Abstract
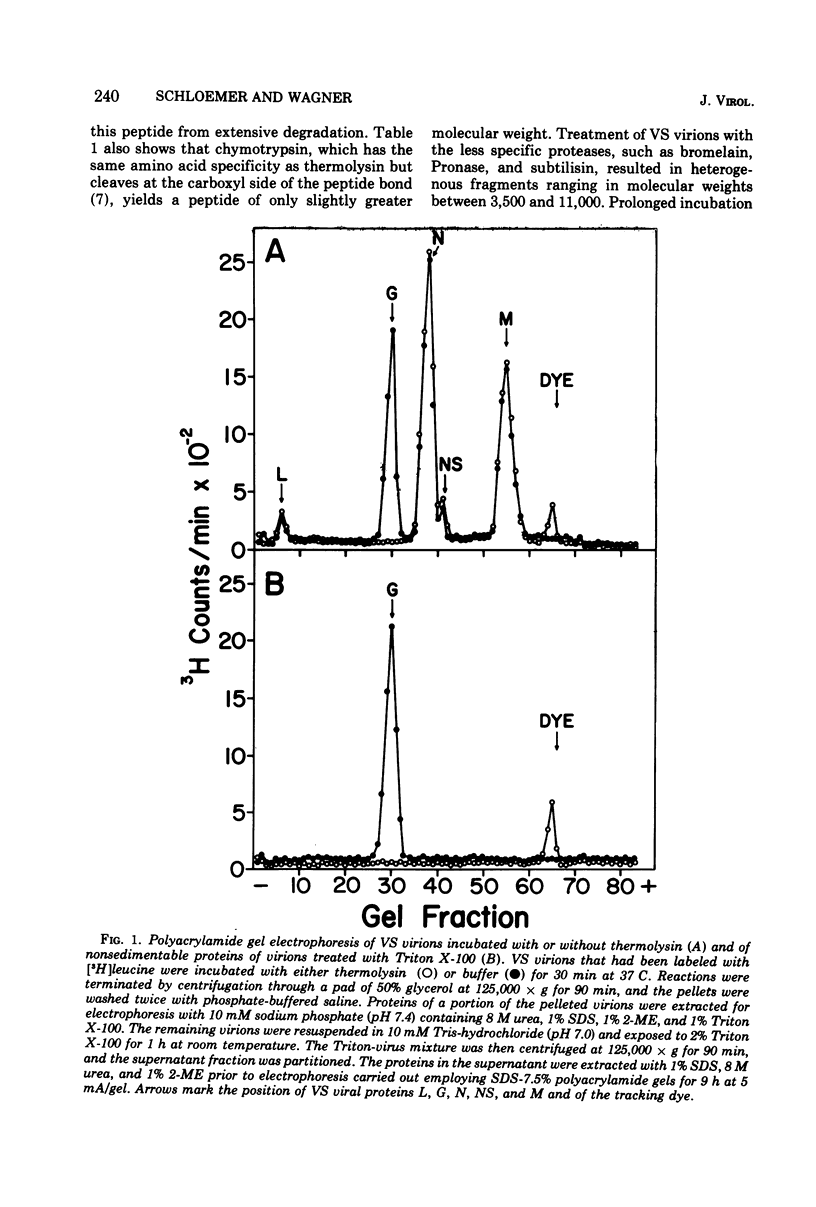
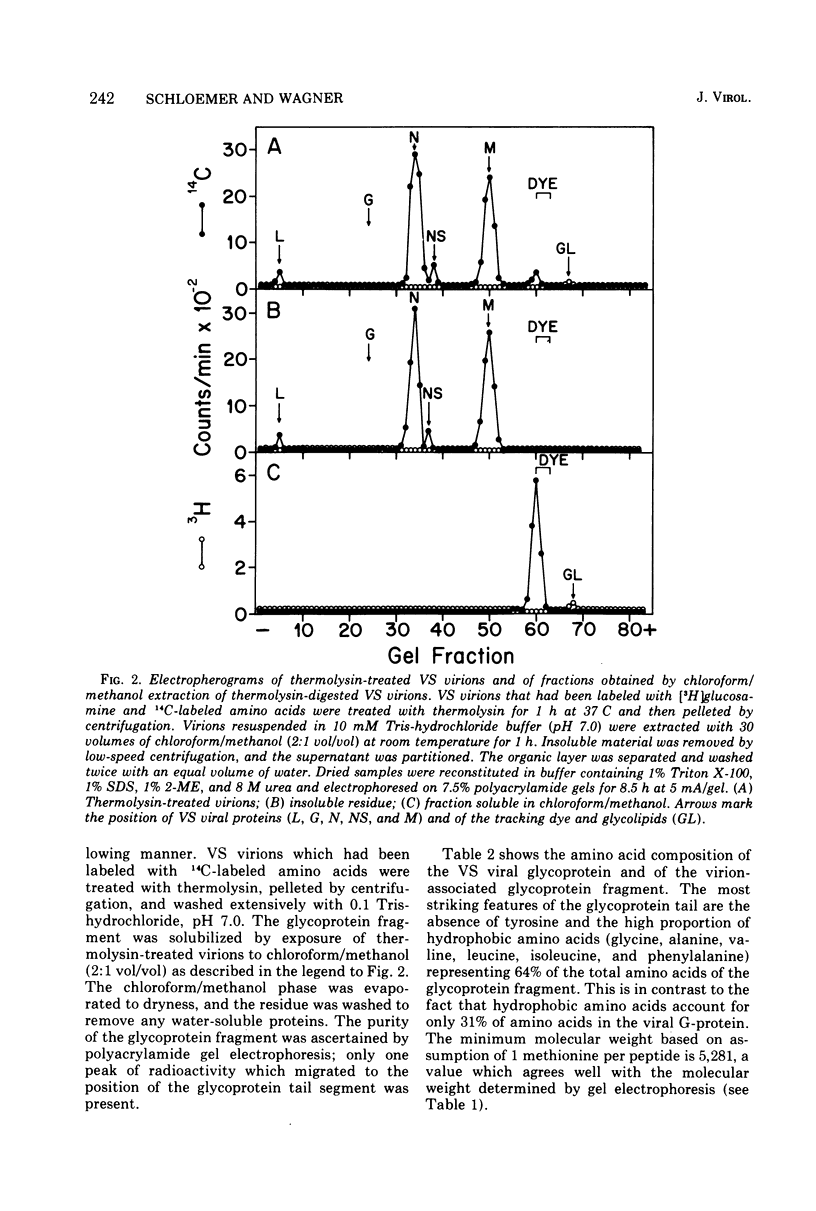
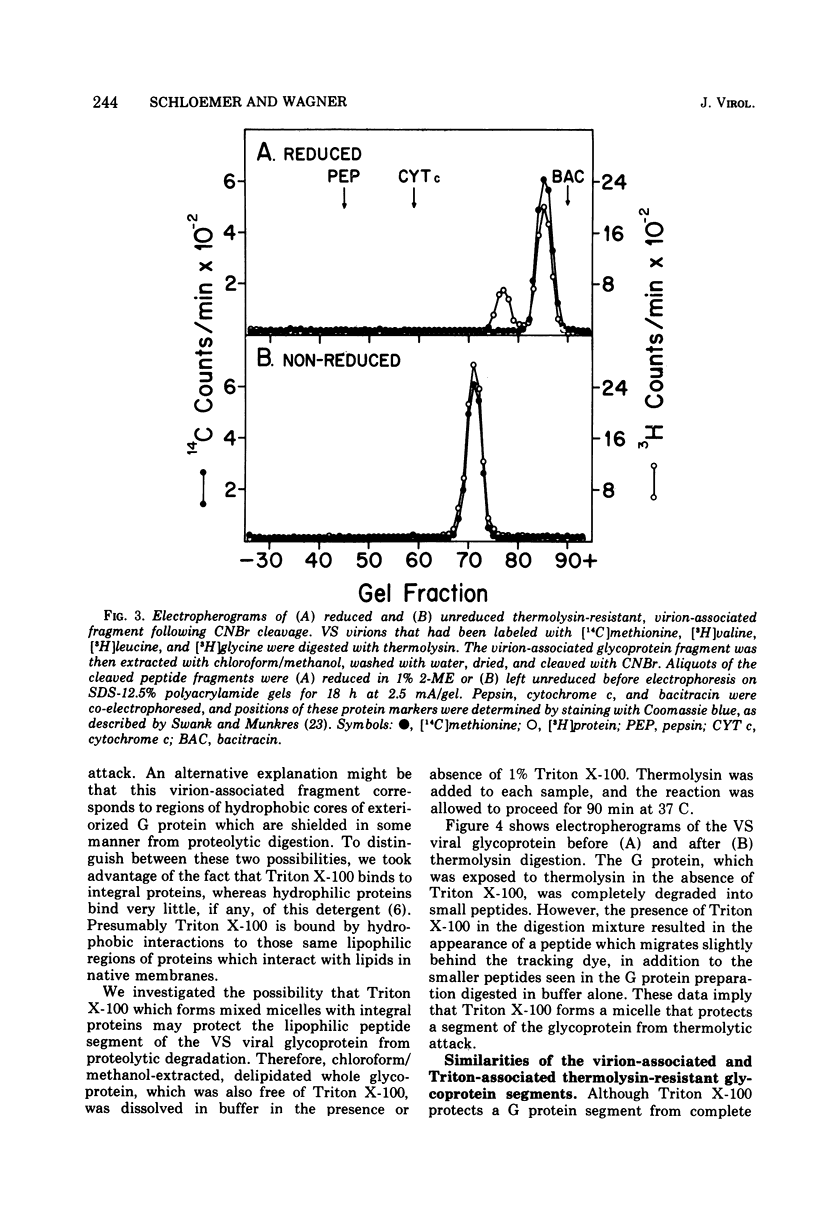
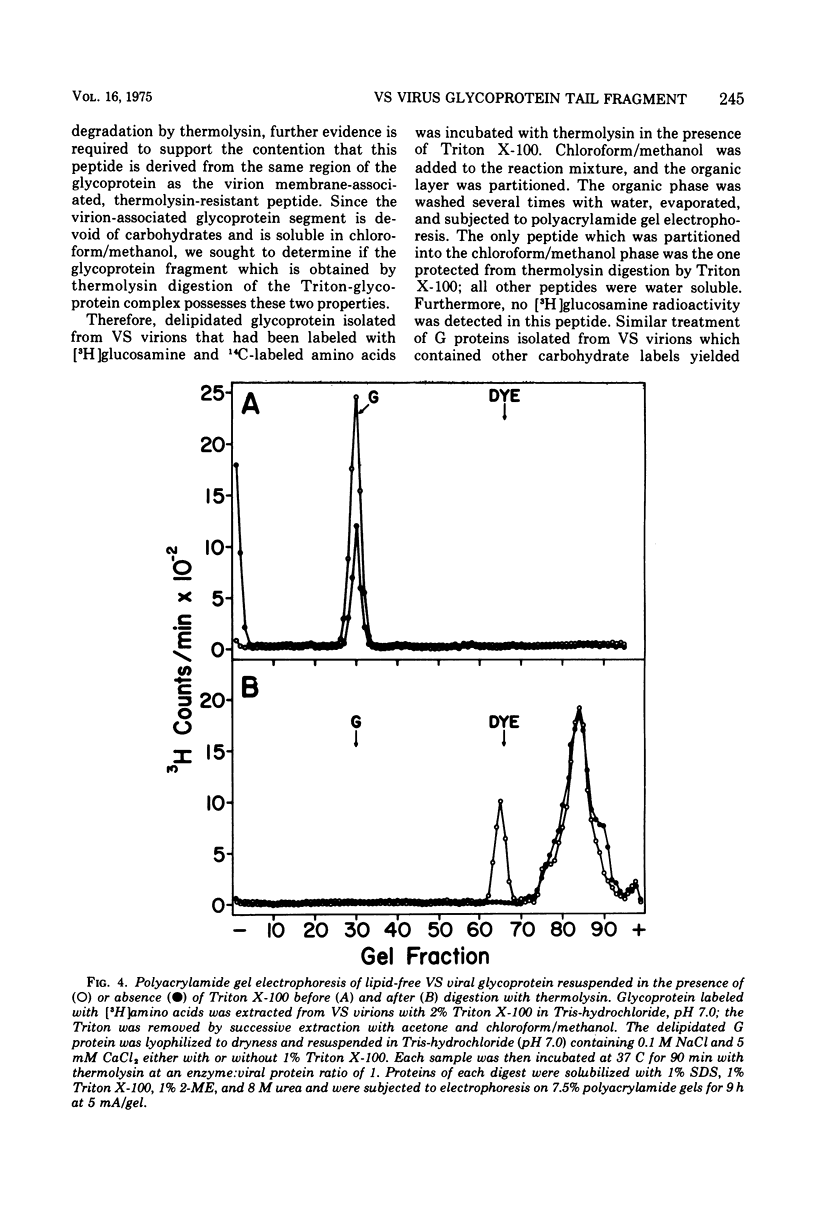
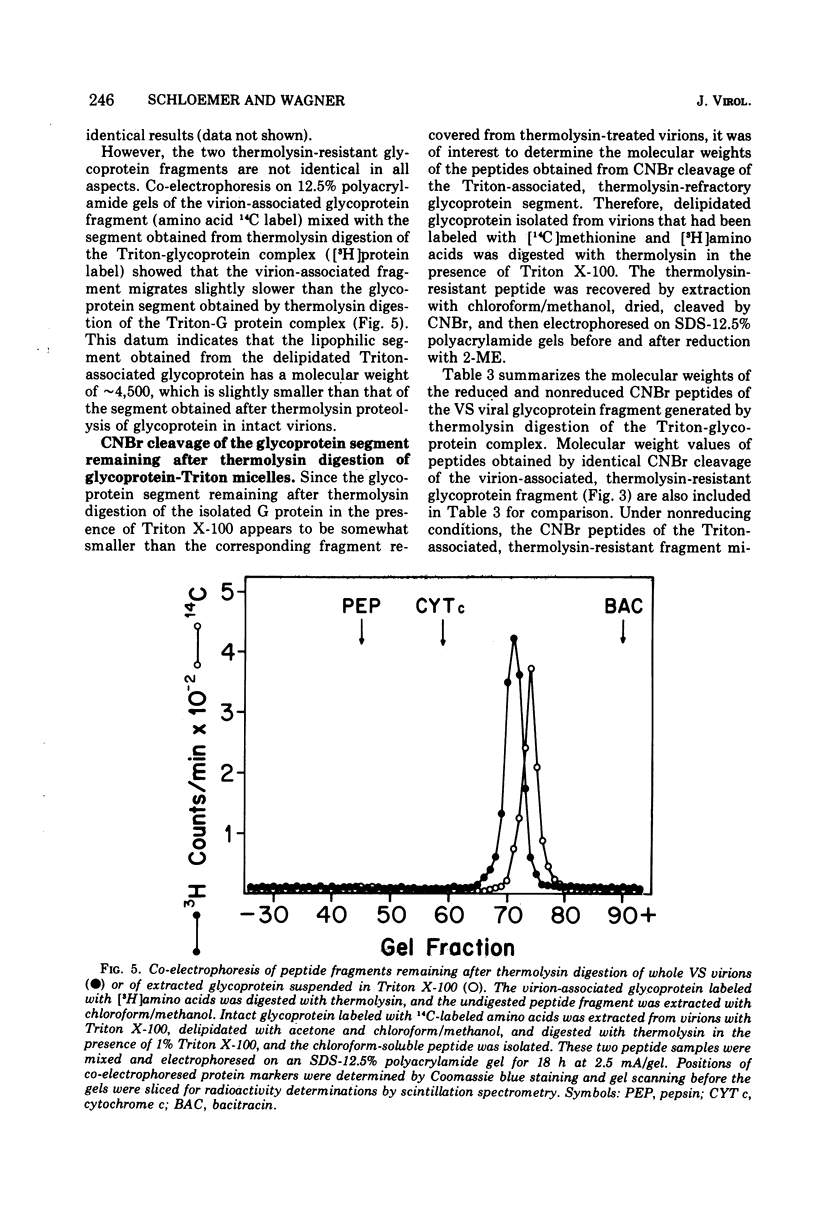
The proteolytic enzyme, thermolysin, degraded the external segment of the membrane glycoprotein of intact vesicular stomatitis (VS) virions but left behind a small nonglycosylated fragment, presumably embedded in the virion membrane. Other proteases generated membrane-associated glycoprotein fragments differing somewhat in molecular weight. The thermolysin-resistant, virion-associated fragment, which can be selectively solubilized by either Triton X-100 or chloroform/methanol, has a molecular weight of 5,200. Amino acid analysis of the glycoprotein fragment reveals a preponderance of hydrophobic amino acids (64% of the residues); the amino-terminal amino acid is alanine as determined by dansylation. Cyanogen bromide digestion of the tail fragment generated two peptides, confirming the presence of one methionine residue per thermolysin-resistant glycoprotein fragment. The secondary structure of this glycoprotein tail peptide is maintained by at least one disulfide bridge. Thermolysin treatment is isolated VS viral glycoprotein in the presence of Triton X-100 also generated a hydrophobic peptide fragment which is very similar to the virion-associated glycoprotein fragment. The amino acid terminus of intact glycoprotein was also found to be alanine as was its dansylated Triton-micellar