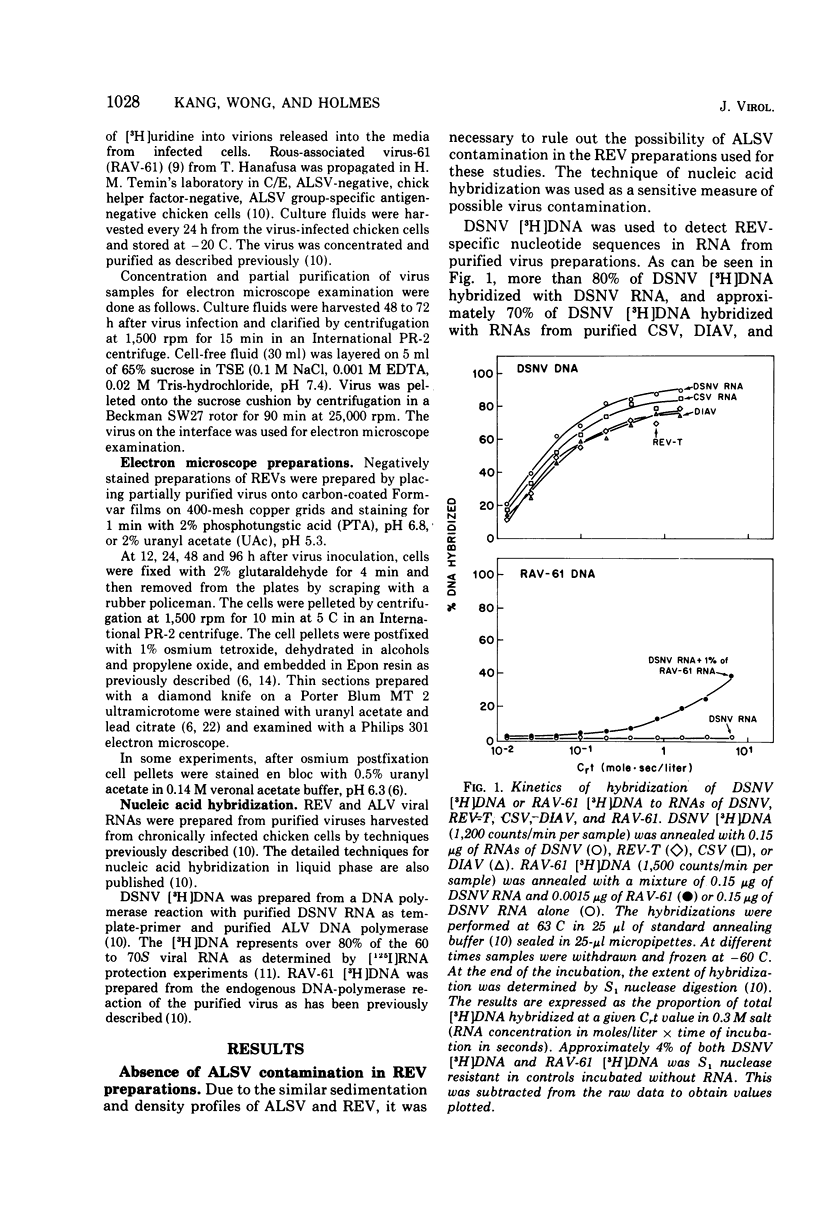
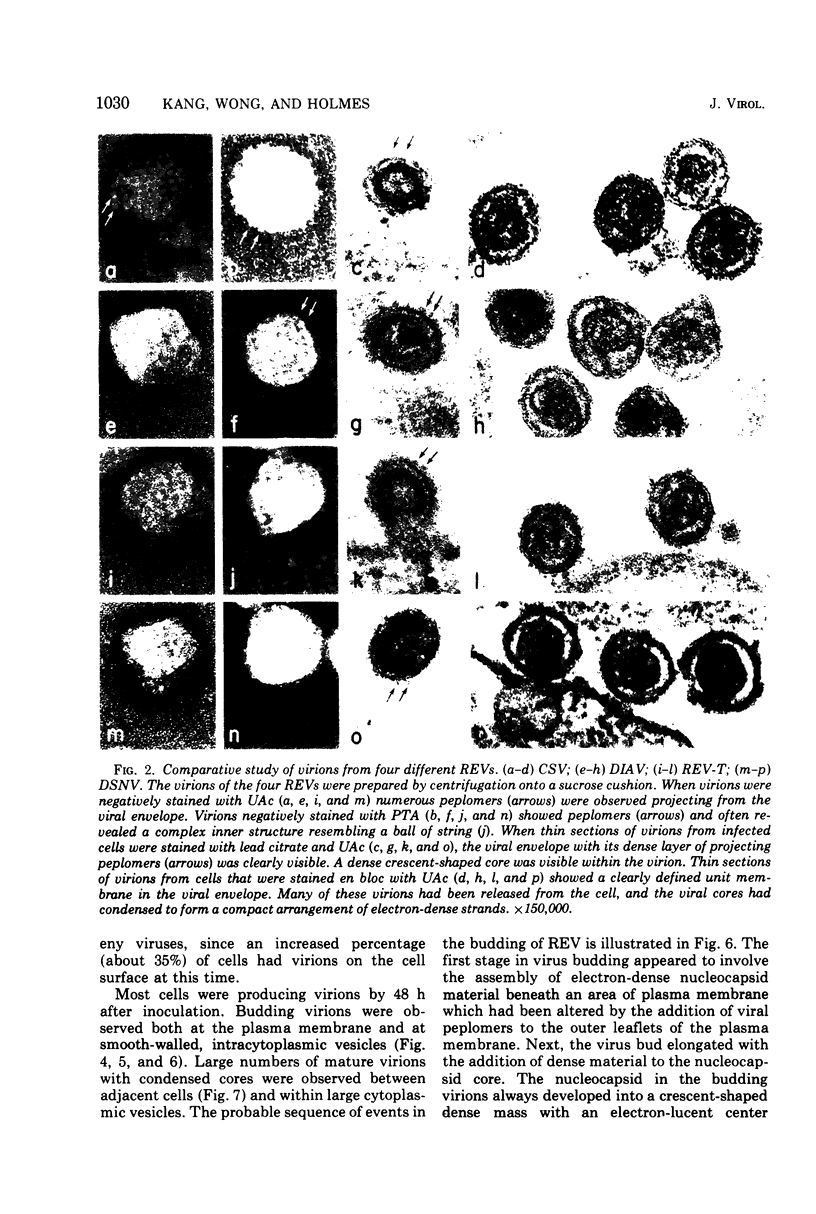
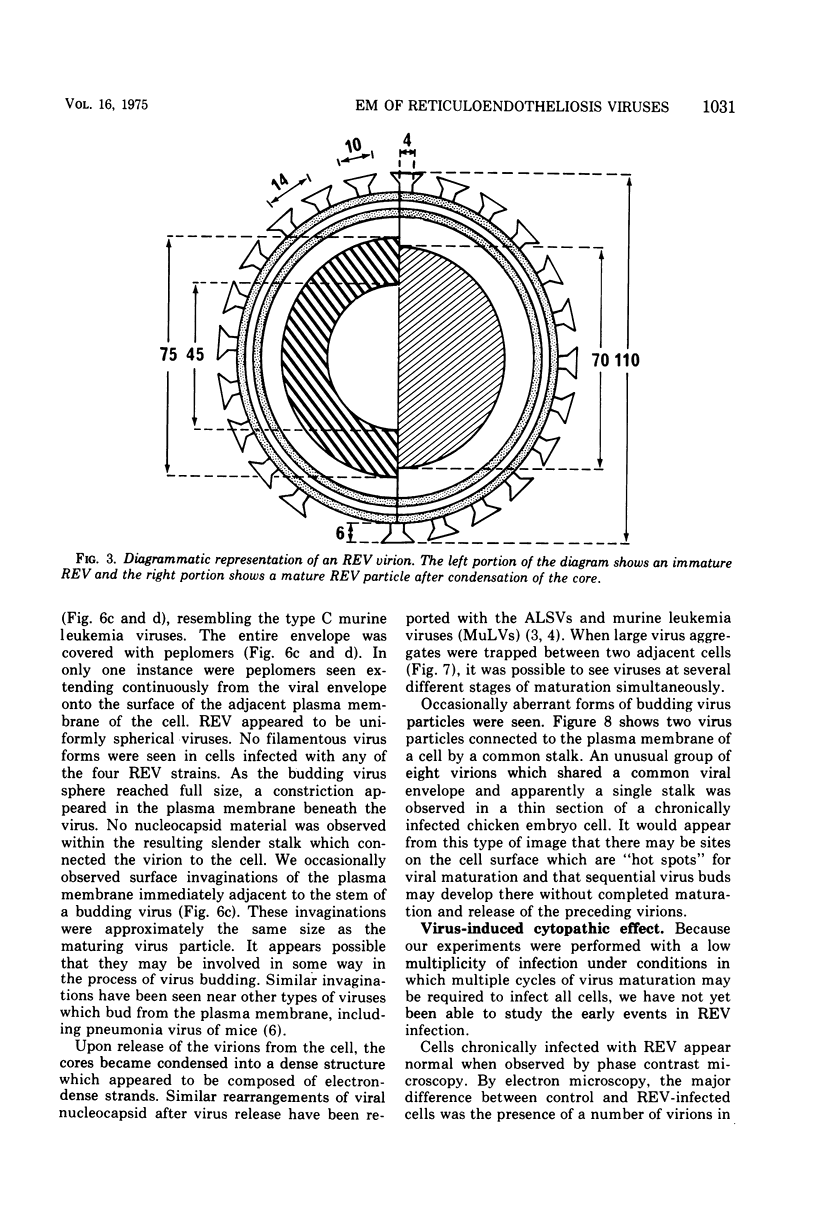
Abstract
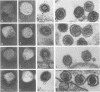
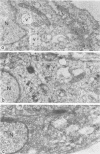
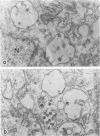
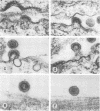
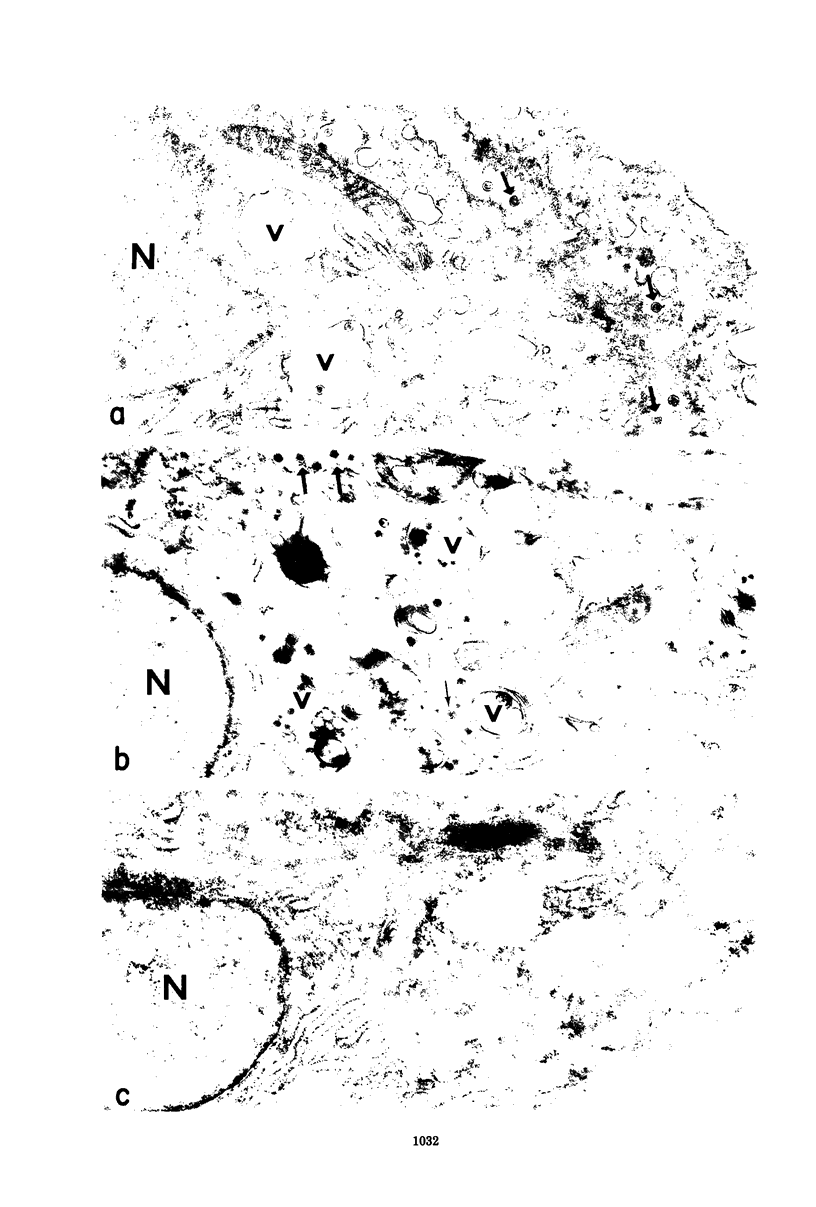
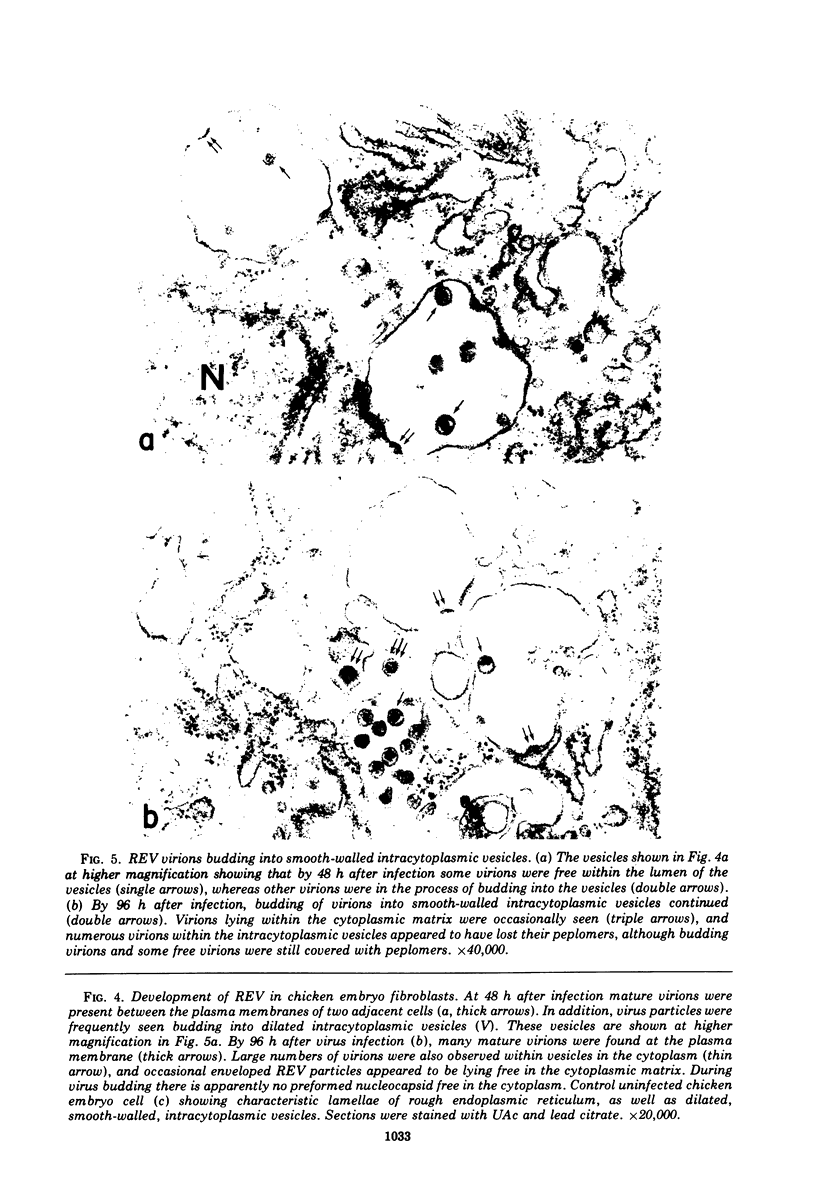
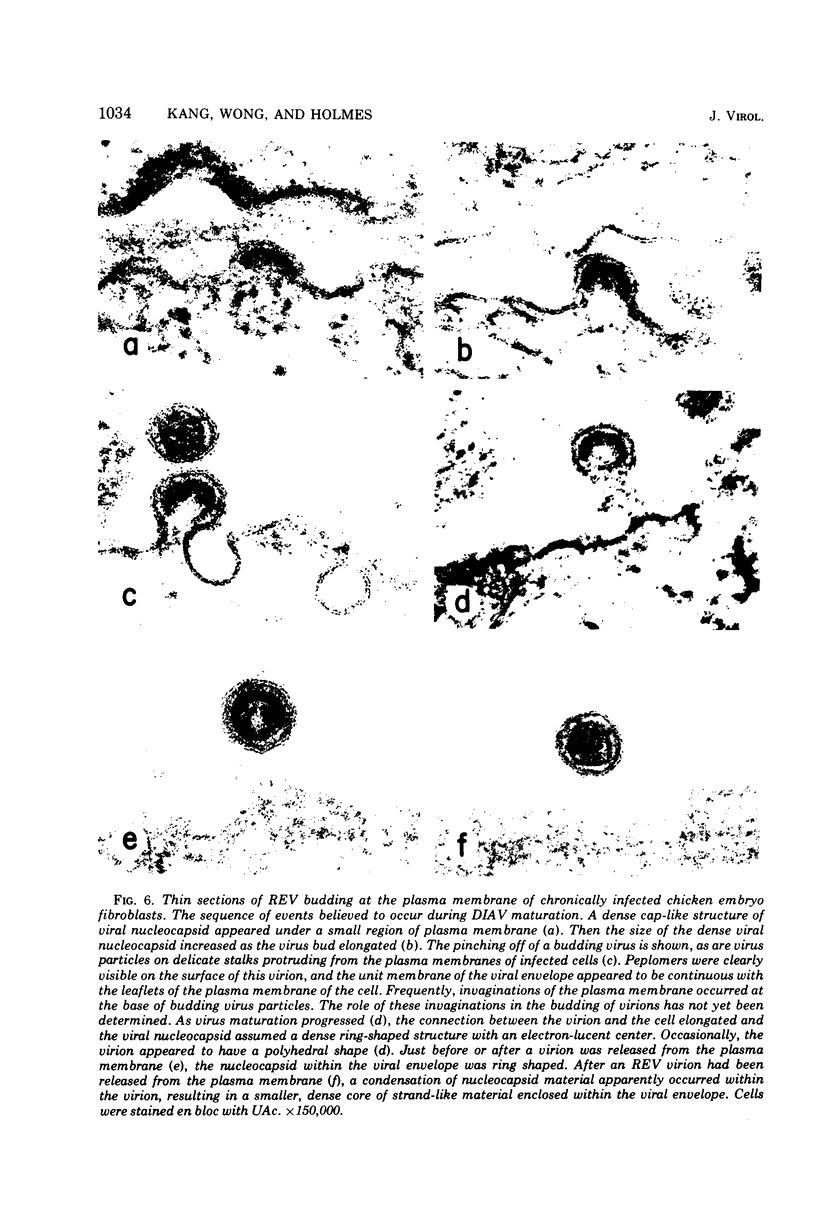
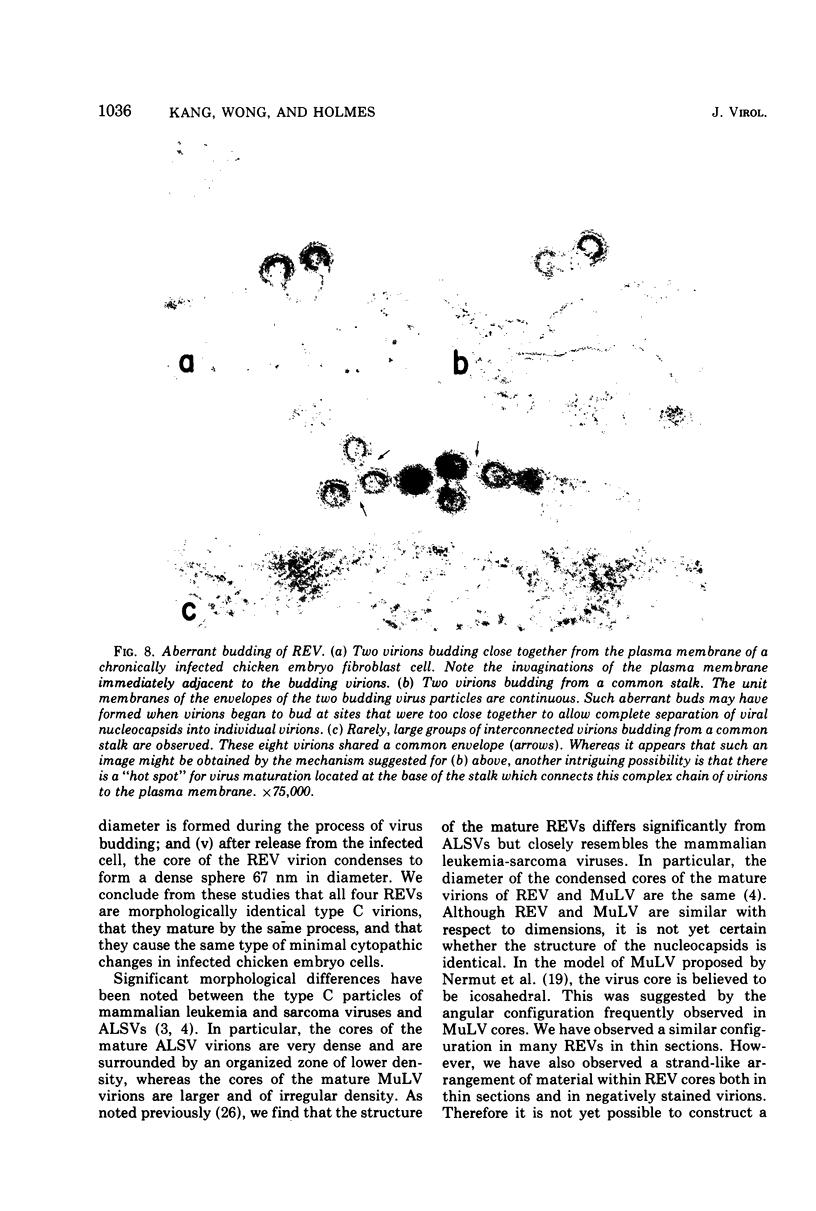
The morphology and development of four members of the reticuloendotheliosis virus group were studied by transmission electron microscopy. Virions of duck spleen necrosis virus, duck infectious anemia virus, chicken syncytial virus, and reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T are sperical with a diameter of approximately 110 nm. They are covered with surface projections about 6 nm long and 10 nm in diameter. The center-to-center distance of surface projections is about 14 nm. The budding virions contain crescent-shaped electron-dense cores 73 nm in diameter with electron-lucent centers. After release of the virions the cores apparently become condensed to 67 nm in