bakhmutov VI, Chernoglazova NI, Kochetkov KA, Vitt SV, Garbalinskaya NS, Belikov VM. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans I. 1988:305. [Google Scholar]; (b) Collet S, Bauchar P, Danion-Bougot R, Danion D. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 1998;9:2121. [Google Scholar]; (c) Belokon’ YN, Tararov VI, Maleev VI, Savel’eva TF, Ryzhov MG. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 1998;9:4249. [Google Scholar]; (d) Ueki H, Ellis TK, Martin CH, Boettiger TU, Bolene SB, Soloshonok VA. J Org Chem. 2003;68:7104. doi: 10.1021/jo0301494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.(a) Lodder M, Golovine S, Hecht SM. J Org Chem. 1997;62:778. doi: 10.1021/jo971692l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Lodder M, Golovine S, Laikhter AL, Karginov VA, Hecht SM. J Org Chem. 1998;63:794. doi: 10.1021/jo971692l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Robertson SA, Ellman JA, Schultz PG. J Am Chem Soc. 1991;113:2722. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Robertson SA, Noren CJ, Anthony-Cahill SJ, Griffith MC, Schultz PG. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17:9649. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.(a) Heckler TG, Zama Y, Naka T, Hecht SM. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:4492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Heckler TG, Chang LH, Zama Y, Naka T, Hecht SM. Tetrahedron. 1984;40:87. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pyren-1-ylalanine has been incorporated into streptavidin previously, albeit in low reported yield. Hohsaka T, Kajihara D, Ashizuka Y, Nurakami H, Sisido M. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:34.Doi Y, Ohtsuki T, Shimizu Y, Ueda T, Sisido M. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:14458. doi: 10.1021/ja075557u.
- 17.(a) Rajagopalan PTR, Lutz S, Benkovic SJ. Biochemistry. 2002;41:12618. doi: 10.1021/bi026369d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Antikainen NM, Smiley RD, Benkovic SJ, Hammes GG. Biochemistry. 2005;44:16835. doi: 10.1021/bi051378i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fierke CA, Johnson KA, Benkovic SJ. Biochemistry. 1987;26:4085. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Most distance measurements by FRET range from 41-73Å (although if dye-quencher pairs are used, the measured distance can be ~23Å). http://search.barnesandnoble.com/Principles-of-Fluorescence-Spectroscopy-Joseph-R-Lakowicz/e/9780387312781?r=1&cm_mmc=GooglePLA-_Textbook-_-Q000000633-_-9780387312781&cm_mmca2=pla
- 20.Inai Y, Sisido M, Imanishi Y. J Phys Chem. 1990;94:8365. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