fragment that resisted thermolytic degradation; this finding suggests that the amino-terminal end of the VS viral glycoprotein is embedded in the virion membrane. These results suggest that the VS viral glycoprotein is an amphipathic molecule, the hydrophilic portion of which contains all the carbohydrate and a lipophilic tail segment which forms lipid or detergent micelles, thus rendering it resistant to proteolysis.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown F., Smale C. J., Horzinek N. C. Lipid and protein organization in vesicular stomatitis and Sindbis viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Mar;22(3):455–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Smale C. J., Brown F. Dissection of vesicular stomatitis virus into the infective ribonucleoprotein and immunizing components. J Gen Virol. 1970 Apr;7(1):19–32. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-7-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Smale C. J., Brown F. Surface structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. Dissociation and reconstitution of the transcriptase and template activities of vesicular stomatitis B and T virions. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):297–309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.297-309.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. The binding of detergents to lipophilic and hydrophilic proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3656–3661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaid J. I., Winzler R. J. Association of glycoproteins with the membranes. I. Isolation and molecular weight of the monomeric unit of the major glycoprotein from human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3635–3638. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaid J. I., Winzler R. J. Association of glycoproteins with the membranes. II. Isolation and partial characterization of "lipophilic fragment" from human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3639–3642. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. M., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. The glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is the antigen that gives rise to and reacts with neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1231-1235.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Glycolipid content of vesicular stomatitis virus grown in baby hamster kidney cells. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):416–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.416-417.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and of phenotypically mixed vesicular stomatitis virus-simian virus 5 virions. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.722-729.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Wagner R. R. Lipid composition of purified vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):59–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.59-70.