Abstract
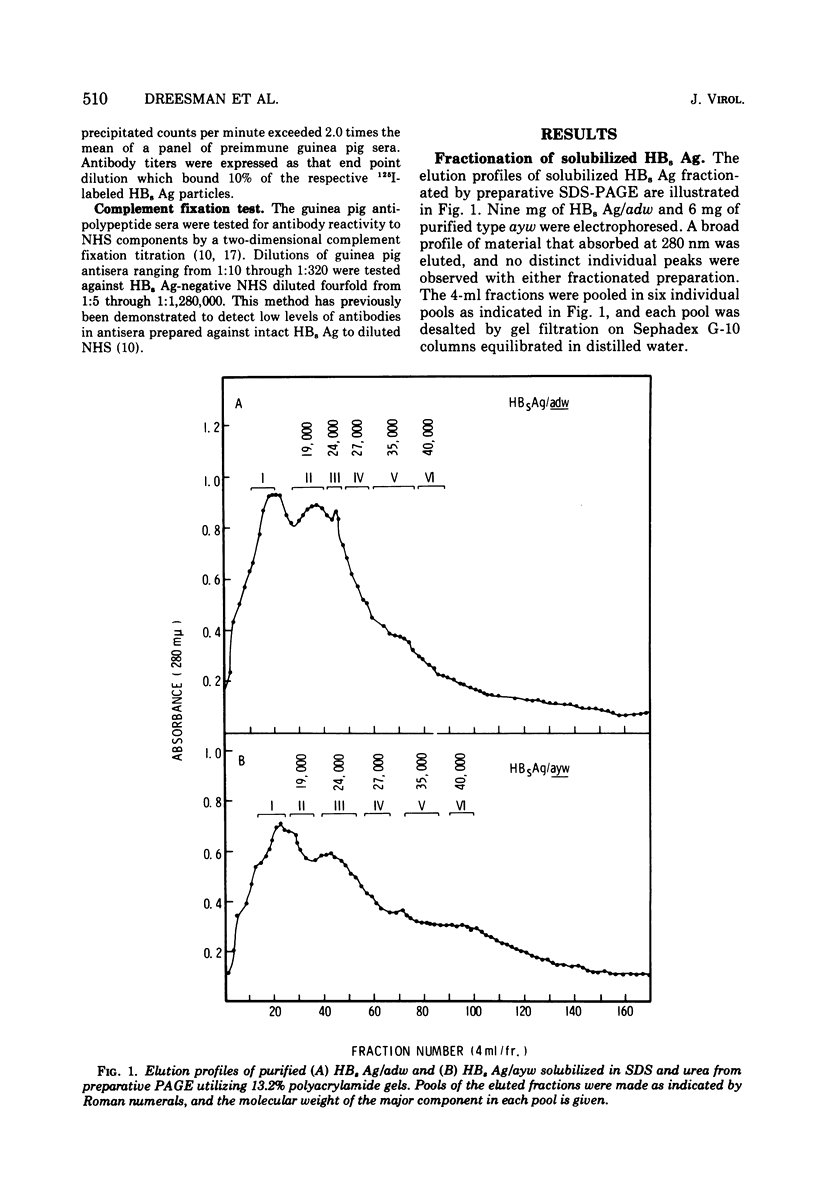
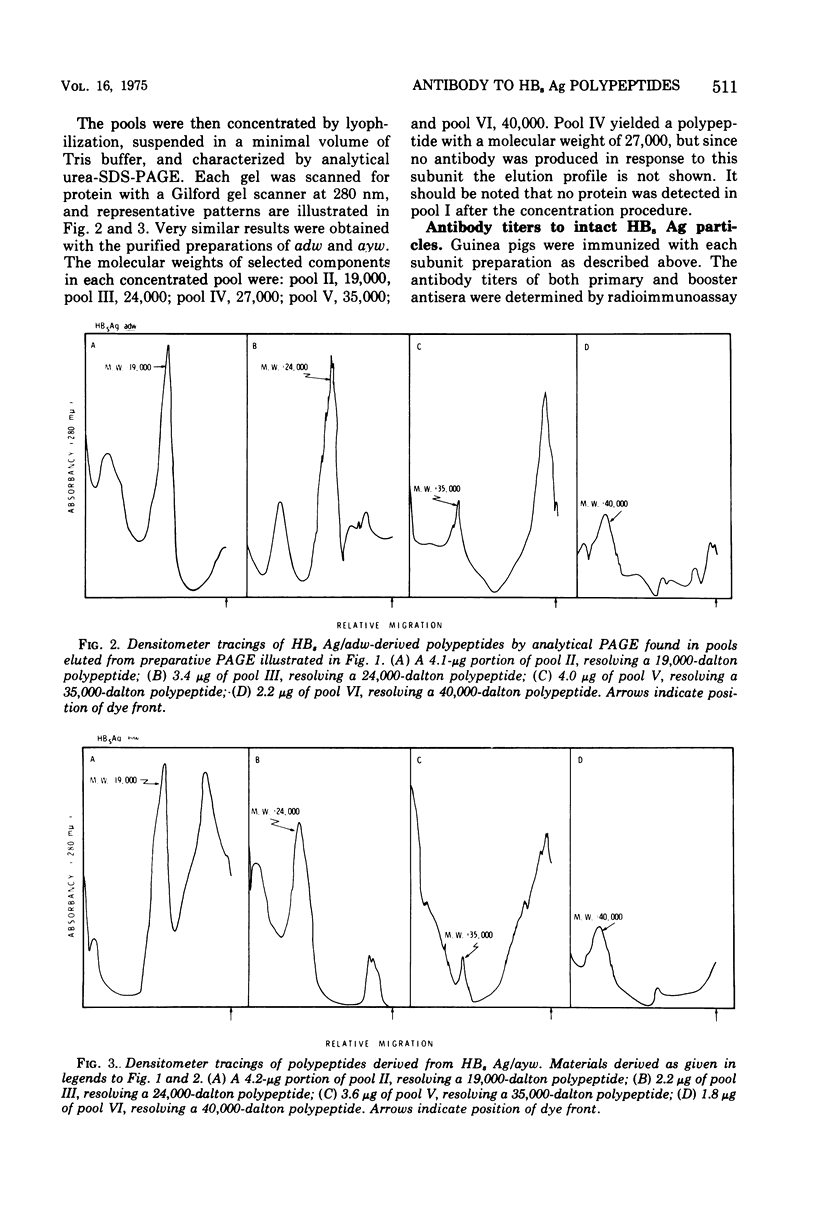
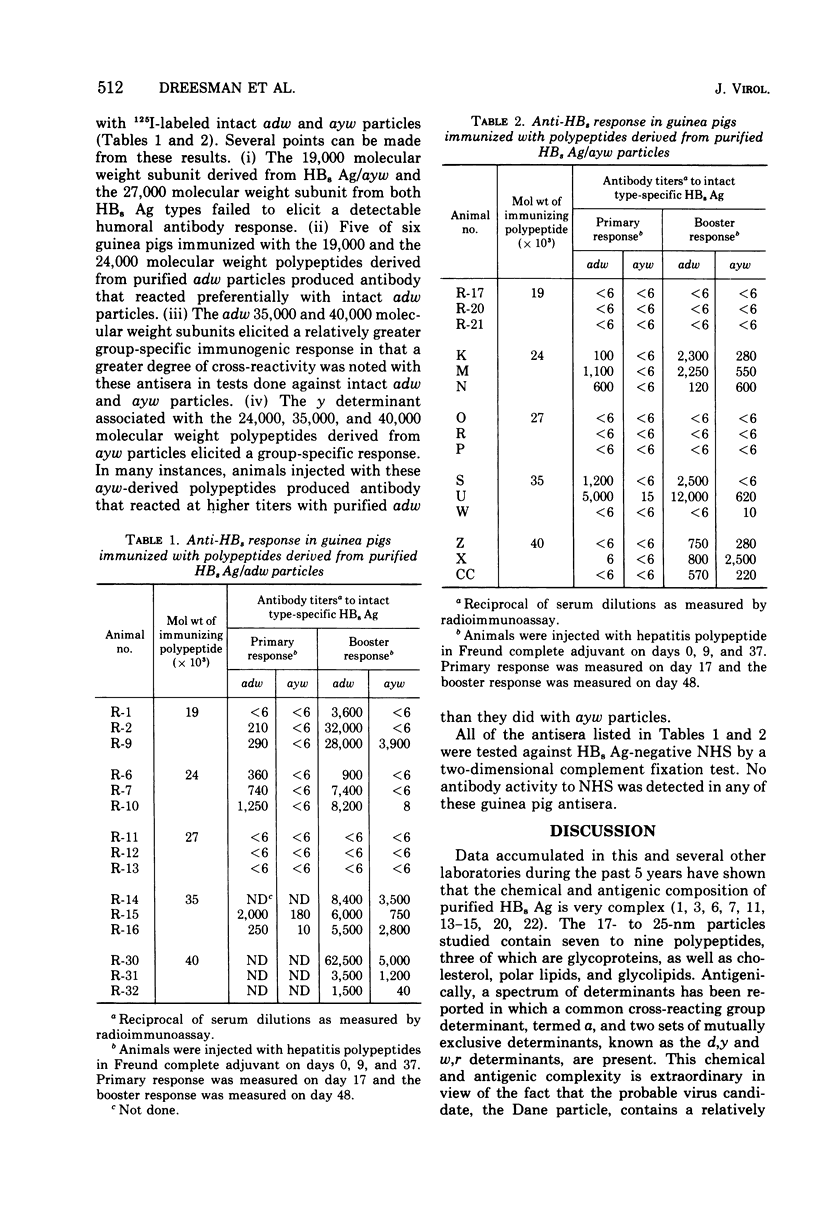
Purified preparations of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) were solubilized with sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea under reducing conditions and subsequently fractionated by preparative sodium dodecyl sulfate-urea polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Pools of the individual fractions eluted from the preparative PAGE were concentrated and purified further by analytical PAGE. Five purified polypeptides were isolated from HBsAg, types adw and ayw, with molecular weights of 19,000, 24,000, 27,000, 35,000, and 40,000. Each preparations was emulsified in Freund complete adjuvant and injected into guinea pigs. Antibody to each HBsAg type was measured by radioimmunoassay. The 19,000 molecular weight polypeptide derived from ayw particles and the 27,000 molecular weight subunit obtained from both types failed to elicit an antibody response. The other three polypeptides derived from the ayw particles elicited group-specific antibody responses. Similar group-specific reactivities were observed in the testing of anti-adw 35,000 and anti-adw 40,000 molecular weight polypeptide sera. However, guinea pigs immunized with the 19,000 and the 24,000 molecular weight polypeptides of the adw type produced antibody that reacted preferentially with adw particles. This indicates that either these subunits carry predominately d determinants or that, because of the low levels of material used for inoculation, no immune response or an undetectable one was elicited to the a or w components.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Rubenstein D., Stott E. J. New antigen-antibody system in Australia-antigen-positive hepatitis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 4;2(7736):1225–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90543-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. Immune complexes in hepatitis. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):983–986. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90540-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S., Werner B. Particles associated with Australia antigen in the sera of patients with leukaemia, Down's Syndrome and hepatitis. Nature. 