diameter. Virions were found budding at the plasma membrane and into smooth-walled, intracytoplasmic vesicles of productively infected cells. The distribution of budding reticuloendotheliosis viruses on cells appeared random over the cell surface, and occasionally aberrant multiple forms of budding virions were observed. The virions appear to resemble mammalian leukemia and sarcoma viruses more closely than avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altaner C., Temin H. M. Carcinogenesis by RNA sarcoma viruses. XII. A quantitative study of infection of rat cells in vitro by avian sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1970 Jan;40(1):118–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter-Gabbard K. L., Campbell W. F., Padgett F., Raitano-Fenton A., Levin A. S. Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus (strain T). II. Biochemical and biophysical properties. Avian Dis. 1971 Oct-Dec;15(4):850–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Harter D. H., Choppin P. W. Studies on pneumonia virus of mice (PVM) in cell culture. II. Structure and morphogenesis of the virus particle. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):267–276. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Holmes K. V., Dales S., Choppin P. W. An electron microscopic study of moderate and virulent virus-cell interactions of the parainfluenza virus SV5. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):411–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. K. Cultivation of a filterable agent associated with Marek's disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Jul;43(1):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. S., Wade E., Rucker E., Baxter-Gabbard K. L., Levine A. S., Friis R. R. A study of the relationship of reticuloendotheliosis virus to the avian leukosis-sarcoma complex of viruses. Virology. 1973 Jun;53(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Isolation of leukosis-type virus from pheasant embryo cells: possible presence of viral genes in cells. Virology. 1973 Jan;51(1):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y. Characterization of endogenous RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity of reticuloendotheliosis viruses. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):880–886. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.880-886.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Temin H. M. Lack of sequence homology among RNAs of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses, reticuloendotheliosis viruses, and chicken endogenous RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1314–1324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1314-1324.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Temin H. M. Reticuloendotheliosis virus nucleic acid sequences in cellular DNA. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1179–1188. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1179-1188.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. A., Garapin A. C., Jackson N., Fanshier L., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific ribonucleic acid in cells producing rous sarcoma virus: detection and characterization. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):891–902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.891-902.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludford C. G., Purchase H. G., Cox H. W. Duck infectious anemia virus associated with Plasmodium lophurae. Exp Parasitol. 1972 Feb;31(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(72)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado R. L., Bose H. R. Relationship of reticuloendotheliosis virus to the avian tumor viruses: nucleic acid and polypeptide composition. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.741-747.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado R. L., Bose H. R. Separation of reticuloendotheliosis virus from avian tumor viruses. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):813–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.813-815.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Lack of serological relationship among DNA polymerases of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses, reticuloendotheliosis viruses, and chicken cells. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):440–448. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.440-448.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Specific serological relationships among partially purified DNA polymerases of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses, reticuloendotheliosis viruses, and avian cells. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1020–1029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1020-1029.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Frank H., Schäfer W. Properties of mouse leukemia viruses. 3. Electron microscopic appearance as revealed after conventional preparation techniques as well as freeze-drying and freeze-etching. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):345–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. A., Baxter-Gabbard K. L., Levine A. S. Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus (strain T): V. DNA polymerase. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase H. G., Ludford C., Nazerian K., Cox H. W. A new group of oncogenic viruses: reticuloendotheliosis, chick syncytial, duck infectious anemia, and spleen necrosis viruses. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Aug;51(2):489–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson F. R., Twiehaus M. J. Isolation of tha avian reticuloendothelial virus (strain T). Avian Dis. 1974 Apr-Jun;18(2):278–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAGER W. A new virus of ducks interfering with development of malaria parasite (Plasmodium lophurae). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jul;101(3):578–582. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Kassner V. K. Replication of reticuloendotheliosis viruses in cell culture: acute infection. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):291–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.291-297.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M. R., Allen P. T. RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity of reticuloendotheliosis virus: characterization of the endogenous and exogenous reactions. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):872–879. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.872-879.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeigel R. F., Theilen G. H., Twiehaus M. J. Electron microscopic observations on RE virus (strain T) that induces reticuloendotheliosis in turkeys, chickens, and Japanese quail. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Dec;37(6):709–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]