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A. Glycoprotein fragment associated with vesicular stomatitis virus after proteolytic digestion. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):573–577. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Howatson A. F. The fine structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):268–281. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Pearlman-Kothencz M. Synthesis and assembly of bacterial membrane components. A lipopolysaccharide-phospholipid-protein complex excreted by living bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):477–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEERS E., Jr, CRAVEN G. R., ANFINSEN C. B., BETHUNE J. L. EVIDENCE FOR NONIDENTICAL CHAINS IN THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2478–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloemer R. H., Wagner R. R. Cellular adsorption function of the sialoglycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus and its neuraminic acid. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):882–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.882-893.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloemer R. H., Wagner R. R. Sialoglycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus: role of the neuraminic acid in infection. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):270–281. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.270-281.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz L., Strittmatter P. A form of cytochrome b5 that contains an additional hydrophobic sequence of 40 amino acid residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1042–1046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Simons K. Studies on the amphipathic nature of the membrane proteins in Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):569–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVEY A. H., SNYDER R. M., RATCLIFF G. A., Jr, HYATT D. F. BIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF TWO PLAQUE VARIANTS OF VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS (INDIANA SEROTYPE). J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:112–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Prevec L., Brown F., Summers D. F., Sokol F., MacLeod R. Classification of rhabdovirus proteins: a proposal. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1228–1230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1228-1230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. C., Snyder R. M., Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the structural components of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):611–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.611-618.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Snyder R. M., Yamazaki S. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: kinetics and cellular sites of synthesis. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):548–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.548-558.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