1968 Jun 15;218(5146):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/2181057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell C. J., Proudfoot E., Keen G. A., Marmion B. P. Carbohydrates in hepatitis B antigen. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 27;243(130):260–262. doi: 10.1038/newbio243260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chairez R., Hollinger F. B., Brunschwig J. P., Dreesman G. R. Comparative biophysical studies of hepatitis B antigen, subtypes adw and ayw. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):182–190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.182-190.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chairez R., Steiner S., Melnick J. L., Dreesman G. R. Glycoproteins associated with hepatitis B antigen. Intervirology. 1973;1(3):224–228. doi: 10.1159/000148850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney R. J., Benyesh-Melnick M. Isolation and characterization of a large molecular-weight polypeptide of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):539–551. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90414-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Hollinger F. B., McCombs R. M., Melnick J. L. Production of potent anti-Australia antigen sera of high specificity and sensitivity in goats. Infect Immun. 1972 Feb;5(2):213–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.2.213-221.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Hollinger F. B., Suriano J. R., Fujioka R. S., Brunschwig J. P., Melnick J. L. Biophysical and biochemical heterogeneity of purified hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):469–476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.469-476.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figenschau K. J., Ulstrup J. C. Staphylococcal radioimmunoassay for hepatitis B antigen and antibody. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):422–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W., May G. Hepatitis assoziiertes Antigen: Reinigung und Eigenschaften. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Jun;224(1):49–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudeau A., Houwen B., Dankert J. Letter: Cross-reaction of human serum-proteins with HBsAg. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1325–1325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90192-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. V., Purcell R. H., Smith H., Alter H. J. Subtyping of hepatitis-associated antigen (HB-Ag); simplified technique with counterelectrophoresis. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):420–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger F. B., Werch J., Melnick J. L. A prospective study indicating that double-antibody radioimmunoassay reduces the incidence of post-transfusion hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 16;290(20):1104–1109. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405162902002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Gerety R. J., Barker L. F. Antibody to hepatitis-B-virus core in man. Lancet. 1973 Oct 20;2(7834):869–873. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. R., Zuckerman A. J. Characterization of hepatitis B antigen polypeptides. Intervirology. 1974;4(1):31–44. doi: 10.1159/000149841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokelainen P. T., Krohn K., Prince A. M., Finlayson N. D. Electrn microscopic observations on virus-like particles associated with SH antigen. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):685–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.685-689.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. The heterogeneity of Australia antigen. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jun;123(6):671–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.6.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Reed W. D., Mitchell C. G., Galbraith R. M., Eddleston A. L., Zuckerman A. J., Williams R. Cellular and humoral immunity to hepatitis-B surface antigen in active chronic hepatitis. Br Med J. 1975 Mar 29;1(5960):705–708. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5960.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millman I., Hutanen H., Merino F., Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S. Australia antigen: physical and chemical properties. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1971 Jul-Sep;2(4):667–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Prince A. M., Lippin A. Hepatitis B antigen: antigenic sites related to human serum proteins revealed by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M. Amino acid substitution and the antigenicity of globular proteins. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:71–123. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Clayton D. A., Greenman R. L. DNA of a human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.384-391.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



